Cisco and Fortinet Release Safety Notices after Data Leakage by Equation Group
 In the last post, we dwelt on the contents of the Equation Group cyber-grouped archive that had leaked into the network in more detail. We also indicated that the names of the exploits and implants (components) of malware correspond to the names from the NSA ANT archive. In a number of vendors mentioned, on which devices exploits were targeted, Cisco and Fortinet (Fortigate Firewall) were indicated. In the case of Cisco, there are two exploits for Cisco ASA, PIX and Firewall Services Module devices with the names ANT EXTRABACON (EXBA) and EPICBANANA (EPBA). The first exploit is of type 0day and exploits a previously unknown vulnerability with identifier CVE-2016-6366 (Cisco ASA RCE vulnerability). The second uses a fixed 1day vulnerability with identifier CVE-2016-6367 (Cisco ASA CLI RCE).
In the last post, we dwelt on the contents of the Equation Group cyber-grouped archive that had leaked into the network in more detail. We also indicated that the names of the exploits and implants (components) of malware correspond to the names from the NSA ANT archive. In a number of vendors mentioned, on which devices exploits were targeted, Cisco and Fortinet (Fortigate Firewall) were indicated. In the case of Cisco, there are two exploits for Cisco ASA, PIX and Firewall Services Module devices with the names ANT EXTRABACON (EXBA) and EPICBANANA (EPBA). The first exploit is of type 0day and exploits a previously unknown vulnerability with identifier CVE-2016-6366 (Cisco ASA RCE vulnerability). The second uses a fixed 1day vulnerability with identifier CVE-2016-6367 (Cisco ASA CLI RCE).The following is information from a Cisco blog that lists the correspondences of the Equation Group exploits and the names of the vulnerabilities. It also refers to the implant JETPLOW, which is used as a backdoor for the firmware network device. The following is a description of JETPLOW from the ANT slide.

Exploit names and related vulnerabilities in Cisco products. Only the JETPLOW component can ensure stability in the system (persistent) and work after a reboot.
')
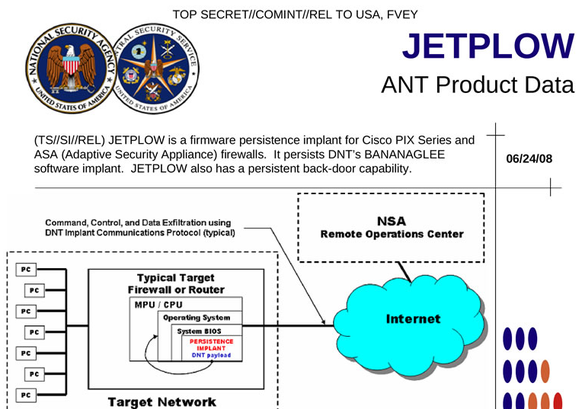
An NSA ANT catalog slide that describes the JETPLOW implant for Cisco devices.
EXTRABACON exploits the RCE vulnerability in the Cisco network device firmware, which is present in the code responsible for processing and parsing the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) packets. Vulnerability is relevant for such families of devices as Cisco ASA, Cisco PIX and Cisco Firewall Services Module. It allows you to remotely execute the code on the device and get full access to it for attackers.
The vulnerability is due to a buffer overflow in the affected code area. An attacker could have cracked the SNMP packets to the affected system. It is a problem to keep track of the system. The SNMP community has to know this vulnerability.
Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance SNMP Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
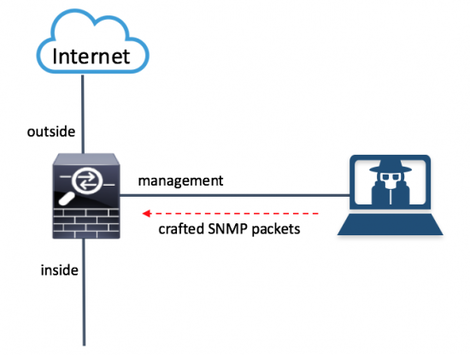
The general scheme of operation CVE-2016-6366 (EXTRABACON).
The following device models are subject to CVE-2016-6366: Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliances, Cisco ASA 5500-X Series, Next-Generation Firewalls, Cisco ASA Services for Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series Switches & Cisco 7600 Series Routers, Cisco ASA 1000V Cloud Firewall , Cisco Adaptive Security Virtual Appliance (ASAv), Cisco Firepower 9300 ASA Security Module, Cisco PIX Firewalls, Cisco Firewall Services Module (FWSM).
At the moment, an update for this vulnerability has not yet been released.
The EPICBANANA exploit exploits a previously unknown, but already irrelevant (fixed) vulnerability with identifier CVE-2016-6367 in the following device and product models: Cisco ASA 5500-Series Next-Generation Firewalls, Cisco PIX Firewalls, Cisco Firewall Services Module (FWSM). The vulnerability has been fixed since Cisco ASA v8.4 (3).
Security policy for the Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) parser of the Cisco Security Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA). An attacker couldn’t mind this device.
Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance CLI Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
If the above exploits are used to remotely execute code on a network device, JETPLOW allows unauthorized users unlimited access to it and the ability to execute commands on it at any time. As indicated in his Cisco blog, a secure boot protection measure called Cisco Secure Boot can counteract the loading of a device compromised by the implant JETPLOW by signing the firmware file with a digital certificate.
Cisco Secure Boot also mitigates this issue. The Cisco Secure Boot is a secure startup process. You must be able to verify the integrity of the computer software. If you’re aware of the error, you’ll see the error message. This prevents the network device from executing compromised software.
Fortinet specialists have released a security notification FG-IR-16-023 (Cookie Parser Buffer Overflow Vulnerability), which deals with a vulnerability exploited by the EGREGIOUSBLUNDER (EGBL) exploit. The vulnerability affects the FortiGate product (FOS) firmware versions below 4.3.8 and can be used to gain complete control over the device due to a specially formed HTTP request. The FOS 5.x version family is not affected by this vulnerability. Update for outdated versions has not yet been released.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/308074/
All Articles