Creating a WebView application based on AWS ApiGateway and AWS Lambda
Over the past year of existence, a large number of tutorials on creating a serverless API based on sabzh have accumulated on the open spaces of the network. In this article I want to talk about another use of API Gateway, which in particular can be used as a backend for a WebView application.
Careful, a lot of screenshots!
Disclaimer:
To begin with, we have the simplest data model:
As a data source, I decided to use S3 for clarity. Create JSON-files with the contents of the type:
')
As a template rendering engine, I will use Python itself. Templates are HTML files of the form:
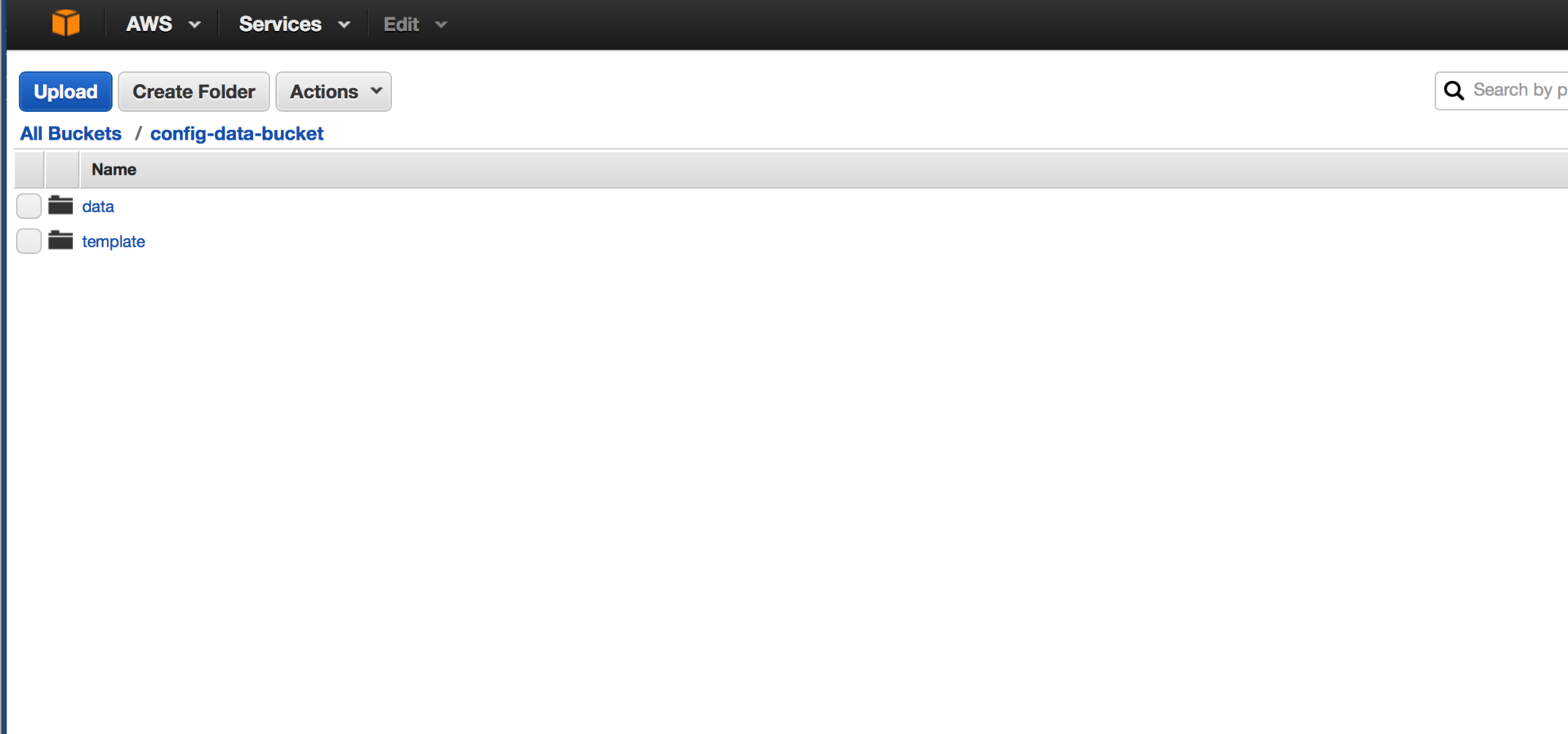
After creating the data, I upload everything onto the bake with the appropriate prefixes (directories):
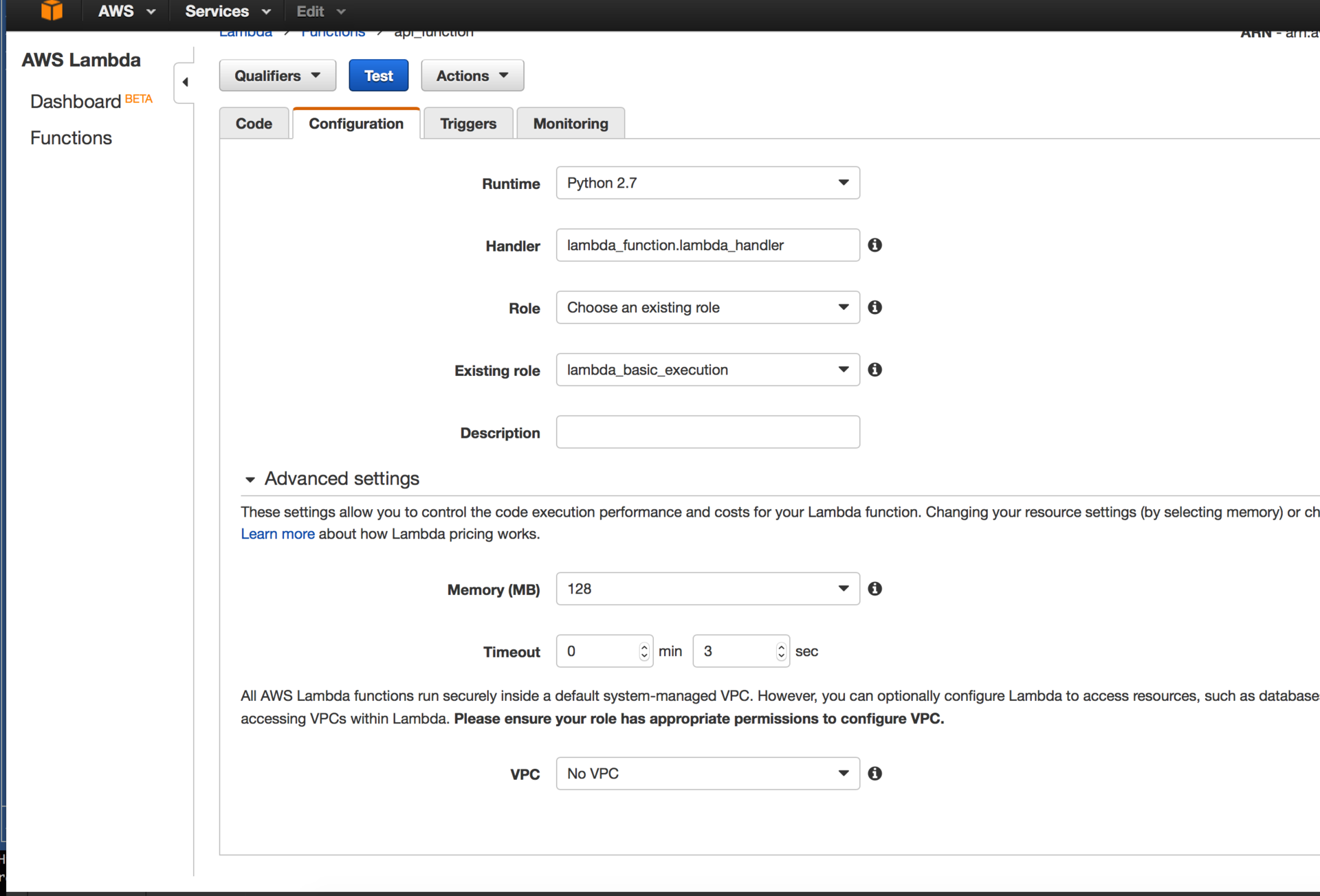
In the AWS console, create a Lambda function using blueprint hello-world-python.
The role used by IAM must first add a policy for access to S3.
Go to the API Gateway console and create an API of the following form:
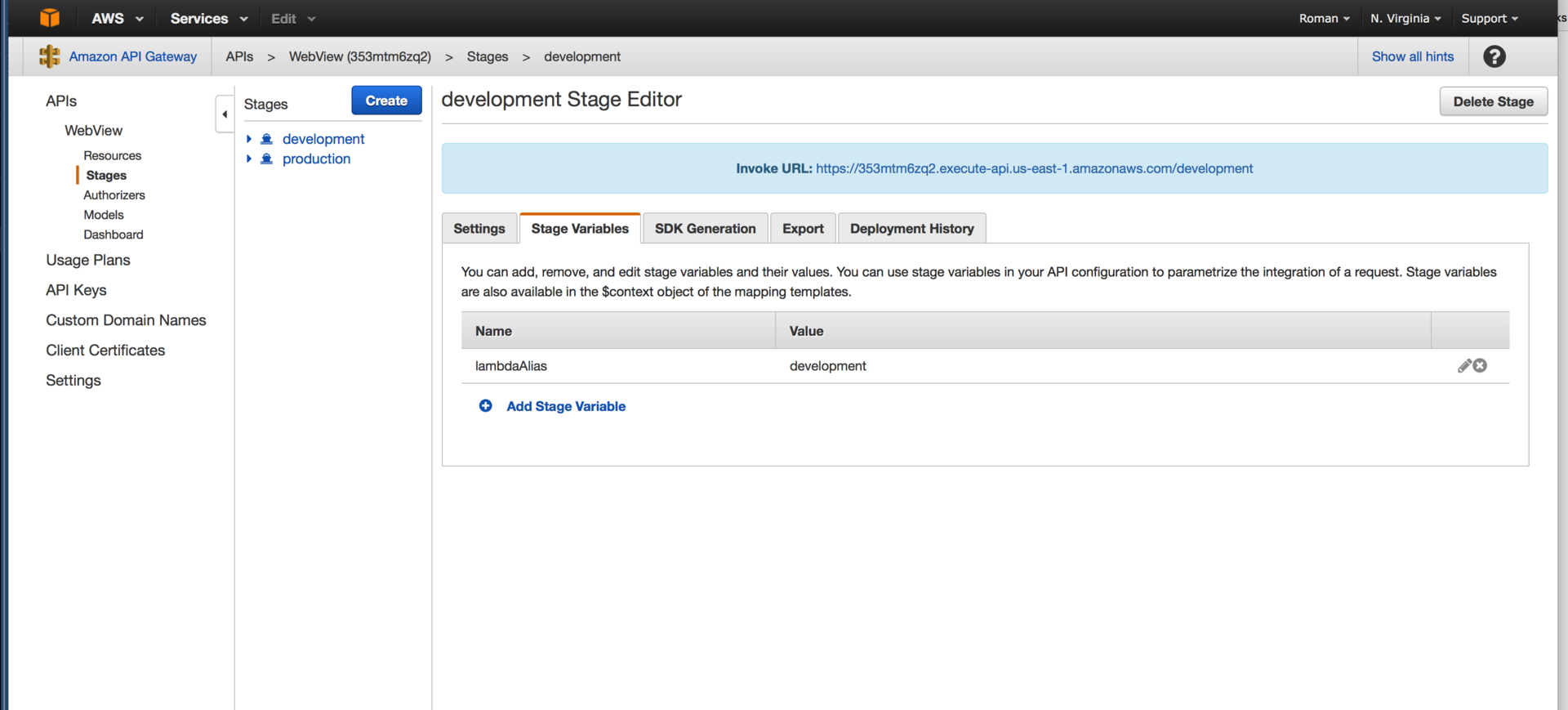
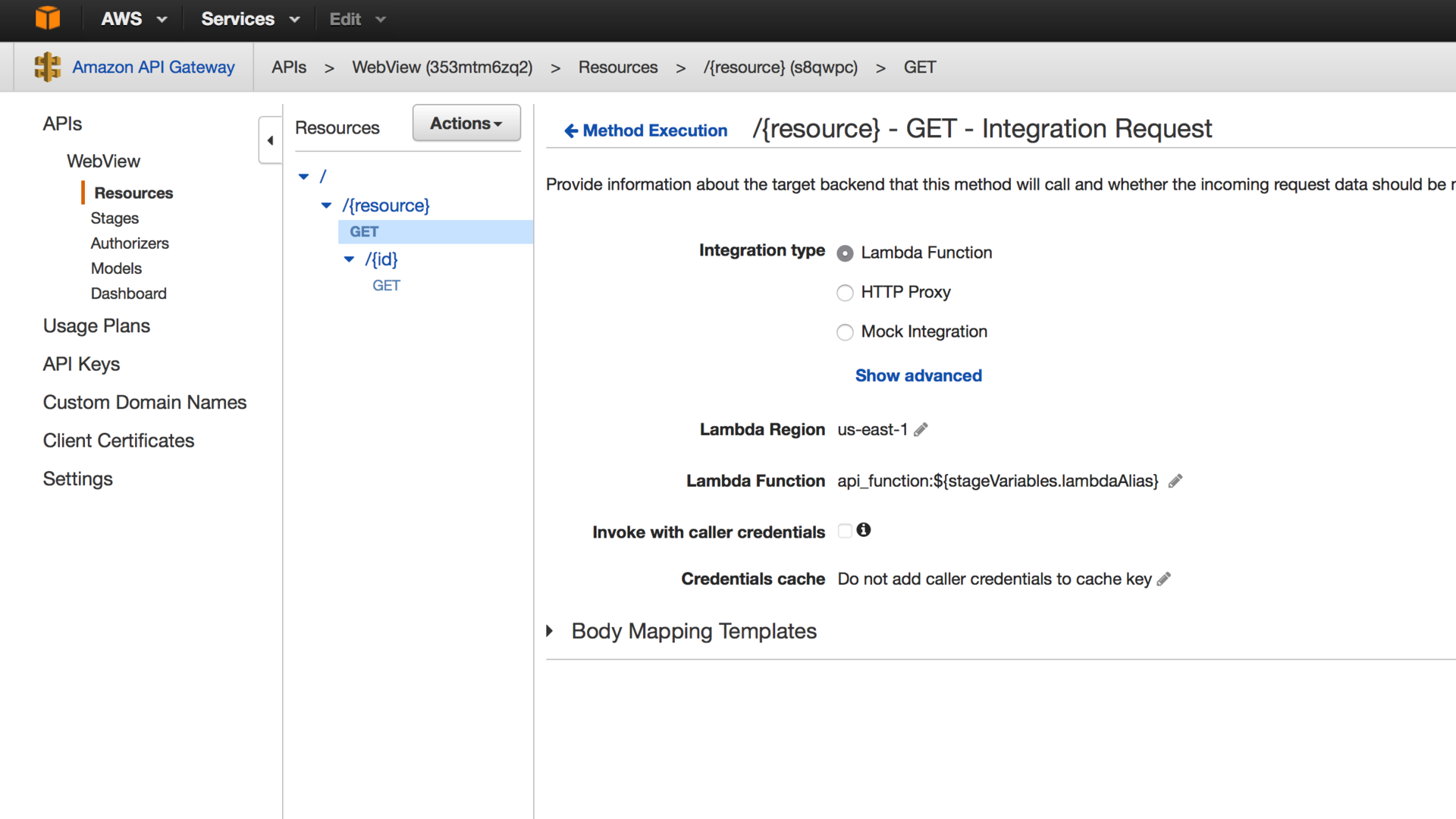
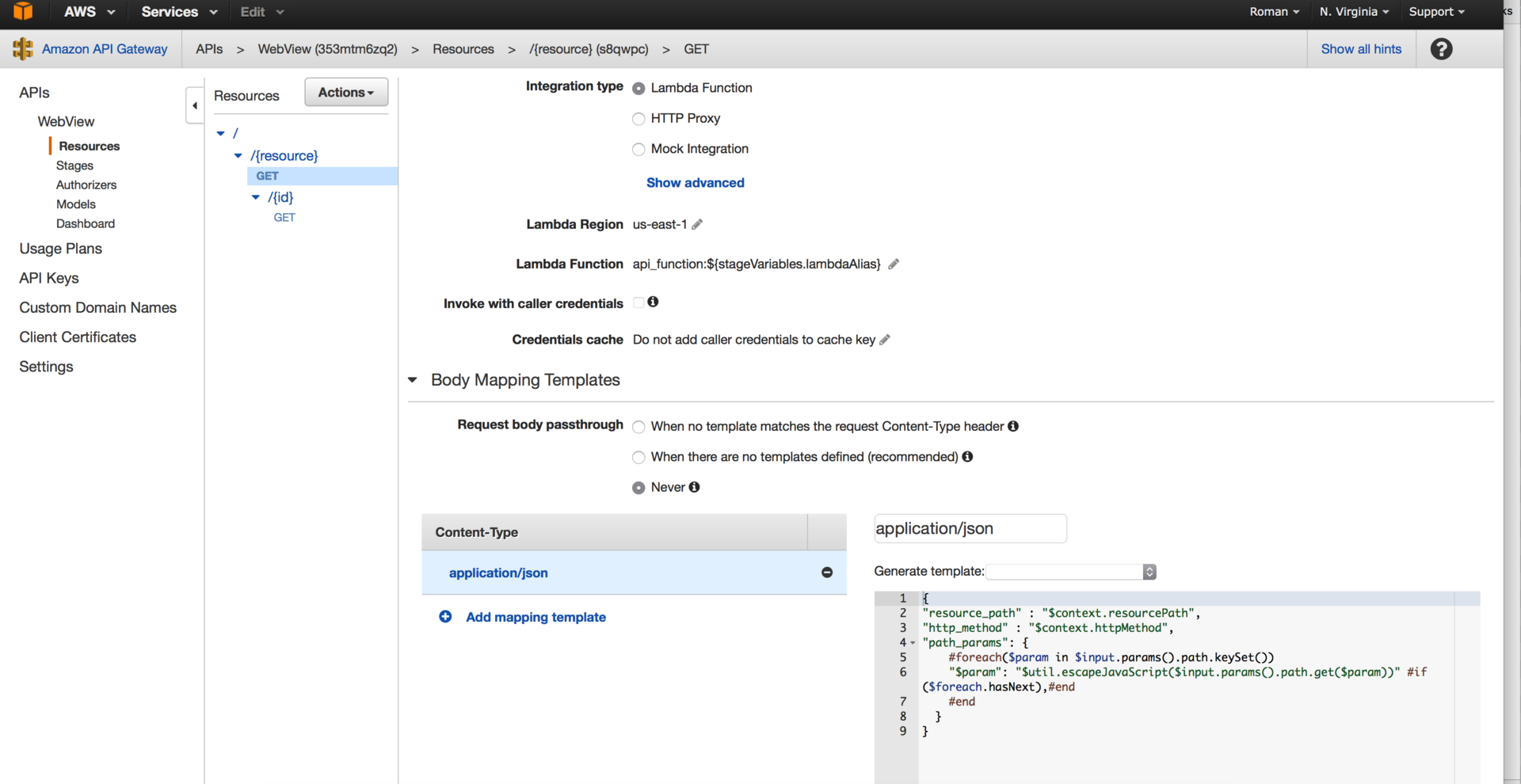
Pay attention to the mapping template - it describes the event given by the lambda. Next, we describe the mapping and content-type for data sent from the API Gateway. Deploy two stage - production and development, we register in each of them the stage variable lamdbdaAlias and for the time being we forget about the API Gateway.

Next, we return to the created lambda and add the following code:
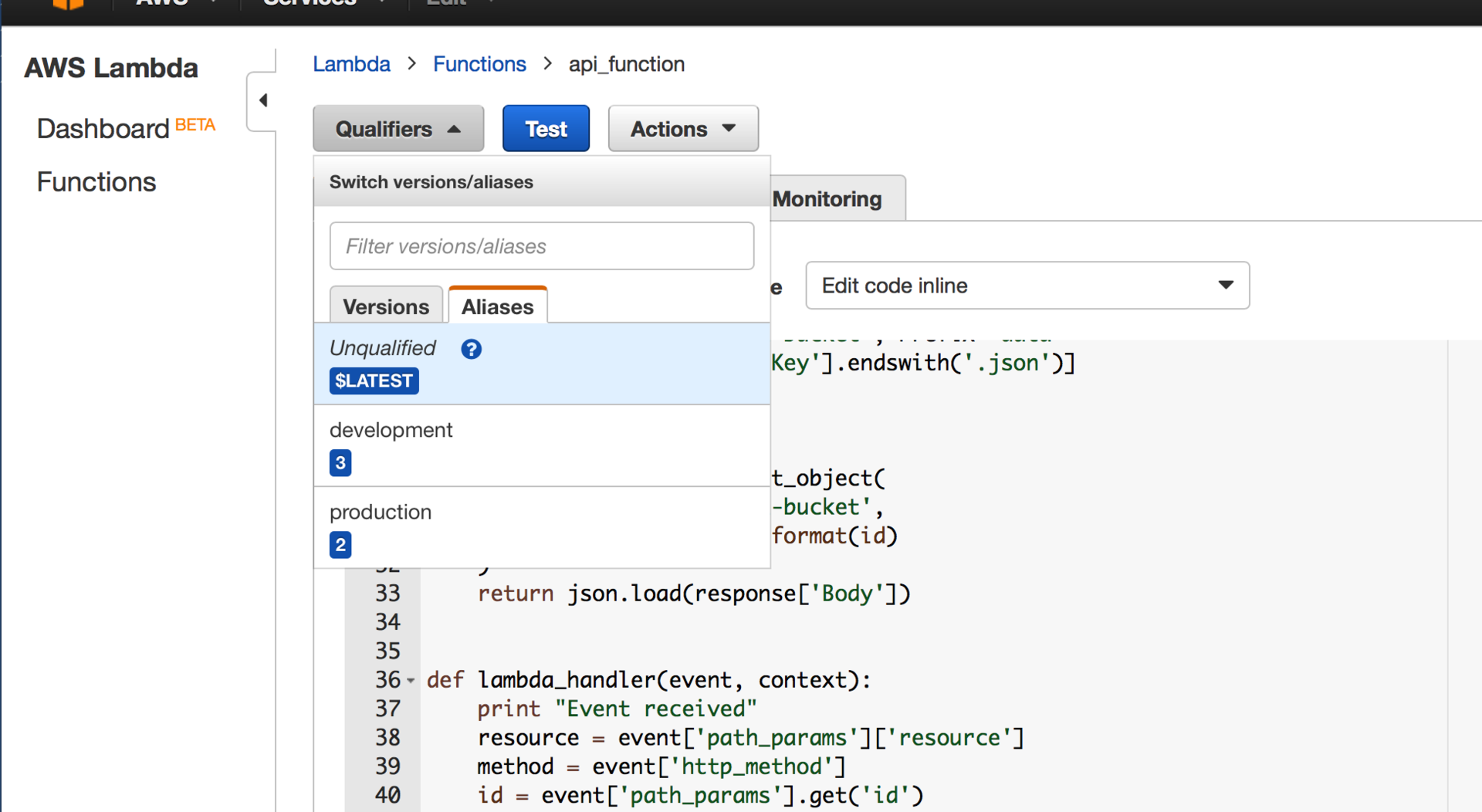
After that, we publish lambda and create two aliases for it - production and development:
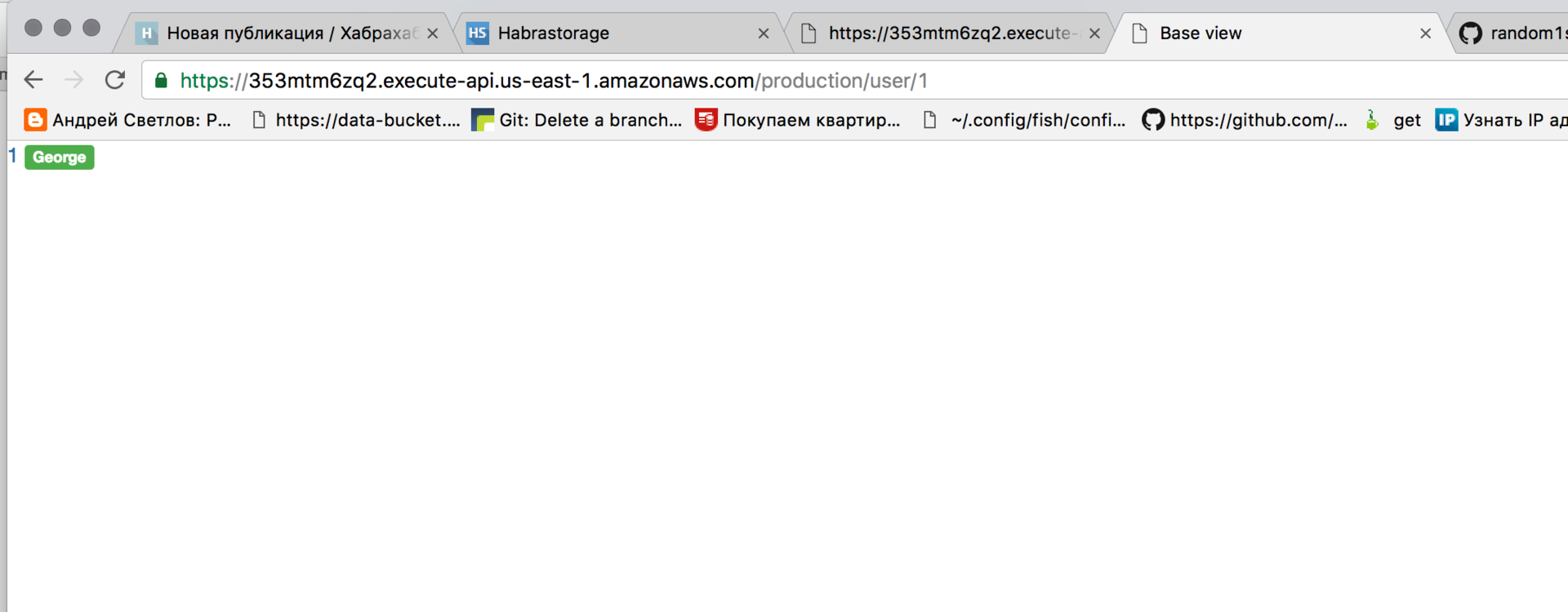
Everything, we got quite a working draft:
Video:
Github: aws webview
Careful, a lot of screenshots!
Disclaimer:
This is just a concept, so you should not consider it as a working use case. At the end of the link is attached to github, if you do not want to go through all the stages manually, as well as the video I recorded, so do not be surprised that I will miss many of the points.
Data preparation
To begin with, we have the simplest data model:
User: id = 'string' name = 'string' As a data source, I decided to use S3 for clarity. Create JSON-files with the contents of the type:
')
{ "id":"1", "name":"George" } As a template rendering engine, I will use Python itself. Templates are HTML files of the form:
base.tpl <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Base view</title> </head> <body> {body} </body> </html> user.tpl <a href="#">{id} <span class="label label-success">{name}</span></a><br> After creating the data, I upload everything onto the bake with the appropriate prefixes (directories):

Creating a function in AWS Lambda
In the AWS console, create a Lambda function using blueprint hello-world-python.

The role used by IAM must first add a policy for access to S3.
API creation
Go to the API Gateway console and create an API of the following form:



Pay attention to the mapping template - it describes the event given by the lambda. Next, we describe the mapping and content-type for data sent from the API Gateway. Deploy two stage - production and development, we register in each of them the stage variable lamdbdaAlias and for the time being we forget about the API Gateway.

Work with AWS Lambda
Next, we return to the created lambda and add the following code:
from __future__ import print_function import json import boto3 s3_client = boto3.client("s3") def get_template(filename): response = s3_client.get_object( Bucket='config-data-bucket', Key='template/{}'.format(filename) ) return response['Body'].read() def get_objects_list(): return [json.loads( s3_client.get_object( Bucket='config-data-bucket', Key=item['Key'] )['Body'].read() ) for item in s3_client.list_objects_v2( Bucket='config-data-bucket', Prefix='data' )['Contents'] if item['Key'].endswith('.json')] def get_object(id): response = s3_client.get_object( Bucket='config-data-bucket', Key='data/{}.json'.format(id) ) return json.load(response['Body']) def lambda_handler(event, context): print "Event received" resource = event['path_params']['resource'] method = event['http_method'] id = event['path_params'].get('id') if resource == 'user' and method=="GET": base_template = get_template('base.tpl') user_template = get_template('user.tpl') if id: user = get_object(id) return base_template.format( body=user_template.format(id=user['id'], name=user['name']) ) else: users = get_objects_list() return base_template.format( body="".join( user_template.format(id=user['id'], name=user['name']) for user in users) ) After that, we publish lambda and create two aliases for it - production and development:

Everything, we got quite a working draft:

Video:
Github: aws webview
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/307692/
All Articles