Choosing backup equipment in a small office

Any office is full of information. Often, it is the most expensive asset of the company. It is bad that this is remembered when there is a real risk of its loss. And even after a failure, after recovering only a portion of the information, this lesson is quickly forgotten.
Another administrator will spread his hands and say: “What to do? There is no budget, there is no understanding from the managers, so we also have no backups. It will break on their conscience. ”But this is only half the trouble, because you can break it too. Incorrect configuration, configuration error, cryptor (encryption virus) - and the data are irretrievably lost. Therefore, backups must be done. Having achieved this understanding, you can proceed to the practical part.
')
In this article, we will look at a possible approach to backing up in a typical small office operating on the Microsoft platform, and recommend several options for copy storage equipment. Of course, in a large office or company, everything is different. There are backup storage systems, and tape libraries, and expensive specialized products. Backing up a datacenter is both a science and an art that you can devote not only an article, but your whole life.
If the reader is interested in our opinion, or maybe there is an opportunity to share our experience and even tricks, we continue under the cut.
First you need to decide what frequency we reserve and how many backups you need to store.
Data types and backup methods
File servers
For quick recovery of files without backups, it is convenient to use the Shadow Copies of Shared Folders mechanism. For its work, as a rule, it is enough to reserve 5-20% of disk space on the file server itself. In the schedule for creating a "snapshot" (snapshot), you can specify the end of the working day and noon. The reserve of 5% allows you to store about 14 images, the actual number depends on the volume of the disk and the intensity of data changes.

Backups can be performed using the built-in Windows Backup. There are also quite reliable tools Cobian Backup and Handy Backup. Cobian Backup is a free application that supports Unicode, FTP, compression, encryption, incremental and differential backup types. Handy Backup has even more features, including synchronization and data recovery from copies. We will consider the work of Windows Backup.
It should be remembered that only one copy of data can be saved to a remote network folder on the backup server. And the next backup task will overwrite it. But in any case, storing a single copy of the data is risky.
To circumvent this limitation, there is a simple and effective way. It is necessary to connect a disk for backups from a backup server using iSCSI protocol. Windows Backup will consider such a disk local.
The first backup will be equal to the amount of stored data. Because Windows Backup uses block, not file backup, the next incremental backup takes as much as the actual disk blocks have changed.
An incremental backup is a record of only changed data. That is, you do not need to copy the entire database every time; you only need to create a complete copy of it once and then make any relevant changes to it. In this case, the previous version of the data is not saved, the new version is written on top of it.
Differential backups, by contrast, implies the preservation of previous versions. For example, daily creating a copy of the database, you save all previous copies of the week. This allows you to quickly roll back to a certain state. In differential copying, the modified data is recorded separately from the full copy.
Windows Backup does not require additional configuration and fully manages the storage :
Automatic management of full and incremental backups. You no longer need to manage full and incremental backups. Windows Server Backup will, by default, create an incremental backup that is like a full backup. But it can be used to make it possible only for an incremental backup. In addition, Windows Server Backup doesn’t require backups — you’ve deleted backups.
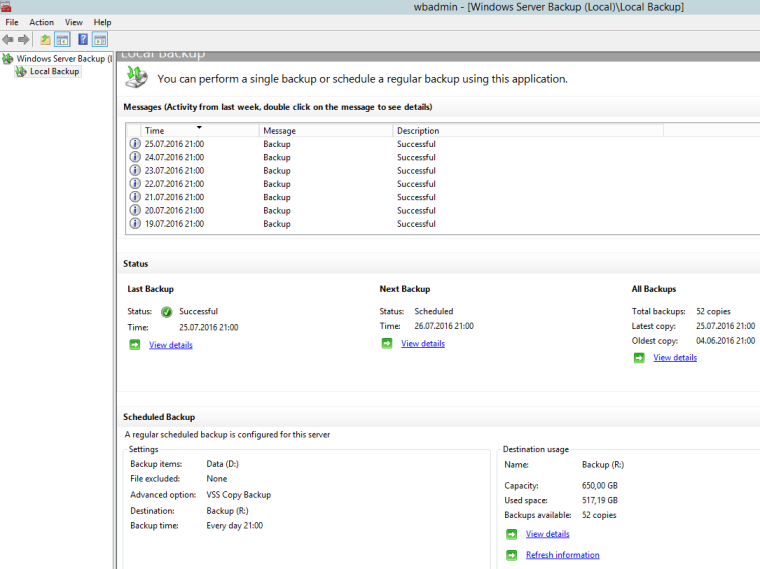
It is advisable to allocate two volumes of actually stored data for backup copies. This will be enough to store daily copies with a depth of approximately one and a half to two months. The frequency is daily.
Microsoft SQL Servers
Microsoft SQL servers support three types of backup:
- Complete . Copies the database completely.
- Differential . Database pages that have changed since the previous backup are copied.
- Incremental . The transaction log is copied (for databases in Full Recovery).
You need to decide how often we create a full backup.
One of the landmarks is the duration of the backup. It must be performed during off-hours or on weekends. The backup operation creates a significant load on the server. If it is not possible to perform a full copy at night or on a working day, then this task is performed on the weekend.
The second landmark is the volume of differential copies and the duration of the differential copy. Each next differential copy becomes larger, as it includes the previous one. The more time has passed from the last full copy, the longer it takes to create a nonlinear longer incremental one. After all, for a full copy, you can read database files sequentially, and for incremental, you need to read the changed pages in random places.
The frequency of incremental copying depends on what part of the database is acceptable to lose as a result of a failure. If you are ready to lose one hour of work (that is, restore the database as of an hour ago), then incremental backups must be performed once per hour. It is possible more often, but remember about the load on the server. It should be remembered that database backup is only one of the ways to ensure data integrity. If data loss is unacceptable, as is simple during data recovery, then use mechanisms such as AlwaysOn and Log Shipping.
An important setting that needs to be done immediately on the server is to enable compression for backups. This will reduce the amount of backup data almost doubled. It should be borne in mind that when you start a backup file, a backup volume of the backup file will be equal to the actual size of the database minus blank pages.
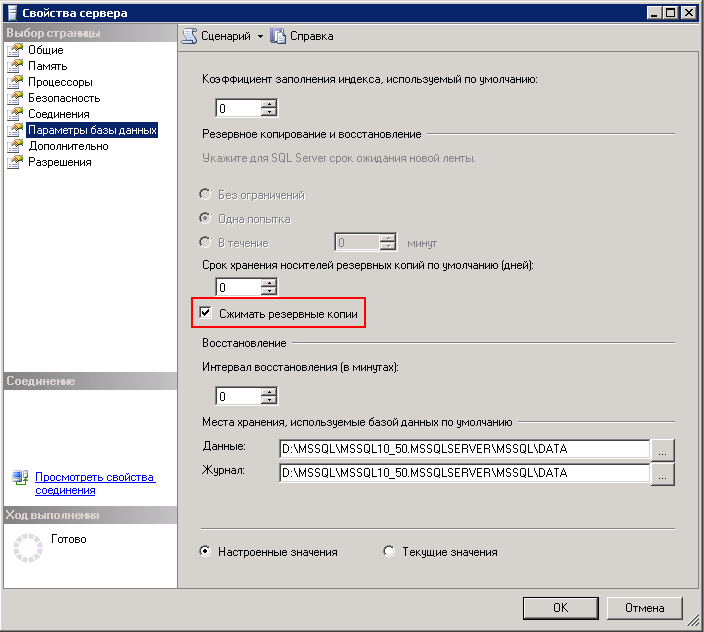
The recommendation for allocated storage on disk is at least two full database sizes. But this is the minimum requirement: often accountants need to keep a full copy of the database for each of the previous years, as well as full copies for the previous reporting periods in the current year. You may also need to make daily copies with a depth of at least a month.
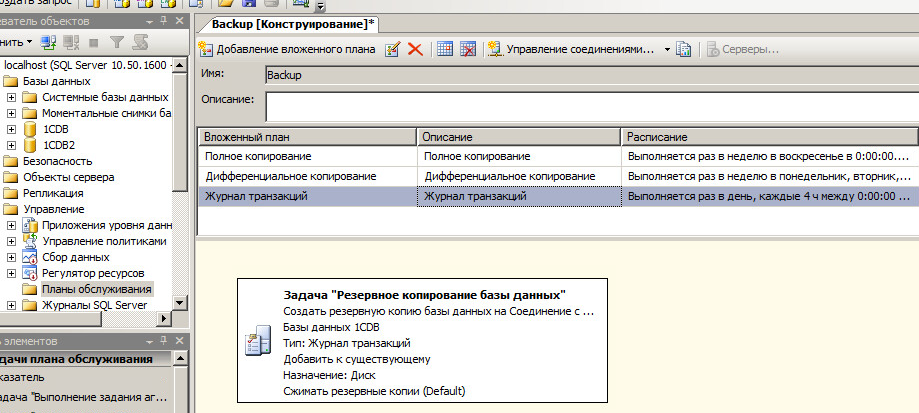
Typical schedule:
| Sat | Complete |
| Sun-Fri | Differential |
| Every 4 hours | Incremental |
To implement the plan, you can create a “Maintenance Plan” that includes all three types of tasks.
Microsoft Exchange Servers
This product supports two types of backup:
- Complete . Fully copied database and transaction logs.
- Incremental . Only transaction logs are copied.
It is important to perform regular backups, as only it allows you to delete (“cut off”) transaction logs for mail databases that are not in circular logging mode.
Windows Backup only supports full backup of Microsoft Exchange. To minimize the volume of stored copies, you can use a disk connected via iSCSI, by analogy with a file server.
The recommendation for allocated storage on disk is at least two full database sizes. Daily.
Virtual machines
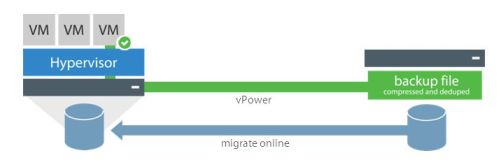
Most backup products allow you to copy a virtual machine with all disks without using agents inside the operating system. Veeam Backup & Replication allows you to perform full and incremental backups, as well as synthesize a new full copy, "rolling" incremental to the old full copy.
The free version allows you to make only a full copy, which adversely affects the backup window and the amount of data transferred. The amount of backup data stored on a disk can be reduced by enabling Windows Deduplication. When a copy is made from a virtual machine, a * .vib file is saved on the disk, and so on for each virtual machine. They are quite effectively deduplicating. At night, we created a backup copy, deduplicating it in a day. This is a repeatedly proven scheme, but it requires the use of a paid version of the product.
Considering the fact that Windows Deduplication works in post-processing mode, the recommendation on the amount of storage allocated to the disks is at least three full sizes of virtual machines. The frequency of copying is server dependent. If this is a web server with static content, then it makes no sense to copy it more often than once a week.
Basic hardware requirements
Disk subsystem
Backup operations, as a rule, do not impose high requirements on the storage subsystem. The main task recording template is linear, and a high load with a random I / O profile occurs only during backup deduplication.

You have the choice between 2.5 "SFF disks and 3.5" LFF disks. There are no weighty reasons for choosing SFF disks. Discs of this type have a smaller capacity and are more expensive. They are indispensable when you need to remove more IOPS from one server (twice as many disks — twice as many IOPS). For the same reason, most of the proposed SFF disks are SAS with a spindle speed of 10 thousand revolutions.
The optimal choice for a backup server is high-capacity SATA / SAS drives with a spindle speed of 7200 revolutions. At the same time, SAS drives, in theory, produce slightly more IOPS than their SATA relatives, therefore, if the price difference is not significant, then they are the ones that are preferable. However, in general, backup time is much more important for backup servers.
If you plan to use the Instant VM recovery feature, then it is obvious that the performance of the backup storage should be relatively consistent with the workload. A braking machine is often worse than a non-working one.
Storage capacity can be calculated based on the recommendations outlined above. But backing up is a subtle thing, and you can accurately calculate and predict growth only if you have actual data on hand.
If you purchased a backup software product, the size of the backup will depend on the method of data storage on the disk and on the effectiveness of the built-in deduplication / compression mechanisms.
RAM and CPU
RAM and processor requirements are dependent on backup media.
For example, for the popular Veeam Backup & Replication, they are:
- One core per competitive backup job
( https://helpcenter.veeam.com/backup/hyperv/limiting_tasks.html ) - 4 GB of memory for the product plus 500 MB for each competitive backup task.
In fact, each concurrent backup job uses several agents — one for transferring data, another for compressing, and a third for deduplicating backups. However, host performance rarely becomes a bottleneck. Note that Windows deduplication is block, with variable block length and compression.
The results of Veeam brand deduplication are rather modest, we prefer to do this using Windows Server 2012 R2. If you plan to use Microsoft deduplication, then you need to be guided by the following system requirements: 1 core and 350 MB of memory for one deduplicated volume. The recommended maximum volume size is 2 TB.
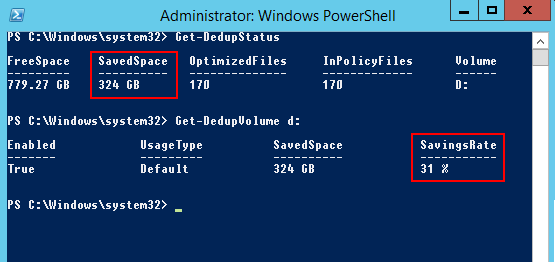
A 1.5Tb disk, 720Gb storage capacity, without deduplication, the data would take more than 1Tb.
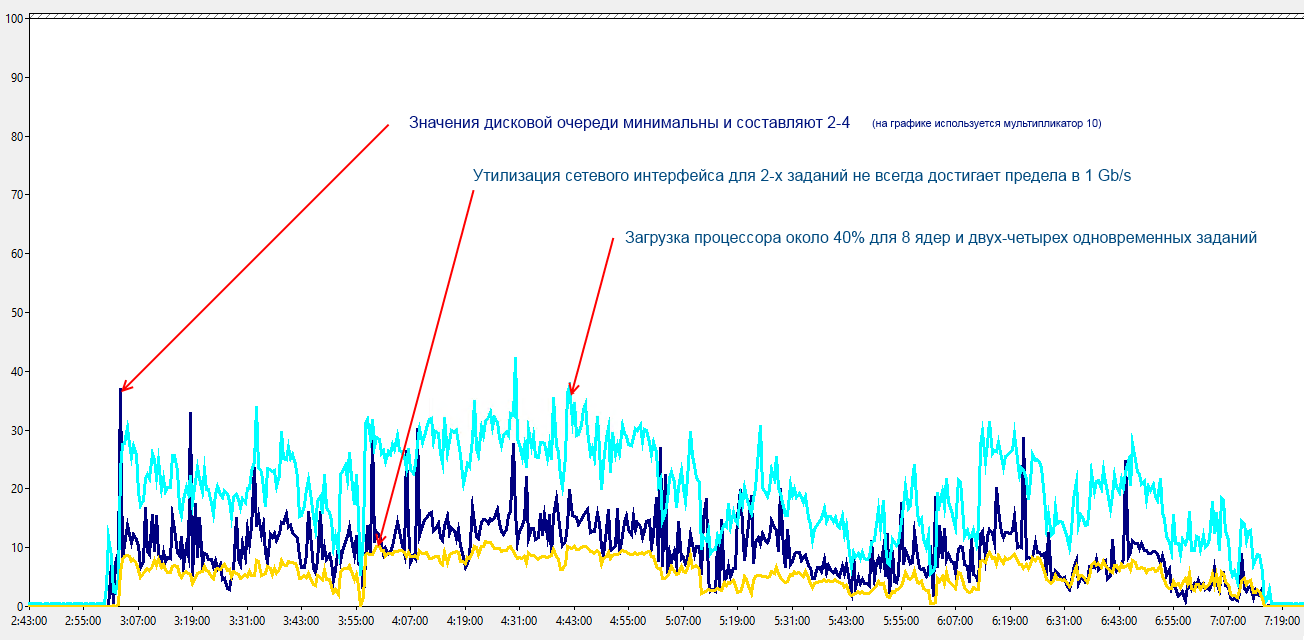
Network
The minimum network interface speed is 1Gbit / s. It is difficult to find equipment that meets this requirement, but can fail the switch — be careful when choosing a network port. At 100mbit / s, a backup of 1 Tb of data will last from 28 hours, which looks relatively acceptable. But when you need to make an additional copy during the working day, wait 10 times longer - more expensive.
You can try to increase the speed using EtherChannel or several IP addresses, but such configurations are more difficult to maintain, and the final speed does not always meet expectations.
If you use VMware virtualization and a dedicated SAN network, paid products can significantly increase the speed of copying data directly from VMFS volumes (SAN Transfer).
Several subtleties in the choice of processor and memory will be discussed in the chapter on server selection.
Simple NAS "business series"
A typical NAS is a device with a closed firmware / operating system designed to store files in a small office. The functions of most modern NAS include storage and distribution of files using SMB / FTP / HTTP / iSCSI protocols. For configuration, a friendly web-interface is used. Often, manufacturers use proprietary technology to create RAID arrays. But for the convenience you have to pay. Business series usually differs from home devices onboard processor - instead of ARM installed more productive Intel Atom or lower Intel Core i3.
A typical representative is NETGEAR RN314 (estimated disk-free price is 50,000).

Pros : relatively inexpensive, hot-swap disk replacement, proprietary software RAID.
Disadvantages : low disk capacity (4 disks), low performance, it is impossible to install backup software directly on the device.
Virtually any NAS, even the simplest, allows you to connect iSCSI-drives. But under load they work “not very”, the smaller the memory in the device and the larger the capacity of the disks, the more problems can be. And the access latency is so high that, except for backups, such disks are not suitable, even the file server will slow down.
Regarding deduplication, Netgear itself writes that it should not be enabled for iSCSI devices . From their article, we can conclude that the method used in their piece of hardware is very similar to the similar Oracle ZFS. And ZFS is famous for the fact that for deduplication of large amounts of data requires a huge amount of RAM, which is not in these modest devices.
As for Windows, the requirements for memory are quite modest. But an iSCSI disk in Windows Server format is a VHD file. VHD deduplication is only supported for the VDI (Virtual Desktop Infrastructure) scenario, so check for backup at your own risk. And risking backups is the last thing.
Deduplication of the data stored in the archives of Windows Backup is meaningless. Since each differential copy only stores changed data, there is nothing to deduplicate.
A number of drawbacks can be leveled out with the purchase of a slightly more powerful and capacious device - NETGEAR ReadyNAS 516.

6 disks, Intel Core i3, with the ability to connect up to three additional five-disk modules. The problem is in the price - without a drive, the device will cost 150,000 rubles.
You can pick up a similarly priced rack-mount model.
The speed of this class of devices is limited by the speed of the two not the fastest Gigabit network interfaces.
Advanced NAS "corporate level"
These devices are already entry-level servers with the same firmware and software RAID.
For example, Netgear RN4220S.

The dual-unit model supports 12 disks with a total raw capacity of up to 48 TB. Two power supply units improve fault tolerance, and you will not be left without backup copies while a new unit is being purchased. Being staffed with only a simple Intel Xeon E3-1225v2 Quad Core 3.2 GHz, 8 GB of RAM and two SFP + slots for 10 Gbit Ethernet, this NAS will cost you 400,000 rubles without disks. It is very expensive and not very flexible, especially for a small company.
General Purpose Servers
A normal server would be a good option if you are ready to tinker with it. Regardless of which operating system you choose, Windows or Linux, you have a wide range of configuration options for your needs. You can entrust data storage to a good RAID controller with a cache, you can assemble a software array on Windows Storage Spaces or ZFS - the choice is yours. You can also install the backup system on the same server.
Choosing a server form factor, it is optimal to stop at a server with a height of 2U. In such a server, as a rule, you can install 12 LFF (3.5 ") or 24 SFF (2.5") disks. In addition, it has now become popular to place two slots for SFF disks in the back of the server. They can be used under the system partition or SSD-cache.
One or two processors? Server processors can contain from 4 chips to absolutely fantastic 22 cores on a single chip, so two processors are not a vital necessity for a backup server.
However, in some cases, two processors may cost slightly more expensive or even cheaper than one with the same number of cores. And installing only one processor, you may encounter the fact that not all PCI-E slots will work.
An example of such a limitation is described on the Intel site . Lenovo also warns that in an x3650 server with a dual-processor motherboard with a single-processor configuration, you’ll get only one slot at all:
With one processor, only two fixed onboard PCIe slots (Slots 0 and 4) can be used (Slot 5 requires the second processor). An internal storage controller occupies PCIe slot 0.
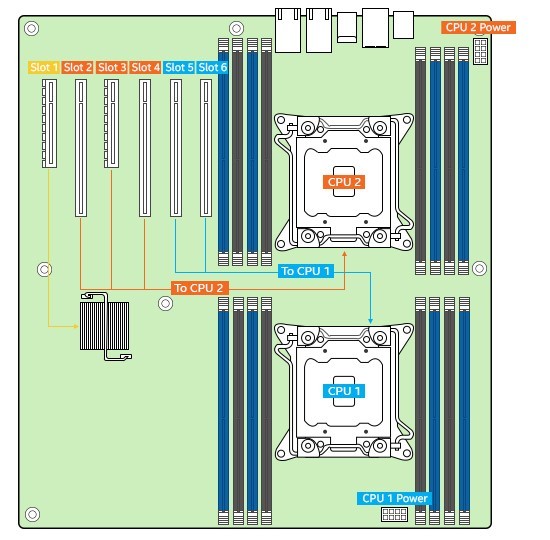
It is necessary to select the number of cores that will optimally match the performance of the network and disk subsystem.
For example, if you have two Gigabit network cards, at best, the server will be able to transfer data in two to four streams up to 100 Mb / s. (in reality, one stream rarely exceeds 50-60 Mb / s). For this, 4-6 nuclear processors are enough. If the server is equipped with a 10-gigabit card and the configuration of the network equipment allows you to get the appropriate flow, then our choice is at least 8-12 cores.
It is not necessary to take a processor of the top-end series, for our task more than enough is not the most powerful E5.
When choosing RAM modules, consider the multichannel processor operation with memory (optimally, one module per channel), as well as the number of processors. On each processor, as a rule, put the same number of modules.
Which server model to choose?
If you choose from HP servers, then even the starting line of dual-unit HPE DL 180 Gen9 servers offers servers with a 12-disk basket. To configure the server, you do not need to think about the necessary cables, available connectors and other fine points in which you can miss. The configuration wizard will help you to do this without errors.
From IBM products, a x3650 M5 model is suitable for a backup server. In the TopSeller configuration - 8871EAG there are only 8 disk slots, it will cost less if you do not need more disks. The most suitable platform is the standard model 8871D4x. To configure the server, use the Standalone Solutions Configuration Tool (SSCT). When starting the program do not forget to choose the right country.
Finally, from the products of the third manufacturer of the “Big Three” - Dell - we can recommend the model R510 .
Successful backup, we wish your data to remain safe and sound.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/306892/
All Articles