Web application vulnerabilities: users hit
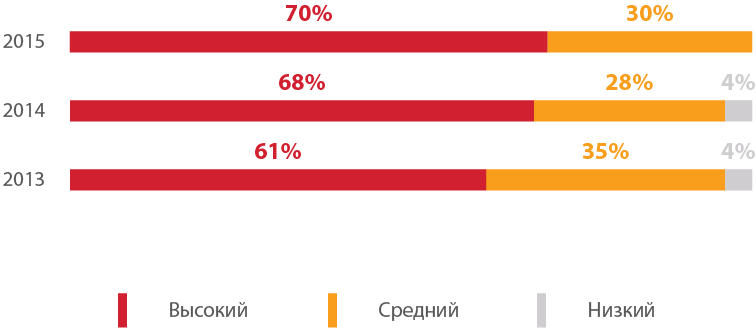
In 70% of websites there are critically dangerous vulnerabilities that allow attackers to gain access to the site and cause serious trouble not only to its owner, but also to numerous users. In terms of development tools, Java applications turned out to be the most full-blown in 2015, and the share of resources with high-risk vulnerabilities based on Microsoft IIS servers significantly increased. The use of an automated source code analyzer allows you to identify 3 times more dangerous vulnerabilities than manual methods of analysis.
Such conclusions are contained in the study of Positive Technologies based on statistics collected during the work on the analysis of web application security in 2015. Comparison with data from similar studies in 2014 and 2013 provides an opportunity to assess the dynamics of the development of modern web applications in terms of information security. This article presents the main results of the study.
')
Sources and methods
Each year, Positive Technologies experts study about 250–300 web applications as part of various activities, ranging from instrumental scanning to source code analysis. According to the results of completed projects in 2015, 30 web applications were allocated, for which an in-depth analysis was carried out with the most comprehensive coverage of inspections. At the same time, only those vulnerabilities that were confirmed by testing on a test bench were taken into account.
The security assessment was carried out using black, gray and white boxes, either manually (using automated auxiliary means) or using an automated code analyzer. The black box method means examining a site on behalf of an external attacker without additional information about the system from the owner. The gray box method is similar to the black box method, but a user who has certain privileges in the system is considered as an intruder. The white box method uses all the necessary system data, including the source code of the applications.
This statistic shows only vulnerabilities related to errors in the code and configuration of web applications. Vulnerabilities were classified according to threats by WASC TC v. 2 , with the exception of the Improper Input Handling and Improper Output Handling categories, as they are implemented as part of many other attacks. The risk of vulnerabilities was assessed according to CVSS v. 2
The applications studied belonged to companies representing telecoms (23%), industry (20%), media (17%), IT companies (17%), finance (13%) and government organizations (10%).
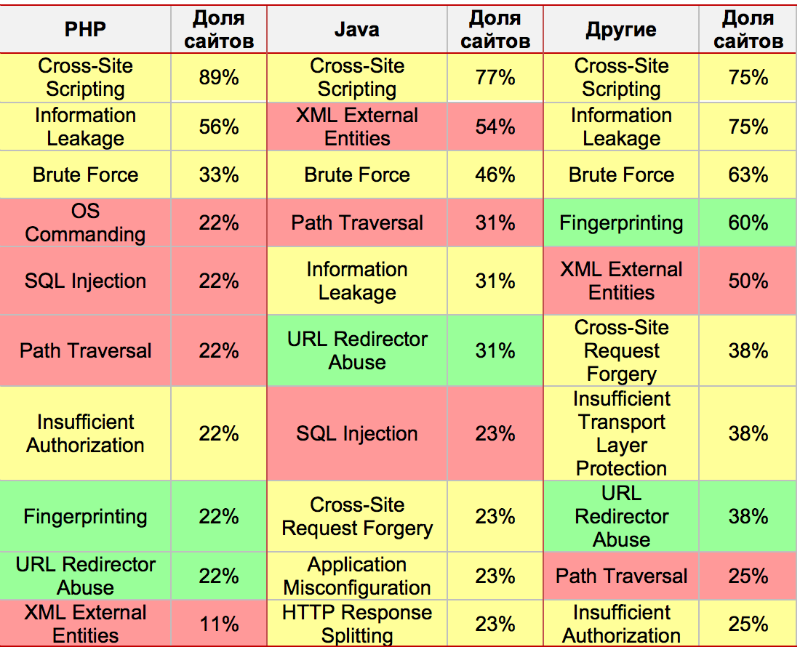
Most of the web applications included in the sample are developed in Java (43%) and PHP (30%); applications created using ASP.NET, Perl, ABAP, 1C, and others have also been encountered. Applications ran under the control of Nginx servers (34%), Microsoft IIS (19%), Apache Tomcat (14%) and WebLogic (14%), as well as under Apache and the SAP NetWeaver Application Server. Approximately half of the resources studied (53%) were productive systems already accessible to users via the Internet, the second half were test sites that are in the process of being developed or put into operation.
Top Vulnerabilities
The disadvantages of at least the average level of risk were found in all the studied applications. At the same time, in 70% of the considered systems critical vulnerabilities were detected. Over the past three years, the share of such systems has been growing: in 2014 there were 68%, in 2013 only 61%.
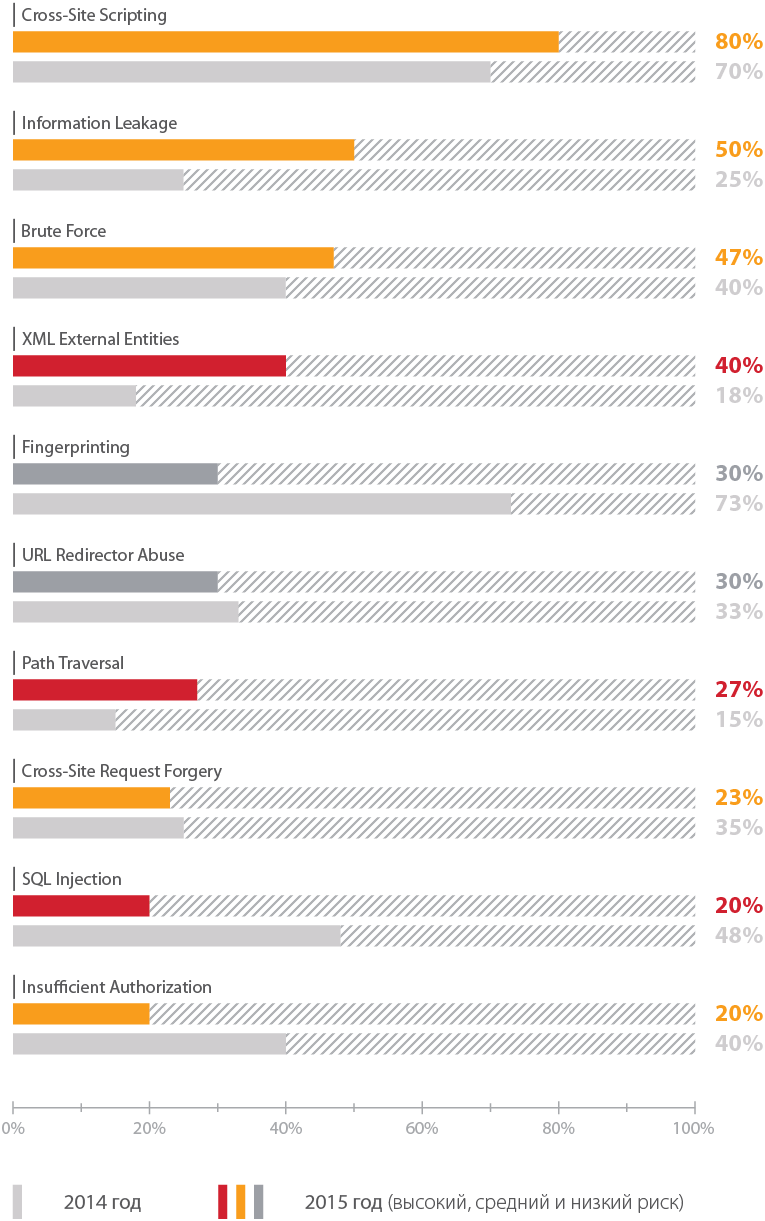
Most of the studied applications allow users to attack. In the code of 80% of the resources, a cross-site scripting (XSS) medium-level vulnerability was discovered. As a result of the exploitation of this vulnerability, an attacker could inject arbitrary HTML tags into the user's browser, including scripts in JavaScript and other languages, and thus obtain the value of the session identifier of the attacker and perform other illegal actions, such as phishing attacks.
Information Leakage ranked second: a vulnerability was found in every second web application. 47% of websites also contain vulnerabilities related to lack of protection against selection of credentials (Brute Force). The most common high-risk drawback in 2015 was the vulnerability of “External Entry XML” (XML External Entities). The vulnerability allows an attacker to obtain the contents of files located on the attacked server, or to make requests to the local network on behalf of the attacked server.
Development Tools: Java is not better than PHP
In past research, PHP applications were generally more vulnerable than systems developed using ASP.NET and Java. However, today the picture has changed: 69% of Java applications are subject to critically dangerous vulnerabilities, while for PHP systems this figure was 56%, which is 20% lower than the 2013 level.
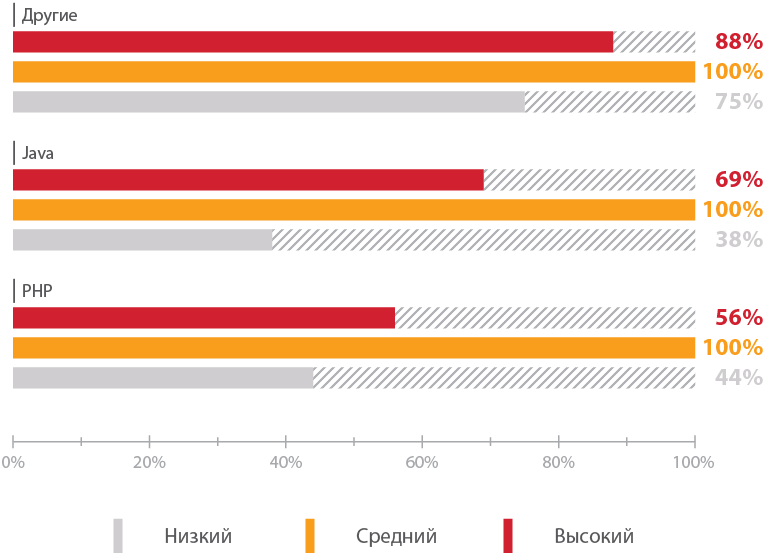
Each PHP web application averages 9.1 critical vulnerabilities, while a Java application has 10.5. For all other programming languages and development tools, on average, each system has only 2 critically dangerous vulnerabilities.
The “cross-site scripting” vulnerability has proven to be the most common for all programming languages. The share of applications affected by the “Introduction of SQL statements” vulnerability decreased compared to 2014: then the vulnerability was revealed in 67% of web resources developed in PHP, and now it is found only in 22%.
Leaky servers on Microsoft IIS
The share of resources with high-risk vulnerabilities based on Microsoft IIS has increased significantly compared with previous years and reached a maximum value. But the share of vulnerable sites managed by Nginx decreased (from 86% to 57%), the same from Apache Tomcat (from 60 to 33%).
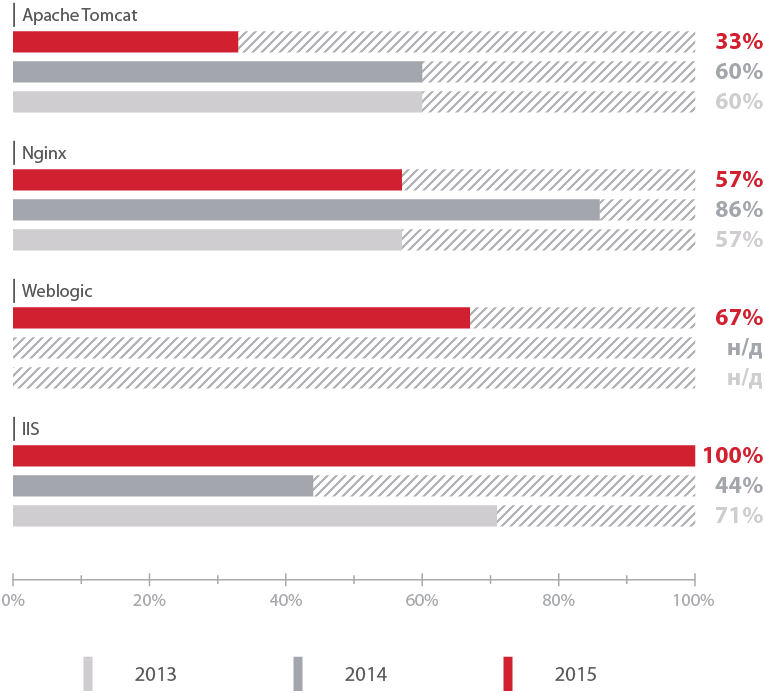
Web applications with high risk vulnerabilities (by type of web server)
For most web servers, the most common administrative error is information leakage. This flaw was found in all investigated applications running on Microsoft IIS servers. In second place - the lack of protection from the selection of credentials.
Sites of banks and IT-companies under threat
As in the past year, critically dangerous vulnerabilities were found on all banking sites. A similar situation is observed in the field of IT. Positive dynamics was noted only for applications of industrial and telecommunication companies.
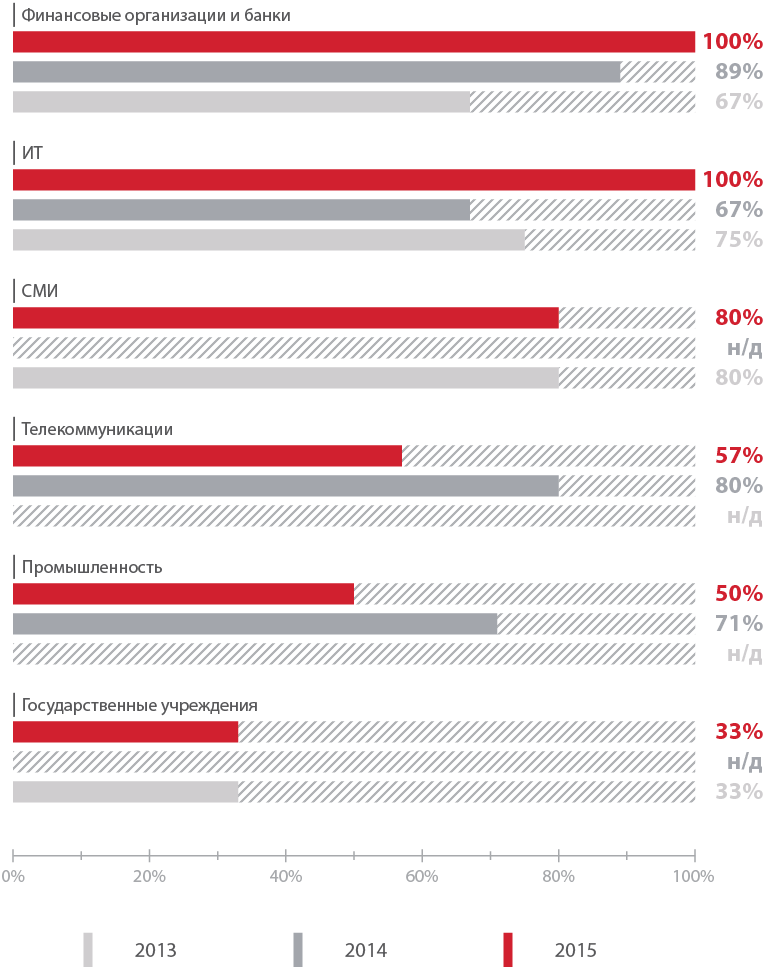
Shares of applications with high-risk vulnerabilities for various industries
Work systems are not much better protected than test ones.
The proportion of vulnerable applications already in use is very large: more than half (63%) are vulnerable to critical vulnerabilities. Such flaws can allow the offender to gain complete control over the system (for example, in the case of downloading arbitrary files or executing commands), as well as to receive sensitive information (for example, as a result of exploiting the vulnerabilities "Implementing SQL statements", "Embedding external XML entities" and others) . The intruder can also conduct successful denial of service attacks.
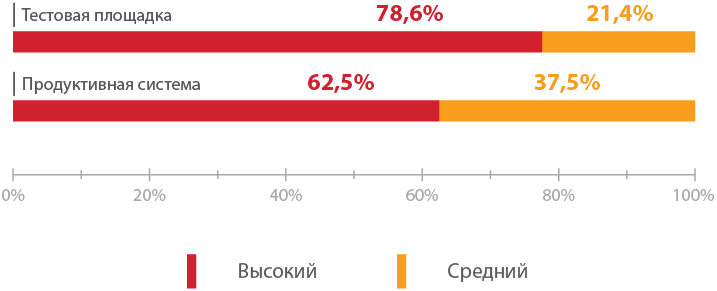
Maximum risk level of detected vulnerabilities for test and production systems (proportion of vulnerable systems)
Source code analysis better identifies dangerous vulnerabilities.
The share of systems subject to critically dangerous vulnerabilities that were detected by the black box method is significantly lower than the same indicator for sites where the source codes of the application were analyzed. However, even for the black and gray box method, the proportion of systems with dangerous vulnerabilities is quite large (59%). Thus, the attacker's lack of access to source codes does not make the web application secure.
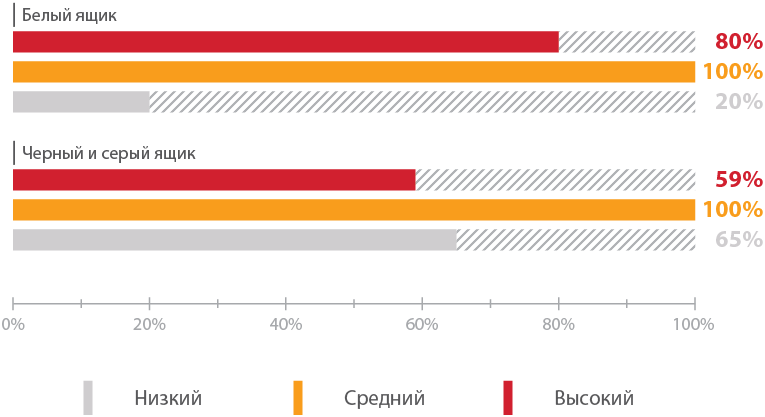
Shares of systems with vulnerabilities of different degrees of risk according to the testing method
At the same time, the average number of vulnerabilities of various levels of risk per system detected by the white box method is significantly higher than when tested using the black and gray box methods.
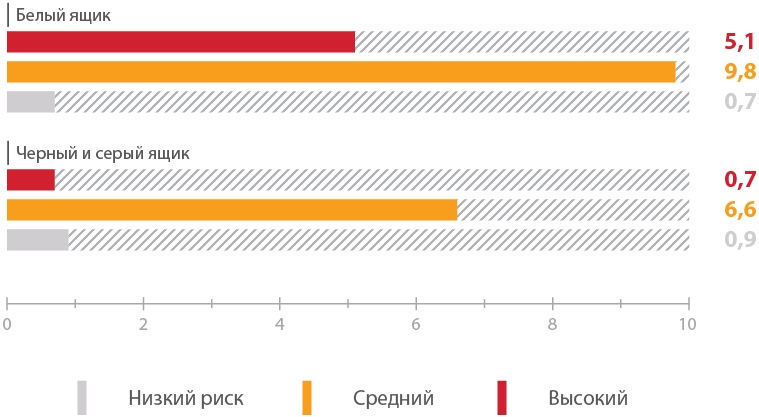
Average number of detected vulnerabilities per system
As part of the study, a comparison was also made of the results of work carried out by the white box method manually or using an automated scanner. On average, each system detected about 15 critical vulnerabilities in the case of using a code analyzer (only confirmed vulnerabilities were taken into account), and only 4 vulnerabilities using manual methods.
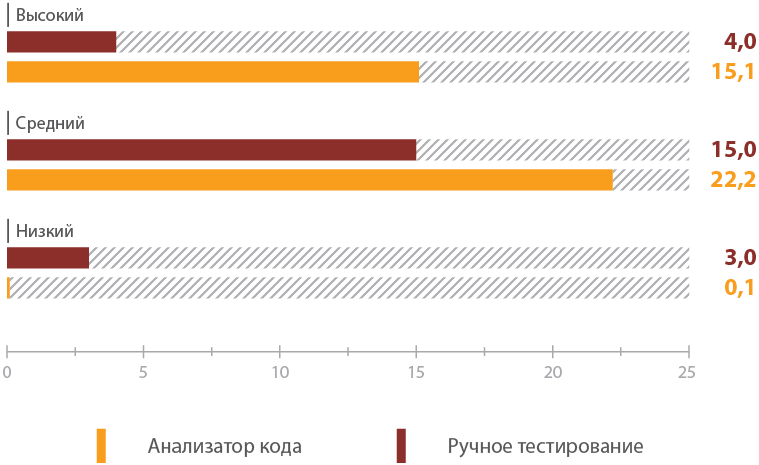
Average number of identified vulnerabilities of a certain level of risk per system using different methods
Thus, security analysis using the white box method is much more effective than other methods that do not analyze the source code of the application. At the same time, automated code analysis turns out to be quite effective, especially if we take into account the amount of code of modern applications that use many libraries.
In general, the data obtained indicate the need to regularly conduct work on the analysis of the security of web applications. It is important to carry out such analysis at all stages of development, as well as regularly (for example, twice a year) during the operation of the systems. In addition, applications that are already in use need effective protection against attacks: more than half of these resources (63%) were exposed to critically dangerous vulnerabilities. These shortcomings can lead not only to the disclosure of important data, but also to the complete compromise of the system, or its failure. To protect against such attacks, it is recommended to use application-level firewalls.
Read the full text of the study at www.ptsecurity.ru/research/analytics/
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/306622/
All Articles