In Q2 2016, encryptors top the list of cyber attacks

Cyber space has become an integral part of our daily life. Digital transformation has affected home and corporate users, because The number of devices connected to the network continues to grow.
Concepts like “digital home” or “BYOD” (Bring Your Own Device) are already part of our digital universe: more and more Internet users are working from home or using their own devices for personal as well as professional purposes. This means that there are more and more security holes.
')
According to the PandaLabs antivirus lab , over 18 million new malware samples were detected during the quarter.
Trojans retained their leading position in the list of identified threats, showing an increase in the number of attacks by cryptographers in this category. The average number of new threats detected each day is 200,000. This indicator is slightly lower than the first quarter of 227,000 samples. Along with encryption attacks, most of the other attacks in this quarter were aimed at stealing personal information and user credentials.
There is also a tangible boom in the “Internet of Things” area. This will generate new attacks and potentially have a significant impact on our lives. For example, in the near future, cyber-attacks will allow cyber-criminals to steal our cars, remotely deactivating anti-theft alarms and allowing the engine to start.
Every day we see more and more vulnerabilities among mobile phones. Recall that most of the problems that arise as a result of these security holes are mostly related to the lack (or lateness) of updates coming from various hardware manufacturers.
Ciphers
We know that cryptographers are a huge business for cyber criminals, but it is very difficult to assess its real scale. In 2015, the US Department of Justice published information that the Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) has received 2500 complaints about attacks by cryptographers.
In total, approximately $ 24 million were paid to the victims of these malicious programs . Cipher operators are a global phenomenon. Taking into account the total amount of ransom in this example and the ubiquitous growth of these malicious programs worldwide, we can conclude that the annual revenues of cyber criminals from cryptographers are billions of US dollars.
Looking back, we can recall the various cases of coder’s attacks on healthcare facilities.
This quarter began with a new victim: MedStar Health. This nonprofit medical organization suffered from the attack of the coder so seriously that they had to shut down their systems for several days.
In the case of MedStar Health, it seems there was a direct attack that exploited the vulnerabilities that existed in their systems. However, most of these attacks are carried out with the help of malicious email attachments or hacked Internet sites. This happened in April with Maisto International, a manufacturer of remote-controlled toys: visitors to its website unknowingly became victims of a cryptographer. Their hacked website infects its visitors with the well-known Angler exploit kit. Its purpose is to identify popular software products (flash, java, etc.) from the user, and then use the various vulnerabilities of these installed applications to damage the computer.
However, attacks via websites are not the only way. Cyber criminals use another popular tactic now known as malvertising (malicious advertising): placing advertisements in public places on highly visited sites to infect users of these sites.

The famous blog perezhilton.com recently became the victim of two malicious advertising attacks. Hackers infect over 500,000 users every day using the Angler exploit kit.
Targeted attacks exploit vulnerabilities in the system. Common Threats: Hacked Sites and Malicious Ads
One of the most interesting cases with cryptographers that we saw in this quarter occurred with a company from Slovenia.
An employee of the company, responsible for IT, received by mail a letter from Russia, which reported on the hacking of their network. Russian cyber criminals hacked the network and prepared it to run a coder on all computers on the network. If the Slovenian company refuses to pay a ransom of 9,000 euros (in bitcoins) within 3 days, the cryptographer will be launched . As proof that they have access to the corporate network, they sent a file with a list of all devices connected to the internal network of the enterprise.
Many victims of encryptors prefer to pay a ransom, but this does not guarantee the return of stolen (encrypted) data. In May, a cardiology hospital in Kansas (USA) was attacked by a cipher operator, and management decided to pay a ransom for the data return. As a result, they were shocked that the password they sent allowed them to decipher only a part of the information. To recover the remaining information, the hackers demanded a second payment. But the hospital refused to pay a second time.
The professional team CSLFR, participating in NASCAR, witnessed the coder’s attack on three of their PCs. He encrypted the information, which was estimated at $ 3 million. In this case, the CSLFR also paid a ransom ($ 500), but, fortunately, in this case they were able to recover all the information.
Is it worth paying a ransom?
Let's say this: if victims pay ransom to cyber criminals, they increase the effectiveness of attacks.
If the attack is successful and made a profit, then hackers will attack an even greater number of users. In the long run, these attacks can harm us all.
Paying a ransom for recovering information further contributes to criminal activity.
Pay or not pay - this question remains controversial. In April, James Trainor, assistant director of the cyber division at the FBI, quite clearly outlined his position in his public statement:
“Payment of the ransom does not guarantee the organization that it will receive its data back: we have seen cases where organizations have never received the key for decryption after paying the ransom. Paying a ransom not only encourages existing cyber criminals to attack more organizations, but also provides an incentive for other intruders to engage in similar illegal activities. And finally, by paying the ransom, an organization can thus contribute to the financing of other illegal activities related to crimes. ”
Evolution of malicious emails
The starting point of attack data is not only the use of malicious advertising or hacked sites. A significant part of such attacks begins with emails that are disguised as accounts or notifications.
One of such attacks was through mail in Poland and Spain, where cyber criminals were disguised as well-known energy companies operating in these countries.
The criminals sent the victims malicious emails that did not contain attachments: the text of the letter contained an account with a link to view the "decrypt account."
When you click on this link, the user is redirected to a false website, which is an exact copy of the site of this energy company.

There the user could download the "account". If the user downloaded and opened the "account", then his computer was infected with the coder.
If you had a chance, what would you say to a cyber-criminal who “laid his eyes on you”?
We have witnessed the evolution of cryptographers. As a rule, victims are provided with detailed instructions on how to pay the ransom. In some variants of encrypters (for example, a new version of the Jigsaw family), hackers went further and offered a chat service where users can chat with extortionists in real time and discuss the terms of the ransom payment.
You can now communicate with cyber criminals to discuss the ransom payment for the stolen information.
One of the most original attacks by the coder for the last quarter (and the most dangerous one!) Occurred in Russia.
Its uniqueness in the distribution method, because the malware was sent by mail but was not actually executed. It was written in the form of a special update for the program of one of the major software manufacturers in Russia (over a million corporate users in Russia and the former USSR), and worked only if the computer had this program.
She forced users to update their program, and if the user did this, then the malware connected to the program database, searched for counterparties in it, and sent itself to the email addresses found. At the same time, he infected the computer with an encrypter, encrypted the files, and then, as usual, demanded a ransom.
Cyber crime
We have seen how this can be done in various ways: through cryptographers, by stealing information from people and businesses, and sometimes using targeted attacks on certain banks. In recent months, these cases have become very serious, and when we study them, we can see what impact they have on enterprises (from charitable foundations or financial companies to pornographic sites and voting sites) ... even the police suffer. Risks everyone.
Theft of information
Team Skeet, a website that distributes porn videos and is owned by the Paper Street Media network, recently survived the attack, which resulted in data stolen from 237,000 users. Moreover, not only the registration data and mail addresses of users were stolen, but also their actual residential address. Later, these data were sold online for $ 400 per user, which in total could be about $ 95 million. But for sure the criminals offered good discounts depending on the amount of data.
Ciphering and stealing data from people and businesses is a tactic of cyber crime.
The charity organization National Childbirth Trust (NCT, London) on April 7 faced a security breach. During the attack, data of 15,085 users, including logins, encrypted passwords and mail addresses, were stolen.
Acer, a well-known hardware manufacturer, was also the victim of an attack on its online store, where the data of 34,500 of their customers were stolen. The worst thing is that their website was hacked throughout the year (from May 2015 to April 2016), which the company did not even suspect .
In June, a hacker nicknamed “TheDarkOverlord” put up for sale patient data from three different American companies. In total, more than 650,000 users of TheDarkOverlord have requested $ 700,000 for the stolen data. Soon, the same person tried to sell the data of 9.3 million clients of one medical insurance company for 750 bitcoins (about half a million US dollars).
In Spain, the Anonymous group published a list of personal data of 5,000 national police officers. The data was not obtained from the police servers, but as a result of an attack on the website of a social security organization.
When it comes to cybercrime investigations, when Chris Vickery is mentioned, you should ring the bells. This security specialist found a server on Amazon, where someone left a database containing 93.4 million voter records in Mexico: postal addresses, official identifiers, etc. Vickery reported this to the Mexican authorities, and the database was destroyed . It can be assumed that someone stole the data and used the Amazon cloud for temporary storage.
Chris Vickery also discovered another information theft incident. In this case, the contact details of 1.1 million users were stolen from the website beautifulpeople.com. Despite the fact that Vickery reported this to the site owners, the criminals sold this database on the black market.
In addition to criminals and organizations whose main goal is to harm everyone on the Internet, there are also quite legitimate tools that can work against us.
In the case of the popular remote access utility TeamViewer, the data of a huge number of users whose computers were opened for remote access were stolen. Due to the huge number of victims, the first thought was related to the fact that someone entered TeamViewer and took their bases for subsequent unauthorized access. Later it turned out that the stolen information came from the users themselves using the same registration data to connect to different services.
This is a common tactic of hackers: if they stole registration data from one site, then they try to access other services using the same combination of username and password. They know that many people use the same registration data on different websites.
In this case, as soon as the hackers got access to the victim's PC, they connected to his PayPal account and robbed all the money.
Rising incidents with PoS terminals
Another widespread and popular method of theft is through terminals at points of sale. PoS terminals are subject to certain malicious infections that are specifically designed to steal data from bank cards through such terminals.
Most often, the victims are hotels, which we could see in the example of the Hard Rock Hotel & Casino in Las Vegas (USA).
It is known that PoS-terminals were infected in the period from October 2015 to March 2016, and during this time the data of bank cards used in this organization were stolen.
Such incidents happen all over the world. Recently, a Spanish luxury hotel chain was attacked. Fortunately, the attack was stopped in time, not reaching the PoS-terminals, and therefore the robbery was prevented. This attack was specifically designed for this hotel chain. To allow external connections and remain undetected, hackers registered a domain named one of the victims from an African country.
PoS terminals in hotels, restaurants and businesses are becoming more attractive to hackers.
But not only PoS terminals and hotels appeared on the “line of fire”. Cyber criminals to steal bank card data turned their attention to restaurants. Over 1000 establishments owned by Wendy's popular fast food chain have become victims of malware for PoS. The criminals were able to extract data from Wendy's customers' bank cards.
We in the Pandalabs antivirus lab found an attack that launches a known malware (PunkeyPOS) that infected over 200 restaurants in the United States.

In the picture: an image of one of Wendy's restaurants. This does not mean that this particular institution is infected.
Financial institutions are also in demand.
What theft can be the most effective? Of course, this is a robbery of the banks themselves, but it is much more difficult than robbing other institutions. Although…

It was found that the Central Bank of Bangladesh was attacked, as a result of which hackers could steal more than 1 billion US dollars. Fortunately, when the bank found out about this, it managed to block a huge number of transfers, although the criminals were able to get about $ 81 million.
Subsequently two more similar incidents occurred: one happened with a bank in Vietnam and the other in Ecuador.
Even if the hunt for cyber criminals is very difficult and time consuming, it can still produce results. In April, Dmitry Fedotov, known as “Paunch” and the author of the Blackhold exploit kit, was sentenced to 7 years in prison in Russia.
Alexander Panin, a 27-year-old Russian citizen, was sentenced in the US to 9.5 years in prison. Panin stood behind the well-known SpyEye banking trojan.
Social networks
If we talk about social networks, in the second quarter there were countless cases of theft of registration data, which almost always fall into the wrong hands. Below are the most popular social networks:

Security 117 million users of LinkedIn was at risk after it published a list of email addresses and passwords. Although the hacking occurred in 2012, the full list has not yet been published.
The best way to protect yourself from these types of attacks is to use two-factor authentication. In this case, even if your registration data will be in the wrong hands,
it will still not be possible to connect to your account.
32 million usernames and passwords for Twitter access were put up for sale for 10 bitcoins, or about $ 6,000. Although this social network denied rumors that this data was obtained from their server. In fact, passwords were in plain text, and most of them belonged to Russian users. This may indicate that they were abducted by phishing attacks or trojans.
VKontakte
“Russian Facebook” faced the sale of 100 million of its users, including email addresses, names, actual addresses, phone numbers and passwords. In this case, the same thing happened as in LinkedIn when the data stolen long before that was put up for sale.
Security consultant Arne Swinnen found a security bug on Instagram that allowed hacking 20 million of their accounts. After reporting this information, Facebook (the owner of Instagram) paid him $ 5,000 as part of his bonus program. Moreover, this is not the biggest reward that was presented this quarter: Facebook paid a reward of 10,000 US dollars to a
10-year-old child from Finland. This Finnish wunderkind found a security bug that allowed the deletion of comments in any Instagram account.
Myspace
Nowadays, it has ceased to be very popular, but it is still vulnerable to attacks that could affect millions of users. The incident occurred in 2013, but it was not known until May of this year. In this attack, hackers stole usernames, passwords, email addresses. Allegedly, over 360 million accounts have been compromised.
You may not have connected to MySpace for several years, but if you are used to using the same registration data for different sites, now is the time to change them and connect two-factor authentication.
If you do not believe us, then just ask Mark Zuckerberg, the founder of Facebook, about this. Zuckerberg witnessed how his Twitter, Pinterest and Instagram accounts were hacked by a group of jokers who called themselves OurMine.
Apparently, the password used in LinkedIn was the same for all accounts, which greatly simplified OurMine’s task to access all of these accounts.
Follow two important tips: use two-factor authentication and do not use the same username and password on different websites.
In addition, it is important to use complex passwords. The Kore Logic study analyzed 117 million passwords and demonstrated that most users choose passwords that are too simple. The following table lists the 10 most frequently used passwords:
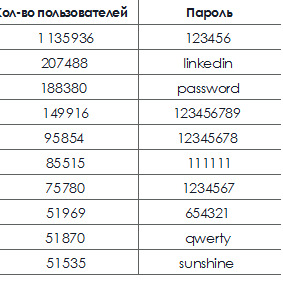
In this regard, we must applaud Microsoft's initiative to ban commonly used passwords, which can be found in the table above. We hope others will follow their example.
The stars in Whatsapp are another good practice in the field of information security. The most popular instant messaging application and its owner, Facebook, decided to increase user privacy by encrypting all messages sent through this application.
Similar actions in the next few months will be implemented in Facebook Messenger.
Mobile threats
It seems that Google decided to seriously close all security holes in their operating systems. Using monthly updates to eliminate all newly discovered vulnerabilities, they were only able to fix 25 vulnerabilities in May (some of them were so serious that they allowed remote code execution).
Although it would seem that none of these vulnerabilities were exploited by hackers, but this was the largest Google update ... so far.
Despite the improvements, the Android ecosystem is still “trembling” due to security issues.
Undoubtedly, one of the biggest problems of Android is their slow updates, which largely depend on each manufacturer of various Android devices. While products that are monitored directly by Google, receive such updates almost instantly (for example, mobile phones and Nexus tablets), other Android users have to wait for months to get patches. And in some cases, patches never reach users.
The lack of updates makes devices more vulnerable to known security problems, as the number of attacks is constantly growing, this makes the Android ecosystem really dangerous.
Internet of things
Recently, in this section of the report almost always there was news about hacked cars, so today we'll talk about the Mitsubishi Outlander. This hybrid has its own Wi-Fi network, which connects to an application where you can control temperature and other parameters.
Security specialist Ken Munro figured out a Wi-Fi password using a brute force attack. Having penetrated into the network, Munro would be able to harm the car (for example, completely using up the battery of an electric motor). But the most serious thing is that he could remotely deactivate the alarm, which real criminals could take advantage of.
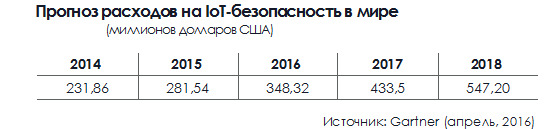
Consulting company Gartner has published an interesting report on the security of the Internet of Things. This document predicts that by 2020 IoT devices will be involved in 25% of attacks on enterprises. It is expected that in 2016, 6.4 billion of such devices will be connected to the Network (30% more than in 2015), and in 2018 it is predicted that the number of such devices will exceed 11.4 billion.
The cost of the security of the Internet of Things will continue to grow, although taking into account the forecasts presented in the table below, they are likely to be insufficient:
Cyber war
Last year, we wrote about how the Hacking Team was completely compromised. It is well known in the world for selling hacker software (malware) to governments and special services in many countries of the world. They hit the headlines after the Italian newspaper “Il Fatto Quotidiano” reported that the “Hacking Team” lost its export license, as a result of which it would not be able to sell its programs outside the European Union, at least without the need to complete lengthy bureaucratic procedures.
When we discuss cyber warfare, in most cases we are talking about attacks that may be sponsored by different countries, although it is very difficult to find facts proving the responsibility of certain officials for organizing and conducting such attacks.
However, the United States went on the offensive, recognizing that they launch cyber attacks against Daesh (also known as ISIS). US Deputy Secretary of Defense Robert Wark said:
“We are dropping cyber bombs. We have never done this before. Similar to the fact that we are conducting an air campaign, I want to have a cyber campaign. I want to use all the features that I have. ”
In June, the South Korean Police Department reported an attack from North Korea. Apparently, the attack began about a year ago, and it was targeted at 140,000 computers belonging to organizations and government agencies, as well as contractors of the Ministry of Defense. This attack was detected only in February of this year. According to the police,over 42,000 documents were stolen, of which 95% were related to national defense issues , for example, the design and specifications of the wings of the American F15 military aircraft.
The National Committee of the US Democratic Party admitted that their systems were hacked about a year ago (possibly more). They are sure that the hackers belonged to the Russian special services. The attackers gained access to emails, chat rooms and all types of research. All computers belonging to the research department were accessible to hackers, and some files were stolen.
Conclusion
The number of attacks used to steal information and money continues to grow. Users are faced with the theft of their registration data or accounts, and in many cases they have not been attacked directly. Instead, their information was found in databases that were stolen from the hacked networks of various companies.
In addition, some users reuse their passwords on other services, which makes it easier to steal, and this problem is quite simply solved by two-factor authentication, available on most sites. Another possibility is connected with the fact that service providers force their users to take
certain security measures, which today does not seem incredible anymore, because Convenience does not have priority over security.
Encryption attacks have become quite complex. Hackers make huge profits. In the coming months, we will see an increase in such attacks.
Another disturbing trend is the theft of data from bank cards via PoS systems, where most of the affected institutions are small businesses (restaurants, bars, etc.), which, obviously, do not have a dedicated team of IT security specialists. Considering how easy it is to sell this stolen information on the black market and make a profit, it seems that cyber criminals will develop this direction of attack.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/306600/
All Articles