Yota on Sakhalin: how the bond comes to the island

Cape Aniva, Sakhalin Island. Image: " World Travel ".
Yota becomes available to subscribers in the most remote corners of the country. We went beyond the limits of the mainland of Russia and launched work on Sakhalin - more than 9,000 kilometers from Moscow. How modern types of communication come to islands, we will tell under the cut.
The most remote internet

One of the most remote from the continents pieces of land on the planet is Pitcairn Island . The nearest settlement is in 2100 kilometers. The entire population of the island - a few dozen people, allegedly descendants of the rebels from the British ship " Bounty ".
')
There is a shop, warehouse, library, medical center, 126 kbit / s Internet and its own domain - .pn. Internet access in Pitcairn is provided by satellite.
But not all islands use space communications. In some cases, underwater fiber optic cables are laid across the islands, which are used to exchange information between continents.
World Underwater Internet
habrastorage.org/getpro/habr/post_images/0af/936/80a/0af93680a6fdfe8398b0b7c7471a3d78.gif
Schematic image of laying the submarine cable .
For laying underwater trunk cable from the ship down a special installation. It deepens the cable into the seabed so that ships or animals do not damage it.

In this photo you can see the installation for burial, resembling a conventional plow.
For cable penetration, underwater chain mechanisms, rotary excavators (for dense sediments) are used, as well as systems washing away the trench with powerful water pressure (for sandy bottom sediments). Now they are able to deepen the cable into the ground at depths of up to 2,500 m.
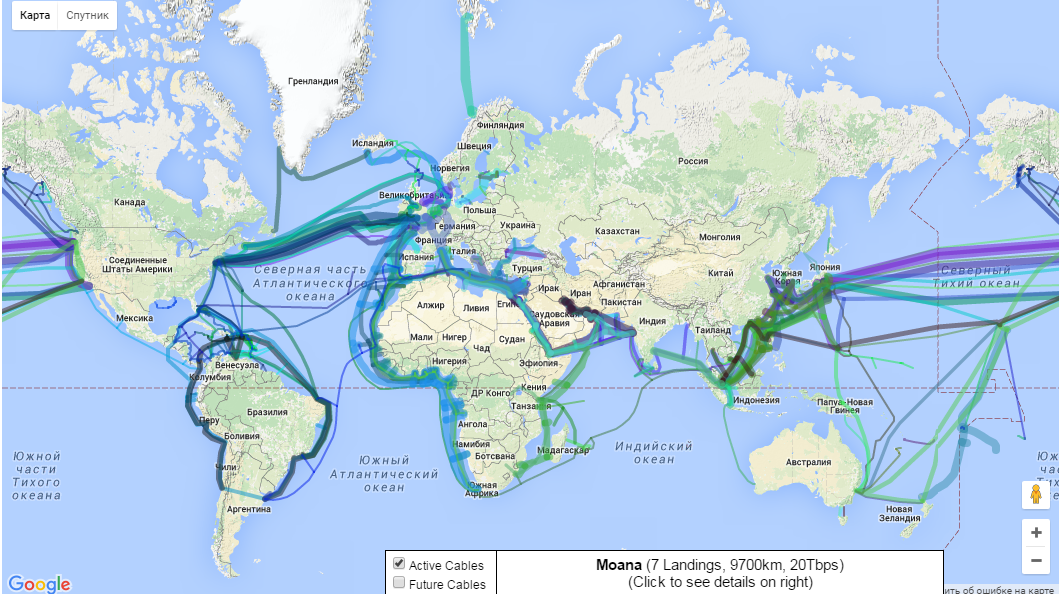
This is the world map of submarine cables. Under the link you can see the cable carrying capacity and their length, as well as the layout of future projects of submarine cables. We are interested in Sakhalin.

On the left you see the existing cable, in the center and on the right - future projects.
Communication history on Sakhalin

The first line of communication was laid from the mainland to the island in 1881: a telegraph cable was connected to De-Kastri (a village on the coast of the Sea of Japan, Khabarovsk Territory) and the center of the Sakhalin prison and the post of Alexandrovsky. In July 1901, the cable failed - this is how the first, but not the last, connection with the island happened.

The accident was so serious that it was not possible to restore the communication line. In 1902, a bypass line was built along the bottom of the Nevelsky Strait from Cape Lazarev to Cape Pogibi - this is the narrowest point of the strait (3.7 km). However, this option turned out to be even less reliable: almost every year, floating ice damaged the cable in the shallow waters. Only the construction of a radio telephone station on the island made it possible to resolve the issue of stable communication with the mainland. However, attempts to lay the cable along the bottom of the strait did not end. In the mid-1930s, when the island belonged to Japan, a cable was laid between Sakhalin and Hokkaido.
In the 1970s, a copper line was laid between Cape Pogibi and the mainland. It worked system ICM-15, designed to organize group telephone paths. On two twisted pairs, the system was able to transmit up to 15 telephone channels. However, this cable periodically broke down due to damage by fishing vessels.
In 1969, the Great Northern Telegraph Company built a JASC coaxial cable line between Sakhalin and Japan, which has successfully worked for several decades. Replaced it in 1995, when the first fiber-optic line was built. Surprisingly, Sakhalin did not connect the “mainland” to the Internet, but another island - the project was implemented by the Japanese company KDD.
In 2005, the cable was finally stretched from the mainland of Russia. Alas, the project was implemented with a large number of violations, and the cable itself was not fixed in the ground. He received several critical damage and soon stopped working .
In 2007, Transtelecom, with the efforts of NEC, extended a new fiber-optic line from Sakhalin to Hokkaido Island. Its length was 570 km, and its carrying capacity was 640 Gbit / s. With the Internet on Sakhalin, it became much better: the cost of the Internet fell from 3,500 to 1,400 rubles at 0.1 Mbit / s.
In the same year, another Transtelecom cable was commissioned: from Sovetskaya Gavan (Khabarovsk Territory) to Ilinsky (Sakhalin Oblast, Tomarinsky District), its total length was 214 kilometers. The designers deepened the cable into the ground to a depth of 1 meter, but this did not help much: accidents happened with enviable periodicity.
Future plans
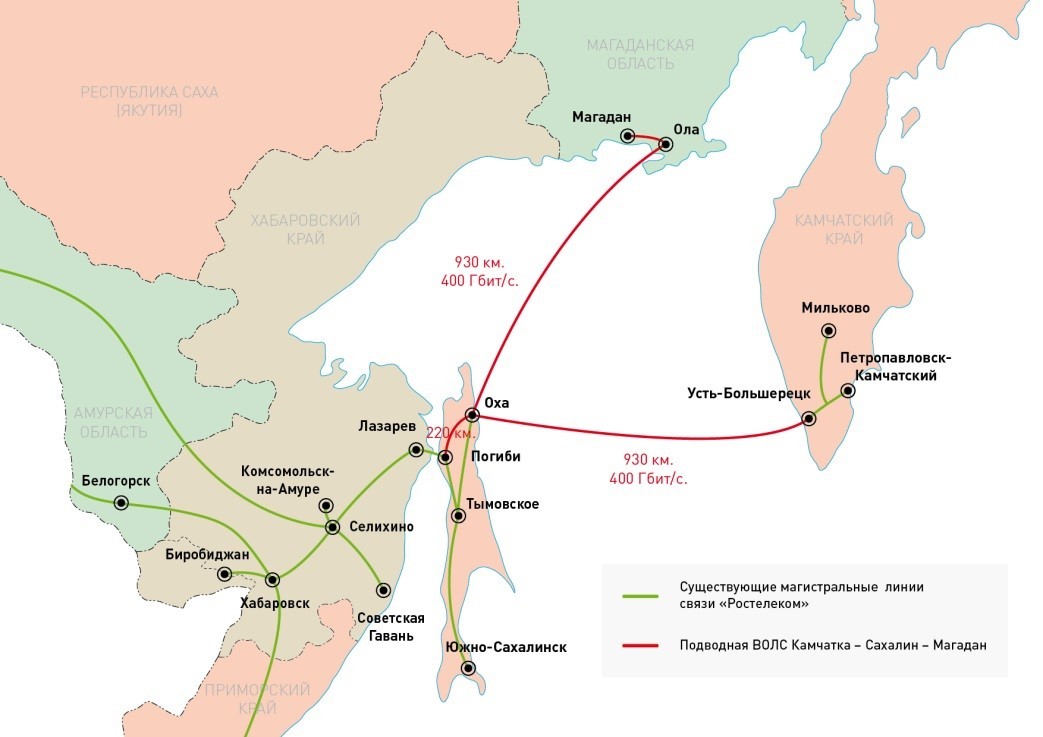
In 2014, Huawei announced that it had launched the development of new submarine cables for the Russian Far East on the request of Rostelecom. After the project is completed, the entire cable infrastructure will have a length of 1,900 kilometers, and will connect the most remote settlements of Kamchatka Krai, as well as Magadan and Sakhalin regions, to the mainland. Commissioning of the first communication line with a length of 930 kilometers is scheduled for 2017.

Cable laying works on the bottom of the Sea of Okhotsk are carried out by Huawei Marine using a special cable ship-paver - Cable Innovator. The length of the vessel is 146 m, width 24 m, transportable cable stock is 8.5 thousand tons.

The cable leading from Vladivostok to Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk and beyond, is part of the Russian Transarctic Cable System project ( ROTAKS ), launched in 1999. A few years ago, the total cost of ROTAX was estimated at $ 800 million. Despite the support of the Ministry of Communications of Russia, the authors of the project have been looking for funding sources for 10 years, and all the time they are shifting the dates for the start of implementation. If construction still starts this year, the stage of testing the system starts no earlier than the first quarter of 2019.
Taking into account the monopoly prevailing in the market, Sakhalin subscribers for a long time could not receive alternative (and good in quality) communication services. According to the FAS, prices for communication services in the Sakhalin region rose to absurd values: 250% higher than in other cities of the Far East, and 1800-5100% higher than in the west of the country.
Today, everything is different: in 2016, the island even ranked third in the ranking of regions with the most affordable mobile communications. The accessibility index shows the real value of the services of operators, taking into account the average income of the region’s population.

Map availability of mobile communications in Russia: the lighter, the more accessible.
The speed of the mobile Internet is also not inferior to the “average for the hospital” and allows Sakhalin residents not to limit themselves to checking email from a smartphone, but to watch videos, use streaming music services, play online games.
With the arrival of Yota, Sakhalin residents and tourists have gained access to truly unlimited mobile Internet and can take full advantage of fast communication without saving traffic.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/306130/
All Articles