Tablecloths or how to deploy Remote Desktop Services on Windows Server 2012 R2
Today, we will explain how the deployment of RDS Session Host on Windows Server 2012 R2 differs from earlier versions of Windows Server and describes the available deployment options. Remote Desktop Services on Windows Server have significantly improved over the last time, but nevertheless, a lot of incomprehensible due to the many components involved in the process remains. RD Session
Rd connection broker
When a remote desktop session is disconnected, applications in the user session continue to run. To track user sessions, RD Connection Broker stores information such as the name of the
Starting with Windows Server 2012, remote desktop connection brokers not only store data about user sessions, but also configuration information. RD Connection Broker uses a Windows internal database to save session and configuration information, except when High Availability Mode (HA) is set up using SQL 2008 R2 server (or later version).
Remote Desktop Connection Broker requires an Active Directory domain, but cannot be installed on a domain controller (DC). You can deploy remote desktop services in a workgroup by installing the server role, although it loses the possibility of centralized management, control panels and the functionality of remote applications Remoteapp.
Centralized application publishing
Windows Server 2012 also introduces the collections concept. In Windows Server 2008 R2, system administrators were required to publish applications for each RD Session Host individually. The Remote Desktop Connection Broker now stores configuration information.
Deployment Options: Fast and Standard
The key to understanding how to deploy RDS on Windows Server 2012 R2 in the understanding that installing the RD Session Host is not enough. Server Manager provides a special deployment mode for installing RDS, so all the necessary components are installed in the right places to make deployment simple and quick.
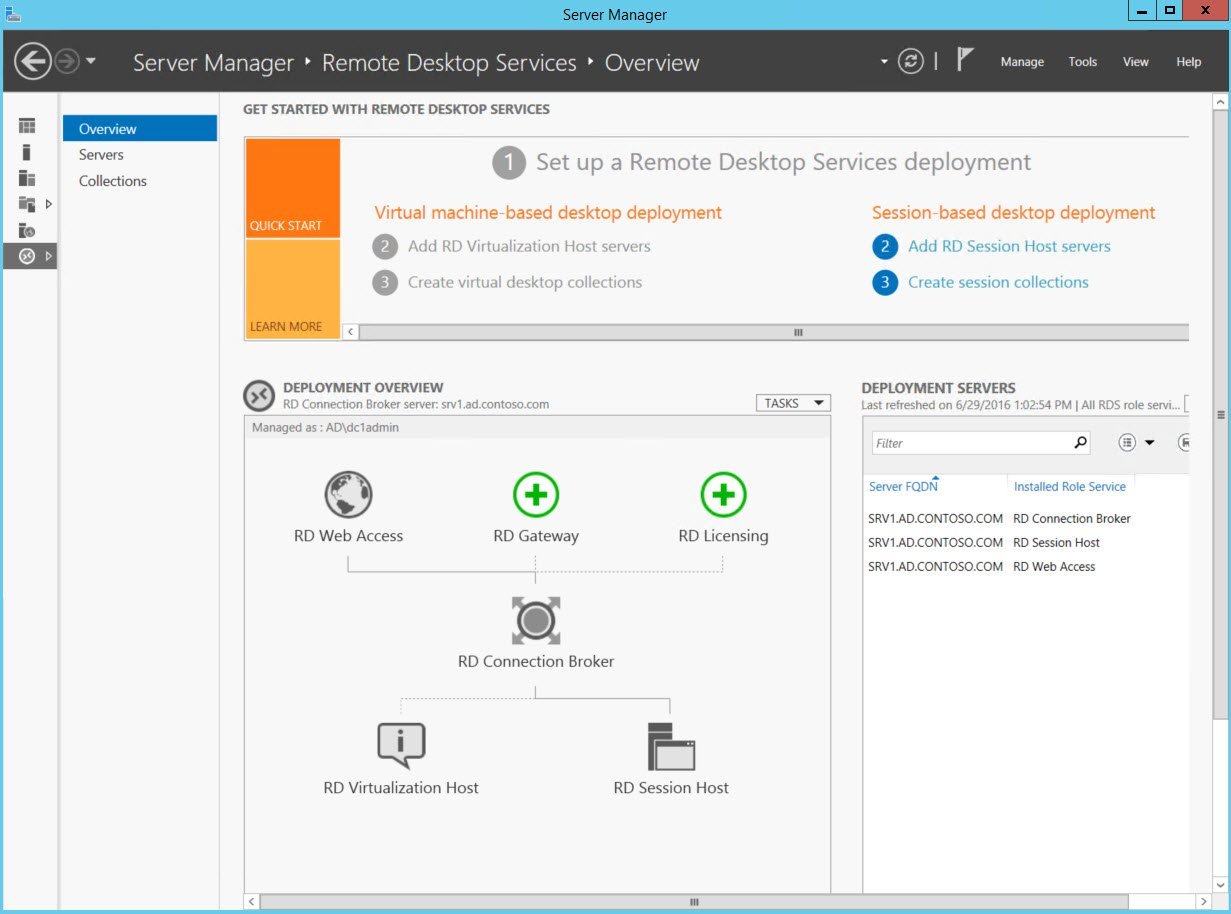
Remote Desktop Services on Windows Server 2012 R2
In the Add Roles and Features Wizard in Server Manager, there is a special installation option, the installation of Remote Desktop Services installation, which you need to select when you deploy Remote Desktop Services. The wording with this option is a bit confusing, but the option allows you to set up hosts for remote desktop sessions without deploying a full virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI).
Standard deployment is the default deployment model, and if you really want to install all the necessary roles on one server, which is not the best practice, then you should select this option. A quick installation can be useful in test scenarios or in small branches where there is only one available server.
Standard deployment allows you to install RD Connection Broker, RD Session Host and RD Web Access on a single server or on multiple servers, which is the most likely deployment scenario in a production environment. Remote Desktop Connection Broker includes the Windows internal database, RD Session Host, and RD Web Access roles. All of this is mandatory, but RD Gateway plays an optional role. RD Web Access provides users with access to RemoteApps or desktops from the Start menu or from a
Management Consoles
All necessary management consoles can be found in Server Manager on the server where the Remote Desktop Connection Proxy is installed, with the exception of RD Gateway and RD Licensing.
Installing Remote Desktop Services on Windows Server 2012 R2
Here we will talk about the standard deployment model, which allows you to distribute the roles of remote desktop servers or install them for a single server.
Standard deployment is the default deployment model, and even if the three server roles per server are installed for the demonstration, this is not the best solution. The Windows internal database is installed as part of the process to support the role of the RD Connection Broker, as well as some of the IIS components for RD Web Access that provide access to RemoteApps or desktops from the Start menu or from the
Licensing
If you want to use deployed Remote Desktop Services for more than a
Deploying Remote Desktop Services
Servers that you plan to use in your
- Open Server Manager;
- Select “Add Roles and Components” in the management menu;
- In the Add Roles and Features Wizard, click “Next” on the “Before You Begin” screen.
- On the Select Installation Type screen, select Install Remote Desktop Services and click Next;
- On the Select Deployment Type screen, select Standard and click Next.
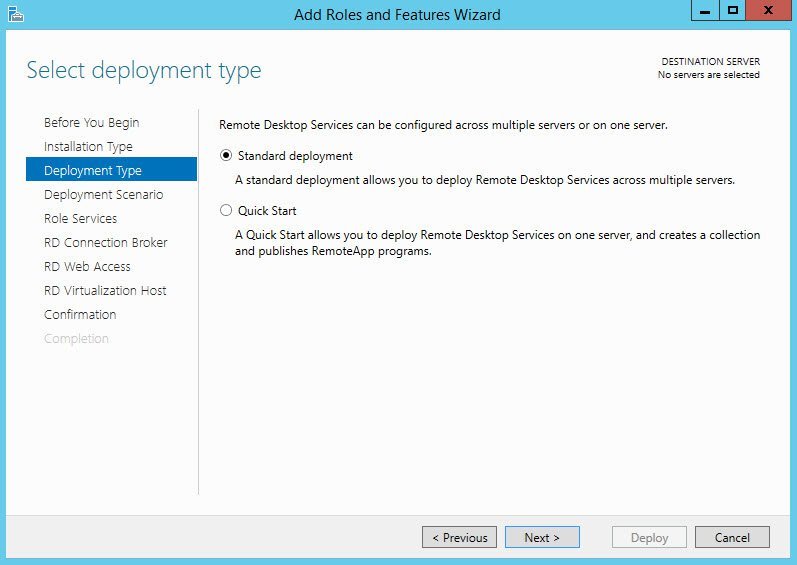
Standard or fast deployment
')
- On the Select Deployment Script screen, select
Session-based Desktop Deployment and click Next. - On the Review role services screen, select the role services to install and click Next.
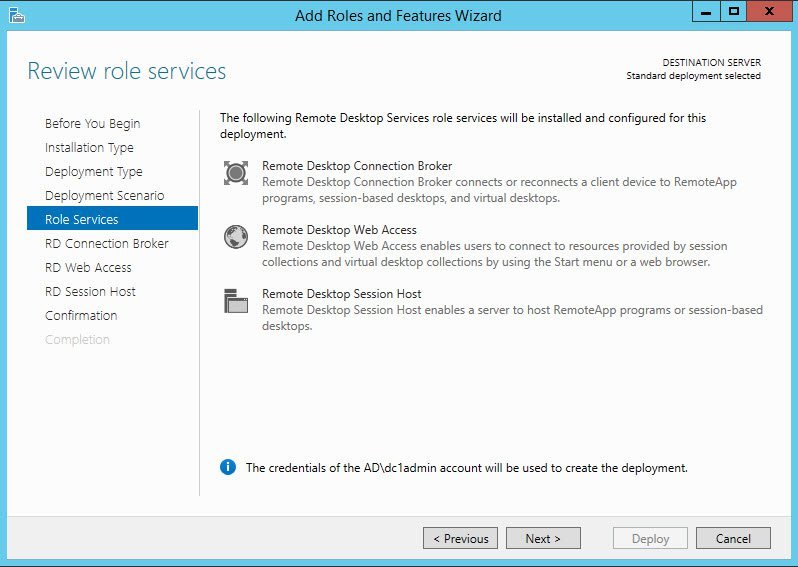
Roles of Remote Desktop Services
- On the definition screen of the broker server for remote desktop connections, double-click on the server in the server pool to add it to the list of selected. This is the server where the remote desktop connection broker role will be installed. Click "Next".
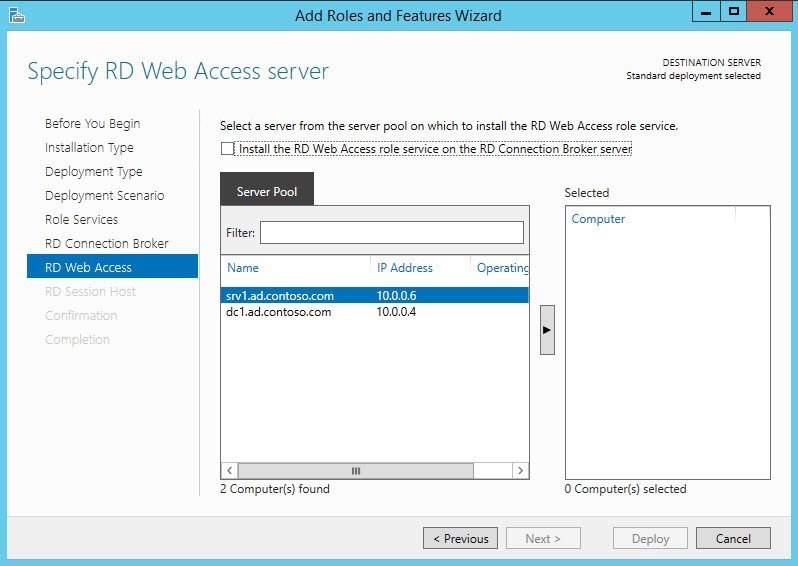
Select server from server pool
- On the RD Web Access server definition screen, repeat the previous step to add the server to Selected, or put a checkmark in the RD Connection Broker server. server), if you want to install this role on the same server as the remote desktop connection broker. Click "Next". continue.
- On the RD Session Host server definition screen, select one or more servers from the server pool by double-clicking or by clicking and clicking the arrow in the center of the dialog box.
- On the confirmation screen, click “Restart the server automatically if required” and click “Deploy”.
- When the 3 server roles are installed, click “Close” on the deployment progress screen (View progress).
Deployment progress
Now you need to log in to the server where the remote desktop connection broker role is installed, open Server Manager and click “Remote Desktop Services” in the options list on the left to see the information on your

Remote Desktop Services Dashboard in Server Manager
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/306002/
All Articles