Network Infrastructure Virtualization and SDN Solution

Our report today is a bit different in a number of other materials from the Cloud Technologies in Russia Forum: Part I , Part II , Part III , Part IV . Speaking of cloud technologies, everything first of all implies, of course, the virtualization of IT equipment, such as storage servers and so on. Nevertheless, the data network is an integral connecting element that actually allows us, on the one hand, to provide cloud technologies, that is, to provide connectivity, on the other hand, we need it for the actual implementation of data centers, for organizing connectivity between data centers, and in fact, at almost 90% in current organizations, the data network today is becoming the bottleneck, the bottleneck, which, in fact, makes it difficult to implement new services in failure of new applications.
')
Sergey Aksenov, Senior Product Manager, Datacom, HUAWEI
Colleagues, good afternoon again, today Sergey Aksenov, Huawei. Huawei has a new concept, a new solution called Agile Network. Agile can be translated into Russian as flexible, manageable, fast and intelligent. These are the values that are laid in the concept of next-generation networks. And if you look into history a little bit more broadly, then for the last 10 years, nothing fundamentally new in terms of network technologies has appeared; there have been no network solutions. There were some improvements, additional innovations, but there were no fundamental changes. And now we are just on the threshold of new generation networks, the so-called SDN network, Software Defined Networking, that is, software-defined networks, and the Agile Network itself is that software-defined network.
What is it for, how to use it, what advantages in relation to traditional solutions I, in fact, today will try to reveal.
In addition to the term SDN, I will give you right away to dot the point and I will say that there is a term NFV - Network Function Virtualization, that is, the main purpose of this term here is that we are essentially moving away from expensive network hardware specialized devices and we have these functions we shift the computing infrastructure for virtualization to the servers, we will also talk about this a little bit now.
Actually, if you look at current trends in the field of information technology, they are shown on this slide, it's not a secret to anyone, for the past 5-6 years we have been talking about them, the annual explosive growth of traffic, the emergence of new television standards, the appearance of ultra high definition video UltraHD, the explosive growth of the number of terminals: this and mobility technologies, this technology and the Internet of things. According to estimates by 2020, about 5 billion devices they will already be connected to the global network, while about 70% of all devices are devices related to the internet of things, that is, the Internet of things. Actually, cloud computing and, again, social networks, which create huge volumes of traffic, the actual exchange of various types of content, all these trends, all these prerequisites became the starting point for developing next-generation networks.
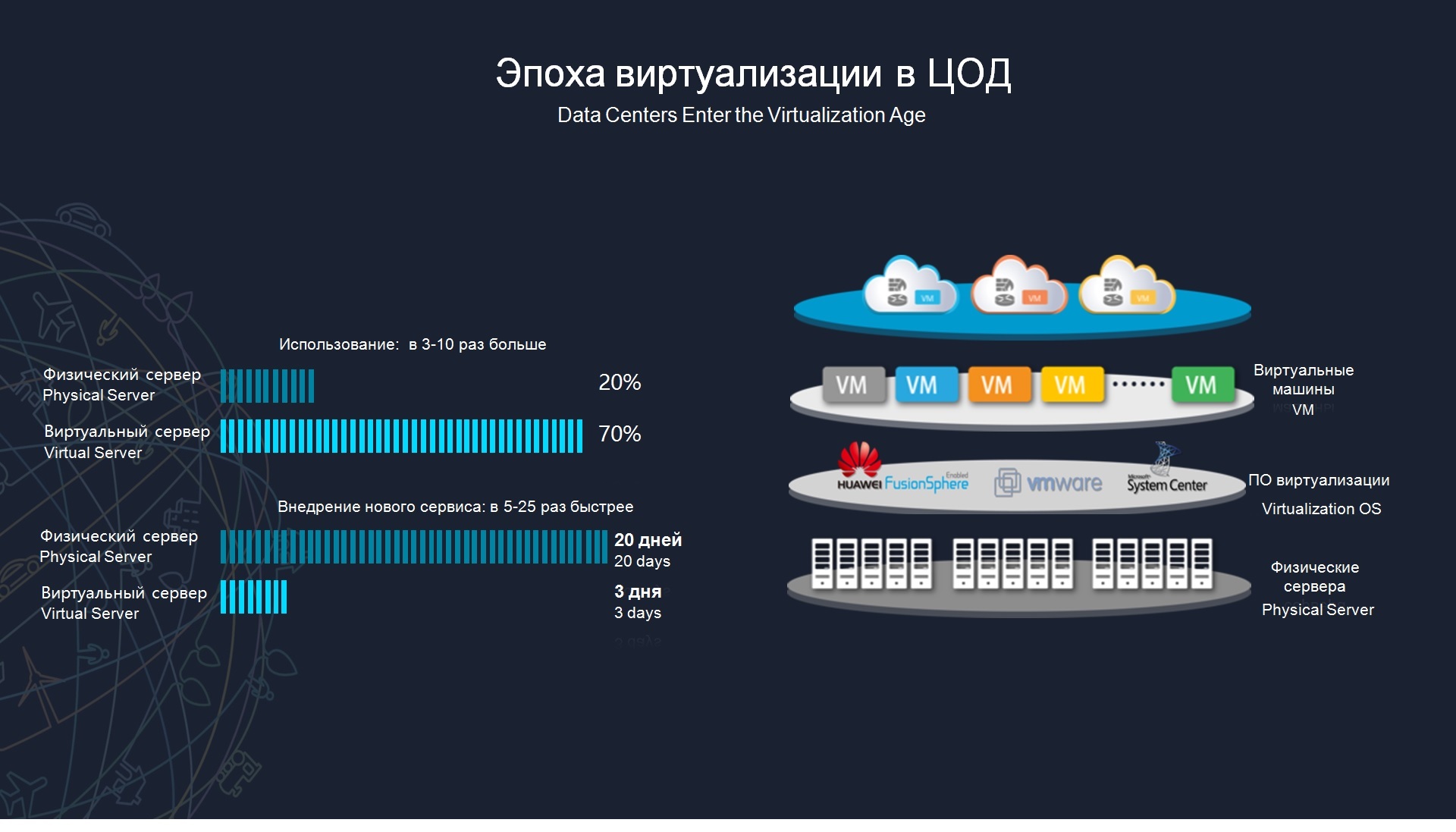
It's no secret that in the data center today is the era of virtualization, that is, hardware servers are used less and less by organizations, probably, absolutely tar-business, that is, the era of virtualization in the data center has actually arrived. This transition to a new resource model, from the point of view of servers and storage, occurred 10 years ago; from the point of view of the network, this change is happening now. The network becomes a bottleneck for the introduction of new services, for the introduction of new applications. That is, if we consider the same virtualization system, then most of the routine tasks are automated there, that is, if we need to deploy a new virtual server for some service, for example, or copy this server from one data center to another data center - there all these operations can be routine run in 15 minutes, nothing complicated for the administrator.

At the same time, the data transmission network often requires manual configuration and manual control. That is, if we want a virtual machine or some kind of new virtual environment to migrate with us, so that it is deployed there in our data center, for this we often need to manually make all these changes, we need to involve a network administrator who will prescribe new routing policies , switching policy, quality of service, security, and thus, it is difficult for us to introduce new services, that is, in this scenario it will not take 15 minutes from the point of view of virtualization of the computing infrastructure, but will already up to 2 days.
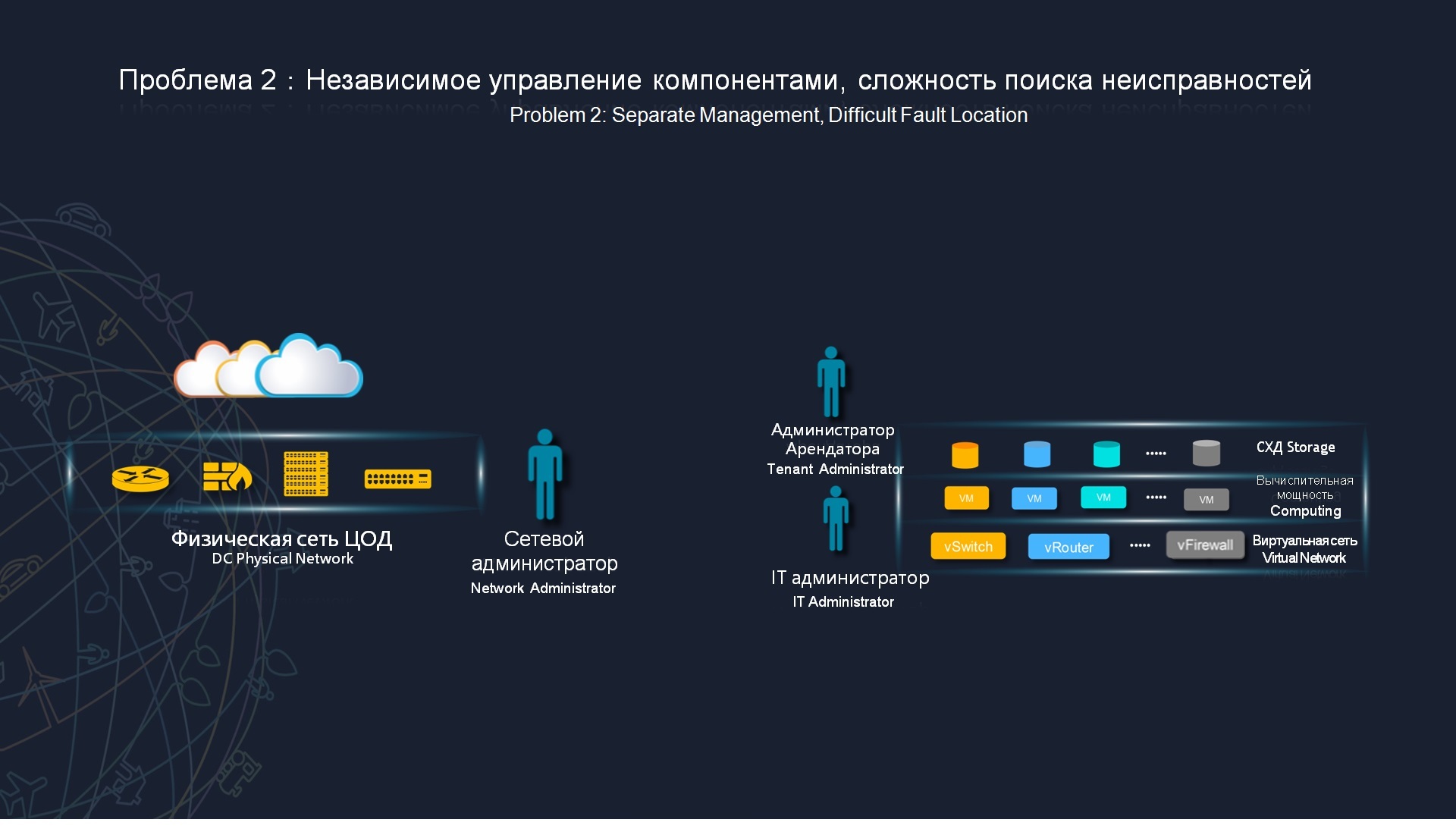
The next negative point, which we often see in many organizations, is that the control of components and the difficulty in troubleshooting are still independent of us. If you look at the structure of any large or medium organization there, then, as a rule, there are 2 types of engineers in the IT service. The first type of engineers - network engineers, who are responsible for the data network and the second regiment of engineers, are the system administrators who are responsible for the servers, are responsible for the storage system. Actually, the slides show, in fact, we have a watershed. As from the point of view of operation, from the point of view of planning, the use of resources, these are different components from the point of view of their interaction. They still despite the fact that interact, however, disparate components.

And here one of the cases is shown, which, due to fragmentation due to the fact that they are not tightly integrated, do not interact with each other, that is, they do not see that some problem occurs from the side of one of the components, this is not reflected in the second. Here is a straightforward case, a simple, short-term problem on the network infrastructure, which means that all the VPS are migrating in one of the areas to one of the servers, thus we are watching the reboot, while the other is idle. This is a network problem, it was quite short-lived, it would in no way affect the quality of the work of various applications and services.

All this became the prerequisites for the development and transition to the networks of the new generation, to networks with software-defined architecture. Here are written the basic values that the network should be more flexible and transparent to users of services and applications. It must become agile, dynamic, faster and more intelligent. Agile Network, as I said, this Software Defined Networking is a software-defined infrastructure and, in fact, it is a whole concept that differs significantly from the traditional principles of building and implementing a data network. If you look at the traditional approach, at the traditional networks that have existed for a long time, then the network administrator operated on physical ports, physical devices, topologies, that is, was rigidly tied to physical devices. Speaking about the concept of Agile Network, about the software-defined network, we are here focusing on the users of services and applications. We define user profiles, determine the quality of work of a service, and, in fact, we can forget about our topology, about physical devices. In traditional networks, we observed such a manual configuration and a separate approach, that is, some, for example, there is an infrastructure consisting of 50 network devices and a separate approach implied that each of the devices required a separate manual configuration, that is, it was necessary to go to each from these glands, connect via the web interface or via the command line and, in fact, individually configure each of these devices. The complexity of operation, the complexity of setting up, the complexity of managing such a network is noticeably complex. In the new concept, we come to universal interaction and to the dynamic management of the entire infrastructure, that is, we have not just configured the infrastructure using the command line, but for example, this configuration lives there, in this SDN scenario, everything changes on the fly, that is not a static network which we configured it, it actually reacts to all these changes that are taking place, these changes can be from the point of view of introducing new services, the emergence of new users, or the introduction of some kind of new security policies, t Oh, we now have such a living organism, and from the point of view of intellectual control, we again have an intellect, but about this a little further. And actually here appears such innovation as constant monitoring and quality management. We do not just configure our network at random, prescribe routing rules, switching policies. We can now in real time control how this or that application works, how this or that service works. That is, in fact, we can set the SLA parameters for the operation of an application and actually monitor and ensure the implementation of this SLA within our infrastructure.
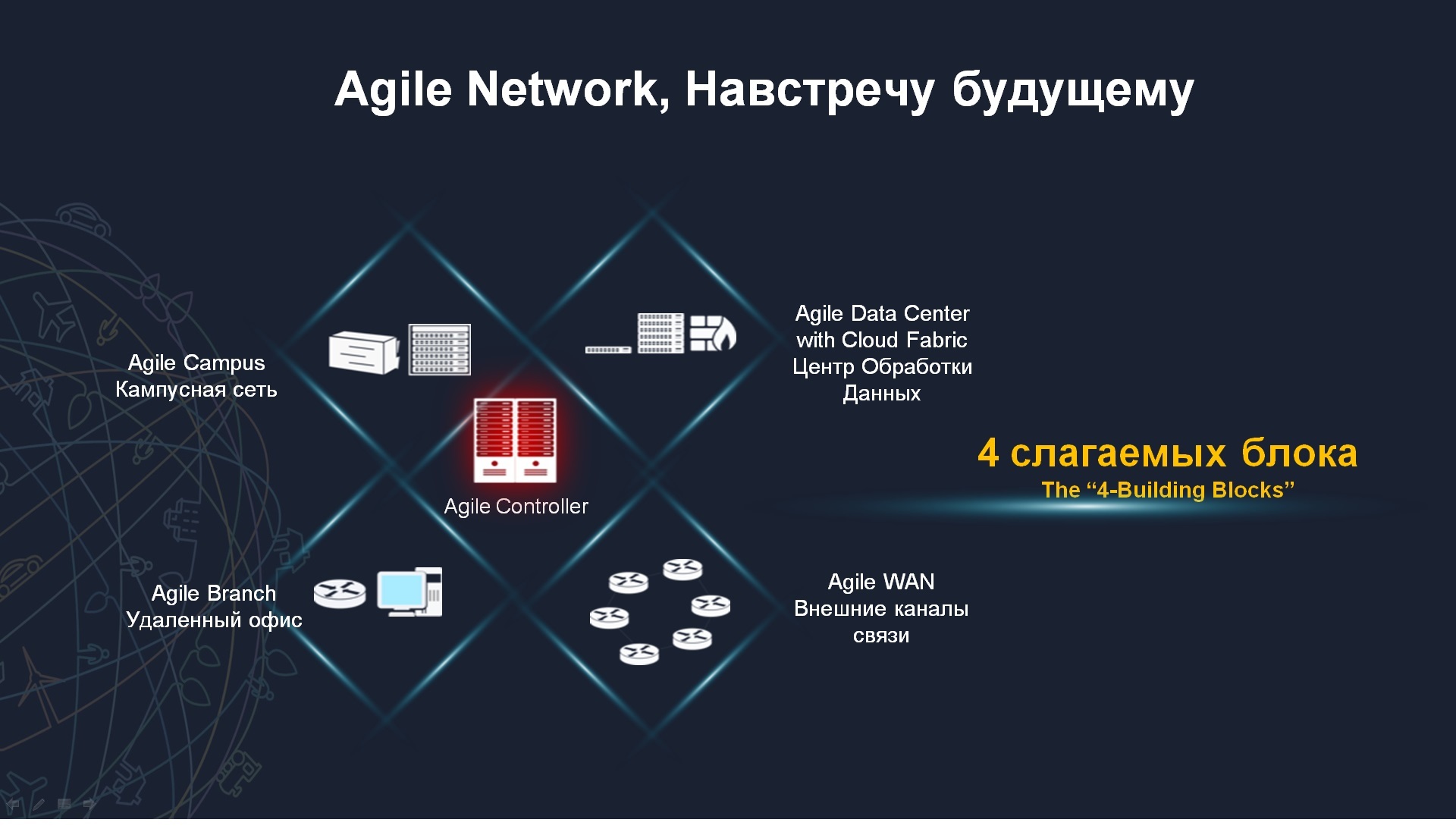
The concept of Agile Network will suit almost any organization, any enterprise and it consists of 4 main blocks. The first unit is the campus network, that is, this is the corporate network that is used by your organization. Even in spite of the fact that you will use cloud services, will use services of external service providers, your internal campus network is necessary to connect users, their terminals, now these terminals may be wireless, but nevertheless you have a campus network there. The second component is the Agile Network component for data centers. There will be separate slides about data centers, I will tell you about them what is being implemented there. Most of the customers who interact with us, such as retail, have such a distributed architecture, for example, a distributed network of stores with several hundred or thousands of objects and a centralized data center, the actual tasks here are exactly the same, it is a fragmented architecture that is centrally controlled, the solution itself is from Huawei allows you to implement it. Finally, the 4 component Agile Wan is the component for controlling the external communication channel. Today, more and more customers are interested in using cloud technologies, are interested in having several data centers geographically separated, and just quality management through external channels, through service providers channels, this also can be seen as an actualizer of a pressing problem. Well, let's go in order, first talk about campus networks.
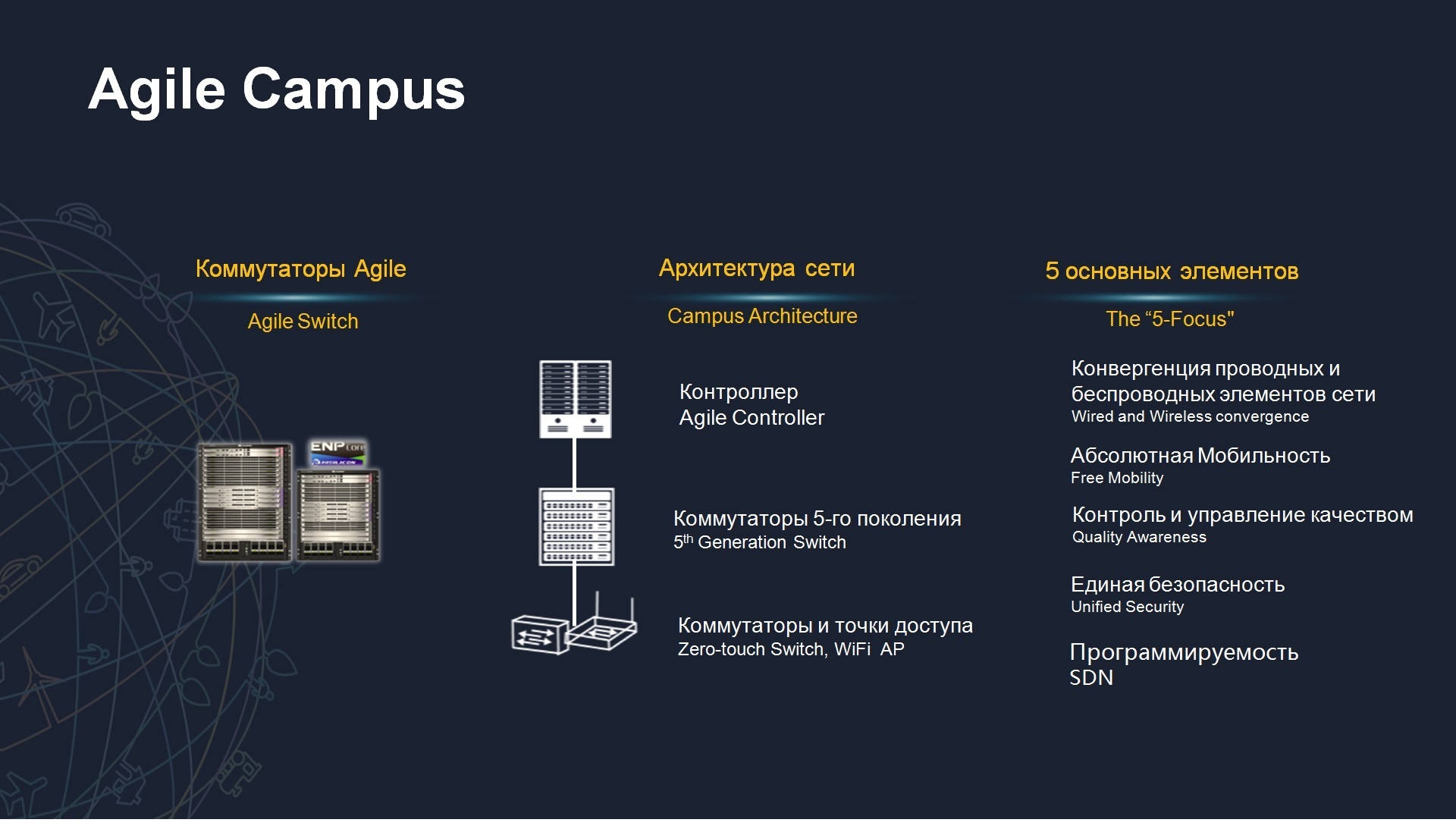
The core and heart of the campus infrastructure is 2 components in the Agile Network solution. The first component is a specialized software called the SDN controller, we have the Agile campus controller, which is the software that allows you to centrally manage policies, user connection profiles, allows you to manage the configurations of network elements and actually manage traffic transmission routes. models that are not 50 separate devices, but 50 devices that are simply connected, that is, they are engaged in data transmission and one point is It is a centralized intelligence system of the brain that controls for absolutely all of the logic for the transfer of traffic, according to the security policy, the quality of service. And actually the second component is the data transmission network, a specialized switch of the new generation is needed here, they are already called Agile switches, that is, these are network elements that can interact with centralized intelligence, with a centralized SDN controller and actually using the OpenFlow protocol, or about NETCONF protocols, they understand how to transmit traffic, how to connect a particular user, how to respond to a particular threat, that is, now these are essentially managed devices twa. In addition to controllability with the help of centralized intelligence, 5 more innovations appear here, which Huawei is talking about; this is the convergence of wired and wireless network elements. Convergence here means that we bring our network to a common denominator. Frequently, the Wi-Fi network in organizations was considered as additional to the wired one, because Wi-Fi for a long time could not provide either sufficient quality or sufficient bandwidth, today with the advent of standard 802.11ac with gigabits of bandwidth through radio interfaces with a full implementation of braid we can say that our wireless network becomes part of our wired network. In fact, this is really a single denominator, we need to centrally manage both components of our infrastructure. The second innovation is absolute mobility, quality control, unified security and programmability. On each element, we now stop in more detail, let's talk in details.

Convergence of wired and wireless network elements. Many data centers have used the architecture for a long time, when there is some kind of main switch, there are top-of-rack switches for directly connecting servers and, in fact, these top-of-rack switches act as switching factories, as remote line cards, whatever data center we would have, no matter how many access switches we had there, for connecting servers, all this could be managed centrally with the help of these large virtual switches. As a matter of fact, we come to the same model about the Agile Campus solution, our entire network infrastructure, consisting of 50 elements, comes to the model that it is essentially one large virtual switchboard, which consists of 50 virtual cards, that is, one we can manage our entire network infrastructure with a single unified centralized management. Here it is actually drawn. Here we had some kind of campus infrastructure consisting of kernel levels, now it all turns into a single virtual switchboard, in which the N-th number of virtual cards appears. At the same time, Wi-Fi access points that we had there all the time looked like such a separate element, required the installation of a specialized BLDC controller, now it all again comes down to one point, that is, the access points will look like access ports.
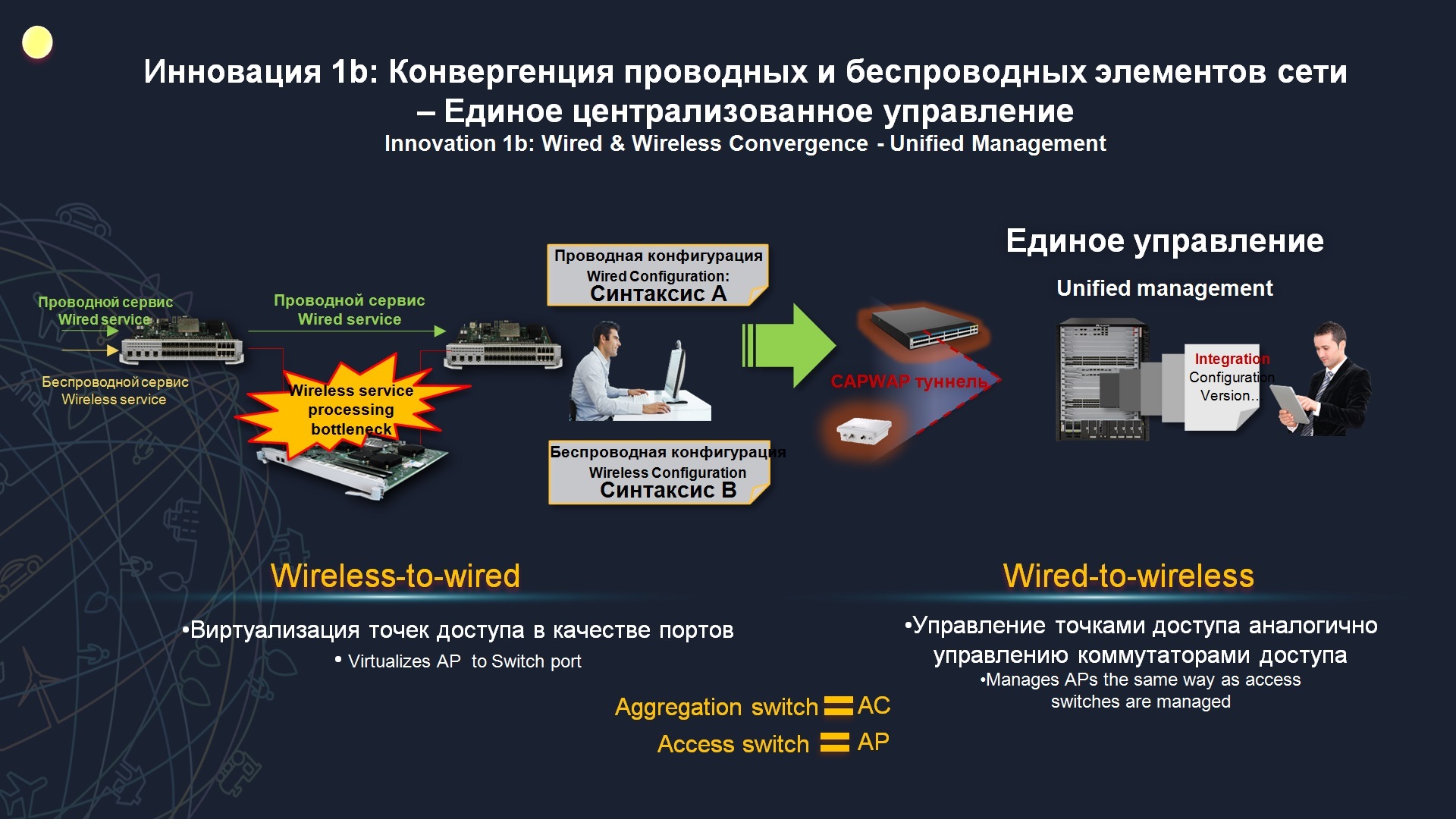
The second. For a long time, the wireless network was considered superimposed on the wired one and required separate management. We built a specialized wireless network, we built CAPWAP tunnels there, set up wireless controllers, we had to think about how to authenticate and connect users, authorize them using a password or via an active directory, or the radius server is there, on the other hand there was a second part of the infrastructure, wired in which there were its own security policy rules, its own user authentication rules. Actually, in the Agile Network solution we come to the fact that no matter where and how a user is connected, we can authenticate him and upload his profile at a single point. For example, we have an accountant sitting in an institution on the 2nd floor, at some point all the accounting moves to the 4th floor. In the traditional approach, this would require network engineers to remove the settings that were on the switchboard on the 2nd floor, they actually deleted everything there, and transferred it to the access switch on the 4th floor. That is, here the position of such an overload of 1-2 days would take. In the Agile Network scenario, since we have a single intellect here that will save all user profiles regardless of what floor they are on, they connect using a laptop or they connect using a wifi, we simply load their profile using an identification mechanism, be it a radius , be it a web portal with some kind of username and password and all these policies themselves, all these rules are loaded onto access ports. That is, here we have the difficulty of operating the network is sharply reduced.
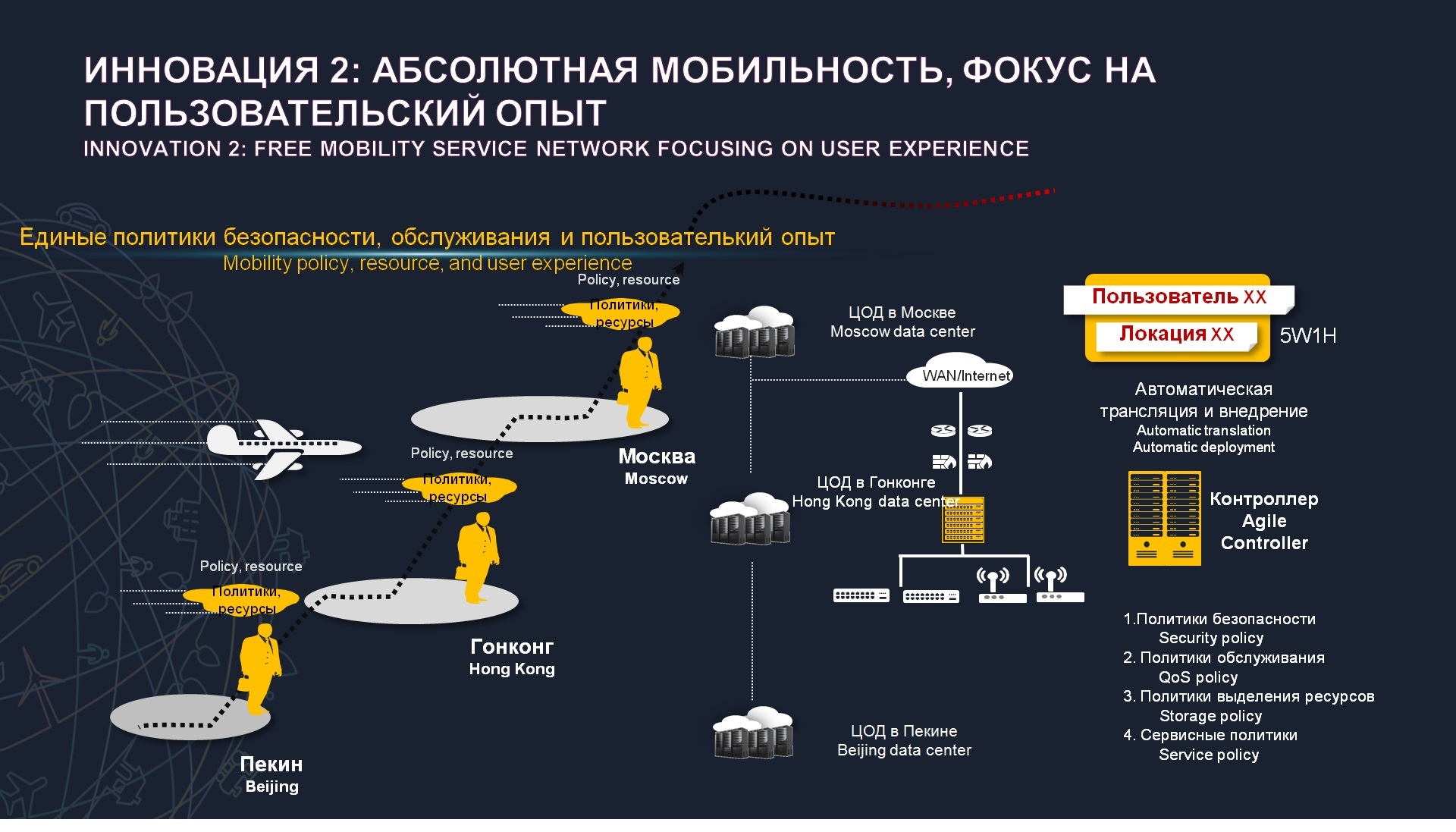
The same thing happens from the point of view of absolute mobility technology, today they are probably already erased from the working time frame, we are working not only from 9 to 6 as we used to, but now we all have a smartphone, we have a tablet, we can remote access, I often observe myself that I spend much less time in the office than on business trips, at events, and the possibility of gaining a unified user experience is very important. Regardless of where and how the user is connected, he will get his bandwidth everywhere, get his rules and security policies. At the same time, we can manage these policies on several levels in order to ensure internal information security. Again an example. For example, I come to the office and from my laptop I connect to the corporate network with my login and password. Actually, I get access to absolutely all internal resources, mail server, ERP system, CRM system, that is, I have no limitations here. At the same time, the employer wants, for example, when I work from home in the evening, I could not copy any information so that I would have access only to corporate mail. Actually, I come home, enter the same username and password, and now the system determines that this is my profile, but my location is out of the office. Actually, new policies are automatically loaded, which will not allow me to get access to internal resources now. The same can be done by attaching to the terminal type. , , , , , , , , , , , . , , . - .
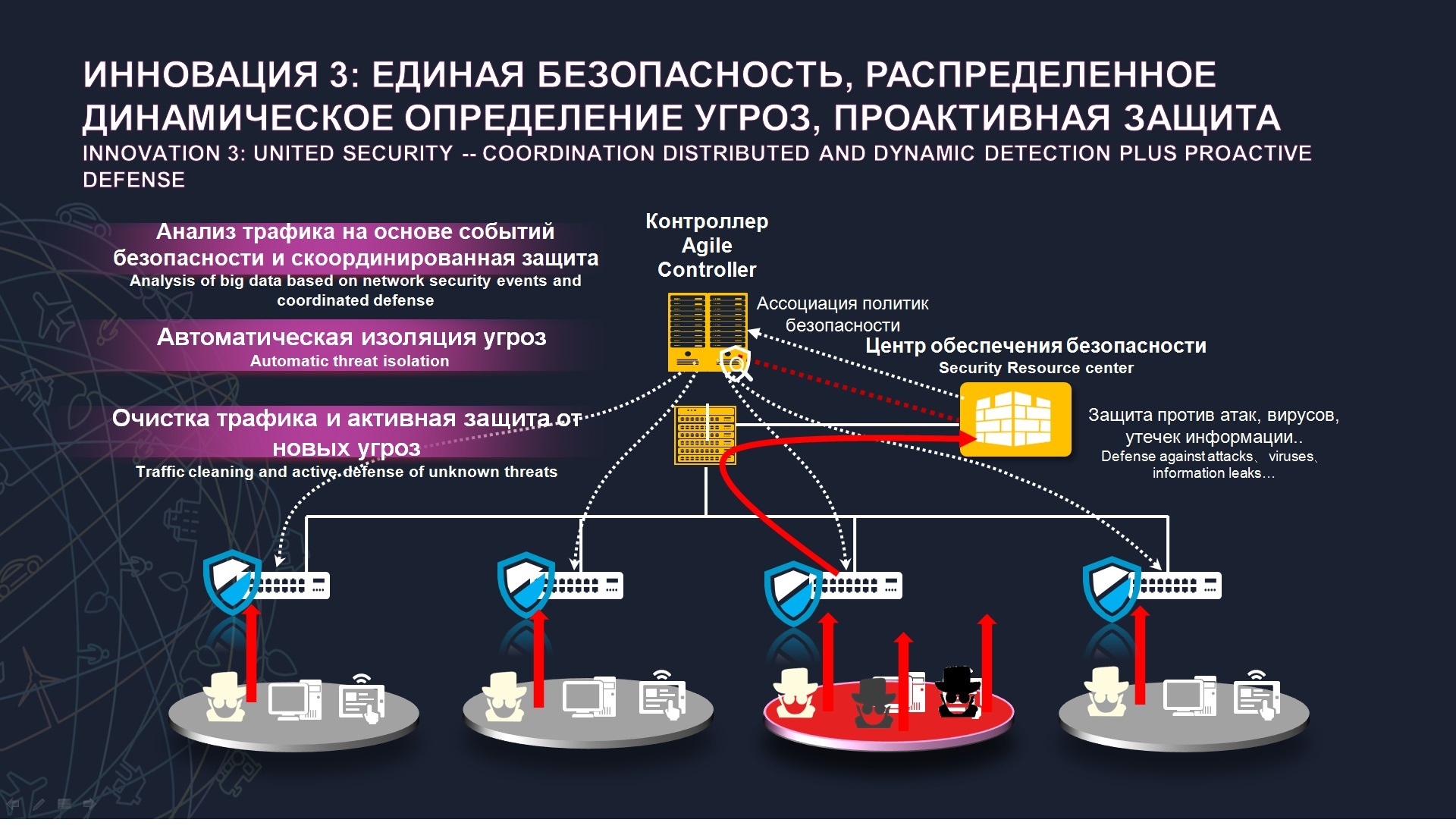
, , — . - , , , . access control - DPI, , , , . . , , . , - , . Huawei , . , , - , - , , , , .
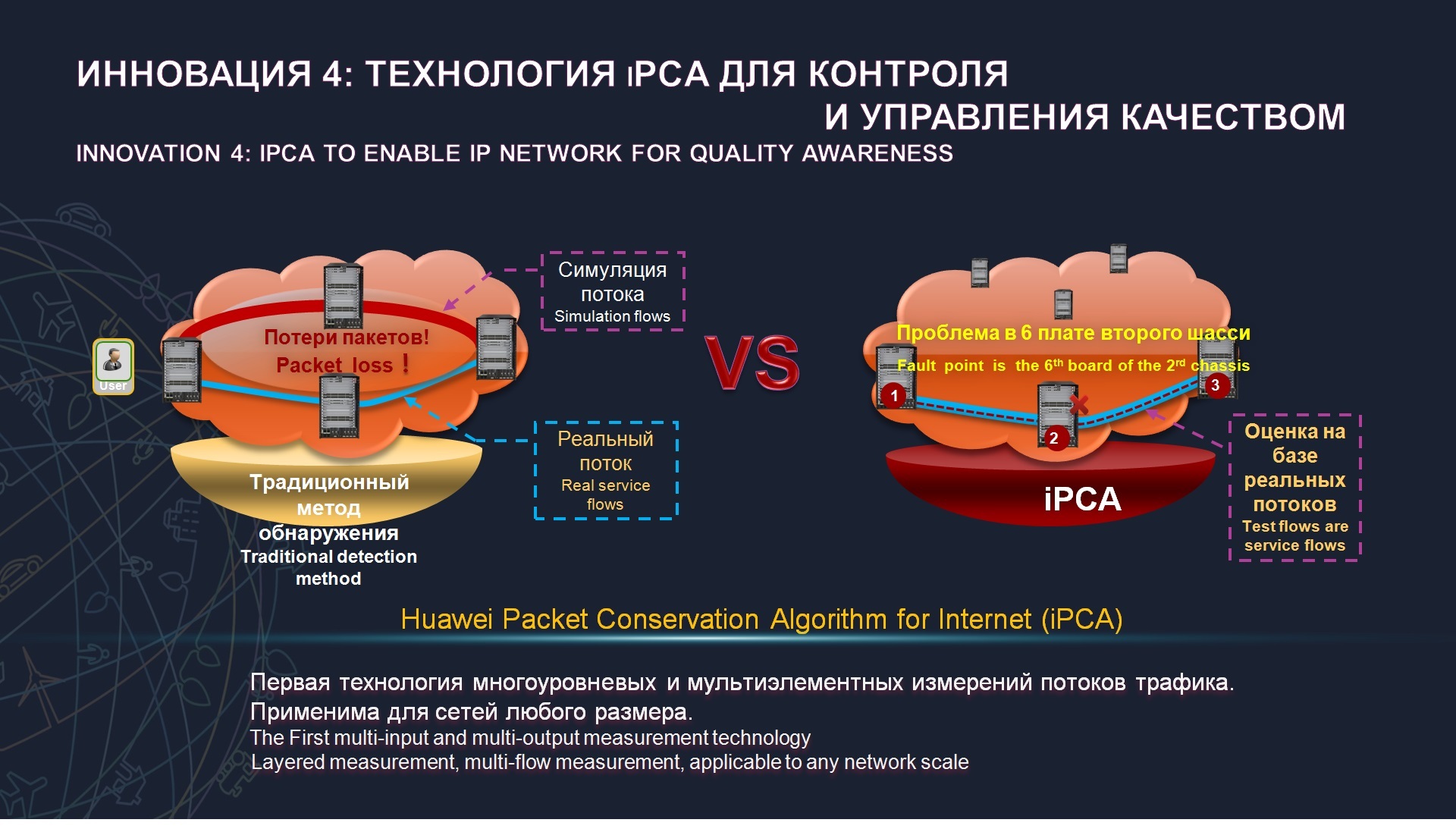
, iPCA . , - , , , , , , , , , . , . , iPCA , , SLA, . - , , SLA .
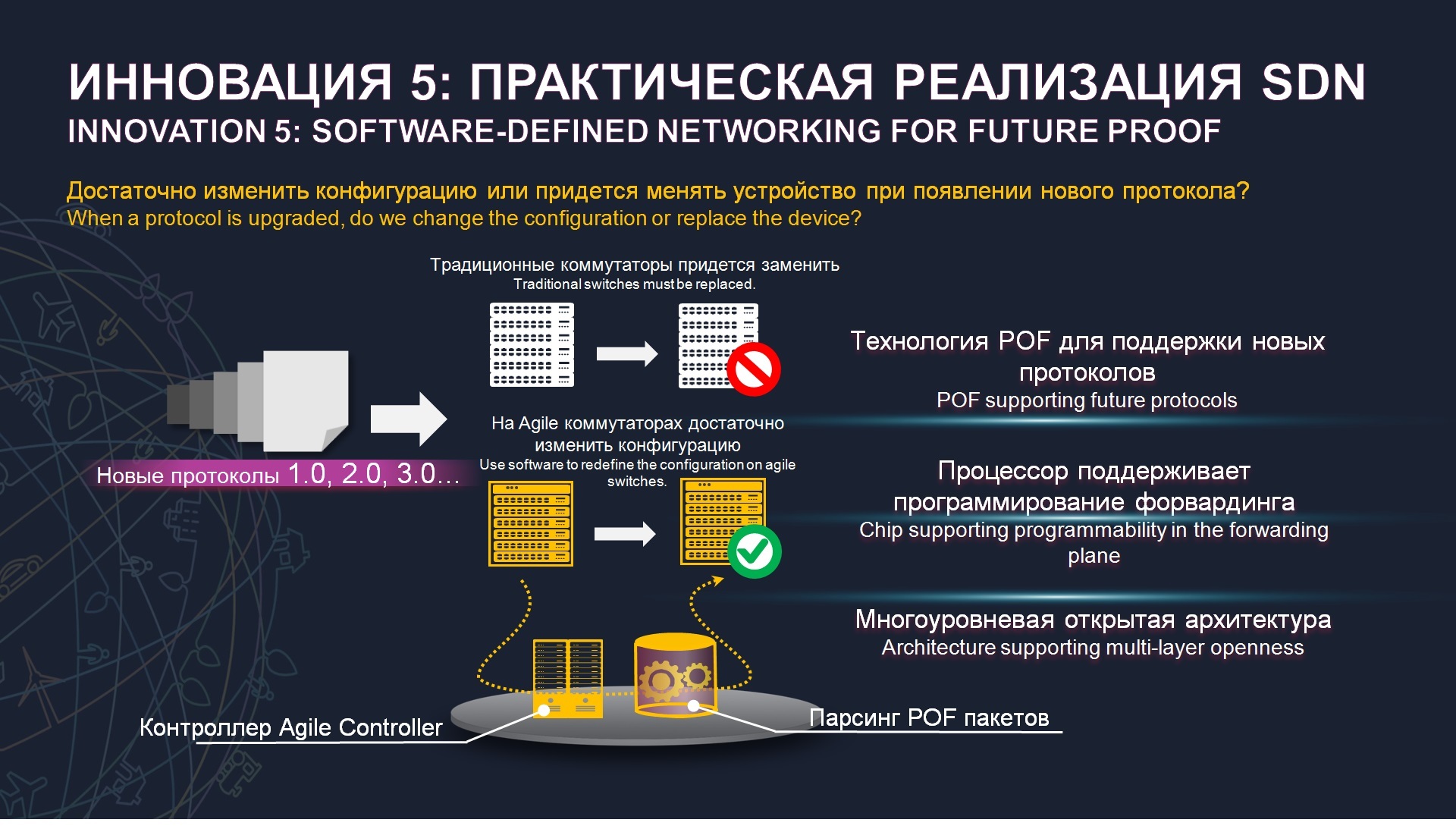
, , SDN, - , Huawei , , . , , , , . , , . - , , . , 5 , Huawei, 1989 , , , , , 4 ASIC, , .

5 , , ASIC, , . ENP . - , - , - ENP , . What is it for? SDN , OpenFlow , , - , . , , , 5-6 , SDN . , .
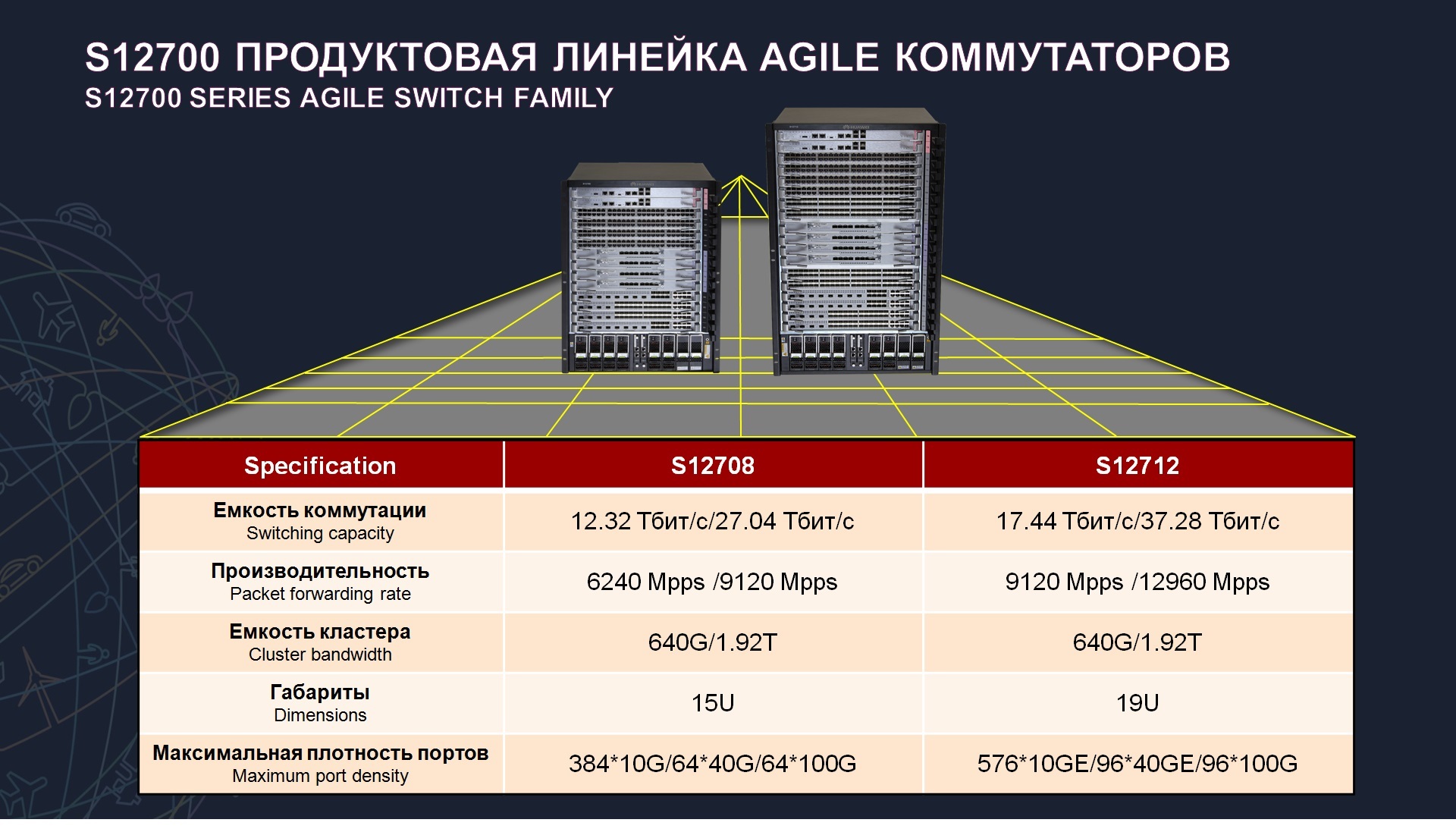
, S12700, , 8, 12 , , ENP .
N- , , Agile Network , 1,5 , . , ( ), , . , , , . , , , , - Cisco - Huawei , - D-Link, MikroTik, , , , . , Agile Network , , , , . , - , , .
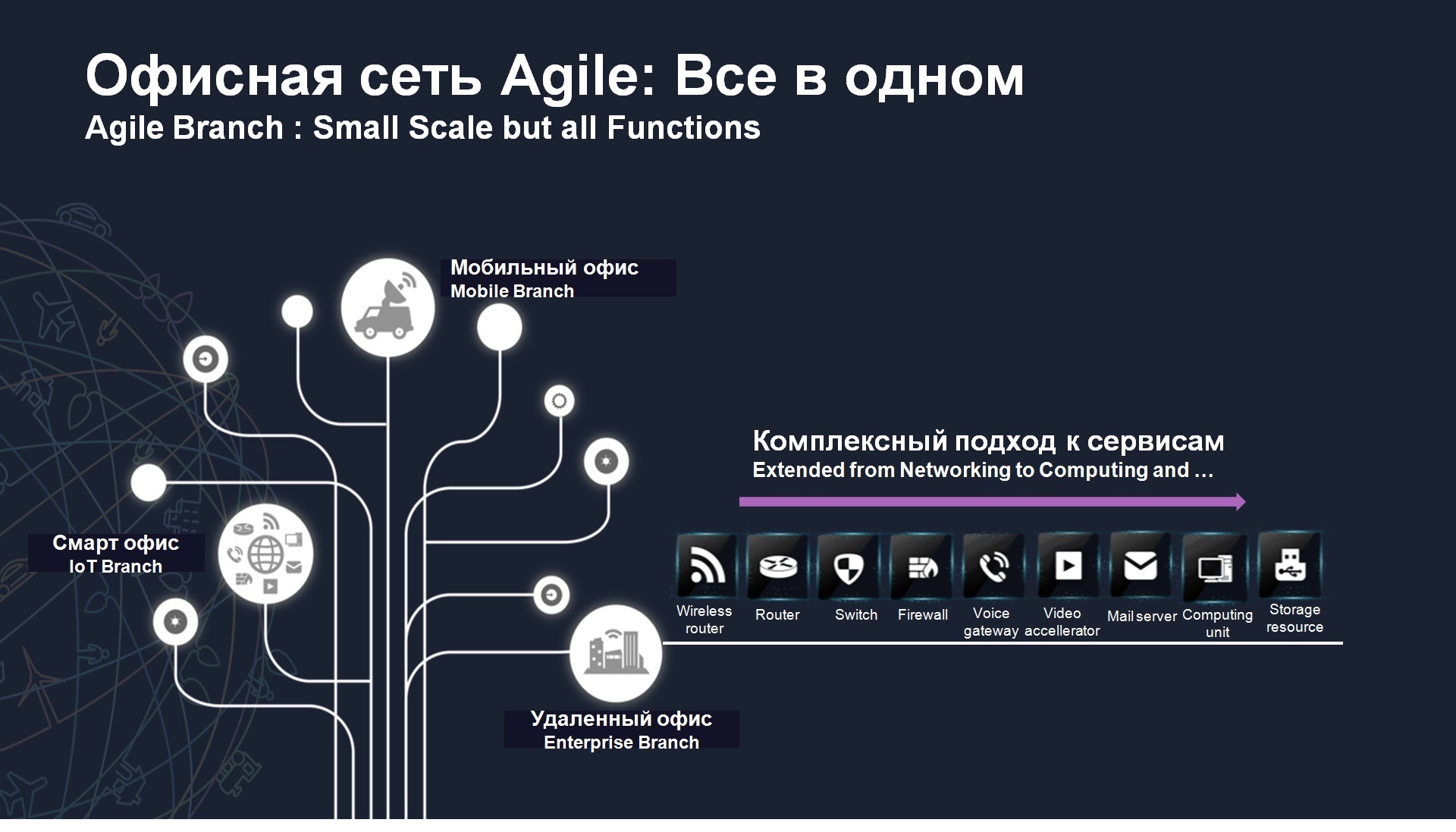
- Agile Branch, , , , , , - , . Huawei , Agile Gateways, , , , , , .
, , , .
X86, , , SSD , : Windows. Linux. Android, , . , , . , , , , , - HDMI. Windows . , - , : /, : . , , . , -, . .
, , , value-added services. ? , - PC, . , , - , - DSL, - 3G, - 4G. , , . – 100 + , 10 . + 1 . 10 . . Agile Network .
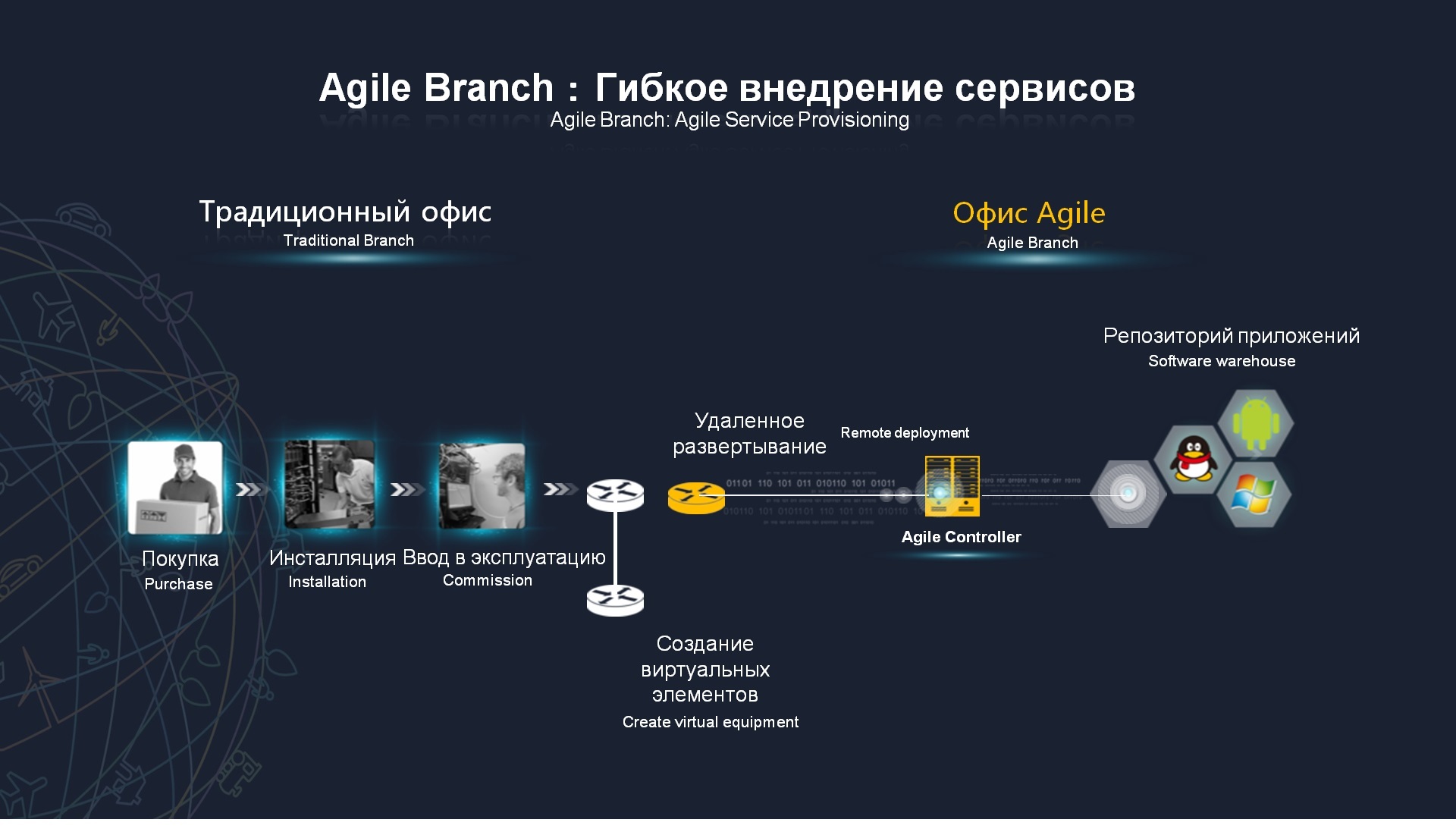
, , , , . 10 . , - , . , . Agile Network , , , USB- LTE-, , , SDN-. , .

, , : , , , n- -, - , . – . , KVM, Linux, Windows -. , , .
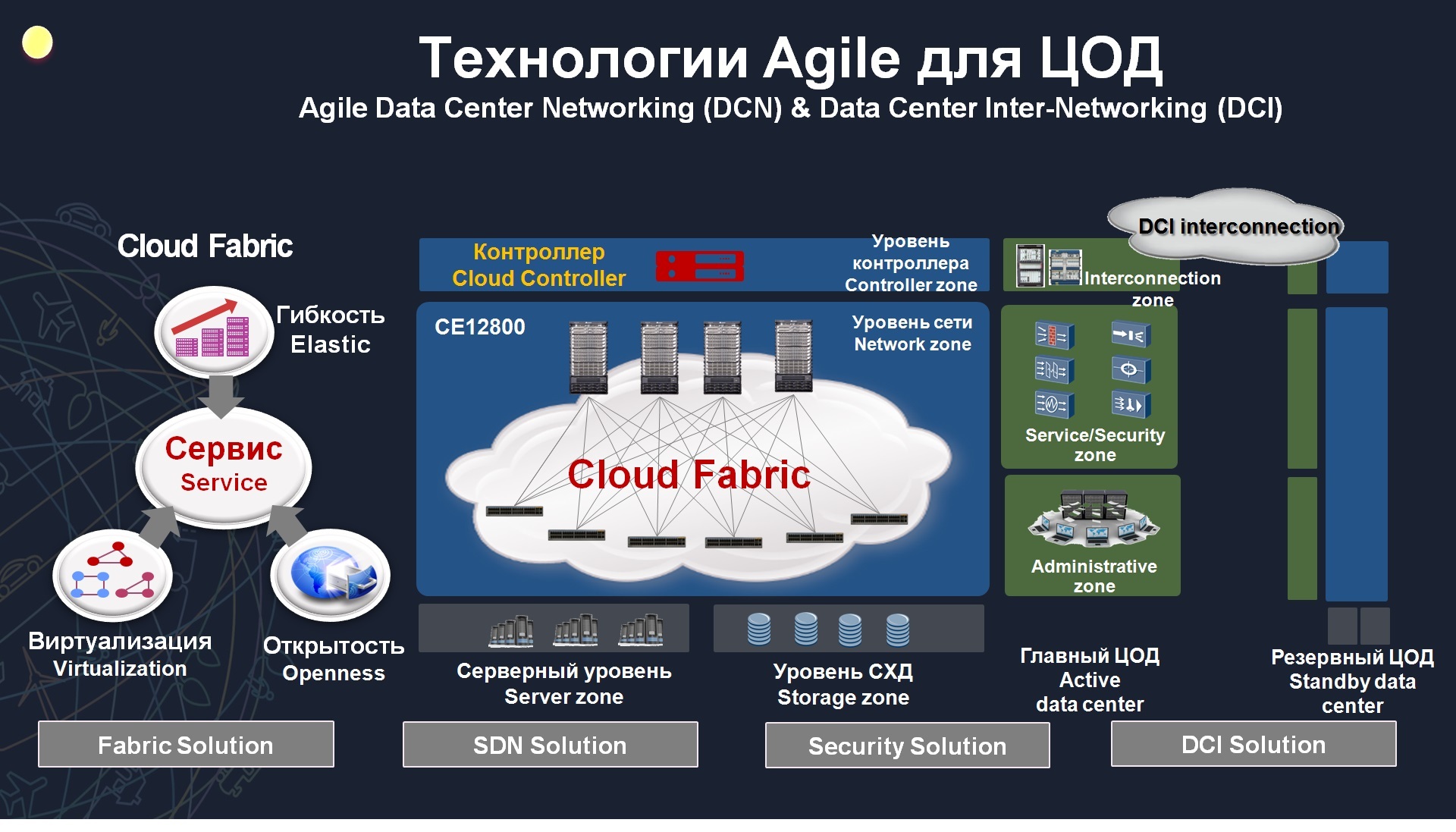
Agile Network, , Cloud Network, Agile Network , . , , -, . – , , , . – . , , , API , .
– . , , .
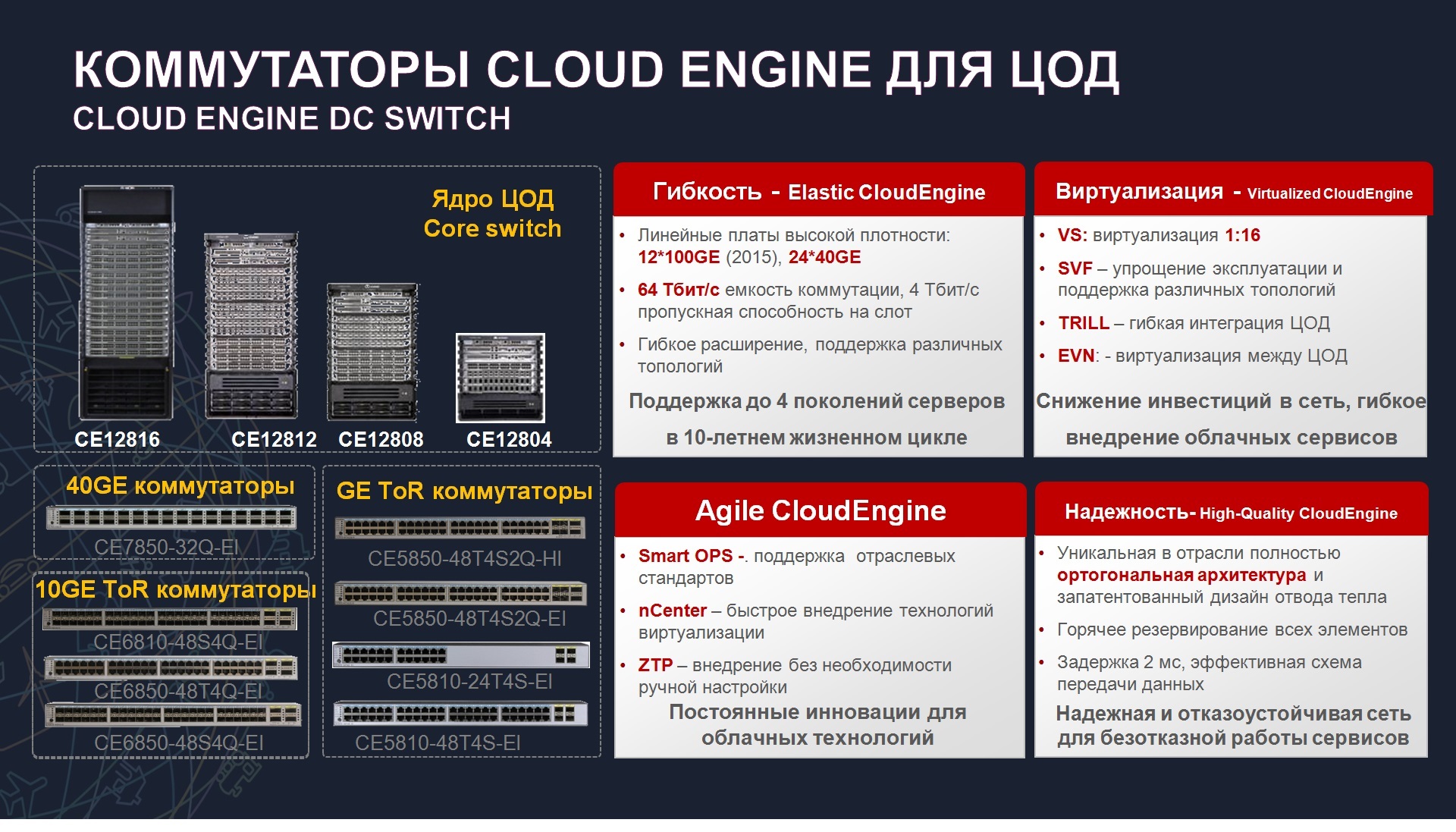
, Cloud Engine, , , – 12800 top-of-rack . , , , , , , Huawei . , , .
, Virtual Switch (VS). , - . , , , , , . VS 16 . , , , 1-7, 23, 25 – №1, 7, 17 25 – №2. , . DDOS-, . .
: SVF – Super Virtual Fabric, . , 100 , , . 40, 50, 100 , . , . disaster recovery, active-active. , . - , , , . . . L2 . , , EVN, , CISCO OTV. , EVPN, , L2-. , .
, VLAN, , . , VXLAN, 4000 VLAN 16 VLAN. Huawei Cloud Engine .
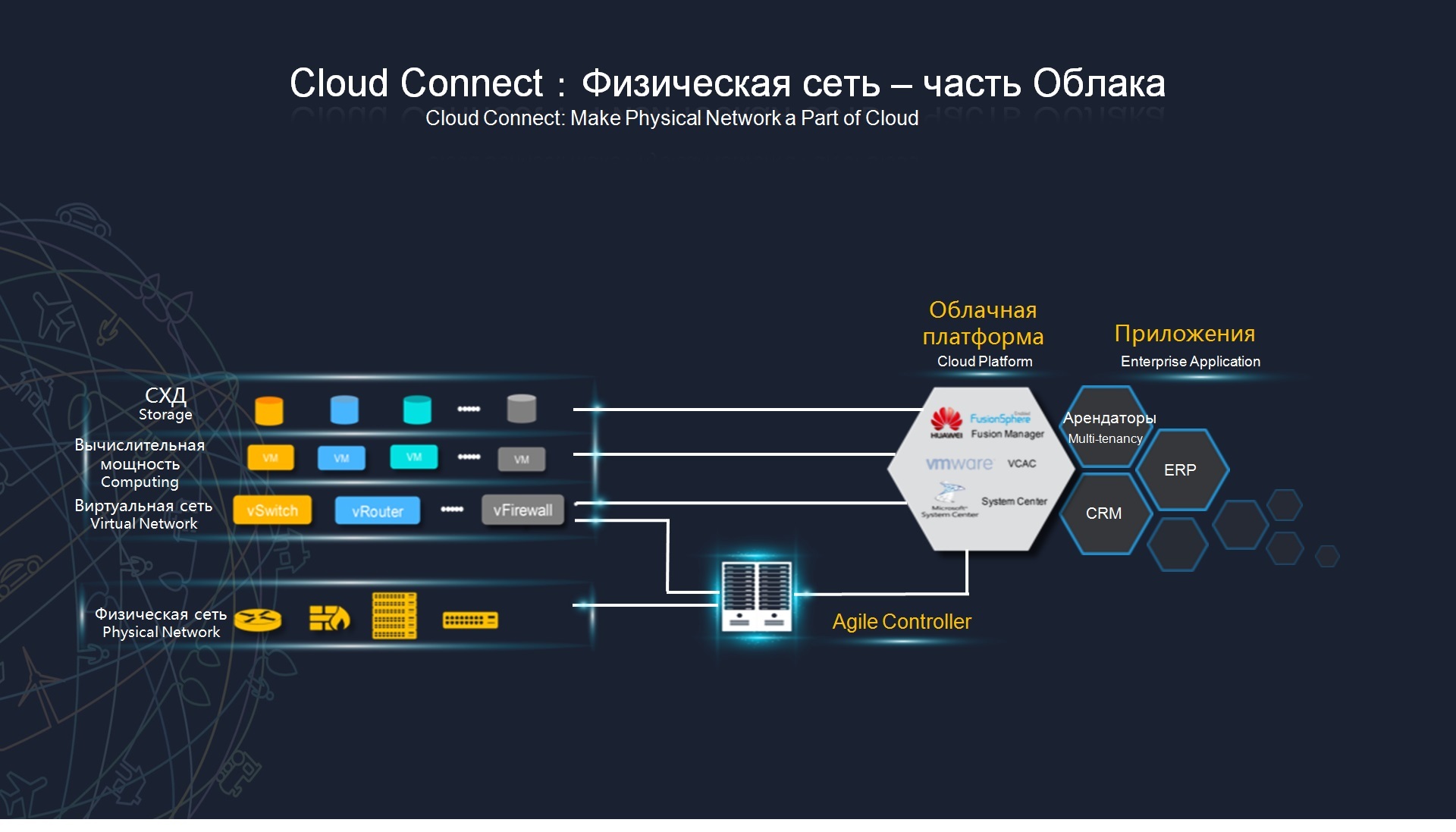
, , ethernet, FCoE, fiber channel, . , , Agile Controller, , value. , , Huawei, Fusion Sphere, . VMware, Microsoft (HYPER-V). , , , . , , , , , .
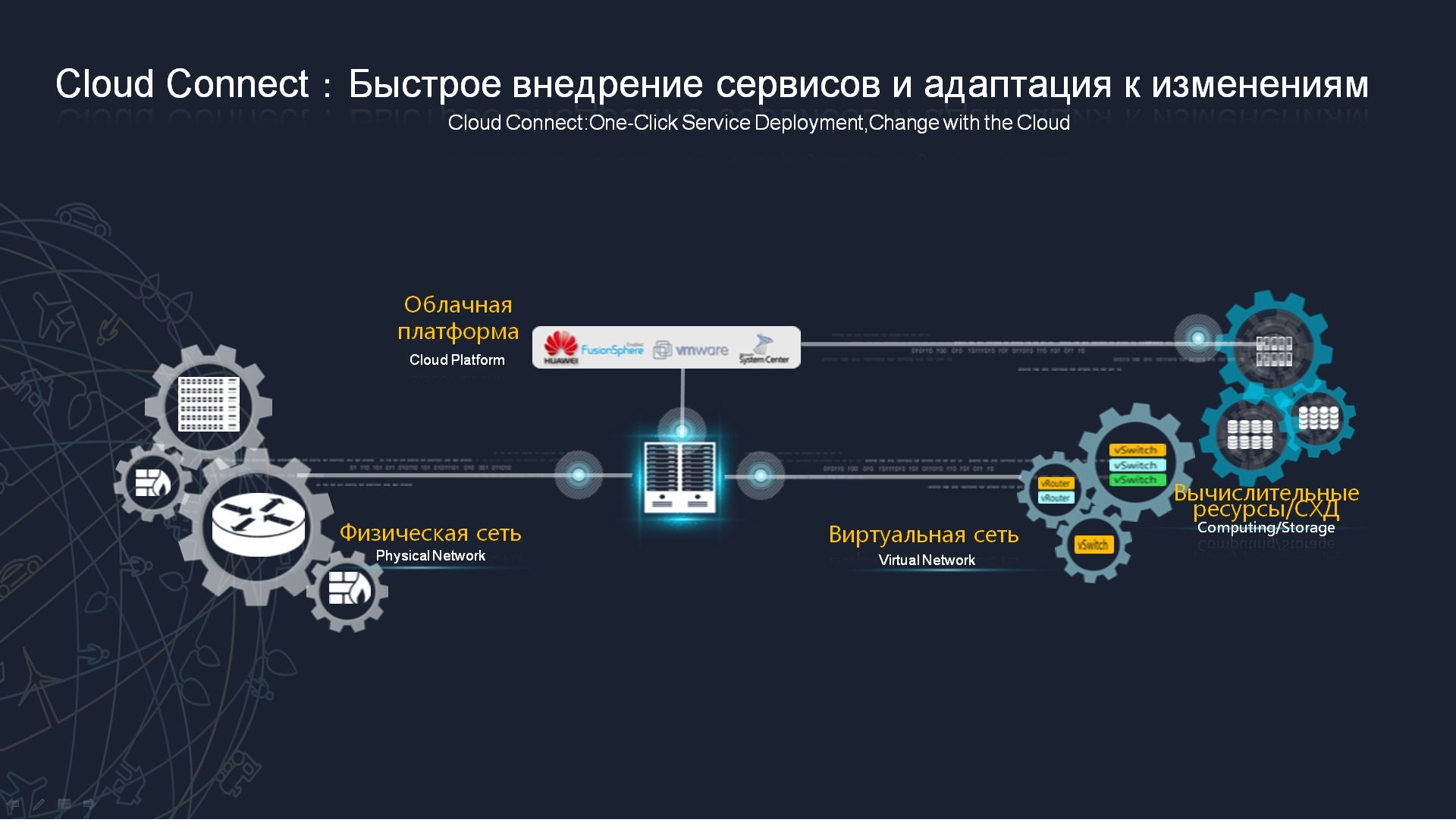
, . - , , , . service provisioning model, , , , , , , .
That's all. , Agile Network. , , , , active-active. , , . , , , , . , n- , .
: — Cisco, Huawei - , cloud engine , , ?
: — , open flow , , SDN , - , . . - step by step , . .
: — iOS - ?
: — , . 90% Huawei, Cisco, , Cisco . Huawei . 95% , . , , . , . , SDN-, . Cisco Huawei . SDN , . , , , , .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/305610/
All Articles