Hyper-Converged Solution - FusionCube and FusionSphere Openstack for the cloud service provider

We continue to publish the forum materials Cloud Technologies in Russia , which our company, together with its technology partner HUAWEI, held on June 23 at LOTTE HOTEL MOSCOW. The first three parts you can read here: Part I , Part II , Part III . Today we are presenting an interesting report by Denis Dubinin on the topic of modern tools for creating cloud solutions.
Denis Dubinin, IT Product Manager, Server, Storage, Virtualization, HUAWEI
')
Good day! My name is Denis Dubinin, I am the product manager of HUAWEI for products, storage systems and virtualization systems. Today's topic of my report is called FusionCube, FusionSphere, cloud creation tools. Has anyone already used our software, cloud, let's say, direction? FusionSphere, any other things? FusionStorage? That is, in general, no one came across? Well, today I will try to reveal the mystery that hangs over these products, what they are. I'll start now with the FusionCube solution, what it is.

A few words about the company HUAWEI. The HUAWEI company is an international leader in the production of telecom equipment for various telecom operators - cellular, fixed-line, and backbone of some kind of lines. I heard that today there was talk about the optics of Vladivostok, Sakhalin, and so on and so forth. Actually, HUAWEI also deals with these issues. Basically, our portfolio is short here, what does HUAWEI do in the direction of the enterprise - cloud solutions, which we will talk about today, servers, storage systems, network equipment, a fairly wide profile from, once again, mainline optics, ending with Wi-Fi, data center switches, standard campus solutions. There are network security solutions, anti-DDOS solutions, anti-virus firewalls, etc., etc., etc. ... traffic spectra and so on. And the engineering infrastructure for the data center, i.e. HUAWEI also produces uninterrupted power supplies, air conditioners, modular data centers, container data centers and everything connected with it.
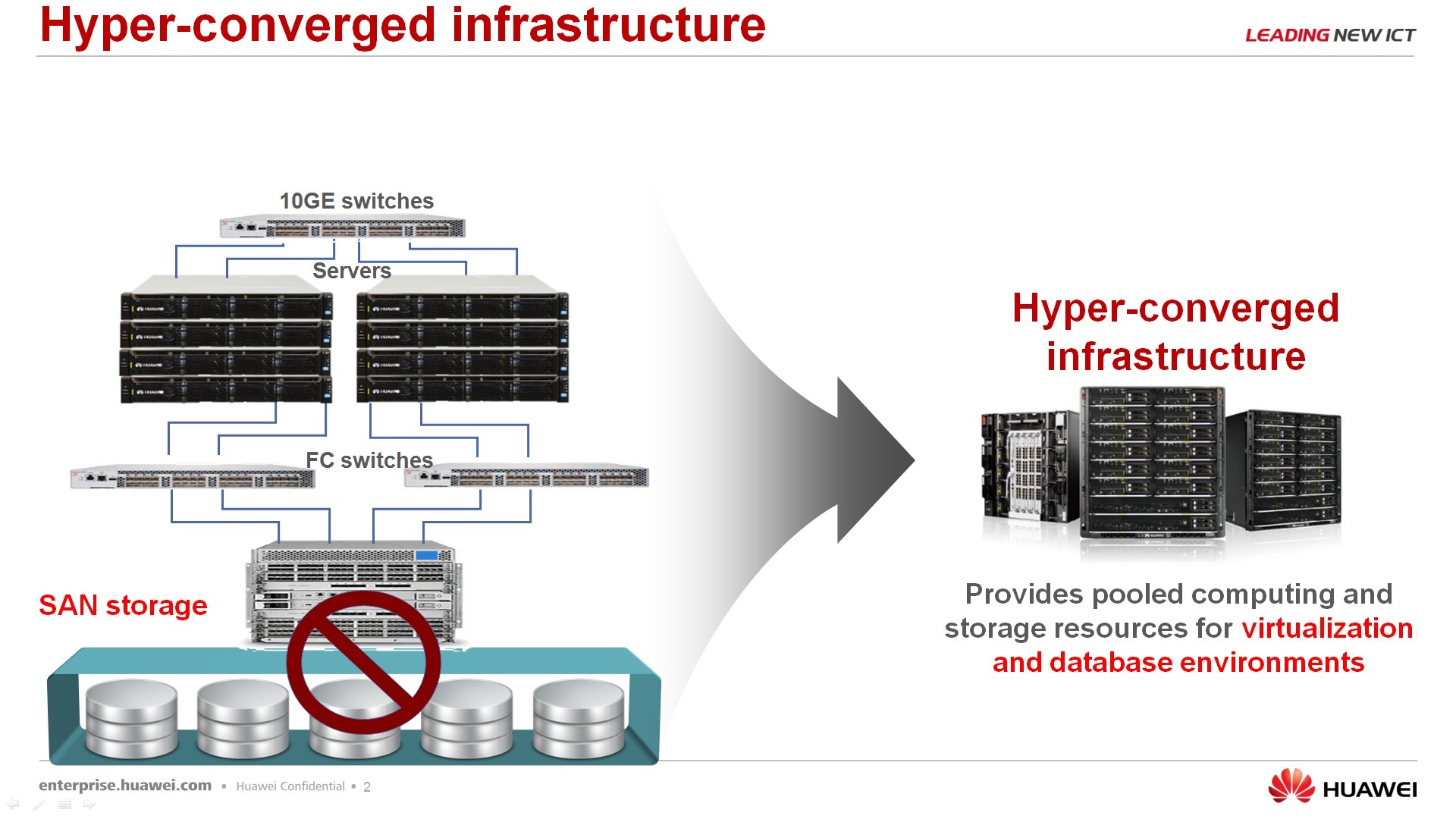
About the solution FusionCube, what is it. FusionCube is a hyperconvergent solution that, let's say, allows the customer to save time, save resources in order to deploy the IT landscape for some of its tasks. Why not just convergent, namely, hyperconvergent - because in a single package, in a single chassis, all three components, the server itself, network equipment and data storage system. Moreover, the data storage system is not separate hardware dedicated elements, but for the data storage system resources of the servers themselves are used, i.e. a certain software is installed, we obtain software defined storage, and we will present this software defined storage to the servers themselves, which rotate on the same hardware platform. At the moment we have, shall we say, two models - FusionCube 9000 and FusionCube 6000.

Their parameters are approximately visible here. So, the older model allows you to get up to 32 processors in one chassis, 12 terabytes of RAM, 172 terabytes for data storage. FusionCube 6000 is a lighter, simpler, smaller solution - up to 8 processors here, up to 2 terabytes of RAM per module and up to 280 terabytes of storage. In principle, there are already indicated general directions for the younger model, for which it is worthwhile to apply, say, this solution, that is, before virtualization 60 of some servers, up to 280 workplaces virtualized. If you need more parameters, then you probably should already consider the decision of the 9000th.

Regarding the use of FusionCube. FusionCube is not a cloud. FusionCube is not equal to virtualization. FusionCube, so to say, is equal to a kind of universal structure, a kind of universal IT-landscape, which you are free to distribute, use at its discretion.
For the 9000s systems, there are already tested, ready, certified for UBD solutions, databases, such as SAP HANA, ORACLE and others. There are hybrid solutions, when a part of the nodes is used for virtualization, a part of the GCD is used for the databases, for example, a part of the nodes is used for SAP HANA nodes.
For the 6000th system, as for the younger system, virtualization is of higher priority, with virtualization of a fairly wide profile - VDI, clouds, server virtualization, and so on.
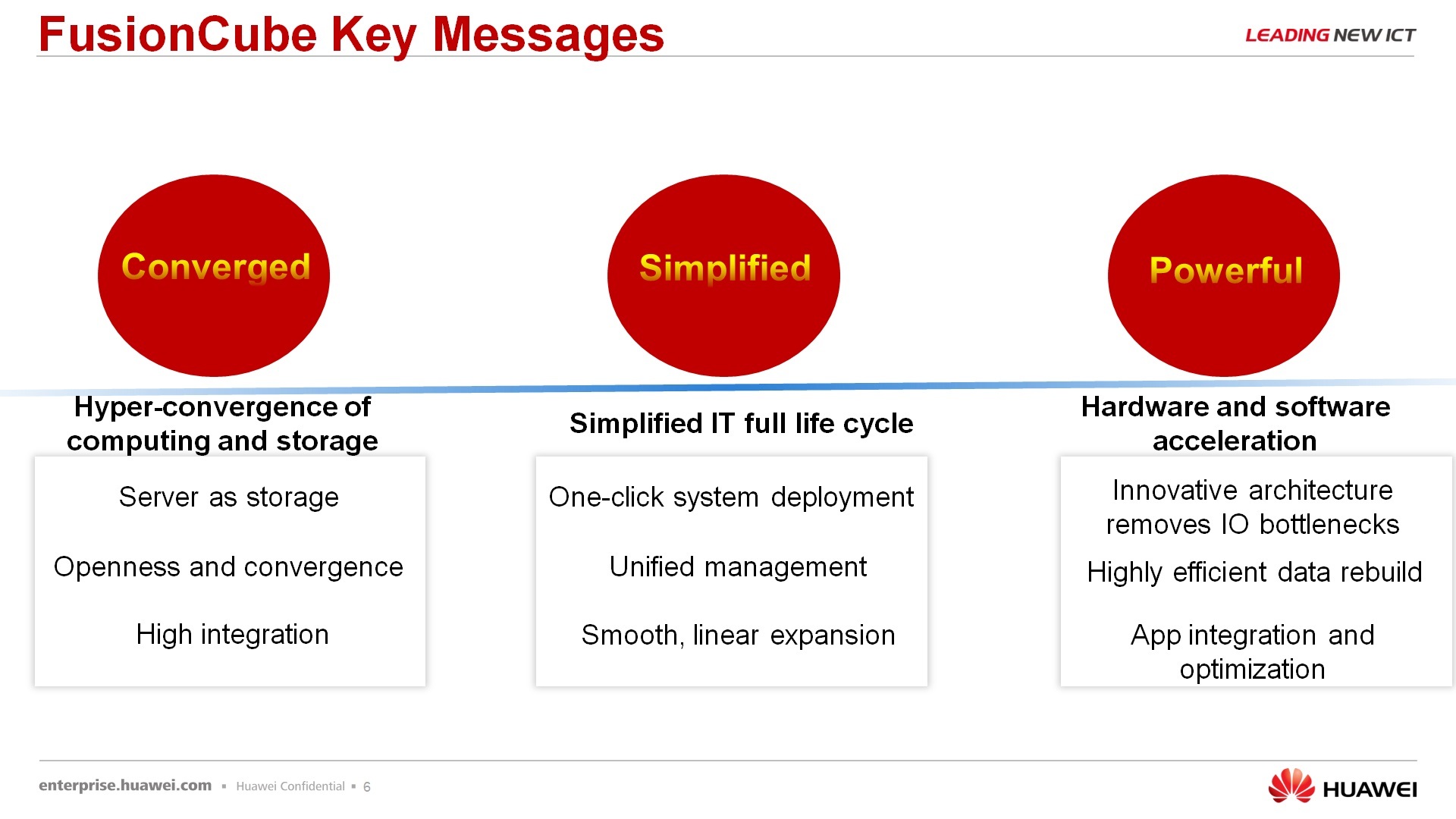
Regarding what FusionCube consists of and why we call FusionCube a certain set of solutions, and not just any of our servers, we call FusionCube. According to the decisions, the first is convergent. This solution has no dedicated storage system. If we put several servers in the same row, attached hardware storage to them, then this is no longer FusionCube. It's just some kind of cluster. Simply, the management of this FusionCube comes from a single window, that is, the management and management of hardware hardware, software things that are installed on it, is done from a single operator console. Well, the solution is quite powerful because it uses, again, a distributed storage system and a number of elements that increase performance. This is an InfiniBand data transfer and the use of our SSD PCI Express cards for data storage and data caching.
The next point is the openness of the solution, that is, I say it again, we do not force the customer or our partner, so you acquire our FusionCube, and are further used in one, I don’t know, direction, in one scenario. You can, in principle, create this script yourself, i.e. from us you get this hardware, from us you get a virtual storage system, you get, say, management models, PU controls, but all subsequent stuffing, like in operating systems, applications, databases, and so on, is your choice.
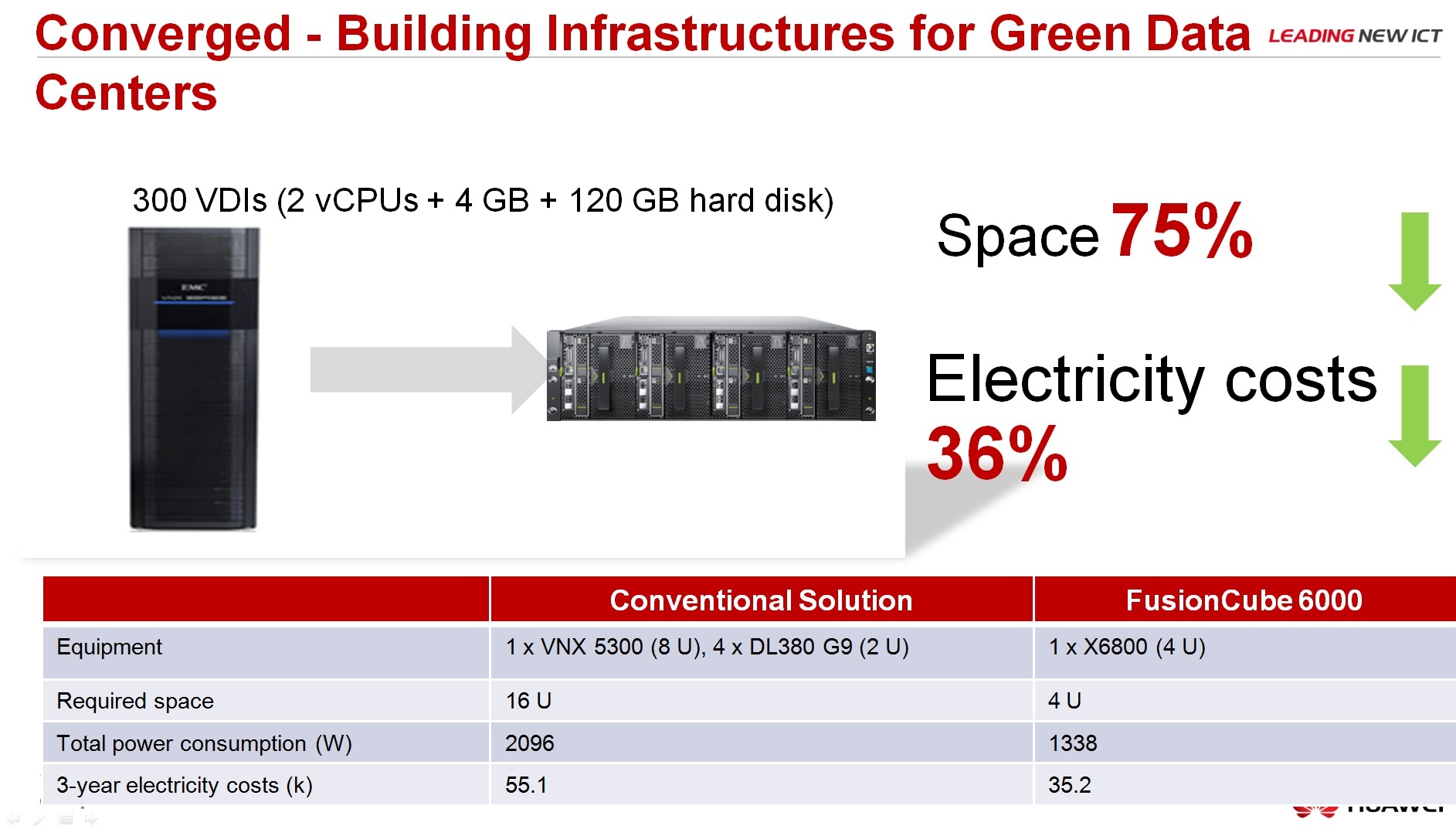
About the comparison with the classical architecture, the advantages: it takes less space several times, energy efficiency, green technologies and so on.
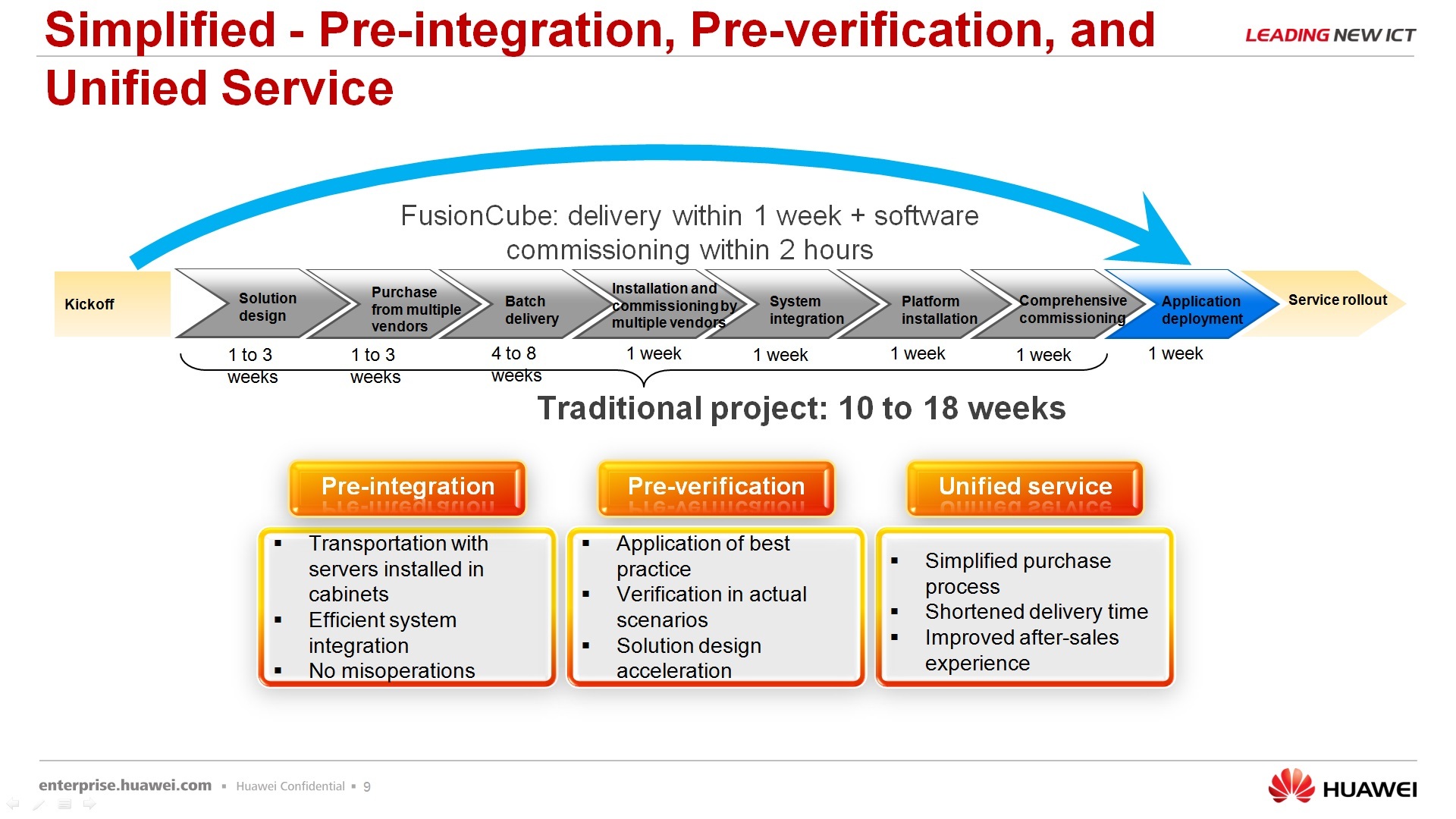
About another plus of this solution - it allows you to reduce the time for deployment, that is, you do not need to receive equipment from different vendors, then integrate it, then receive software from a third vendor, integrate it too, run everything into work, hand it over to the customer, then fight with bugs, let's say, from all together. Our solution always comes with a single support, with a single entry point, under a single specific solution.
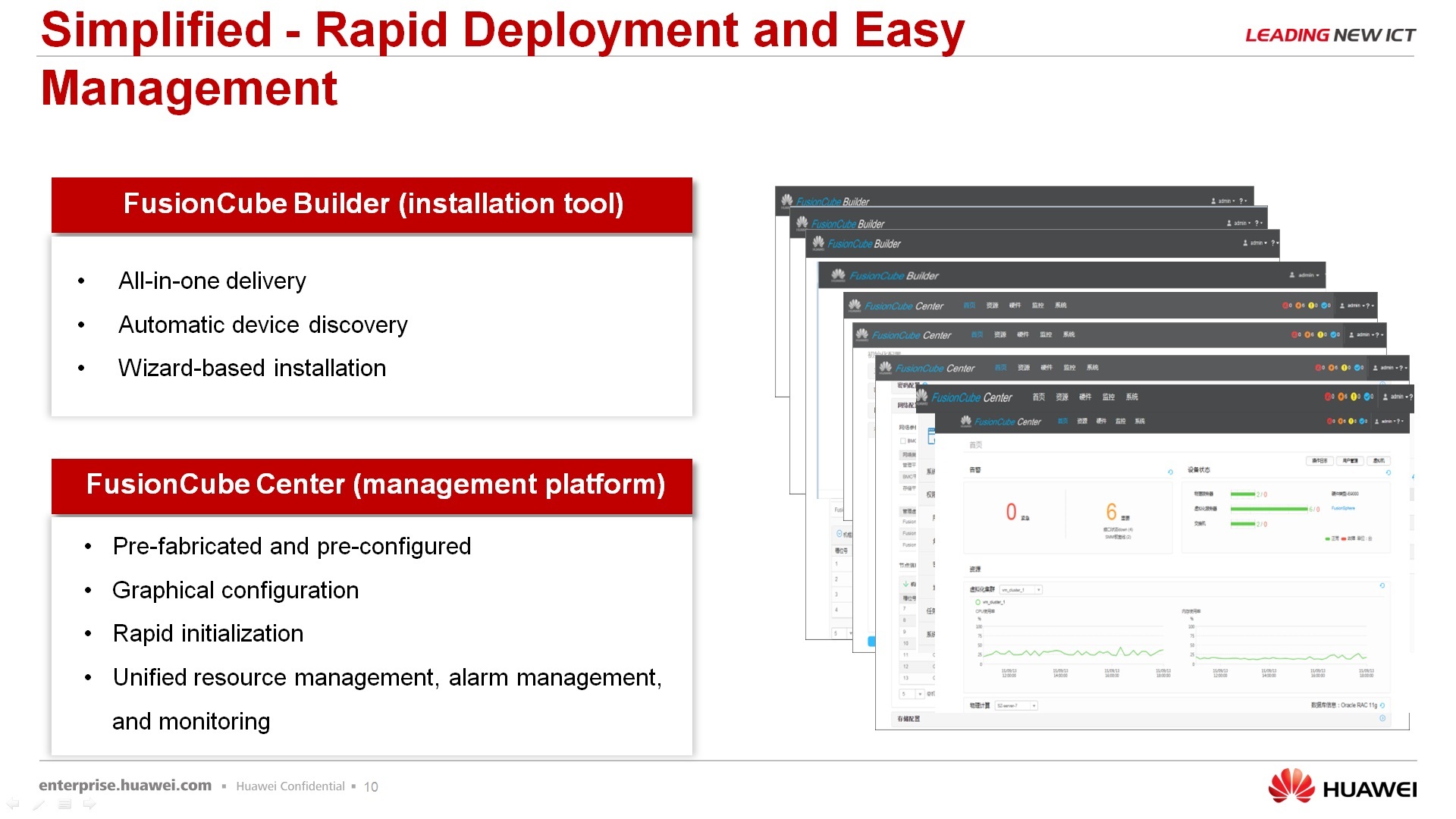
Regarding the rapid deployment - for those, let's say, tested scripts that we offer using FusionCube, already ready there are tools that allow you to quickly deploy this FusionCube for a specific task. There is software called FusionCube Builder - this is the installation tool, i.e. you run it on your laptop, connect it to the FusionCube via the network, as in the wizard you are doing - next, next, next, as a result you get the landscape that you ordered. And FusionCube Center is, in fact, a management platform that allows you to integrate it all, well, I won’t say to manage it completely, but at least monitor it 100% exactly.

The next moment is linear growth. Since there is no dedicated storage, as the number of servers increases, the performance of the servers themselves and the performance of the storage systems increase linearly, that is, how would you increase the number of users, the VDI did not grow, or the number of servers used in the solution, the performance remains on that same level. Increasing the number of users will not cause you any reduction in the performance of these users available.

Of the advantages, about software defined storage will be further discussed, but in fact, how it differs from the classical architecture. In the classical storage system there are data network, san network, either 10 Gbit, or 8 Gbit fayber channel, or 16 Gbit fayber channel, then there is a controller, in classical systems there are 2 controller machines, now multi-controller systems are being developed, As a rule, the number of controllers in the storage system is limited. I, say, do not know any storage in which there are more than eight controllers. Let's just say, we can increase this figure - more than 16 controllers are definitely not in the storage system. And, in fact, the number of disks that this controller can serve. When using the classical storage architecture, we can all rest at one of these limiting factors at any time. Either the san network starts to slow down, there is not enough performance, or the controller in the storage system that exists, starts to slow down, there is not enough performance, or the number of disks - we have reached the limit that there is simply no place to put disks. All these problems are eliminated by the distributed storage itself, where each server is, firstly, a storage node, so as you increase the load, naturally, the number of servers grows, which should digest this load and the number of nodes in the virtual storage automatically grows . Thus, we get rid of the bottleneck about hard drives. More servers, more disks, if you need even more disks, we simply add servers to our infrastructure, with almost no limits.
Data transfer between nodes, service information, I mean, occurs via the InfiniBand protocol with minimal latency, with minimal latency, at a speed of 56 Gbit per second. Out of this can be given over a gigabit Ethernet, a 10-gigabit Ethernet, or, if you have specific tasks for the same InfiniBand, it can be given. The number of caches, the number of I / O ports, the number of processors in the virtual storage controller is also proportional to the number of nodes. Therefore, when using a distributed system, you, in principle, do not need to face the current realities.

I’ll come back a little bit, I said that Fusion Cube does not mean cloud, even private, it does not mean 100% virtualization, it means some kind of universal IT landscape, and it can already be tested and there are recommendations, certifications, about how this landscape is used. You can use it under Oracle, under IBM DB2, Sybase, under SAP HANA solutions, if you work with such, under FusionSphere, again with sub applications and under, in principle, just virtualization based on VmWare, in principle, you can use it with our FusionSphere , it was necessary to add, probably, still the seventh line, as if the most obvious option.
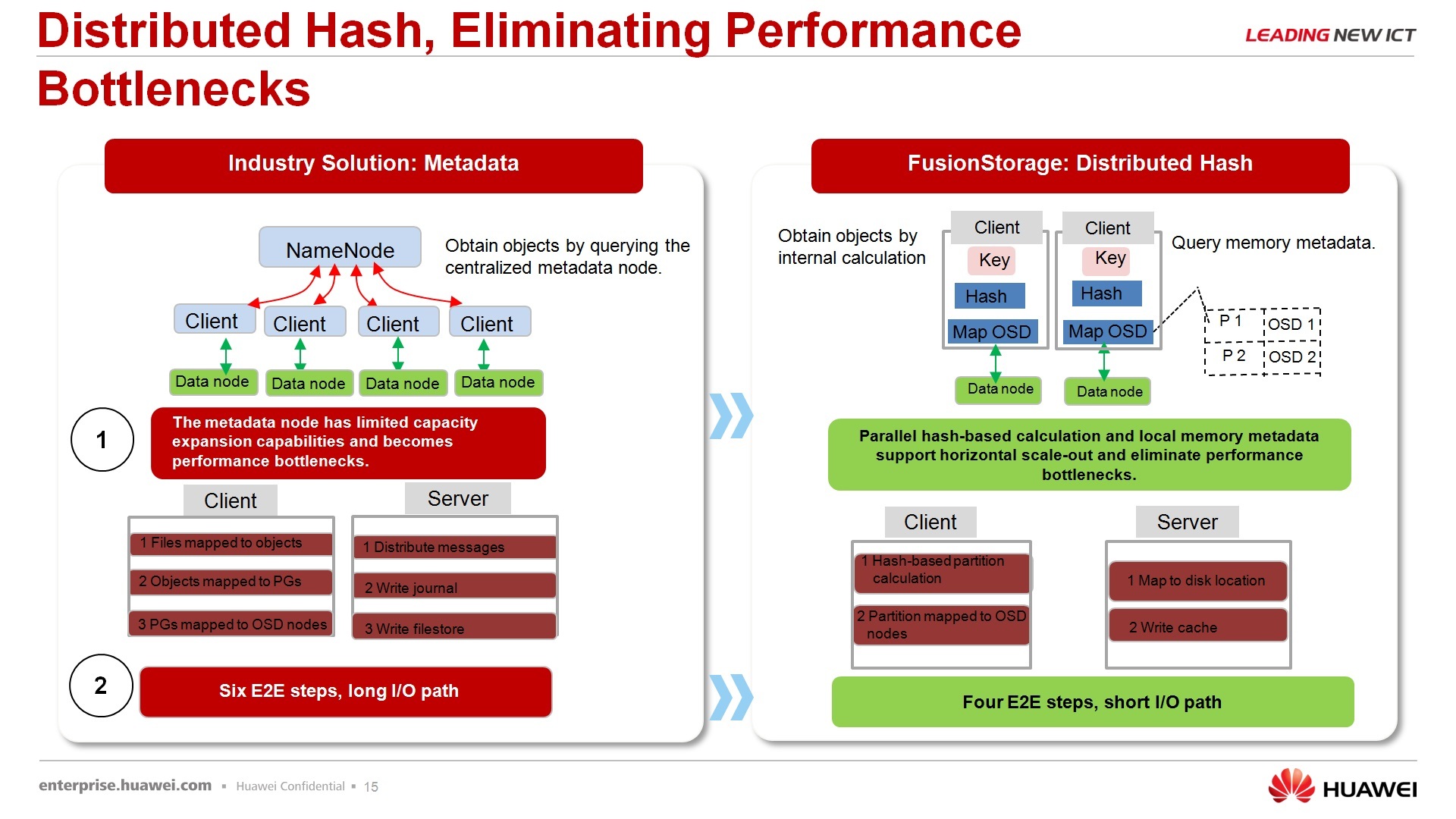
About distributed storage - not only we offer distributed storage in the market. In general, there are other vendors who, for example, only deal with the software part of this issue, there are vendors that offer both software and hardware solutions, but, as a rule, all these solutions are implemented according to the following structure: there is a data warehouse or an object the repository is the metadata repository. As a rule, the bottleneck is the metadata store, i.e. these are those servers or dedicated storage systems of a small volume, but rather productive, on which, roughly speaking, the data on where all other data lie, some such, if translated to file systems, a fat table, i.e. this server knows where all the other data is. And, in principle, this one here, the metadata server, is a bottleneck.
Why it is not a bottleneck for our solution - because we do not store metadata explicitly, we only store hash sums, i.e. when the server sends a request for some data block, it does not send it explicitly, i.e. a block such and such a cylinder, such a file such and such, etc., the embedded driver that is installed in the system calculates the hash sum from the given request and sends to the side of our virtual storage only this one request consisting of the hash -sum. This minimum request, in principle, the volume of the hash table is 232, I don’t know how many billions are there, the olympiards are in decimal form, and, in principle, the whole table is 6 MBytes, and each node participating in the storage system stores a copy of this table. We call it, however, not a table, but a ring, but the meaning is that it is functional, that it is a table. That is, this entire 6MByte is always stored on the node in RAM, I will even say more, it is often stored in the processor cache, i.e. in the most high-speed place, and, in principle, it is distributed evenly between all nodes that are involved in storage. Therefore, due to this appeal by the hash sum, i.e. the server accesses “where my data is,” the driver processes the request, says “that's the address of this hash,” hash is sent to the store, the store processes this cache, says, “that's what this storage node corresponds to this hash,” a request comes to the storage node , and already this request parses the storage node and he already knows where he has what lies on the shelves. That is, at the expense of this reduction of the transmitted data by addressing and paralleling these requests, which can be calculated by the hash sum in parallel on several machines, and so on, and so on, higher performance is obtained.

What else we have used from the positive is the distributed cache. The cache can be distributed between storage nodes, i.e. there are no dedicated cache islands when a separate node has its own cache and nobody knows about this cache. You can use the following mechanism when the cache of this node is partially replicated with the cache of another node. And when a request to another node occurs, these data will already be in the hot cache, which, in turn, also improves performance.
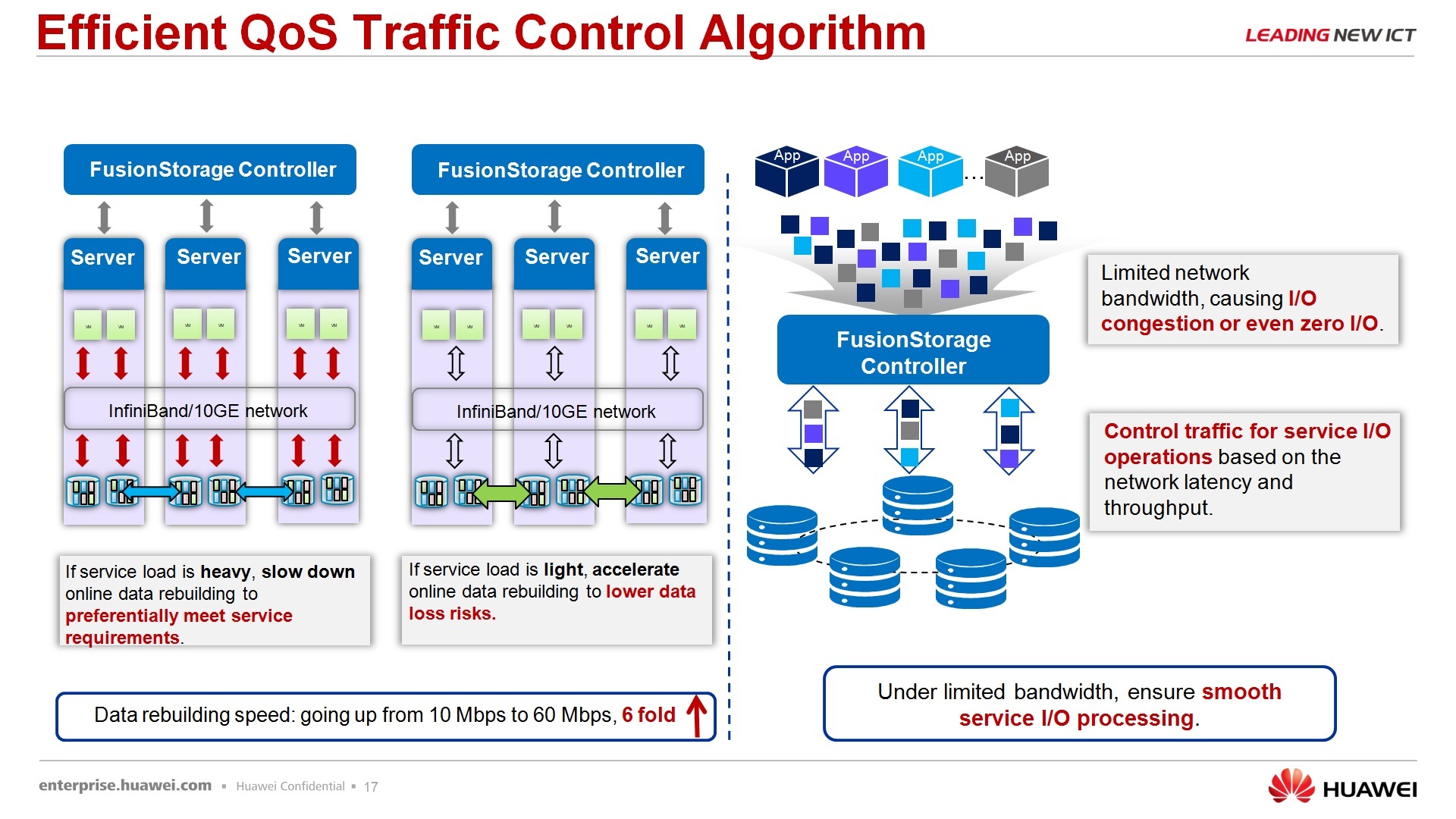
Regarding speed control, there is also a weak point for these systems, but our systems have a built-in, let's say, vallyti of intelligent service, which, depending on what task is used, whether the system is in the process of rebuilding or is in stable operation , changes priorities for secondary or priority tasks.
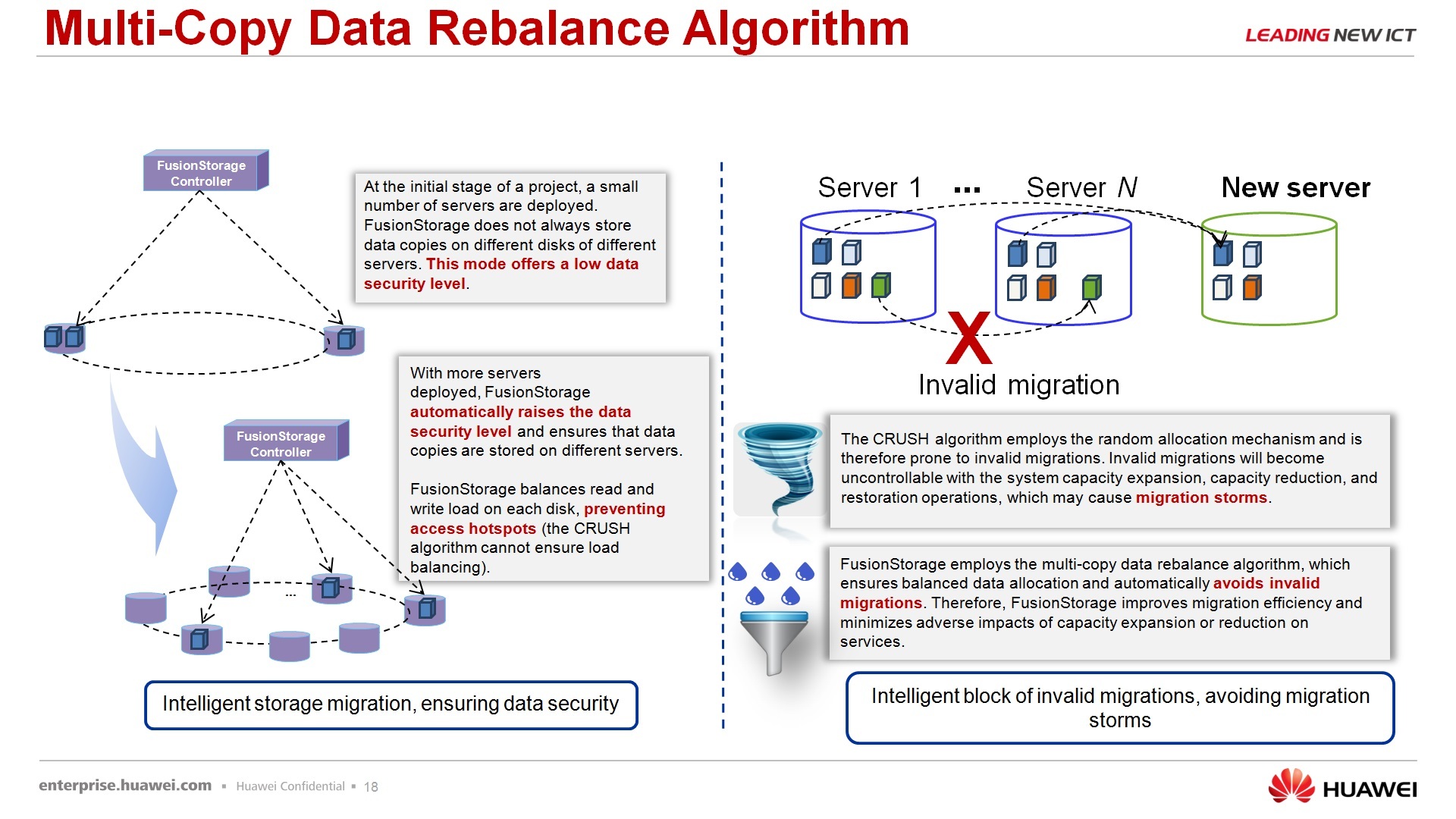
It seemed to be an obvious thing about the rebalancing algorithm, but for some reason I often get a question: “if we had 10 nodes in the storage system, we added another 20 nodes, will this redistribute to increase performance?” Yes, the increase redistribution of data on the nodes will occur, in fact, for the sake of it all started. There is a separate mechanism that deals with this issue.
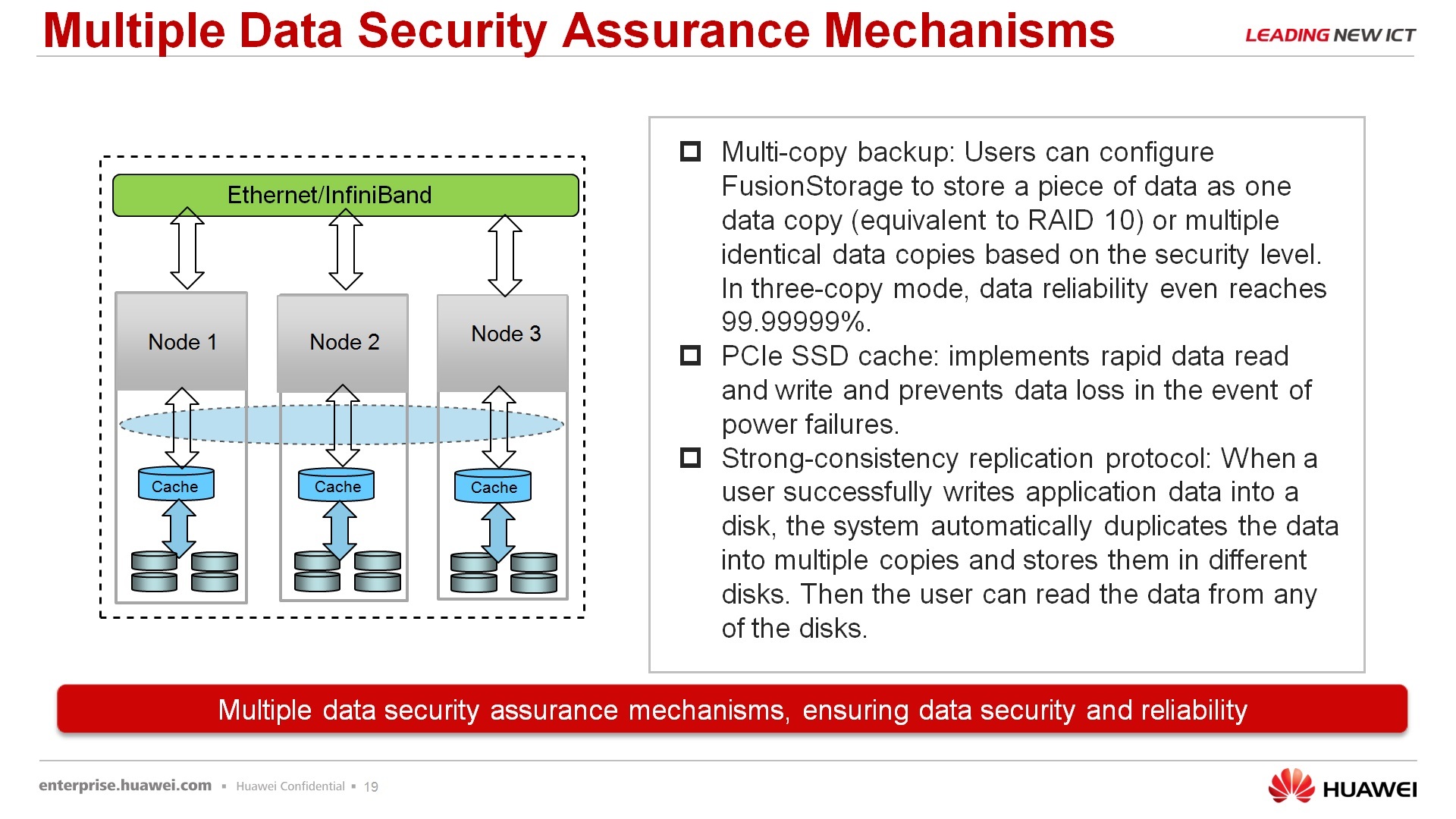
Regarding reliability, fault tolerance - the consumer has two options for the protection that he can receive - he can restrict himself to double data duplication, when there is a main copy of the data and its backup, which must be on another node or in enhanced reliability mode when stored not one copy, but two more copies. Such reliability in the number of nines gets seven nines, i.e. if the customer is willing to sacrifice a volume twice as much as information merely takes to improve reliability, he can take advantage of it. Taking into account the fact that servers use cheaper disks than storage systems, in principle, often this cost, let's say, is justified. Using a PCI SSD cache, in principle, it’s not that our know-how, these cards are made by many vendors, but we use them, among other things, to cache the optimization of our virtual storage.
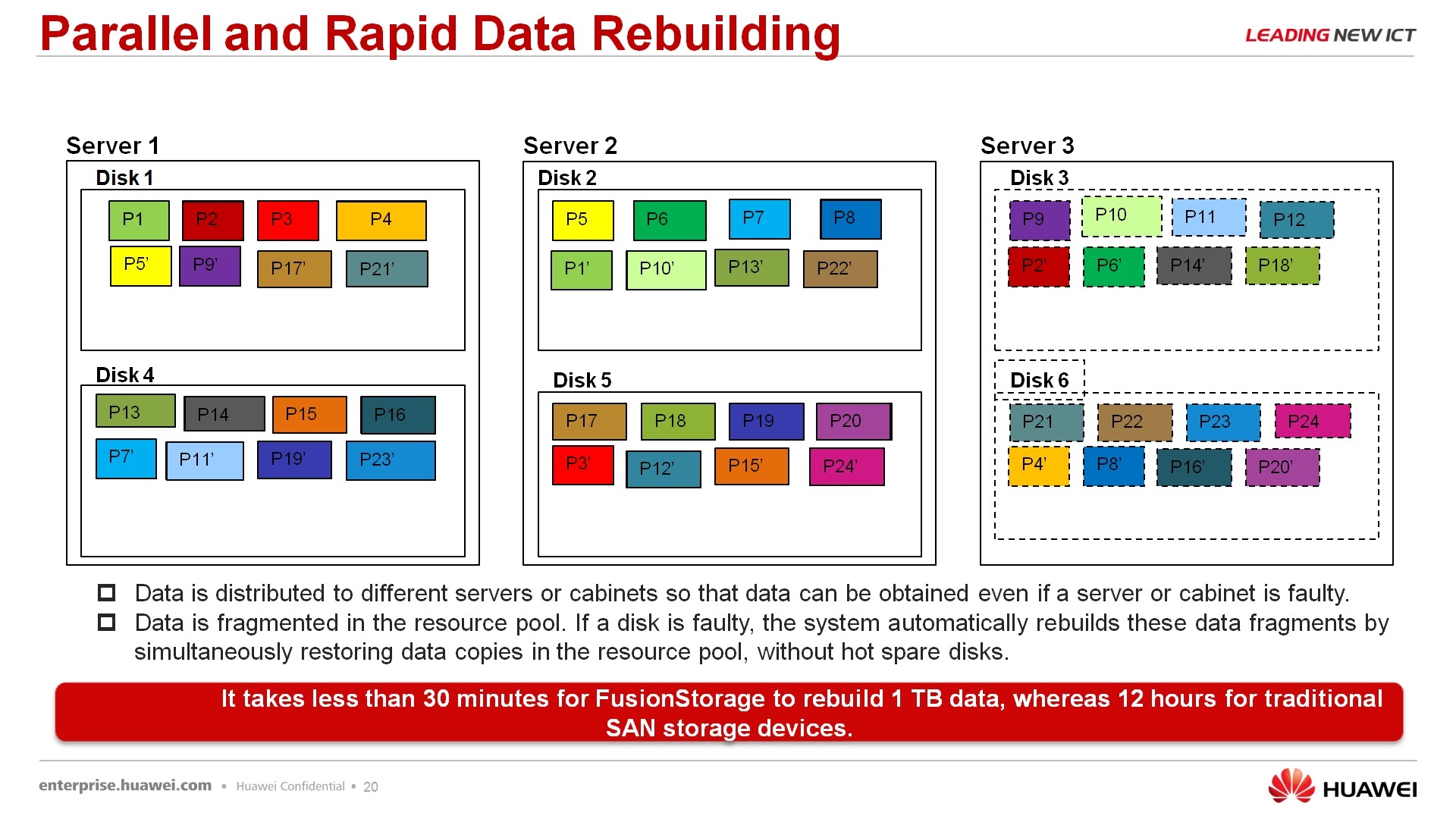
Regarding data recovery, due to the fact that there is no single controller through which recovery takes place, due to the fact that all data is distributed between nodes, as a rule, evenly more or less, the rebuild process in these systems is quite fast, i.e. you do not need to wait, here are examples below, in 30 minutes one terabyte of data is rebuild, i.e. if you crashed a server on which you had 4Tbytes of data, the system will return to its original steady state in less than two hours. If we recall the classic storage systems, they can recover for weeks after the fall of 4-terabyte systems, 4-terabyte disks. Actually, it is shown, demonstrated how the rebuild occurs. In principle, nothing cosmic, incomprehensible, strange, everything is the same, it just goes in several streams, in parallel, therefore this process goes much faster.

There are snapshots for this system, again, taking into account the architecture, it affects the performance less, as in comparison with classical systems. Regarding integration with applications and other, in principle, at the moment, so far open, i.e. Snapshot consistency requires clarification and not for all applications as long as it is available.

The existence of resource pools - we do not force the customer to combine all nodes into a single pool, and determine its entire security policy, storage policy, and accessibility for the entire pool at once. You can divide your large pool into pieces and each piece will have its own security policy, a policy of denial of stability, a policy of replication, a policy on snapshots, and so on, and so on. Well, I do not know, with network technologies such collision domains, i.e. What happens in this segment does not bother me, because I am autonomous with respect to other segments.
In principle, on software storage is all. Why she stands as if alone. I will continue to talk about FusionSphere, it’s there too, but, in principle, I’ll not talk about it again. Here Fusion Storage can be purchased separately without our virtualization, it is a separate marketing product, with its price tag, which you can put, in principle, on any server, any vendor. It is not rigidly tied to our hardware, you can have your servers, if they meet the requirements, in general, use this system for this.

Regarding the hardware, what our FusionCube consists of, what it is: in fact, the 9000th consists of our blade chassis, in fact, the basket itself, front view, you can install 16 half servers, or 8 4-processor servers, or , , – , , , .

, – , , , , , , - , , high performance . FusionCube – - , 24 , 2 Xeon 5, , 4, E3 , 222- , , 15 , , Fusion Storage. RAID LSI, , , , . , , , , 15 , 12 , NVe, .. PCI-express , . 226- 3- , .. 8-10 , . 220- – c 6- pci- , PCI- , , , , , NVIDIA Cuda , , Intel Fixion . , , , 121- – - PCI- , , .. , - , , PCI-express, SSD- , , , 1 , - , , .. - . , , 242 – 4-, 1 , 4 Xeon 7.
, FusionCube. 310- – 10- , CX611 – InfiniBand . , 40- , , , 40 100 InfiniBand, .. , , , .
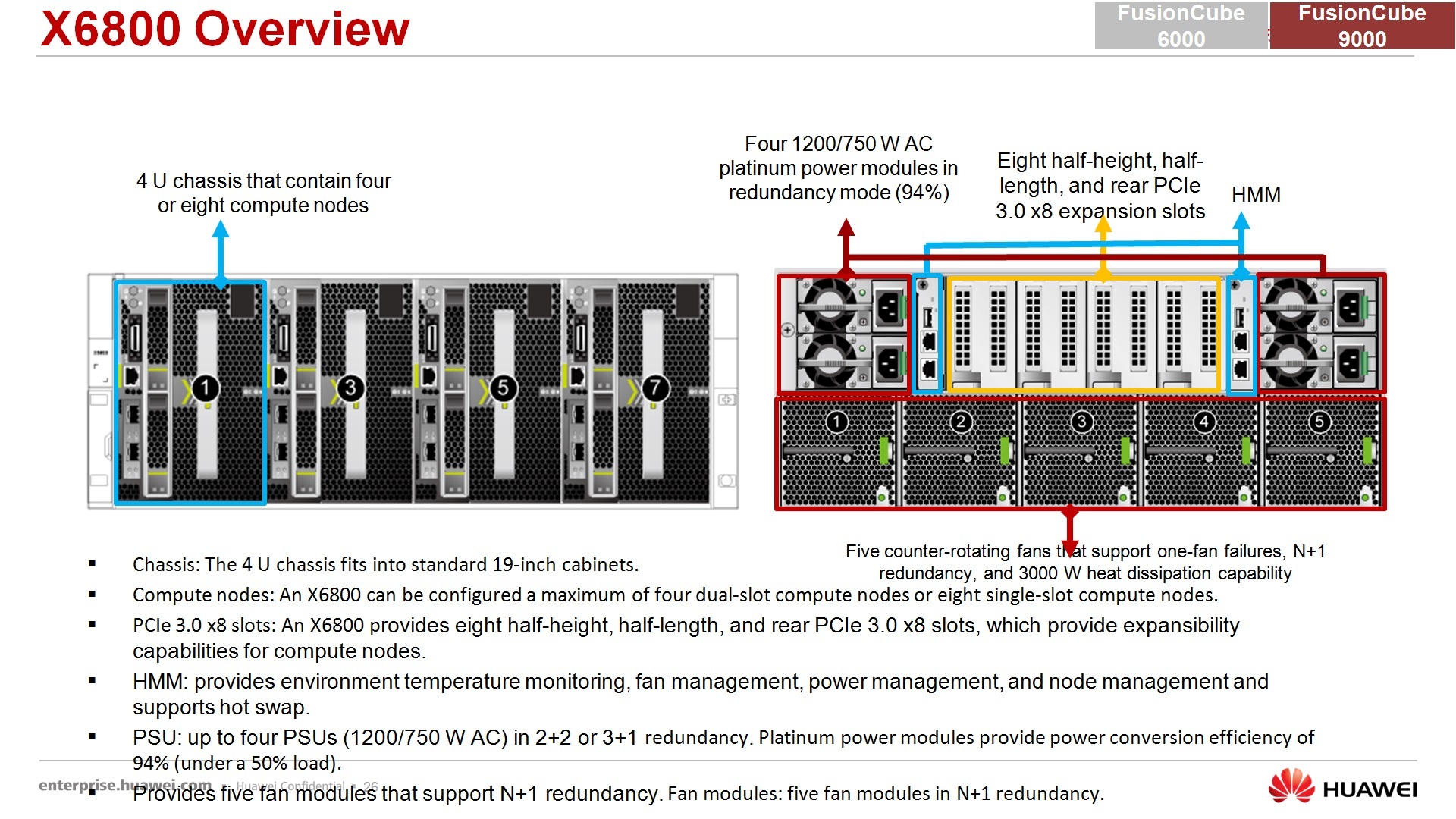
FusionCube 6000, , , , , , 6000- – 4- , 8 . 4 , , … , 4 , , , . pci-, .
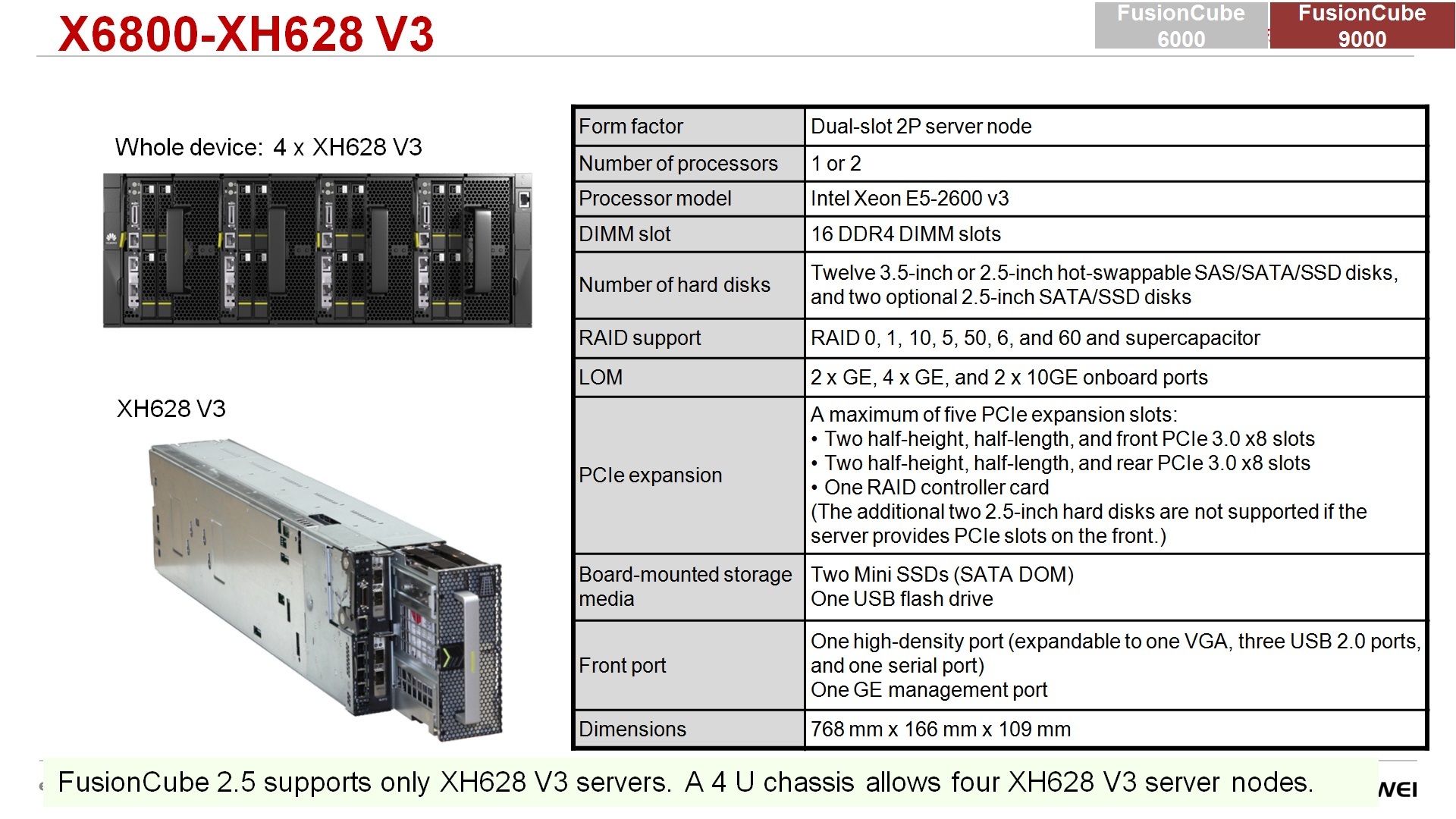
– , , , , sas-, pnvme-, , , 12 - , - - . sas, NVe, PCI-express, .. pci- , NVIDIA Cuda , , , PCI- .
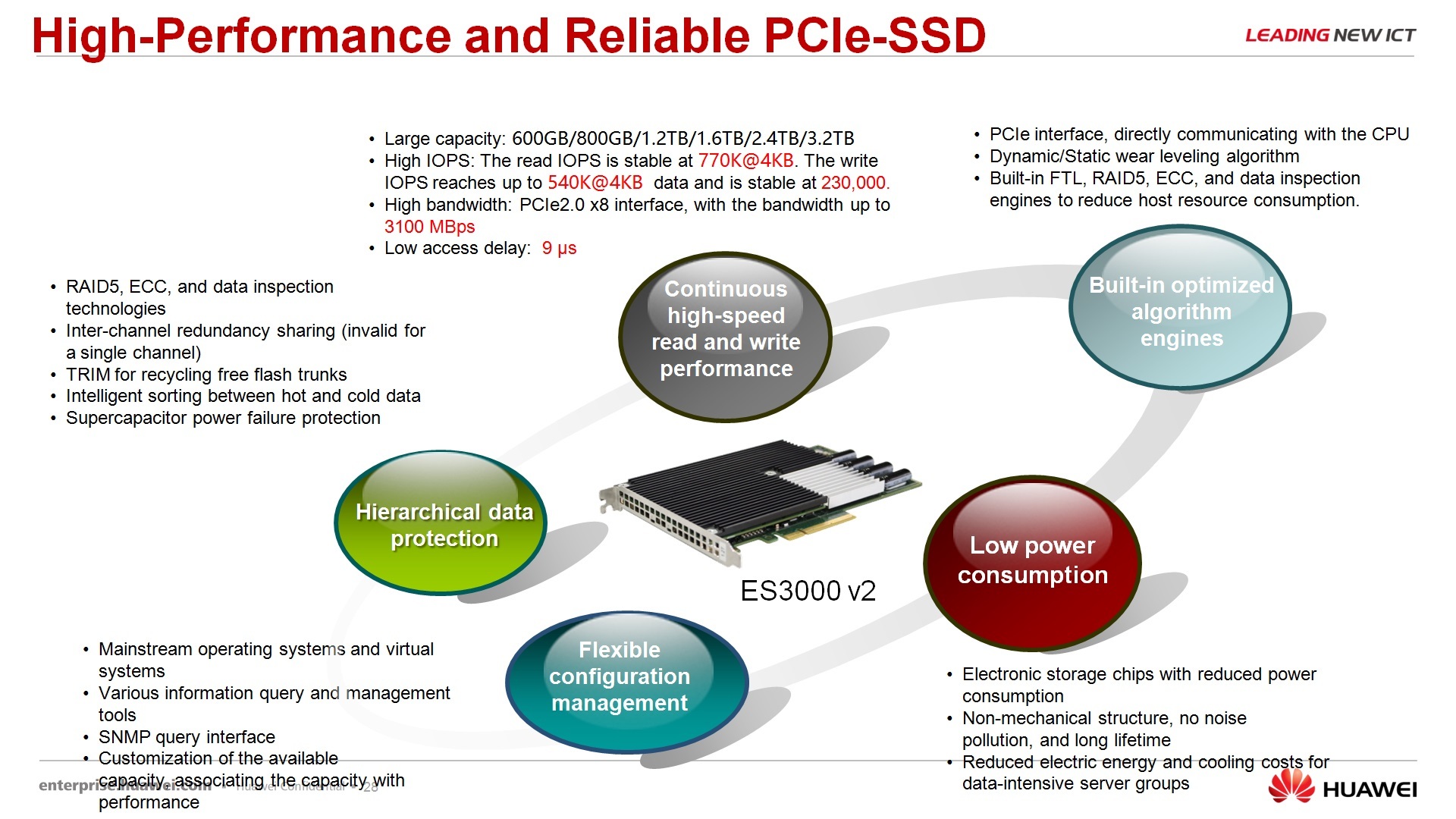
, , PCI- – , , : HUAWEI , , .. , , - , , , - , , , , , PCI- SSD- HUAWEI . SSD , PCI- , sas-, sas- RAID . 9 , , , , -, 1000 , . IOPS-, , 770 230 . - . , SAS-, SATA- , , , .
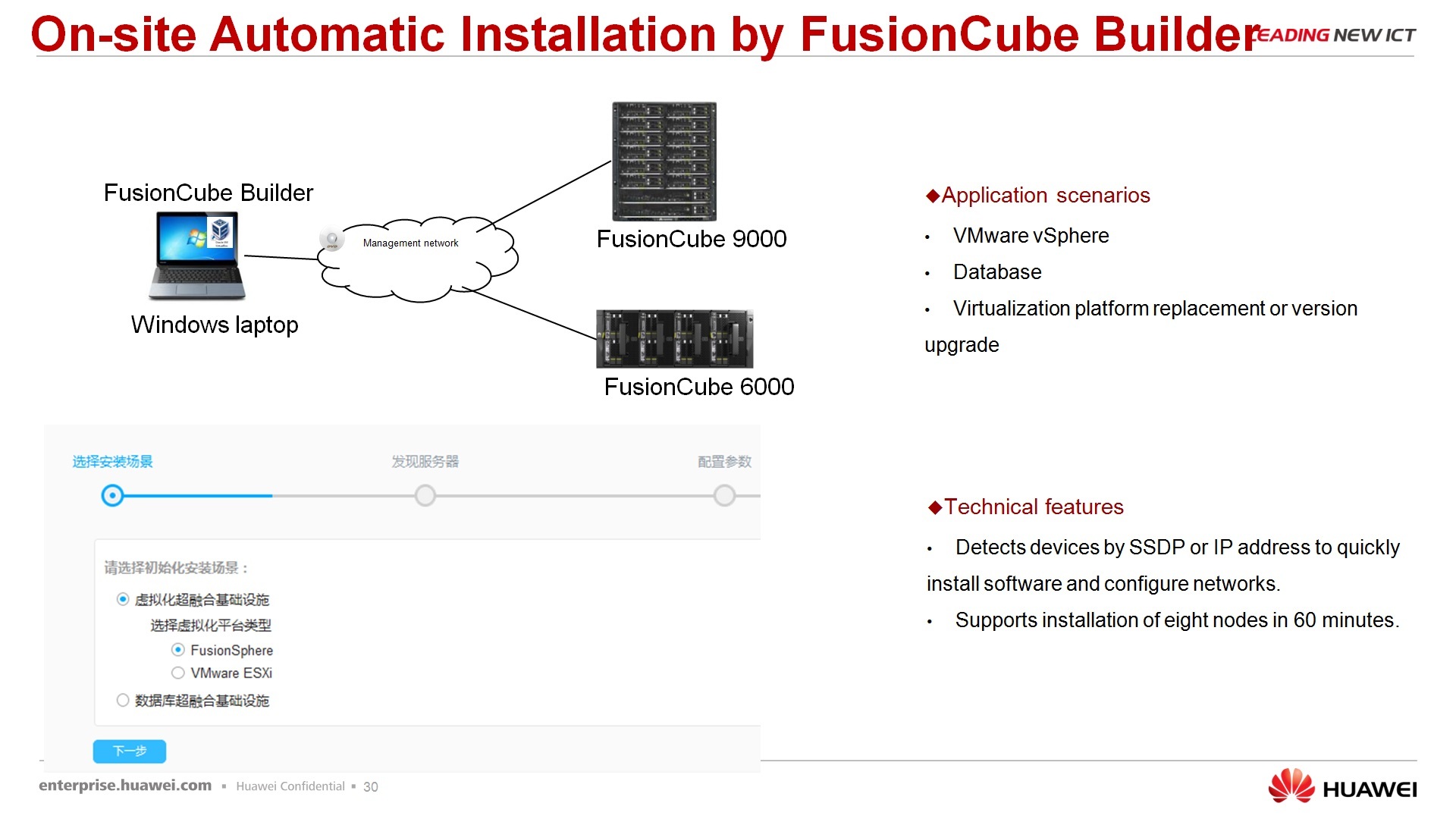
– , , FusionCube Builder, , FusionCube, next, next, next, , . , , .. … , 1, , . FusionSphere Vmware ESXi. next, next, next, 8 , , , .
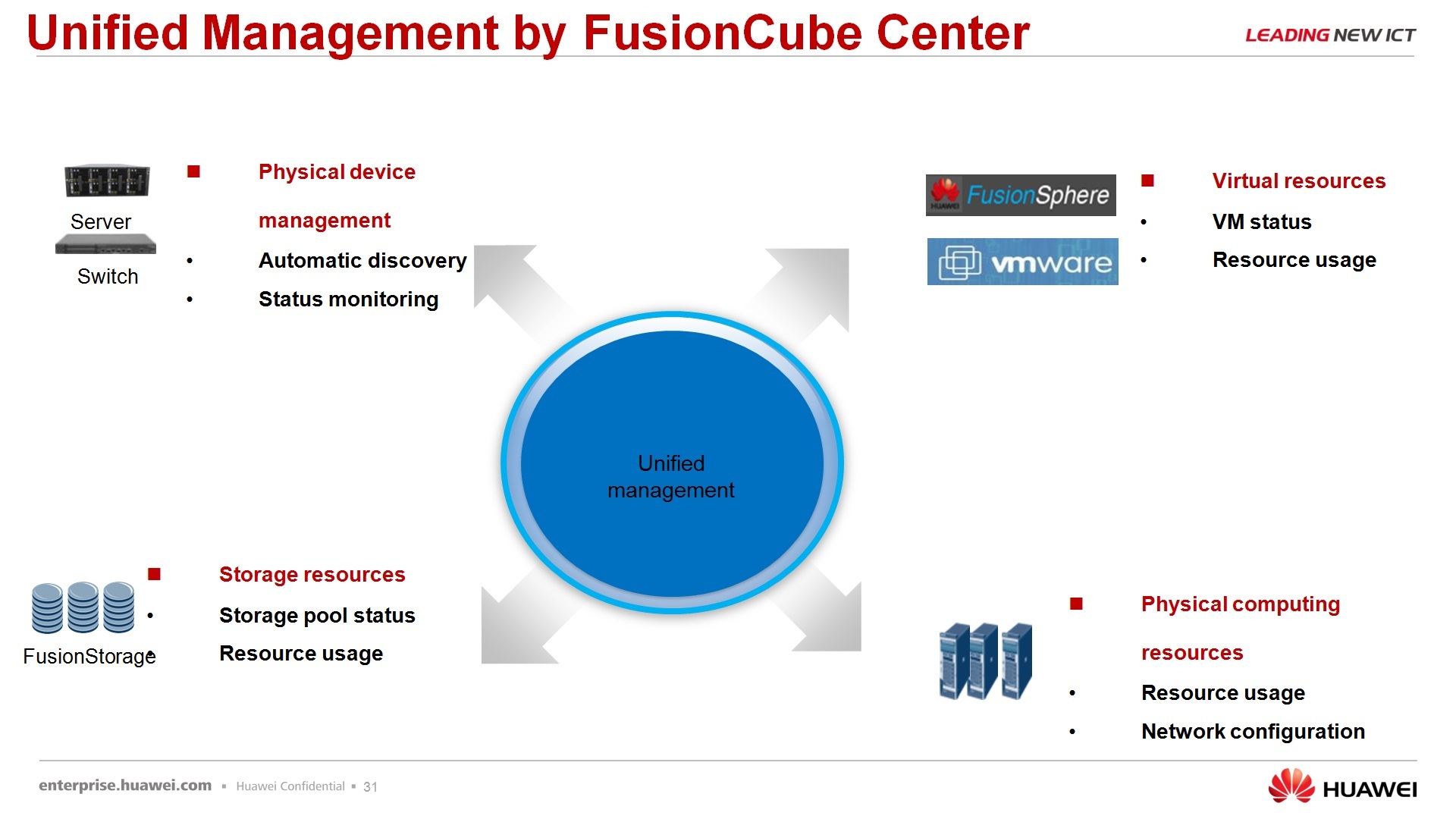
. , , Fusion Storage, , , , FusionSphere VmWare .
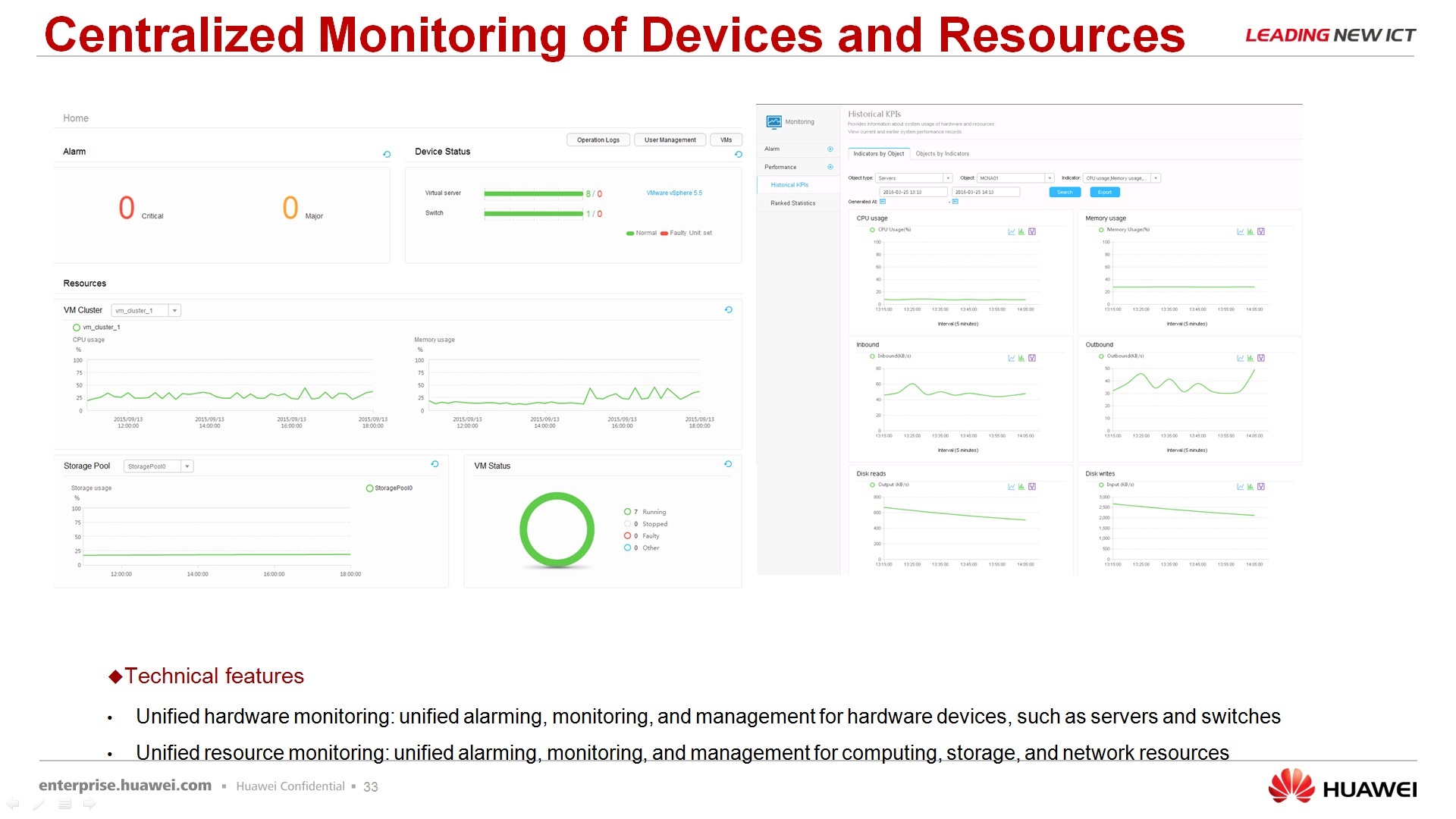
– , , , , , , , . , , . , , , , , , .
: FusionCube , software defined storage. FusionCube, -, , . , FusionCube , , , 100%.
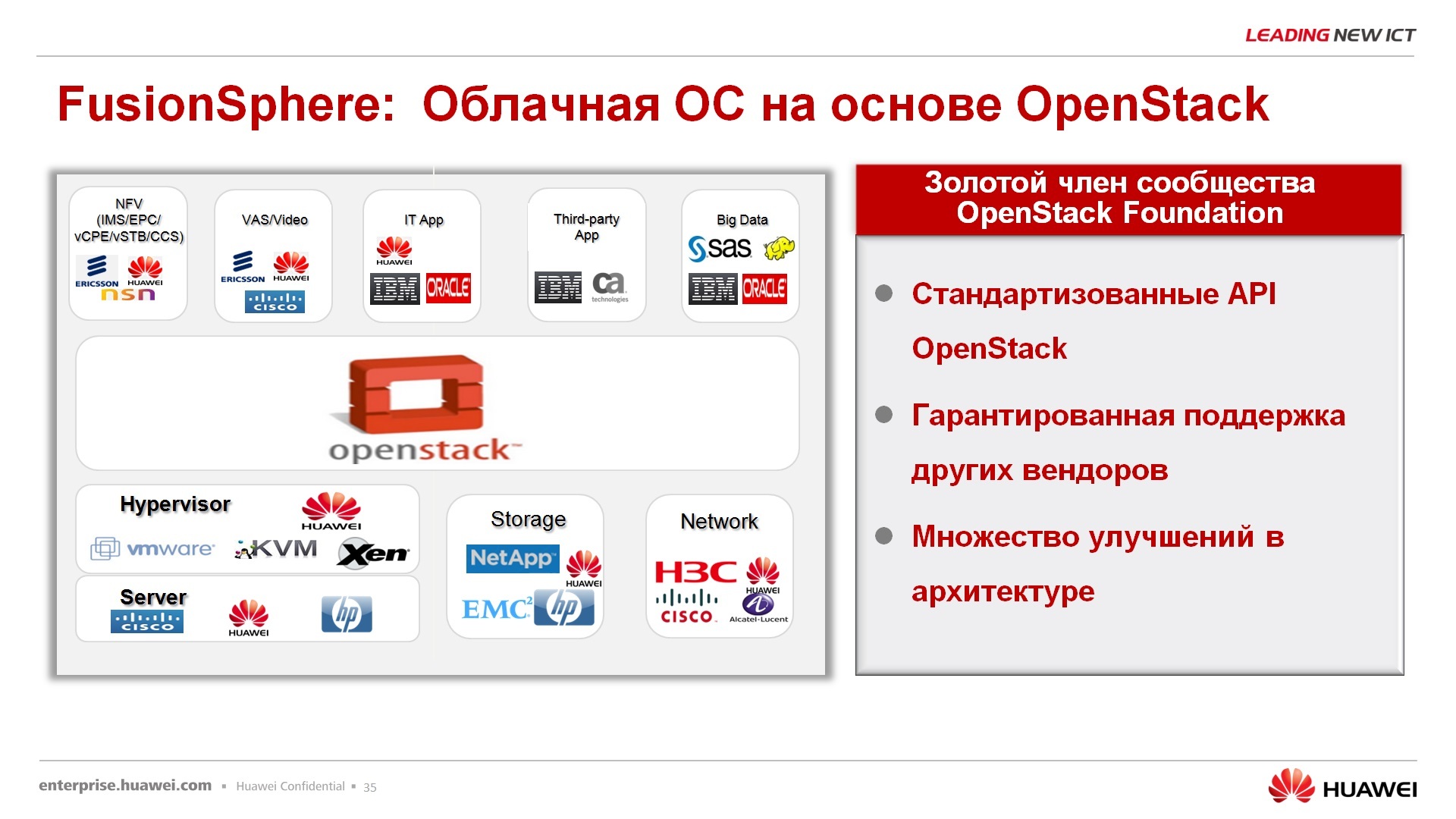
FusionSphere. FusionSphere – , , , , OpenStack.

HUAWEI , OpenStack Community : 23 , 63 , , HUAWEI , .. , , OpenStack Community, , -, , .
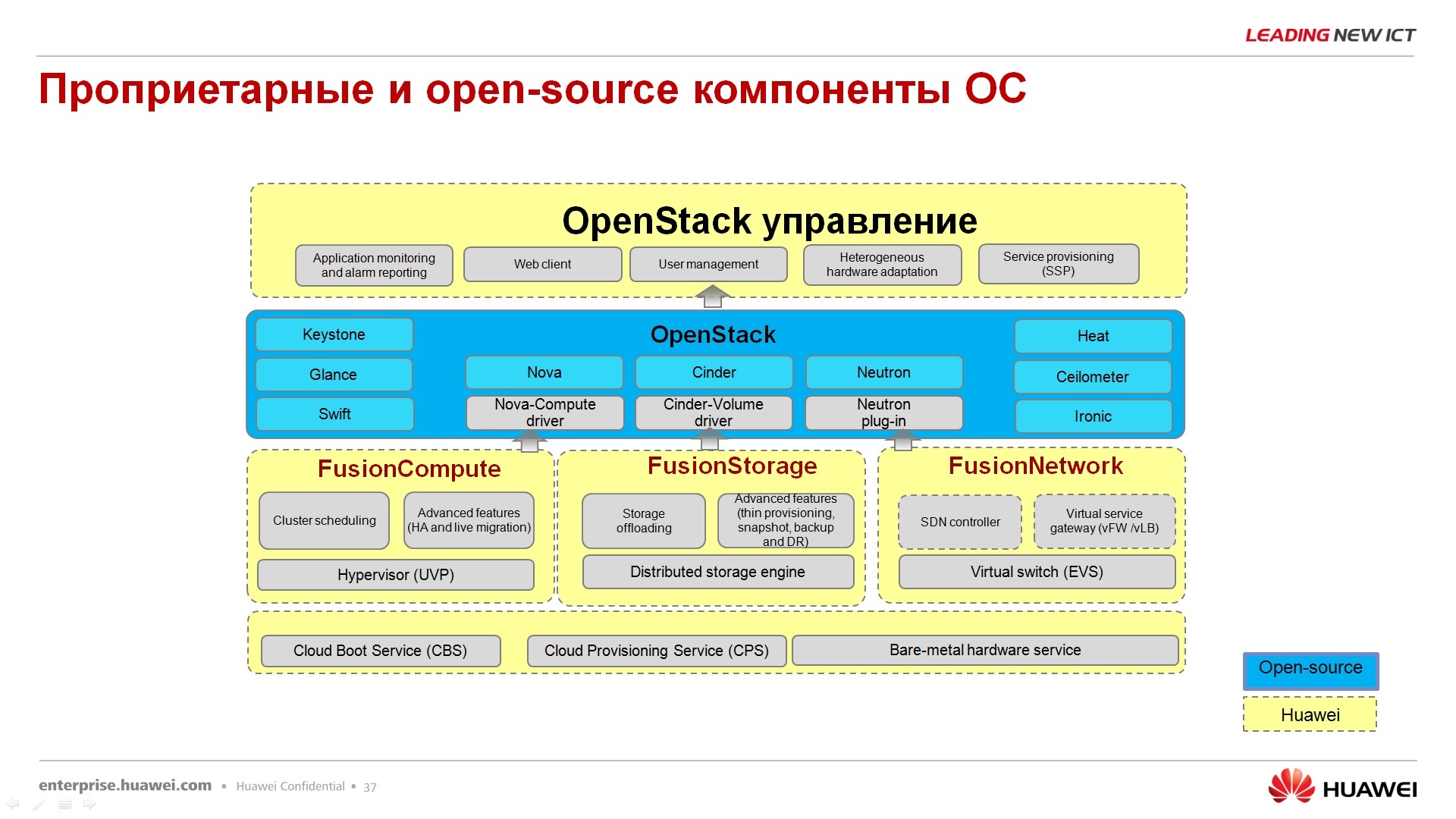
- , HUAWEI OpenStack. , . FusionStorage FusionSphere, , , .
Fusion Compute – , , . Virtual Resource Manager VRM , VmWare- V-center. VRM , ( VPS ) . , , FusionStorage.
– FusionNetwork. , – , , SDN-, , .. . « ». , , OpenStack, , , , ManageOne, .. , , . , HUAWEI OpenStack. , , , , HUAWEI. OpenStack .
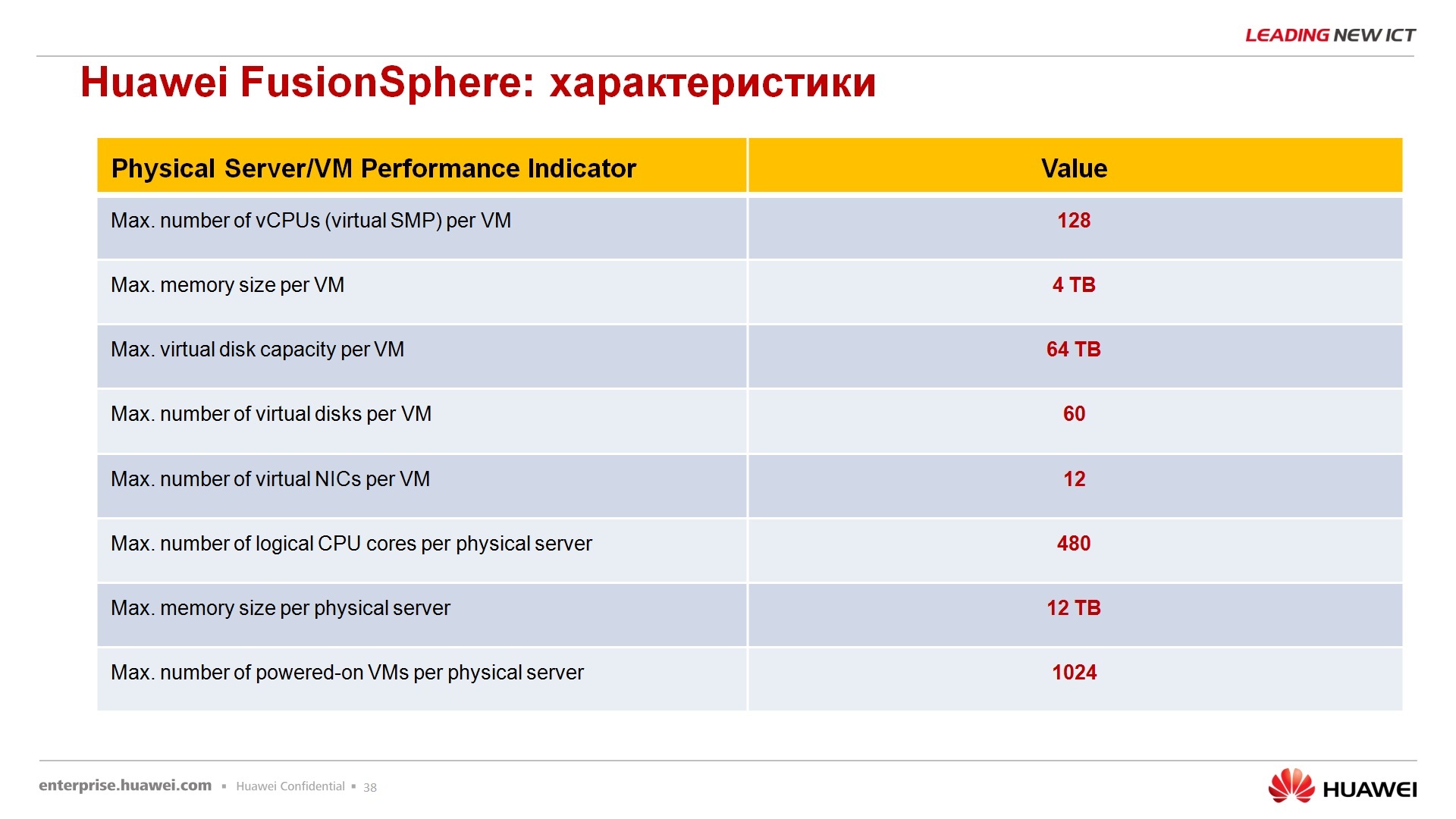
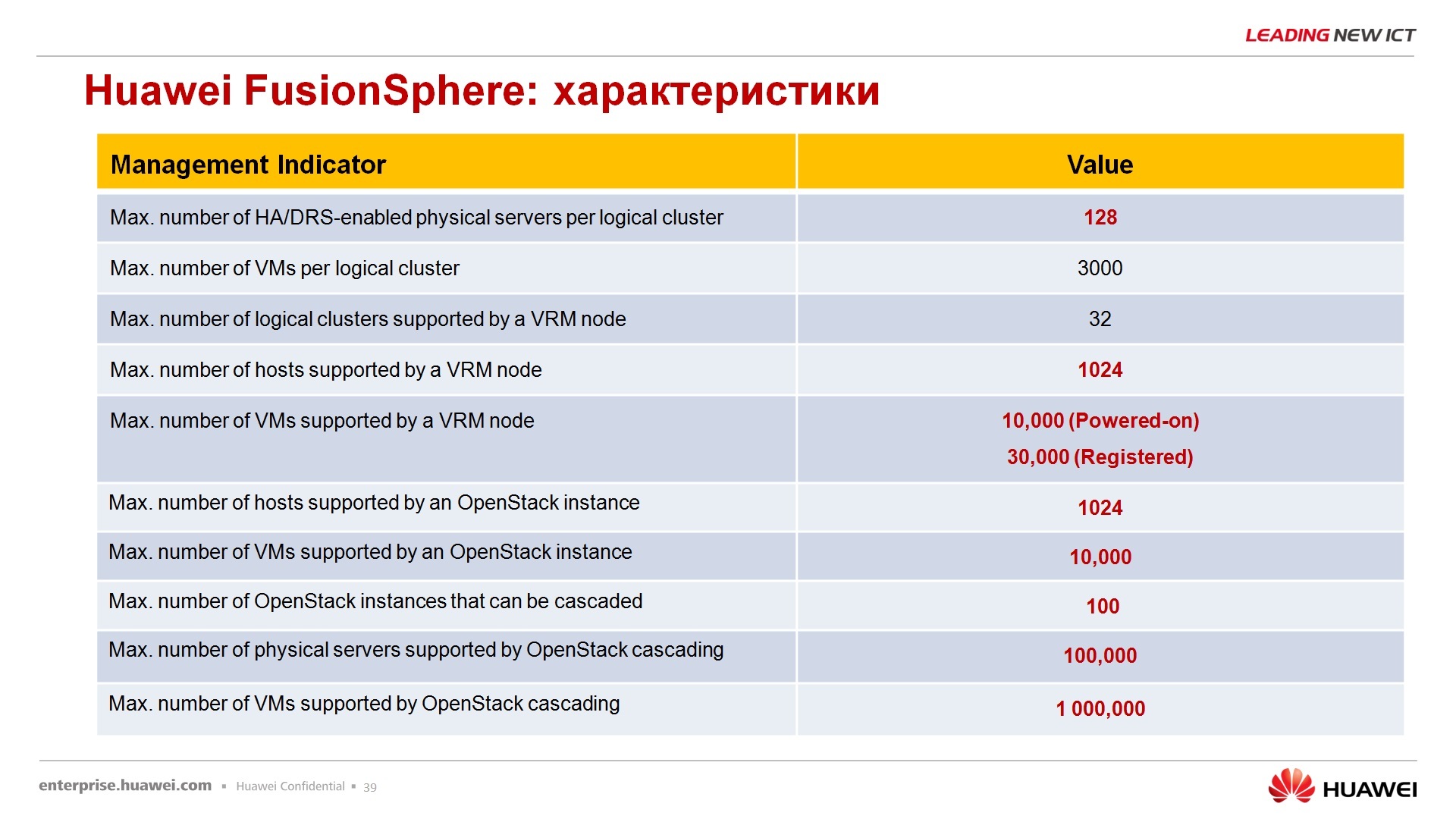
FusionSphere, – , , , – 128 , 4 , 64 , 60 , 12 , 480, , Fusion , 12 , 1000 . , - , - , , , , .. Hyper-V ESXi Vmware .
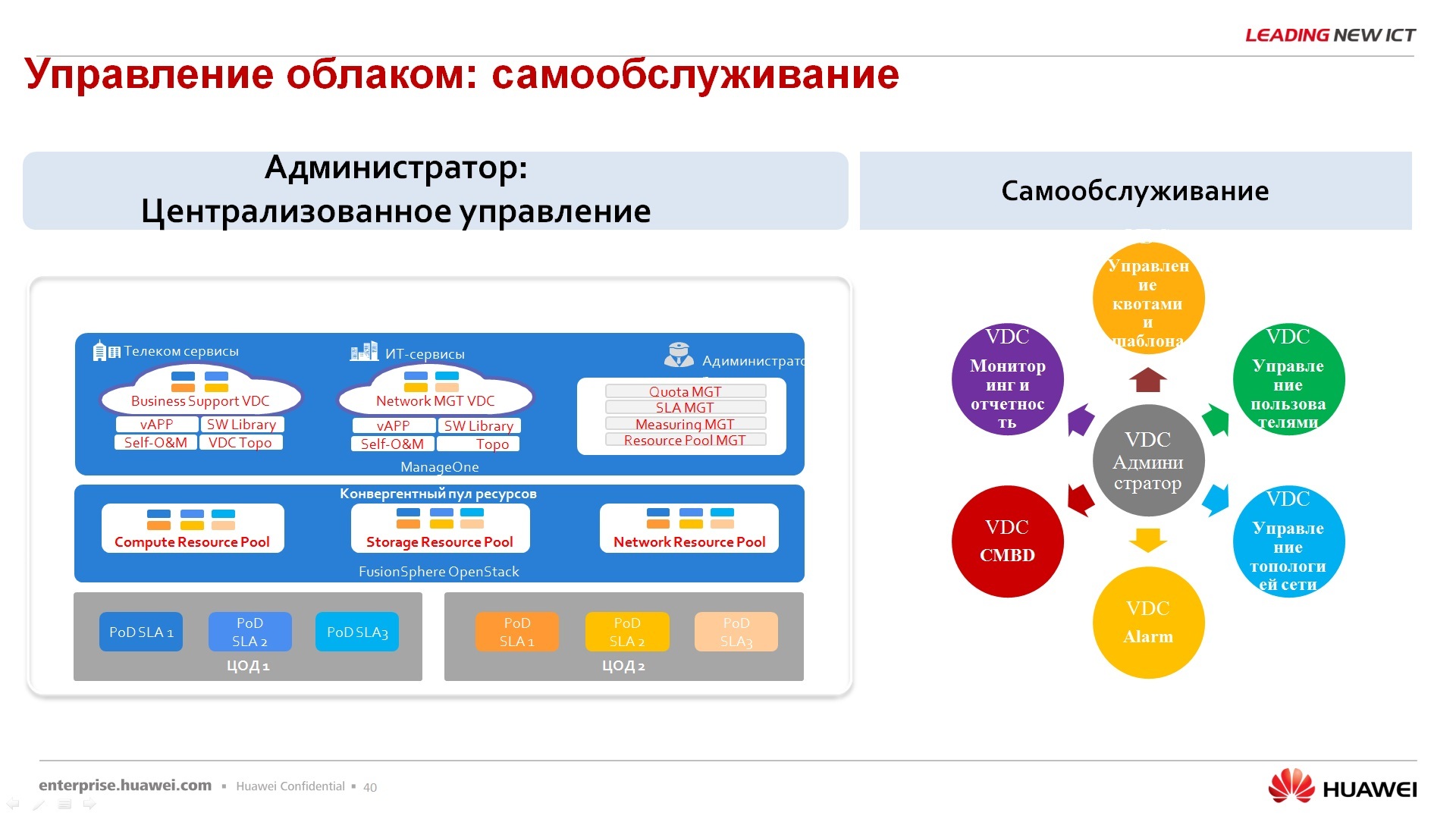
– , , – , ManageOne, , , .
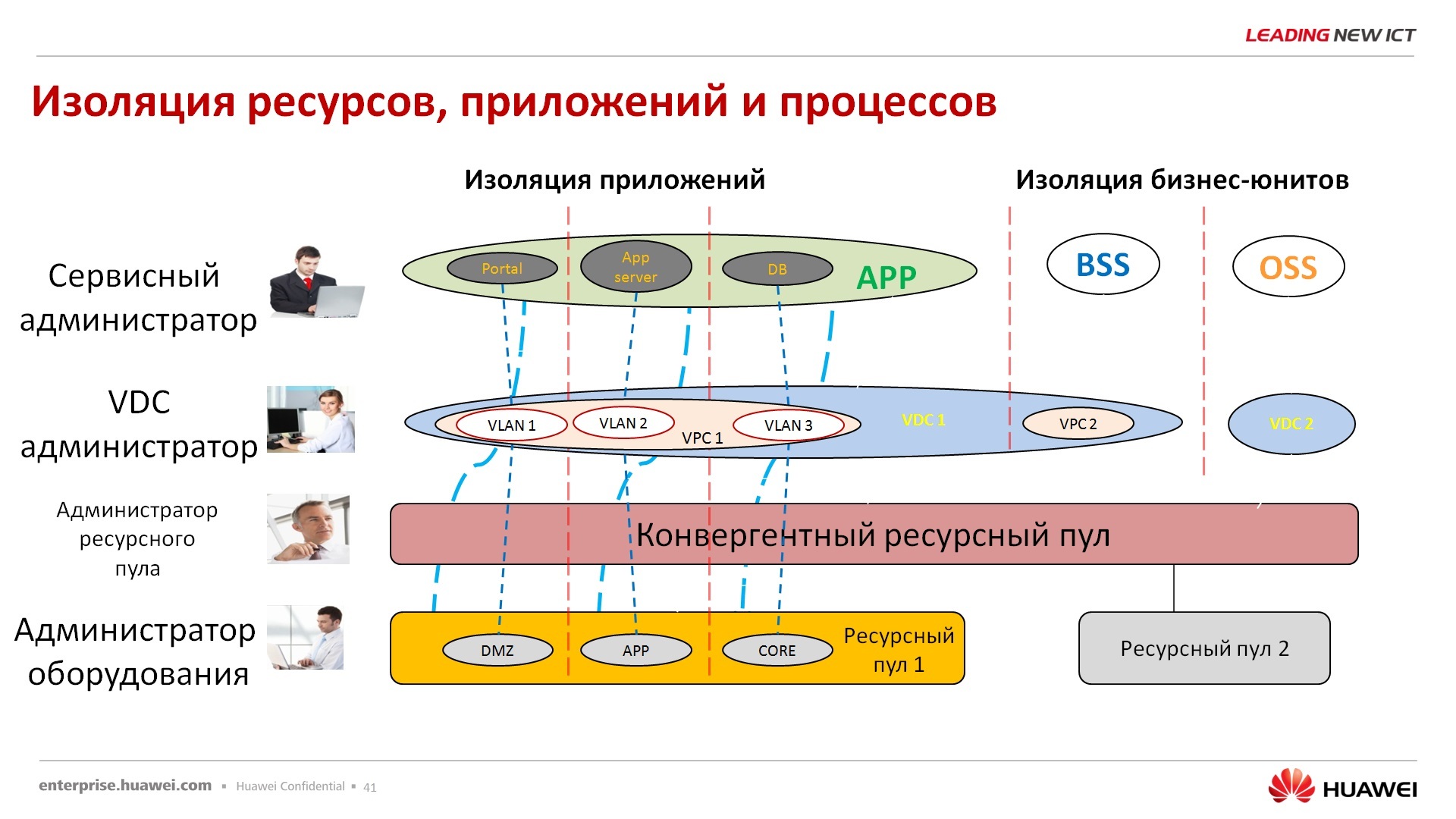
— , .. -, -, , , , , , , 4 . , . , , - - . .

– . , , full tolerance , - -, - -, , , -, - . , , , , , , , , , , , .
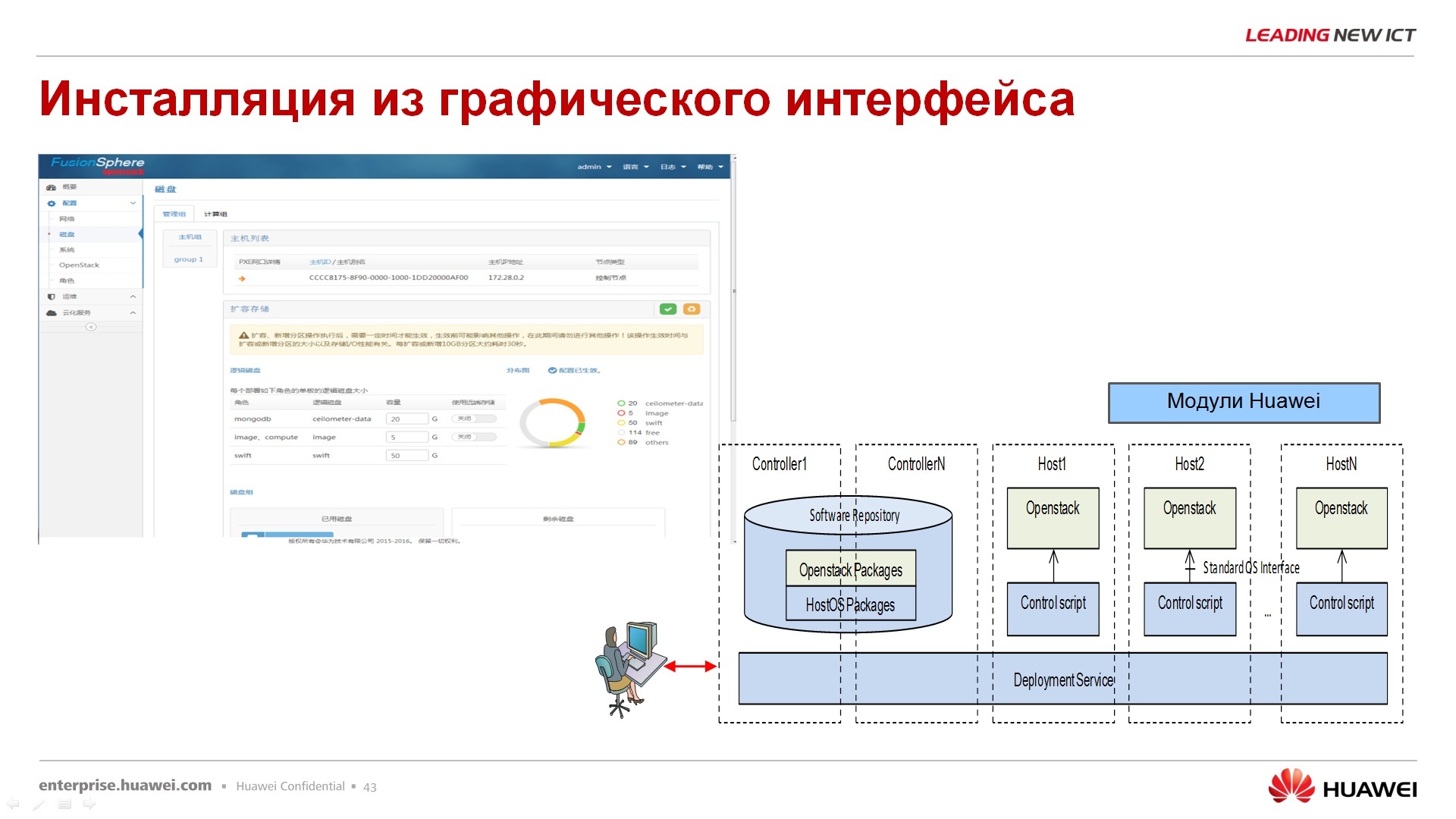
– , .. , , , .

– , Windows-, -, , , , -, , , . – , .. Fusion , - , , R&D .
. FusionSphere , , , , .
, , , , . , , , , , , , , .. , - , , , , , FusionSphere.
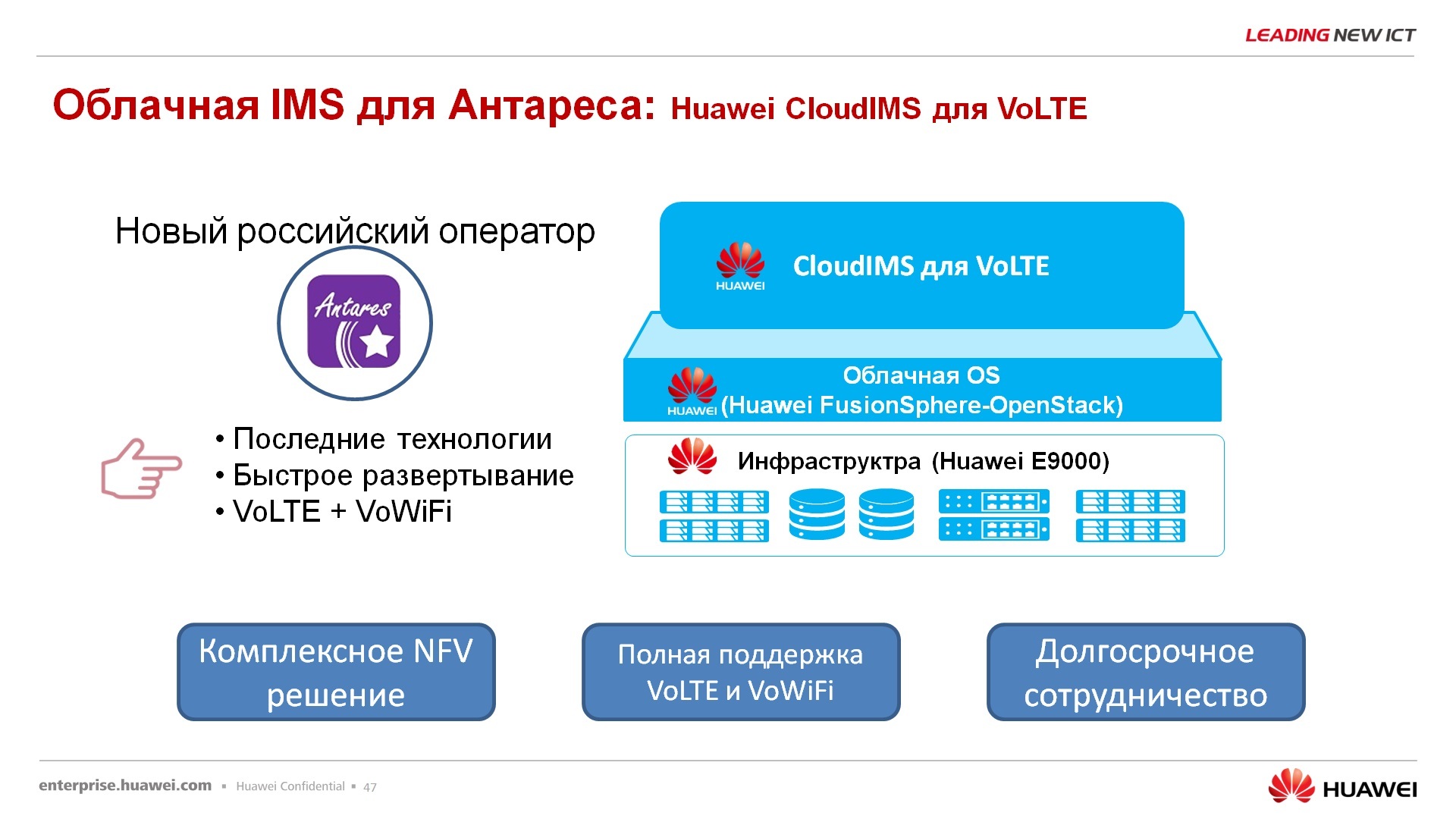
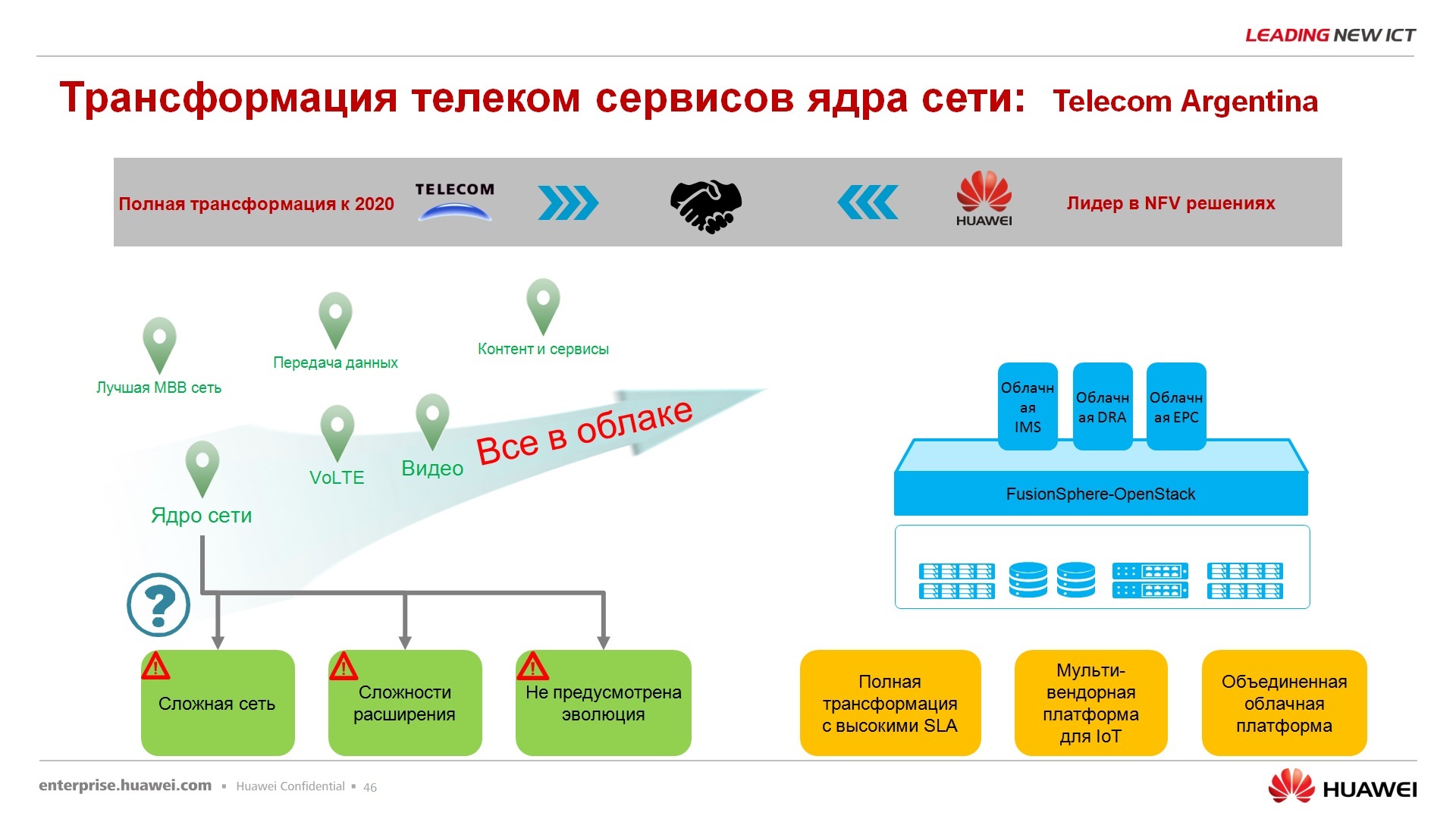
– , – voice over lte, voice over wi-fi, , lte, wi-fi , .. 2G, 3G , . , . , , FusionCube FusionSphere .
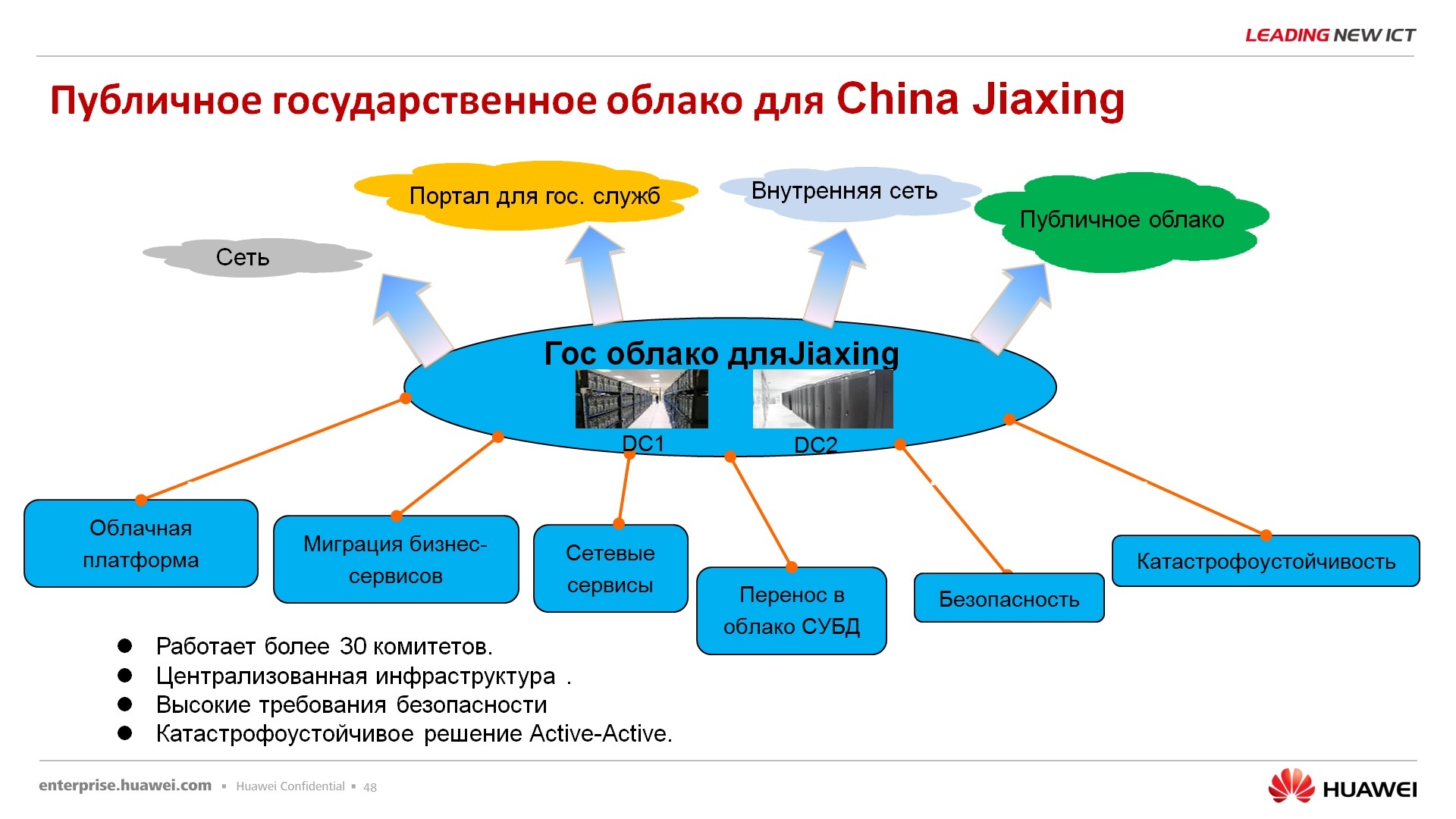
– . , , , , , OpenStack , HUAWEI, , .

– HUAWEI. , , , . , R&D VDI, , , .. , , , . , , R&D, , .

, , , – Deutsche Telecom, T Systems. , . , Amazon, Amazon – , , , , , , . , , , , - Deutsche Telecom , , , , , , , -, , 24/7, , Amazon, -, . HUAWEI 2016 CeBIT , .

, -, , , , , -, , HUAWEI, - , .. , , , , , . - FusionSphere.
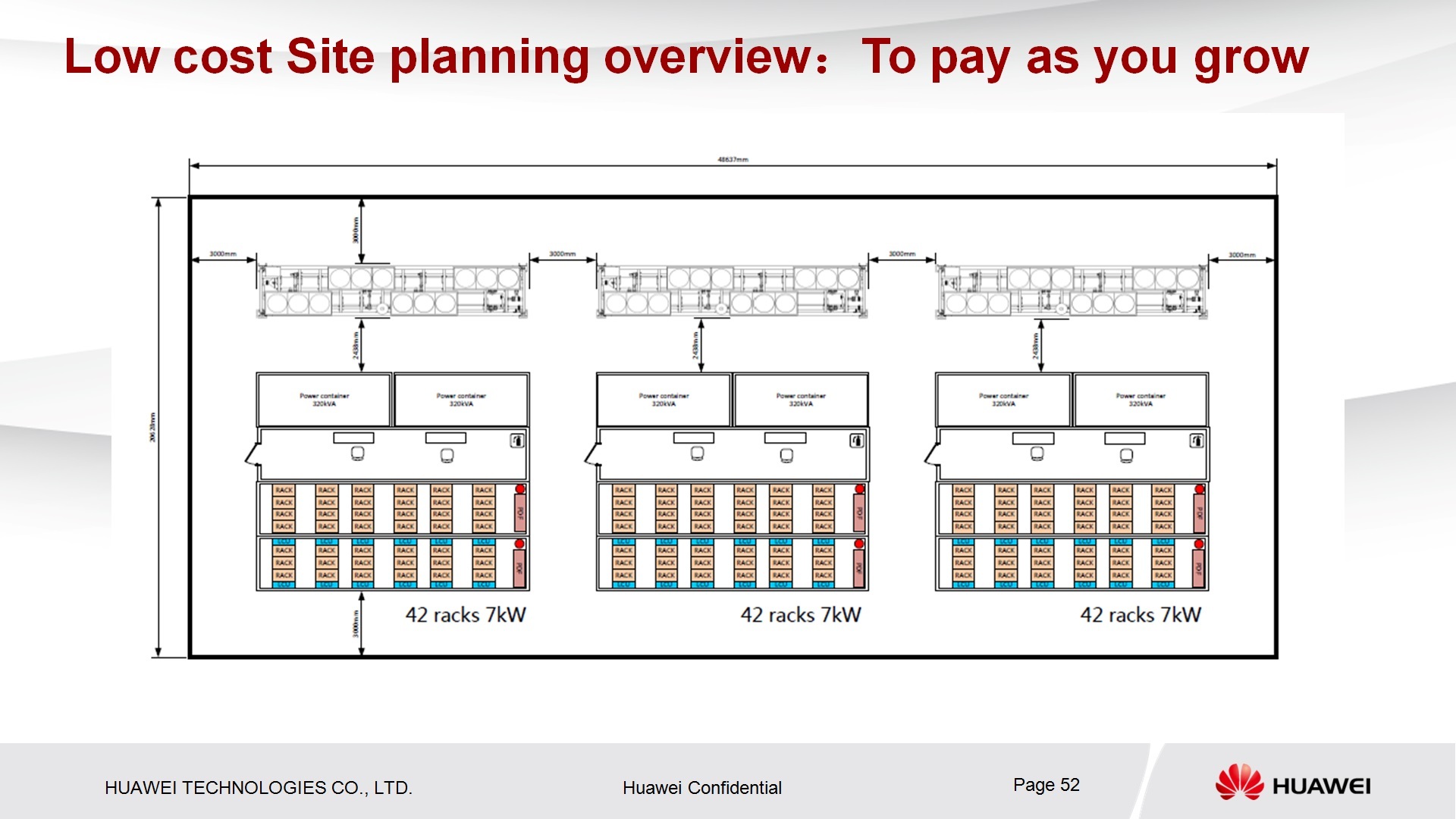
- , 4 , . , , , IT-. , , , .. .

, , , , , VDSand, in principle, right now to see what FusionSphere is, i.e. you don’t need to install it, you don’t need hardware somewhere, to look for resources, so Deutsche Telecom has deployed FusionSphere on its own hardware, intellectual resources. It is clear that this was a big project, and the support from HUAWEI was significant, however, this is already a ready resource on which you can practice. It is clear that it may not be possible to launch production in line with our legislation right away, but at least technological issues can be resolved, this resource will help you.


Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/305430/
All Articles