Organization of access to the Moscow metro WI-FI network from a security point of view
Introduction
This study analyzed the operation of the Moscow Metro's wireless network from the point of view of a regular user. As part of the test, an Android phone was used. Cases where the phone has never been authorized in the network are considered in a limited format.
Connection process
When connected to a WI-FI network, the following happens:
The device is initially associated with a WI-FI point. The device then establishes a TCP connection with the Google server.

Figure 1: Establishing a TCP Connection
')
Next, the Android phone checks for the need for network authorization by sending a GET request to the Google server. If the answer comes - authorization is not required; if it does not come - authorization is required, if there is a redirect to the authorization web page, the phone displays it.

Figure 2: Check for authorization required
The gateway, in turn, responds to any http request, replacing the responses of the requested server with a redirect to the authorization page.


Figure 3: redirect to the login page
Next, we press the button "enter the Internet." Here is the package itself, it is clear that it goes to the address from the private segment:

Figure 4: a packet with a request for authorization wi-fi.ru
And the query itself looks like this:
GET / HTTP/1.1 Host: wi-fi.ru Connection: keep-alive Cache-Control: max-age=0 Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,*/*;q=0.8 Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1 User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Linux; Android 5.1.1; HUAWEI MT7-L09 Build/HuaweiMT7-L09) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/47.0.2526.83 Mobile Safari/537.36 Referer: https://login.wi-fi.ru/am/UI/Login?org=mac&service=coa&client_mac=66-a0-f6-dd-d2-9e&ForceAuth=true Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, sdch Accept-Language: ru-RU,ru;q=0.8,en-US;q=0.6,en;q=0.4 Cookie: adfoxUserID=19:154848341; _ym_uid=1449217853212630314; _ym_isad=1; device_type=mobile; surf_prev_url=undefined; surf_curr_url=http://wi-fi.ru/; crtg_rta=; _mtp=0:ijk1njsr:69XJtN~ZNVIaYHb4OT3NHAOjPvLS50k4; _ga=GA1.2.1994719851.1449217854; amlbcookie=01; t=AQIC5wM2LY4SfcxCV1htnKzHF3mtmXJCDcvGniOTgqxvUMc.*AAJTSQACMDIAAlNLABQtNTkwNDE0MjY2MjYxNzMzMzgwOAACUzEAAjAx* If-None-Match: W/"74f5335bcd0524bfcd031469fc9c52e5" Analysis
It can be seen that, as a parameter, the MAC address of our device is also transmitted. This suggests that the poppy address is an identifier, and it is for him that the network understands whether we have paid for the Internet or not. It should be noted that the addresses login.wi-fi.ru and wi-fi.ru are available, including from the public Internet. This allows us to check any MAC address for its status. It looks like this:
MAC address, which was not in the subway:

Figure 5: MAC address that has never been in the subway
MAC address that is not paid for internet:

Figure 6: MAC did not pay for internet
The MAC address that paid for the Internet gets to the error page (since we are not inside the network), but then successfully redirected to wi-fi.ru:
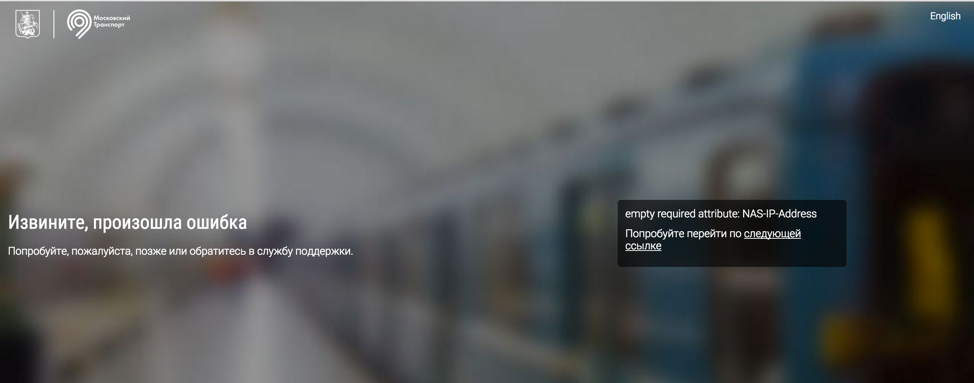
Figure 7: Connection Error
Figure 8: successful connection
It turned out that during authorization the server sends to the page the type of the connected MAC address:

Figure 9: Groups to which our MAC belongs
It is also evident that if we have mosmetro_premium registered in our group, then we are happy owner of paid internet.
Test
To automate the search for various types of MAC addresses, a script was written in Python: https://bitbucket.org/hollow1/metro
With his help, a couple of "paid" addresses were found:
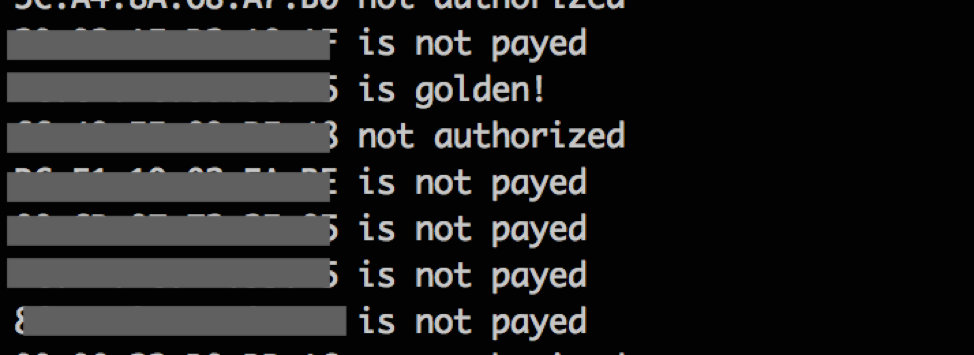
Figure 10: "paid" addresses
And for experimental purposes directly, the MAC of the test device was replaced by the “paid” one:
sudo ifconfig en0 ether xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx And everything started successfully, without registration and SMS.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/304222/
All Articles