Flash flash strikes: new Hitachi Accelerated Flash modules
Over the past few years, flash technologies have become widespread in data centers. However, the high cost, limited reliability and sub-optimal performance when performing write operations hinder their implementation. IT departments have to find a compromise between performance and capacity in order to achieve cost targets that are acceptable within a limited budget. Another important issue for the implementation of solutions based on flash technology is the choice between storage platforms, which are based solely on flash drives, and hybrid architecture.

As a global leader in flash technology development (more than 350 patents), Hitachi Data Systems introduces Hitachi Accelerated Flash (HAF) enterprise-class flash modules for the most demanding in terms of workload production. The new HAF features integrated into the Hitachi Storage Virtualization Operating System (SVOS) unified operating system provide higher performance, capacity and lower cost per bit compared to traditional solid state drives (SSD) present on the market today.
Customers were able to achieve a high return on investment in flash-based solutions while reducing operating costs, and the Hitachi Accelerated Flash storage module is the first optimized flash device to provide the level of performance and reliability that is required for mission-critical applications. These include, for example, OLTP databases, ERP systems, financial systems, indexing systems, and working with metadata. An advanced operating system for enterprise platforms has significantly increased the speed of the I / O stack to speed up access to flash drive devices.
')
The second generation of Flash Module Drive (FMD) DC2, drives, which are an essential part of Hitachi Accelerated Flash solutions, allows you to achieve even greater performance indicators, speed up the work of the company's services, and improve operational efficiency. The advanced FMD DC2 drive controller technology improves the performance of flash memory with MLC (Multi-level cell) technology to a level that exceeds the performance of more expensive SLC (Single-level cell) memory.
The patented design of the Hitachi FMD DC2 drive uses a high-speed architecture with parallel processing, allowing, in comparison with standard solid-state drives (SSD), to perform 5 times more I / O operations per second when writing and 3 times - when reading. Another innovative innovation implemented on second-generation FMD DC2 drives is real-time data compression technology, which improves the efficiency of disk space utilization by up to 80%.

Structurally, FMD DC2 drives are adapted for installation in a disk shelf that supports placement in a standard rack and provides high data storage density - more than 154 TB of effective capacity in a disk shelf with a height of 2U. They can be used in any disk array of the Hitachi Virtual Storage Platform G family, starting with the middle class models - VSP G200 / 400/600/800 and ending with the flagship Hitachi Hi-End storage system - VSP G1000. For each of these platforms, you can create both a fully built on flash memory, and a hybrid solution. With the support of more processing threads, HAF significantly accelerates I / O and data processing. In addition, the response time of the disk subsystem is significantly reduced.

Business Benefits
- Unique performance;
- The minimum cost of a storage unit;
- Highest capacity;
- Improved reliability.
A new expansion for storage systems based on solid-state drives is offered in the form of disk shelves with a height of 2U connected to controllers using the standard SAS protocol, which can hold up to 12 large-capacity drives based on flash memory modules (FMD). The Hitachi Accelerated Flash solution is much more profitable compared to a 1.6 TB small form factor enterprise-class SSD. It provides the following benefits:
1. 3 times more performance per device when performing random read I / O operations;
2. 5 times more performance per device when performing random I / O write operations;
3. reducing the cost of a storage unit of information up to 70%;
4. 60-fold increase in formatting speed;
5. decrease peak response time to 60%;
6. Excellent data integrity.
Main technical characteristics of FMD modules
FMD combines flash memory chips and a dedicated Hitachi controller, used to control operations on chips and implement advanced functionality that provides intelligent storage and management of information on a flash disk.
Flash Module Drive (FMD) DC2 second generation has the following components:
- Controller based on 4-core processor ASIC;
- 20nm MLC NAND flash-drive;
- DDR3 8 GB;
- SAS 12 Gbit / s interface;
- Available to order in versions with a capacity of 1.6, 3.2, 6.4 TB.

Summary table of FMD types and their main characteristics.

FMD controller
The built-in multi-core controller of the Hitachi flash drive provides many unique features designed specifically for high-loaded enterprise-class systems with increased requirements for reliable information storage.
It includes a specially designed ASIC, consisting of a quad-core processor with more than 60 million transistors (which is two times more than the previous generation), two co-processors (for calculating compression and parity) and direct memory access (DMA). The new ASIC for FMD DC2 has eight times more channels and 16 times more NAND flash chips than regular 2.5-inch solid-state drives.

Using data from more than two billion system-hours of work in the most demanding corporate environments for production analysis, Hitachi engineers improved the algorithms of the new ASIC, resulting in an increase in its efficiency, functionality and speed, which provides unprecedented data processing capabilities for the FMD DC2 module, avoiding many pitfalls and bottlenecks faced by other manufacturers.
Key features of the new ASIC:
1. 4 x nuclear, 1GHz, 32-bit processor.
2. 8 x PCIe 2.0 with a parallel I / O control unit on a chip.
3. 32 x channel to flash memory with patented on-chip control unit.
4. Built-in DDR-3 interface.
5. Support 128 NAND chips.

The main strategy of efficiency of the new flash controller ASIC from Hitachi can be briefly called “high-intelligence parallelism”. A large number of channels in combination with new control algorithms help distribute data streams for parallel execution of several tasks, allocating only a certain part of data to a separate channel for processing by different services without changing the speed of movement in other streams.
Main functional features
Inline compression
One of the most important innovations implemented in second-generation FMD DC2 drives is real-time data compression technology. The real-time data compression engine (Inline Compression), which uses the VLSI (very large-scale integration) architecture, allows lossless data compression based on the LZ77 algorithm. It should be noted that data compression operations are carried out at the level of the FMD DC2 processor integrated into the drive. This allows you to increase the speed of compression operations up to 10 times compared with traditional software implementations offered by other companies on the market.
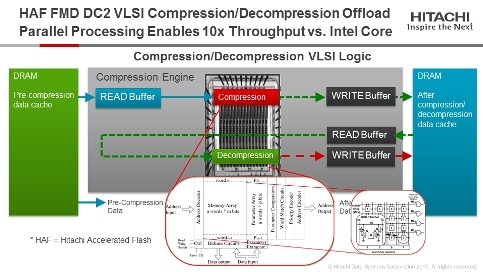
FMD DC2 ISIC Inline Compression Offload Engine

FMD DC2 ASIC Inline - Lossless Compression Operation
Reducing the load on the ASIC flash controller for data compression provides the following benefits:
1. Resources are freed up to perform key storage operations, such as I / O operations, data integrity protection, snapshots, various types of replication;
2. Provides better system efficiency and scalability in terms of recalculation per unit of energy expended;
3. Provides consistently low response time even when processing a large I / O unit.
Workload Priority Access
The technology of granting access priority to an application (Workload Priority Access), built into the controller of the FMD drive, together with the SVOS operating system, ensures that the critical resource is guaranteed to be provided with necessary resources in the form of dedicated flash chips.

Smarter Garbage Collection
The garbage collection function allows you to reduce I / O latency from background tasks and improves response time due to multi-channel and more NAND flash chips, if necessary, reallocating the queue to other NAND targets.

VMware vSphere End-to-End Quality of Service
VMware vSphere Virtual Volumes VVOL support by the Virtual Storage Platform arrays, along with the use of the Workload Priority Access function, allows you to create unique VMware virtual environments with application-specific focus, while providing the necessary level of service from the virtual machine to a specific flash resource

Error-correcting Code
The improved data integrity feature fixes up to 59 single-bit errors in every 2 KB of data, providing higher integrity rates than enterprise-class disk drives — SAS 10K, SAS 15K. Each memory block has its own indicators of wear, i.e. durability. To accommodate these differences in performance, the flash controller performs a memory block analysis. Through continuous scanning and diagnostics of each unit, it is possible to effectively determine the optimal time for its decommissioning, which guarantees that the requirements for ensuring the integrity of corporate data are met. The adaptive data update function dynamically replaces pages with new ones in accordance with the applied error correction algorithm. In addition, this feature reduces the overhead associated with performing background tasks, ensures stable performance and increases the durability of flash memory cells.

Figure 20. FMD DC2 Error Correction
Block Write Avoidance
The null block warning function speeds up write operations and improves performance. Thanks to this algorithm, data streams consisting only of zeros or ones are compressed in real time by up to 94%. In this case, embedded coding mechanisms process data blocks of 128 KB in size. The incoming data is replaced by the pointer and the corresponding checksum. This function, without increasing response time, allows efficient use of flash memory capacity, freeing it up both for highlighting new pages, which improves the average performance of the recording process, and for running background tasks such as garbage collection and cell wear leveling. flash memory. It also reduces the time of commissioning of the array, since the formatting of flash memory is performed 60 times faster, and increases the service life by eliminating redundant data rewriting cycles.
Conclusion
Hitachi Data Systems' future development plan for flash memory technology encompasses a variety of applications - servers, storage systems, and software and hardware systems designed to speed up computing, caching systems, and high-performance storage media. Compared with alternative or narrow-target products based on flash memory technology, new solutions should provide a higher return on investment and lower operating costs.

As a global leader in flash technology development (more than 350 patents), Hitachi Data Systems introduces Hitachi Accelerated Flash (HAF) enterprise-class flash modules for the most demanding in terms of workload production. The new HAF features integrated into the Hitachi Storage Virtualization Operating System (SVOS) unified operating system provide higher performance, capacity and lower cost per bit compared to traditional solid state drives (SSD) present on the market today.
Customers were able to achieve a high return on investment in flash-based solutions while reducing operating costs, and the Hitachi Accelerated Flash storage module is the first optimized flash device to provide the level of performance and reliability that is required for mission-critical applications. These include, for example, OLTP databases, ERP systems, financial systems, indexing systems, and working with metadata. An advanced operating system for enterprise platforms has significantly increased the speed of the I / O stack to speed up access to flash drive devices.
')
The second generation of Flash Module Drive (FMD) DC2, drives, which are an essential part of Hitachi Accelerated Flash solutions, allows you to achieve even greater performance indicators, speed up the work of the company's services, and improve operational efficiency. The advanced FMD DC2 drive controller technology improves the performance of flash memory with MLC (Multi-level cell) technology to a level that exceeds the performance of more expensive SLC (Single-level cell) memory.
The patented design of the Hitachi FMD DC2 drive uses a high-speed architecture with parallel processing, allowing, in comparison with standard solid-state drives (SSD), to perform 5 times more I / O operations per second when writing and 3 times - when reading. Another innovative innovation implemented on second-generation FMD DC2 drives is real-time data compression technology, which improves the efficiency of disk space utilization by up to 80%.

Structurally, FMD DC2 drives are adapted for installation in a disk shelf that supports placement in a standard rack and provides high data storage density - more than 154 TB of effective capacity in a disk shelf with a height of 2U. They can be used in any disk array of the Hitachi Virtual Storage Platform G family, starting with the middle class models - VSP G200 / 400/600/800 and ending with the flagship Hitachi Hi-End storage system - VSP G1000. For each of these platforms, you can create both a fully built on flash memory, and a hybrid solution. With the support of more processing threads, HAF significantly accelerates I / O and data processing. In addition, the response time of the disk subsystem is significantly reduced.

Business Benefits
- Unique performance;
- The minimum cost of a storage unit;
- Highest capacity;
- Improved reliability.
A new expansion for storage systems based on solid-state drives is offered in the form of disk shelves with a height of 2U connected to controllers using the standard SAS protocol, which can hold up to 12 large-capacity drives based on flash memory modules (FMD). The Hitachi Accelerated Flash solution is much more profitable compared to a 1.6 TB small form factor enterprise-class SSD. It provides the following benefits:
1. 3 times more performance per device when performing random read I / O operations;
2. 5 times more performance per device when performing random I / O write operations;
3. reducing the cost of a storage unit of information up to 70%;
4. 60-fold increase in formatting speed;
5. decrease peak response time to 60%;
6. Excellent data integrity.
Main technical characteristics of FMD modules
FMD combines flash memory chips and a dedicated Hitachi controller, used to control operations on chips and implement advanced functionality that provides intelligent storage and management of information on a flash disk.
Flash Module Drive (FMD) DC2 second generation has the following components:
- Controller based on 4-core processor ASIC;
- 20nm MLC NAND flash-drive;
- DDR3 8 GB;
- SAS 12 Gbit / s interface;
- Available to order in versions with a capacity of 1.6, 3.2, 6.4 TB.

Summary table of FMD types and their main characteristics.

FMD controller
The built-in multi-core controller of the Hitachi flash drive provides many unique features designed specifically for high-loaded enterprise-class systems with increased requirements for reliable information storage.
It includes a specially designed ASIC, consisting of a quad-core processor with more than 60 million transistors (which is two times more than the previous generation), two co-processors (for calculating compression and parity) and direct memory access (DMA). The new ASIC for FMD DC2 has eight times more channels and 16 times more NAND flash chips than regular 2.5-inch solid-state drives.

Using data from more than two billion system-hours of work in the most demanding corporate environments for production analysis, Hitachi engineers improved the algorithms of the new ASIC, resulting in an increase in its efficiency, functionality and speed, which provides unprecedented data processing capabilities for the FMD DC2 module, avoiding many pitfalls and bottlenecks faced by other manufacturers.
Key features of the new ASIC:
1. 4 x nuclear, 1GHz, 32-bit processor.
2. 8 x PCIe 2.0 with a parallel I / O control unit on a chip.
3. 32 x channel to flash memory with patented on-chip control unit.
4. Built-in DDR-3 interface.
5. Support 128 NAND chips.

The main strategy of efficiency of the new flash controller ASIC from Hitachi can be briefly called “high-intelligence parallelism”. A large number of channels in combination with new control algorithms help distribute data streams for parallel execution of several tasks, allocating only a certain part of data to a separate channel for processing by different services without changing the speed of movement in other streams.
Main functional features
Inline compression
One of the most important innovations implemented in second-generation FMD DC2 drives is real-time data compression technology. The real-time data compression engine (Inline Compression), which uses the VLSI (very large-scale integration) architecture, allows lossless data compression based on the LZ77 algorithm. It should be noted that data compression operations are carried out at the level of the FMD DC2 processor integrated into the drive. This allows you to increase the speed of compression operations up to 10 times compared with traditional software implementations offered by other companies on the market.

FMD DC2 ISIC Inline Compression Offload Engine

FMD DC2 ASIC Inline - Lossless Compression Operation
Reducing the load on the ASIC flash controller for data compression provides the following benefits:
1. Resources are freed up to perform key storage operations, such as I / O operations, data integrity protection, snapshots, various types of replication;
2. Provides better system efficiency and scalability in terms of recalculation per unit of energy expended;
3. Provides consistently low response time even when processing a large I / O unit.
Workload Priority Access
The technology of granting access priority to an application (Workload Priority Access), built into the controller of the FMD drive, together with the SVOS operating system, ensures that the critical resource is guaranteed to be provided with necessary resources in the form of dedicated flash chips.

Smarter Garbage Collection
The garbage collection function allows you to reduce I / O latency from background tasks and improves response time due to multi-channel and more NAND flash chips, if necessary, reallocating the queue to other NAND targets.

VMware vSphere End-to-End Quality of Service
VMware vSphere Virtual Volumes VVOL support by the Virtual Storage Platform arrays, along with the use of the Workload Priority Access function, allows you to create unique VMware virtual environments with application-specific focus, while providing the necessary level of service from the virtual machine to a specific flash resource

Error-correcting Code
The improved data integrity feature fixes up to 59 single-bit errors in every 2 KB of data, providing higher integrity rates than enterprise-class disk drives — SAS 10K, SAS 15K. Each memory block has its own indicators of wear, i.e. durability. To accommodate these differences in performance, the flash controller performs a memory block analysis. Through continuous scanning and diagnostics of each unit, it is possible to effectively determine the optimal time for its decommissioning, which guarantees that the requirements for ensuring the integrity of corporate data are met. The adaptive data update function dynamically replaces pages with new ones in accordance with the applied error correction algorithm. In addition, this feature reduces the overhead associated with performing background tasks, ensures stable performance and increases the durability of flash memory cells.

Figure 20. FMD DC2 Error Correction
Block Write Avoidance
The null block warning function speeds up write operations and improves performance. Thanks to this algorithm, data streams consisting only of zeros or ones are compressed in real time by up to 94%. In this case, embedded coding mechanisms process data blocks of 128 KB in size. The incoming data is replaced by the pointer and the corresponding checksum. This function, without increasing response time, allows efficient use of flash memory capacity, freeing it up both for highlighting new pages, which improves the average performance of the recording process, and for running background tasks such as garbage collection and cell wear leveling. flash memory. It also reduces the time of commissioning of the array, since the formatting of flash memory is performed 60 times faster, and increases the service life by eliminating redundant data rewriting cycles.
Conclusion
Hitachi Data Systems' future development plan for flash memory technology encompasses a variety of applications - servers, storage systems, and software and hardware systems designed to speed up computing, caching systems, and high-performance storage media. Compared with alternative or narrow-target products based on flash memory technology, new solutions should provide a higher return on investment and lower operating costs.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/303934/
All Articles