Now your HTTPS will be monitored, and you must install the certificate for MitM yourself.

While not Russia. But already Kazakhstan. As ValdikSS wrote in his post, Kazakhstan introduces its CA to listen to all TLS traffic :
The state provider Kazakhtelecom, in connection with the innovations of the Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan "On Communications", intends to listen to all encrypted TLS traffic starting January 1, 2016, replacing the site certificates with a national security certificate issued by the Committee for Communications, Information and Information of the Ministry of Investment and Development of the Republic of Kazakhstan .
What new has happened since then? Beeline and Telecom.kz (the main monopolist provider) rolled out updated instructions for installing the state certificate, which will allow to carry out a man-in-the-middle attack with a certificate substitution. Link to the state certificate .
Briefly about certificates
As you know, the modern Internet is largely based on strong cryptography. Many encryption protocols and areas of their application. A few decades ago, strong cryptography was the exclusive prerogative of the special services and the military. They can store information encrypted securely, the rest can not. Until now, echoes of these times are heard in strange laws and bylaws, which de facto no longer work. What has changed?
')
Open-source came, which gave into the hands of anyone who wanted algorithms, allowing to preserve the privacy of correspondence and to be sure that the data will not leak to any person on their way to their destination. While the sluggish state machine was wondering what to do with the new threat, suddenly strong encryption algorithms were hardware supported by each iron and made available to everyone. Moreover, every year, despite pressure from the authorities and intelligence agencies of all countries, security continued to increase. The HTTPS protocol has become the standard for any more or less significant connections. HSTS (HTTP Strict Transport Security) - a mechanism that activates the forced secure connection via the HTTPS protocol.
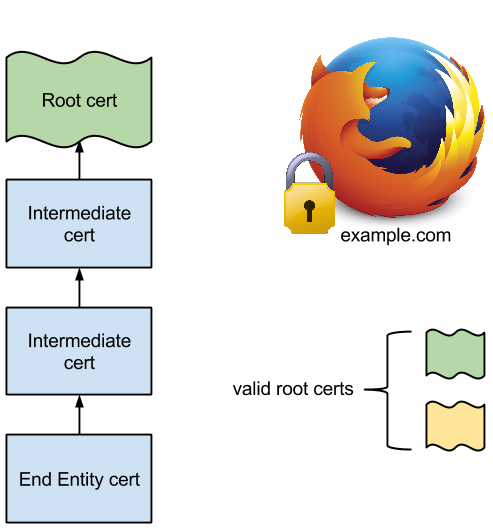
There was Certificate pinning (storing the list of allowed certificates for the domain or CA in the source code of the browser) and HTTP Public Key Pinning . These methods allow you to avoid the imperceptible replacement of the certificate by comparing with the reference in the secure storage of the browser. Due to the fact that browsers have become mostly open source software, it has become very difficult to influence the state level. Especially given that any country will not allow backdoors from the other side.

Security of certificates is based on certification centers and a hierarchical structure for checking its validity. A Certificate Authority (CA) is a center that everyone trusts as a trusted third party certifying the authenticity of encryption keys using electronic signature certificates. At the same time, the only asset of such an air trading center is its reputation. Since there are a lot of certifying centers, in the event that CA is noticed after draining certificates for MitM, it will be immediately added to the blacklists of all operating systems and browsers. Therefore, CAs behave very carefully. Moreover, frauds with certificate spoofing will be immediately noticed by browsers that automatically throw out the threat message and often do not allow the user to go any further if the end resource activated HSTS and Certificate pinning.
What does the state want?
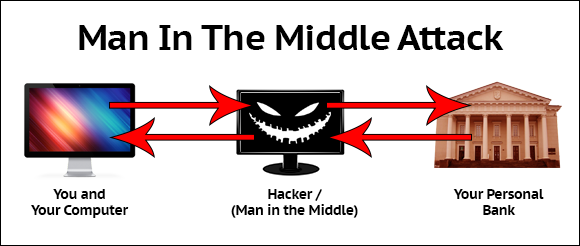
As usual, the state wants to control its citizens under any pretexts. The new law passed in Kazakhstan essentially obliges providers to carry out an attack man-in-the-middle. With this option, instead of the Gmail certificate issued by Google Inc., you will see the Gamma Technologies Certificate Authority , which will honestly repack your TLS-encrypted traffic, while listening to everything you need, looking at personal correspondence, collecting your logins and passwords from any services. Of course, solely for your safety. As already mentioned, browsers will not miss such chaos without notice and simply will not let you on the target resource in order to avoid data leakage. However, in this situation, the task is not to be imperceptible . You are faced with a fact: either you install the state certificate as trusted and allow MitM, or you lose all services using TLS encryption . Applause curtain. Especially touches the cynicism of filing the need to install these certificates:

The security certificate protects transactions on the Internet and is completely free. Just benefactors. As before, they lived without them.
Who will suffer?
In addition to the most blatant fact of state censorship and the possibility of viewing personal correspondence, there will be big problems with devices and software that do not allow adding a left certificate. They will turn into a pumpkin. But nobody cares. An equally important factor is the potential leakage of personal data, passwords to services that are likely to be centrally collected. Otherwise it makes no sense to arrange this circus with horses initially.
What to do with it?
Panic and run in circles. This is already very, very serious and is almost not solved by technical means. You can raise the VPN channel to a server from outside the country to avoid intercepting the certificate. However, the same OpenVPN with TLS encryption will turn into a pumpkin. Most likely, the next step will drop encrypted VPN connections. Moreover, if you need to get "clean access" to Gmail or Twitter, then there is no problem. However, if the service is located within the country with the substitution of a certificate , then nothing will help. It remains only to put up with wiretapping.
PS Everything is sad, gentlemen. I would like to hear at least suggestions on technical solutions to the problem.
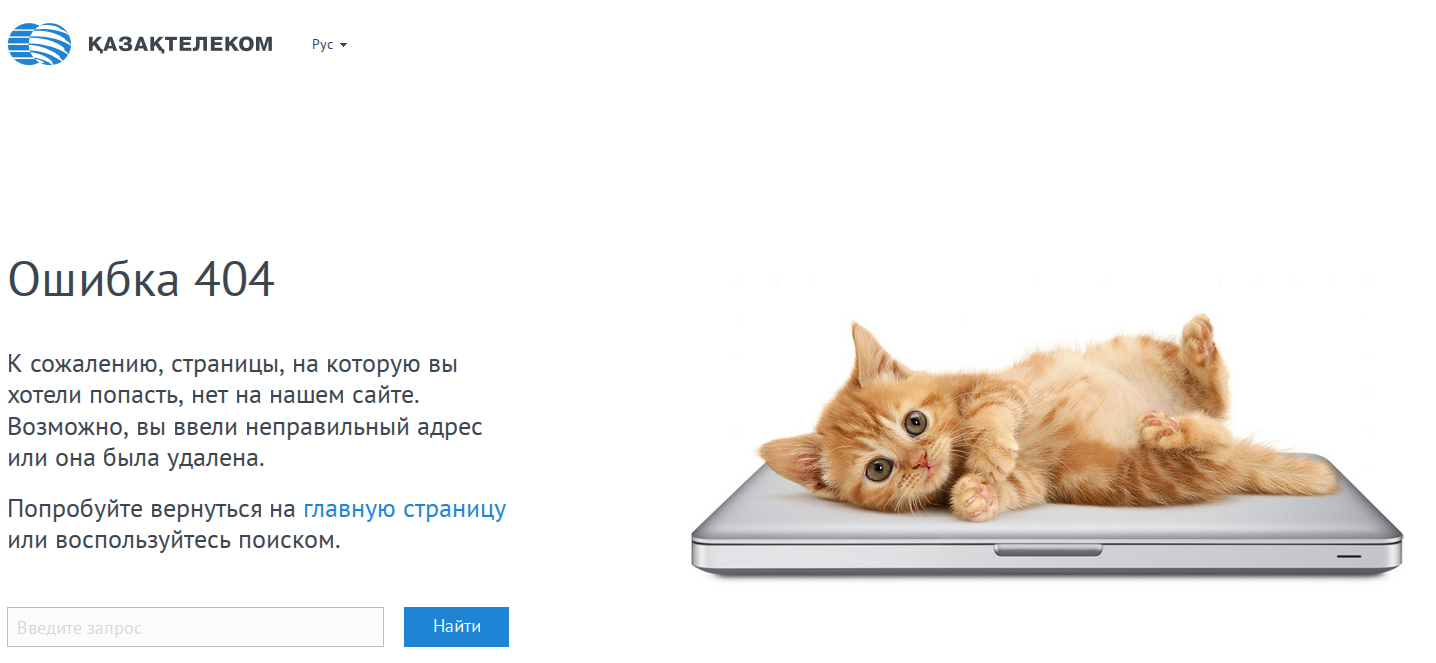
UPD After publishing Kazakhtelecom abruptly deleted the page and certificate
Now, instead of the page on the screen from the post, error 404 is given.
Beeline's page is still alive , but links are no longer links, and they have become simply underlined words.
UPD Links to certificate bug reports
Thanks ibmpc .
Report a problem in Mozilla:
bugzilla.mozilla.org/show_bug.cgi?id=1229827
mozilla.dev.security.policy:
groups.google.com/forum/# ! topic / mozilla.dev.security.policy / wnuKAhACo3E
Please add the certificate (root.gov.kz) to the trusted ones:
bugzilla.mozilla.org/show_bug.cgi?id=1232689
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/303736/
All Articles