Security Week 24: black market hijacked RDP, zyrodey in Flash, GMail refuses SSLv3 and RC4
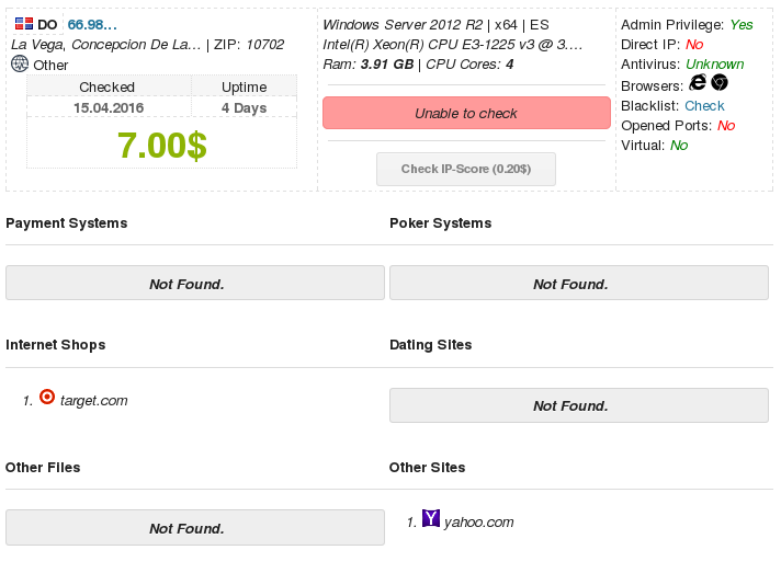
 One of the most resonant news of this week is devoted to the black market of remote access to servers. Experts of "Laboratory" investigated the service, where anyone can buy inexpensive information to access one of the more than 70 thousand servers worldwide via the RDP protocol. Hacked servers are fairly evenly distributed across the globe, about a third is in the countries where the choice is the maximum: Brazil, China, Russia, India and Spain.
One of the most resonant news of this week is devoted to the black market of remote access to servers. Experts of "Laboratory" investigated the service, where anyone can buy inexpensive information to access one of the more than 70 thousand servers worldwide via the RDP protocol. Hacked servers are fairly evenly distributed across the globe, about a third is in the countries where the choice is the maximum: Brazil, China, Russia, India and Spain.It will probably be interesting for unsuspecting owners of these servers to find out what attackers can do with them, but then I even find it difficult to choose where to start. In short - you can do everything. Further hacking of the victim's infrastructure - no problem. Spamming, DDoS attacks, criminal hosting, information theft, targeted attacks with effective tracing are also possible. Theft of credit card data, money from accounts, financial statements - yes, if the hacked server has access to such information. All this - at ridiculous prices: 7-8 dollars per account .
XDedic and similar services (it can be assumed that he is not one) are criminal ecommers and fintech, it unites criminals of different profiles, who are not very cool, uses modern technologies, provides high-quality service. The stolen data itself is provided by more than 400 sellers - here you have both the competition and the struggle to increase the number of hacks. The best time to remind you - you can be hacked, even if you think that your data is not needed by anyone. First, they are needed, and in any case you will not like the way they are used. Secondly, resources also cost money, and when the price of a question is three kopecks, everybody comes down to small business. They will steal money from an account, or credit card dumps, or at least customer contacts for sending spam, will attack another company through you, and if nothing happens at all, they will install a bitcoin generator and consume electricity.
')
It is difficult to fight such evolutions of cybercriminal, but this study allows you to get an idea of how to do it.
All releases of the series - here .
It is not excluded that many xDedic victims did not have any hacking, and the password to the RDP was obtained by a simple search. Potential soldiers of this underground army do not even have to master such primitive skills: an application for brute force attacks on the RDP is provided there. Another utility - essentially a Trojan - helps maintain the relevance of the server database and collect information about available resources. She also scans the system for the presence of interesting software for crime. Look for tools for mass mailing (for spam), applications for accessing gambling services (to steal money from there), financial software (similarly). Separately, there is a long list of software for payment terminals and cash registers: in general, it is also clear why.
How to deal with this is not very clear from the point of view of potential victims. The traditional approach, already outdated, but universally applied, is to try to close the threat with technology, that is, software. But in this case, it simply does not work - it is impossible to close the propensity of cybercriminals to unite for joint earnings with software. OK, I suspect that many xDedic victims did not follow simple RDP access protection guidelines. But it's not about RDP, if you close this hole, there are still a hundred others.
But getting information about such criminal activity, and not just in the format of a fascinating reader, but with ready-made indicators of hacking (the presence of an analyzer utility, connection to the characteristic C & C, etc.), the sooner the better, it will completely allow you to erase a couple of zeros from the recovery check after hacking. Welcome to the future of information security, where knowledge and ways of using it in practice work and are valued above all.
Zero-day vulnerability in Flash, waiting for a patch
News Adobe Advisory . Research "Laboratories".
Recently, there have been a lot of Flash vulnerabilities, including critical ones, including zero-day vulnerabilities - which are actively exploited in the absence of a patch. The difference in the CVE-2016-4171 vulnerability was that the Laboratories experts found a bug in one fell swoop and investigated the operations of a relatively young APT group known as Starcruft. The study provides several more technical details about vulnerability than usual. The exploit uses one of the metadata processing modules, where data is read without border control, which naturally can lead to a buffer overflow. Several consecutive data recording operations, and attackers are able to execute arbitrary code.
The hero of the occasion is framed
In addition, an interesting circuit for circumventing protective solutions was discovered in Starcruft’s arsenal. This is done using a bug (perhaps it would be correct to call this an undocumented feature) of the Windows DDE library, as a result of which the latter is used as an interlayer between the operations of executing an exploit and the launching of malicious code. Since Adobe Flash is a well-known source of problems, a defensive solution can track suspicious code execution operations on behalf of a process, but in this case, it can skip such a cunning move. It's time to say that the antivirus is not a cake, but no. A new vulnerability was discovered in April using an automated exploit detection system used in our products.
Be that as it may, there is no patch for vulnerability from Adobe, although it may appear right in the near future (promised on June 16).
Gmail stops supporting SSLv3 and RC4 protocols for IMAP / POP connections
News Google Announcement .
Google has consistently eliminated support for insecure data encryption protocols for its own services, primarily for GMail. Both protocols have long been recognized as unsafe and easily breakable, and although Google says that the vast majority of clients pick up mail using the TLS 1.2 protocol, some limited amount of mail software may stop working - from June 16, support will gradually be disabled for another month.

In general, users of ancient smartphones and antique computer software may have problems. Google's actions, like previous initiatives to abandon SSLv3 in browsers, can be called proactive: there has not yet been information about attacks for poorly protected connections (perhaps those who are listening do not advertise this much). Despite the fact that RC4 was declared unsafe back in 2001 (the first works were generally in 1995), they continue to investigate it, because, alas, it is still used. One of the latest research (PDF) shows the possibility of partial decryption of traffic in 52 hours.
What else happened:
The next hardcoded keys were found in Netgear routers.
The new crypto-fiber is written in pure Javascript.
 Antiquities:
Antiquities:"Warrior-1024"
Nonresident very dangerous virus. Standard is written to EXE files. While the carrier file is running, the virus remains in memory, intercepts int 21h and when writing to the file (ah = 40h) replaces the recorded information with the text: "... and justice for all! (US constitution) Dream Over ... And the alone warrior is warrior . The powerfull WARRIOR! ".
Quote from the book "Computer viruses in MS-DOS" Eugene Kaspersky. 1992 Page 94.
Disclaimer: This column reflects only the personal opinion of its author. It may coincide with the position of Kaspersky Lab, or it may not coincide. Then how lucky.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/303492/
All Articles