Errors and problems of the Big Three servers: part three. Ibm

Hi, Habr! In the previous articles, we dealt with errors and problems with Dell and HP servers, and our story about errors of refurbished servers would be incomplete without mentioning the products of the third “big three” vendor - IBM. Although this glorious corporation has already moved away from the production of servers, its products are still actively used. Therefore, we hasten to share with you the accumulated experience of "taming" IBM servers. This is not an exhaustive list of problems, but it may still be useful to someone.
RAM
IBM servers are sensitive to memory configurations. Often, after an independent upgrade - adding memory or replacing it - the server does not load, or it sees less memory than is actually installed. Fortunately, in such situations it is not long to guess about the reasons for the failure: on the diagnostic panel (if there is one) two Config and Memory indicators light up.
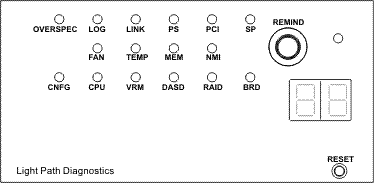
')
Therefore, before upgrading the memory, be sure to read the specification of the type and size of memory supported by your server. Also important is the number of processors in the server - the order in which the modules are placed in the slots depends on it. This also needs to be clarified in the specification.
In general, the memory is exactly the same situation as described in the article about HP , for example. In short:
- Observe the memory channel.
- Put ECC REG 1 (2) Rx4 memory in dual-processor systems and UDIMMs in single-processor ones.
- Put the same amount of memory on each processor.
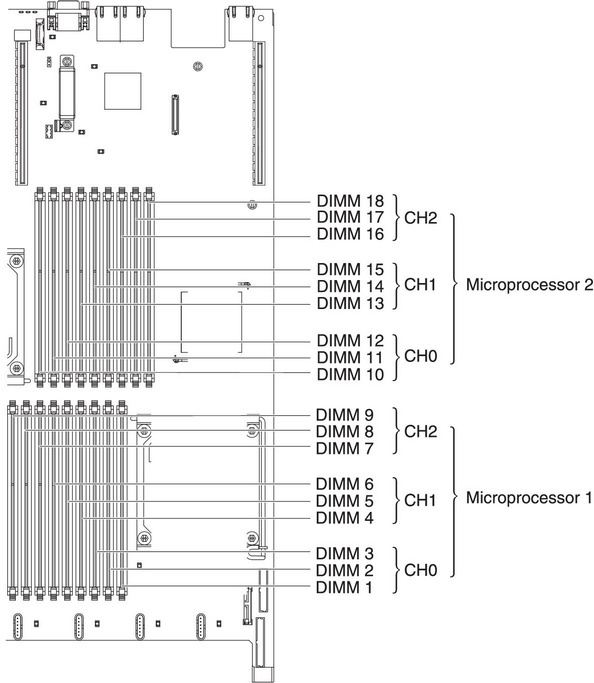
What to do if you inserted the memory in accordance with the instructions, but the server still does not work and the Memory indicator is flashing? In this case, you will have to check different options:
- This type of memory is not supported by the server . Check the specifications carefully.
- The memory was “bat” . Replace the line with the exact same one and check if the server starts up.
- Dust clogged slot on the motherboard . This is quite a popular reason if the server has been working for several years, and even more so if you are not its first owner. Blow out the slots with compressed air.
- Bent contact in the socket . This happens very rarely, but it still happens: the memory refuses to work due to the bent contact in the socket of the processor. If the previous options did not help find the cause of the failure, remove the processor and carefully inspect the socket. If you are among the few "lucky ones", you can try to carefully straighten the bent contact, but this is solely at your own peril and risk.
Many system administrators are faced with the fact that when checking RAM with MemTest86, they receive error messages even in obviously working modules or on the same tracks. This is especially common in M4 generation servers. This is not at all the fault of machines or memory: MemTest86 is not recommended for checking server memory. If the memory starts to fail, the server will report this through the diagnostic panel. It is better to check the memory on IBM servers using standard self-diagnostic tools.
Drives
We have repeatedly mentioned that it is not at all necessary to install “native” drives in servers. Neither IBM nor other vendors produce them; they only acquire them from well-known manufacturers, reflash and glue their logos. Therefore, you can easily save on upgrading or restoring disk arrays by choosing analogues instead of “native” drives. Two to three times the price difference justifies this, especially when it comes to refurbished servers . On the network, you can easily find model matching tables, for example:
| IBM model | Original |
|---|---|
| IBM 49Y2003 | Seagate ST9600204SS |
| IBM 90Y8872 | Seagate ST9600205SS |
| IBM 90Y8908 | Seagate ST9600105SS |
| IBM 81Y9650 | Seagate ST900MM0006 |
Nevertheless, situations of incompatibility of "non-native" drives with the server are still possible. In this case, the server does not load properly, or does not see the drive. This is usually solved by installing a fresh firmware RAID controller. By the way, it is recommended to upgrade the firmware and backplane / expander, the IBM Bootable Media Creator (BoMC) application will help you with this.
When you turn on the server and pass the POST check, you may receive an error:
This has been the case for the system.
This signals a problem with one of the drives. It is easy to calculate it: the indicators on its sled constantly flash, even when all other carriers have passed the test and stopped blinking.
There are more exotic problems with the disk subsystem. For example, when using RAID-1 in a proprietary MegaRAID Storage Manager application, errors may appear:
ID = 63
SEQUENCE NUMBER = 48442
TIME = 24-01-2016 17:03:59
LOCALIZED MESSAGE = Controller ID: 0 Consistency Check found inconsistent parity on VD strip: (VD = 0, strip = 637679)
Most often this is not talking about the dying of the disk, but about the error of the parity error - the discrepancy between the data on the primary and secondary disks. Possible reasons:
- Often, such errors appear immediately after configuring a new array or after replacing one of the disks.
- During the pancake surface diagnostics session, the disk is initialized and I / O operations are performed. On RAID-1, this may lead to a temporary volume mismatch, which is automatically corrected with the next compliance check. This does not occur during any diagnostic session, but when the stars converge:
- o Uses a RAID controller without caching, or Write Through mode is activated.
- o Lack of RAM, in which active paging is performed from the disk.
- o Just very heavy disk usage.
To solve this problem, it is recommended to reduce disk swap activity: use a RAID controller with caching and increase the amount of RAM.
Upgrade firmware and software
A curious problem can lie in wait for installing from scratch Windows 2012 or Windows 2012 R2 - a freshly installed OS does not see a single drive. And this happens not only with IBM servers. The fact is that all the drives in the server are connected via RAID, and the mentioned OS versions do not have embedded drivers for working with RAID. And so they simply ignore them. How to be? The most reliable way: use the IBM ServerGuide utility. When installing the OS, she forcibly slips all the necessary drivers for this model and version of the operating system. Please note that the OS image must be installed from the disk, not from the flash drive: ServerGuide will not work with the image on the same USB-drive from which it is launched.

When buying servers, there are situations when you first need to update all the firmware, and then roll the system. This can be done using the above IBM Bootable Media Creator :
- Boot from a bootable flash drive or disk.
- Run BoMC as Administrator.
- Choose what you want to do: update and / or diagnose.
- The program will ask where to get the drivers: download it yourself or pull it out of the archive you specified.
- Select the media for recording the boot image: a flash drive or disk. Recording may take several hours, do not worry, the program is not frozen.
- After recording, boot from this media, and then follow the instructions.
This procedure helps in a number of problematic situations. For example, if you didn’t wait for the Integrated Management Module to complete the upgrade and clicked the “Cancel” button, the next time the server boots, it may not be able to load IMM and uses the default settings. You can first try to recover with the help of the “UEFI & IMM recovery jumper” jumper on the motherboard, due to which the firmware IMM is loaded.
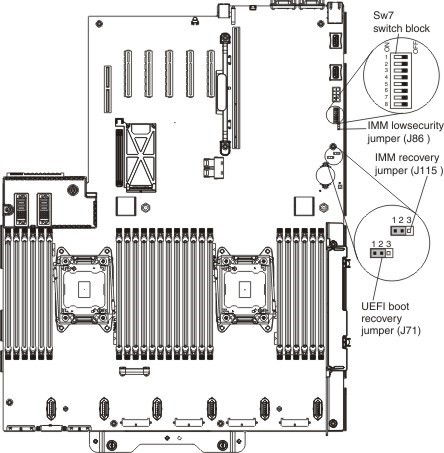
But if it does not help, then use the update procedure through BoMC.
There are also more unpleasant situations when, according to the law of meanness, a power failure occurs during the installation of a more recent BIOS version.

After that, the server can no longer download the main firmware, and uses a backup. If the standard BIOS recovery procedure does not help, then do ... downgrade: install an older firmware than the one before the power failure. This usually helps. After that, you can try again to put the latest version of the BIOS. As they say, a step back is two forward.
Other problems
Sometimes when trying to remotely manage the server, an error “Login failed with an access denied error.” Occurs, and in any browsers. If rebooting the server and client does not help, then it is recommended to reset IMM to factory settings.
In the article about HP server errors, we mentioned problems with the cooling system: immediately after starting the server, the fans went up to high speeds and did not reduce them. It happens such a disease in IBM servers. The server howls like a jet airliner on takeoff. We were not able to find out the cause of such failures, but we can advise the following:
- Check the density of the power connectors.
- Turn off all fans and remove the basket.
- Check each fan on other servers.
- Collect the cart again by swapping the fans. Or completely replace them.
There was such an interesting failure in our practice: when loading the server, IMM is regularly initialized, then UEFI initialization begins, and ... everything. Further the server is not loaded without explanation. Any manipulations did not help: disconnection from the network, complete de-energization, disconnection of various components. Loading the UEFI backup using a jumper on the motherboard did not help either. Experienced it turned out that if you wait about 20 minutes, you can still wait for the server to load. So it works since then - each time it loads 20 minutes. It was not possible to figure out the cause of the failure.
IBM server benefits
IBM servers are deservedly very popular:
- These are simple and very reliable cars.
- Excellent extensibility even on initial models and a rich package.
- IBM servers are usually cheaper than competitors and are not inferior in performance. For example, the M3 and M4 generations are cheaper than their counterparts from HP (Gen7 and Gen8) and Dell (11G and 12G).
- The most inexpensive consumables. Easy to find in Russia.
- Convenient diagnostic panel on many models.
The main thing is what IBM servers are inferior to competitors - they have a very long “cold” start.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/303424/
All Articles