Apple improves security of its services
Apple held its annual conference WWDC 2016, at which it presented its new products and announced the release of new products. The company introduced a new version of its desktop OS called macOS Sierra, as well as iOS 10. In the new versions of these platforms, emphasis was placed on the user's privacy and security settings (privacy & security). Earlier, we wrote that starting with iOS 8, Apple integrated data encryption for their smartphones based on the default unlock code (passcode), and in iOS 9 it expanded to six digits. iOS also uses the MAC address randomization security mechanism when searching for Wi-Fi networks.

In iOS 10, Apple announced end-to-end encryption for its FaceTime, iMessage, and HomeKit applications. In addition, personalization in iOS 10 will be based on a local basis, the data offered by Apple cloud services will not be based on a user’s ( differential privacy ) profile. Another news was the emergence of a new file system in macOS Sierra called the Apple File System (APFS). The new file system supports data encryption (full-disk encryption), as well as encryption of system file metadata.
')
In iOS 10, Apple uses the differential privacy approach, which can significantly increase the privacy of user data and anonymize it.
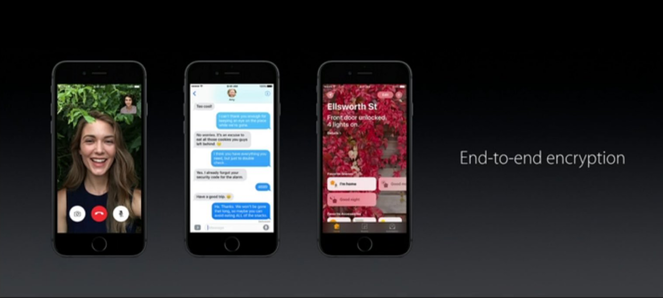
Fig. The iMessage messenger, FaceTime call app and HomeKit app use default end-to-end encryption. Thus, no one can access the data sent between users.
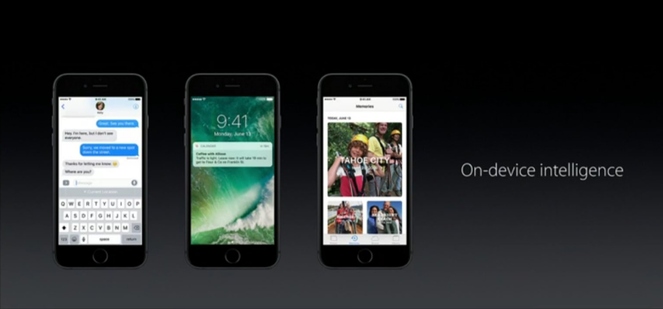
Fig. Processing of user data for AI is performed locally, which excludes the possibility of sending them to the Apple server and allows you to generate answers based on user preferences only on the device itself.
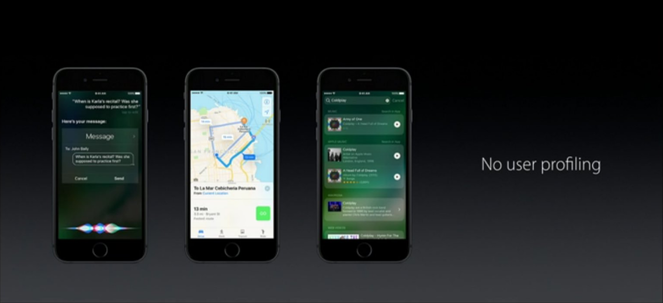
Fig. If it is necessary to send data to a remote server and exchange data with it, they are as anonymized as possible, without using a user profile, but using the concept of differential privacy.
MacOS Sierra includes a new file system with full-disk encryption functions, and the system file metadata is also encrypted.
The container mentioned above is the basic storage unit in APFS, it corresponds to an entry in the well-known GUID Partition Table (GPT) disk partition table. A container may contain several volumes, each of which has its own FS namespace. Data encryption uses AES-XTS or AES-CBC algorithms, depending on the hardware configuration.
APFS should come to replace the outdated HFS + file system, which Apple uses by default for its computers. Although the APFS documentation has already been published for access by everyone, the file system itself is still in the status of a developer preview and is available only to developers.
A more detailed overview of the new Apple file system can be found here .

In iOS 10, Apple announced end-to-end encryption for its FaceTime, iMessage, and HomeKit applications. In addition, personalization in iOS 10 will be based on a local basis, the data offered by Apple cloud services will not be based on a user’s ( differential privacy ) profile. Another news was the emergence of a new file system in macOS Sierra called the Apple File System (APFS). The new file system supports data encryption (full-disk encryption), as well as encryption of system file metadata.
')
In iOS 10, Apple uses the differential privacy approach, which can significantly increase the privacy of user data and anonymize it.

Fig. The iMessage messenger, FaceTime call app and HomeKit app use default end-to-end encryption. Thus, no one can access the data sent between users.

Fig. Processing of user data for AI is performed locally, which excludes the possibility of sending them to the Apple server and allows you to generate answers based on user preferences only on the device itself.

Fig. If it is necessary to send data to a remote server and exchange data with it, they are as anonymized as possible, without using a user profile, but using the concept of differential privacy.
MacOS Sierra includes a new file system with full-disk encryption functions, and the system file metadata is also encrypted.
Security and privacy are fundamental to the Apple File System.
On OS X, Full Disk Encryption has been available since OS X 10.7 Lion. On iOS, it has been available since iOS 4, as described in iOS Security Guide. APFS combines both of these features into a file system metadata.
APFS supports encryption natively. You can choose the following options for the individual metadata. APFS encryption uses AES-XTS or AES-CBC, depending on hardware. Multi-key encryption is secured by user data even when its physical security is compromised.
The container mentioned above is the basic storage unit in APFS, it corresponds to an entry in the well-known GUID Partition Table (GPT) disk partition table. A container may contain several volumes, each of which has its own FS namespace. Data encryption uses AES-XTS or AES-CBC algorithms, depending on the hardware configuration.
APFS should come to replace the outdated HFS + file system, which Apple uses by default for its computers. Although the APFS documentation has already been published for access by everyone, the file system itself is still in the status of a developer preview and is available only to developers.
A more detailed overview of the new Apple file system can be found here .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/303244/
All Articles