How to manage giants Vol.2: tools for planning the development of Internet projects
In the previous article, we carefully considered the details of the organization of processes and building teams for the implementation of complex web projects. But how to monitor compliance processes and plan time specialists? Theoretically, you can do with a notebook and pen, but this reinforces the influence of the human factor, and, therefore, there are additional risks. Many tools are available to minimize these risks, increase efficiency, and ease planning. For 10 years of AGIMA work, we have tried a great variety of software for project management, and in this article I will tell you about the tools that have passed our most rigorous selection and that our managers use daily.
What awaits you in the article:
')
Rules for building work planning processes in custom development and tips on optimizing labor costs.
For whom the article is intended:
The article will be interesting and useful to the heads of departments and projects - everyone who in one way or another belongs to the control processes and development planning.
Disclaimer:
This article is not a panacea, but a description of the measures and tools used by AGIMA in planning (Evgeny Lobanov, executive director).
§one. PROJECT KNOWLEDGE
Any manager must understand that specialists will not be involved in a single project for years. People come and go, their career growth continues, many people are simply not interested in doing the same thing all the time. As a result, in one year the project goes through a dozen specialists (programmers, team leaders, designers, QA, and others), and everyone needs to be introduced to the project and its subtleties. Therefore, the first and main aspect of planning is the organization of quick and comfortable immersion into the project of any specialist. This allows you to quickly switch performers between priorities and reduce risks when disruptions occur in the production plan. To do this, we use the Confluence knowledge base and strictly control the timely updating of knowledge on projects.
The structure of our knowledge base

Each project is represented by a separate space (besides commercial projects, there is space AGIMA by internal rules and workflow). Each space contains a dashboard with categories available to the role:
- Project manager,
- Designer,
- Front-end,
- QA
- etc.
Access to information for each role is determined at the level of global access rights of the knowledge base itself. A project manager, for example, has access to all categories. Categories, in turn, are divided into sections, where a set of knowledge and rules is written for each project, for example:
- Organizational matters,
- Weekly releases (release report),
- Licenses and domains
- Accesses,
- DEV-sites
- Description of the infrastructure
- AutoTest Server
- etc.
Inside the sections describes all the necessary information. In addition to the text description, it should be possible to attach links to the project documentation: BRD (Business Requirements Document, business requirements), functional requirements, etc., as well as store the source materials created during the work on the project (these can be source files - psd layouts, examples of xml request-responses for integration, database dumps, scans of original legal documents, etc.).
It’s not very convenient to store files as an application to a specific section in the knowledge base itself due to the lack of flexible groupings and local access, so we attach document files as links to corporate Dropbox .
Folder structure in the cloud storage (Dropbox)

Outdated projects are moved to the Archive folder. The administrator creates a backup and cleans the archive, saving disk space.
File and folder name
Unified file naming system takes into account the most important parameters of the document. Any specialist who is familiar with the internal rules of the company (internal workflows are described in detail in our knowledge base) is quickly oriented in the project documentation.
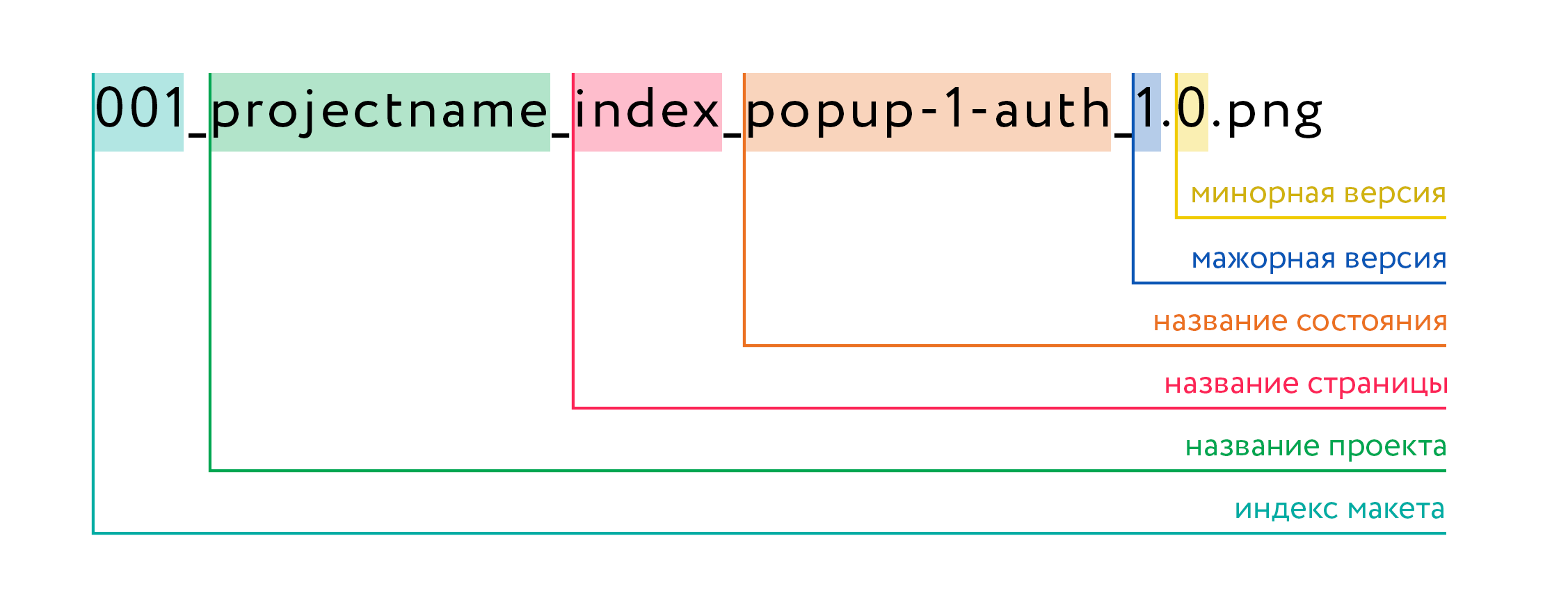
We decipher:
- Layout index - serves to sort the list of layouts and is specified in accordance with their sequence;
- Project name - the project to which the layout belongs;
- The name of the page is a specific page drawn on the layout;
- State name - the state of a specific page rendered on the layout (for example, pop-up authorization);
- Major version - the number of external iterations of edits / approvals with the client (sent the client layouts for approval for the first time - index 1; received edits from the client, contributed them, sent the client - index 2; etc.);
- The minor version is the number of internal iterations of edits.
Other requirements:
- The preview format is PNG; JPG - for photos only;
- Name folders and files in Latin letters only;
- We specify the file version in the name;
- Use underscore to separate the block, a dash for a phrase from several words.
§2. PRODUCTION PLAN
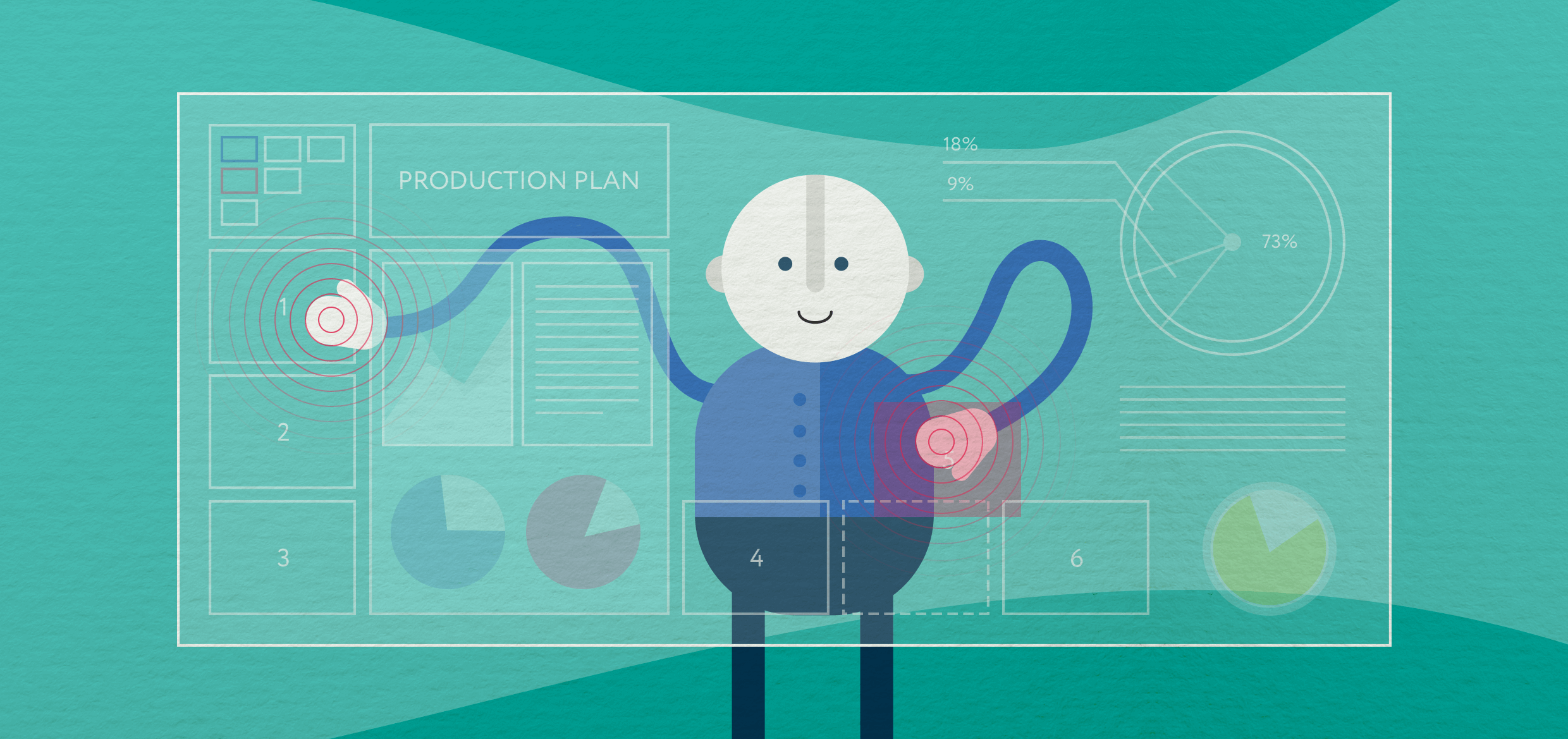
The second important aspect of planning is a correct and minimally risky production plan for a certain period of time. The development of any complex project is the interaction of a large team. In addition to managers and team leaders assigned to a specific project, we have a lot of specialists from different departments (there are more than 90 employees in the company) who are involved in the work on the project if necessary. As a rule, they work on several projects at once, which means that their time and tasks must be carefully planned. To do this, we draw up a weekly production plan for each department. Every Thursday, the project manager applies for all the resources he needs for the coming week to the head of the relevant department - design, engineering, development, etc. The heads of departments, in turn, update the internal preliminary production plans for three months ahead, for which a weekly cut is carried out, so they are already aware of the planned load. The application is the updated ticket in the task-system with all the necessary information: the information is validated at the stage of acceptance of the ticket in the production plan. Next, the priority of the task is determined, all tickets affixed to the executors later than midnight on Thursday, or reduced in priority, or postponed for the next week at the discretion of the head of the relevant department (depending on the load).
Let's talk about specific tools: we usually use ticket systems in conjunction: Intervals + Jira or + Trello . It depends on the chosen methodology and the specifics of communication with the customer. If the project does not have a complex technical implementation (communications do not require the interaction of technical specialists with each of the parties) and flexible methodologies are chosen, you can safely use Trello. For technically challenging projects - bundle exclusively with Jira. Consider these tools more closely.
Intervals
This is an easy-to-use "client" tracker, where the project is broken down by ticket into the main Milestones . From there, we pull up the time worked by specialists in our accounting system. As a rule, communication and coordination with the client is conducted through Intervals. This system allows you to flexibly configure the rights to view comments and receive notifications on a ticket. Thus, the client is only involved when it is really necessary, and current work issues are resolved within the team.
The main modules that we create in Intervals, depending on the composition of the project:
1. Data collection
2. Formalization
3a. Score,
3b. Approval of the assessment
4. Design,
5a. Design
5b. Concept development,
6. Layout
7. Fulfillment of planned,
8. Bug
9. Verification code
10a. Testing,
10b. Business testing
11. Analytics
12a. Release
12b. Testing after release,
13. Filling.
14a. In the report
14b. Separate account
.Study,
.Backlog,
.Organizational,
.A meeting,
.System administration.
The structure of the ticket on the project is as follows:
- Parent Task for Milestown Project
- Sabtask on data collection,
- Sabtask on formalization,
- Sabtask for evaluation,
- ...
- Sabtask on any other activity corresponding to the available project module.
- ...
- Parental task to any other mailstone project.
Jira and Trello
The main purpose of these “internal” ticket systems is the detailed control over the development process and the efficiency of the internal team. How do we use them?
I'll tell you on the example of setting up a project in Jira (the work with Trello is similar). For each project we create our own workflow (depending on the required stages and milestones). The whole project is divided into stages that fight for the smallest tasks, each not more than 24 hours. All tasks are recorded in the backlog of the project, in the same place they are tied to sprints and planning takes place according to the “epic” (corresponding to the Milestone in the Intervals) and versions (if necessary).
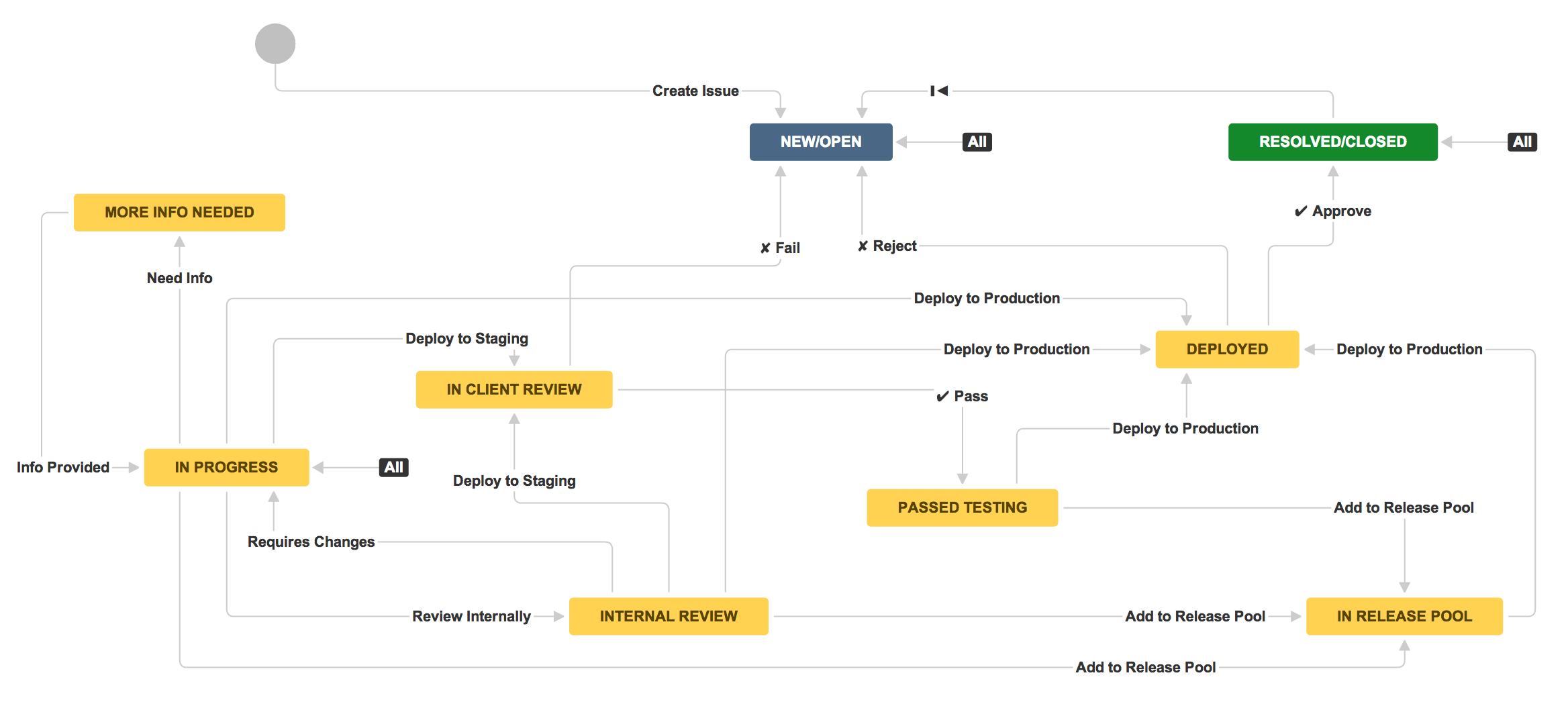
Next, we configure the available task types for the project (for example: task, improvement, new feature, bug, story, etc.) and screens when switching between the states of the ticket for the workflow project. For each project, a kanban or scrum board is formed (depending on the chosen methodology), which are available only with the Agile plug-in. The set of activities on the board corresponds to the modules in the Intervals, and for each activity a column is added with the waiting queue for it.
It looks like this:
1. Data collection → 2. Formalization
2. Formalization → 5a. On shipment design
2. Formalization → 6a. On shipping layout
2. Formalization → 7a. On shipment programming
2. Formalization → 10a. Testing Queue
2. Formalization → 11. Analytics
2. Formalization → 3a. The queue for evaluation
3a The queue for evaluation → 3b. Evaluation
3b. Assessment → 2. Formalization
3b. Score → 3c. Approval of the assessment
3c. Approval of assessment → 2. Formalization
...
5c. Concept development → 6a. On shipping layout
6a. On shipping layout → 6b. Layout
6b. Layout → 2. Formalization
6b. Layout → 5a. On shipment design
6b. Layout → 10a. Testing Queue
7a. On shipment programming → 7b. Fulfillment planned
7b. Planned accomplishments → 2. Formalization
7b. Execution planned → 5a. On shipment design
7b. Execution of planned → 6a. On shipping layout
7b. Execution planned → 10a. Testing Queue
8. Bug → 2. Formalization
8. Bug → 5a. On shipment design
8. Bug → 6a. On shipping layout
...
13. Filling → 14b. Separate account
14a. In the report → 10a. Testing Queue
14a. To report → 2. Formalization
14a. To report → 8. Bug
14a. In the report → 14b. Separate account
14b. Separate account → 10a. Testing Queue
14b. Separate invoice → 2. Formalization
14a. To report → 8. Bug
It is important that a specialist in the real time in the work should have only one task (column on the board with the action). This allows you to understand at any time what each team member is doing now and how the work is progressing in accordance with the planned timing. At the end of the work day, the specialist changes the status of the task, passing it to the waiting column (thus, the remaining volume of tasks in the column on the blackboard with the queue is always clear).
In addition, we have Jira integrated with the Stash plugin (now called Bitbucket) . This allows you to see at any moment what exactly is happening on the task in the version control system ( Git ), what commits are made, whether push and pull are done within the ticket.
We use two more useful plugins: Bamboo for CI ( Continuous Integration ) and Tempo for preparing reports.
UPDATE: but by the way, read at the same time the rating of task managers from Tagline .
Roadmap for loading departments
In order to monitor the loading of departments on a project and respond quickly to disruptions in the production plan, after preparing a preliminary long-term plan, we draw up a roadmap . Roadmap is updated weekly and is available online.
To prepare a roadmap, you can use the Cacoo online service or any desktop application to develop software structures and models, such as OmniGraffle or ArgoUML .
I will not talk in detail about our method of grades (this is a topic for a separate article), but I note that we use such a system to compare the complexity of a project with the competencies of specialists. We have only 7 grades, it is important at the project evaluation stage to form an understanding of the necessary qualifications of the specialists who will be involved. The internal rate of a specialist depends on the grade, and this must be taken into account when forming the cost of work. Costa at domestic rates, we also put in the roadmap (but on the screen they are naturally removed).
§3. TIMEPLAN PROJECT
The third key to successful project management is the most detailed and always current timeplan in the form of a Gantt chart . If the roadmap is used for high-level control over the loading of departments with specific tasks, then the timings are for detailed control of the progress of this task and the possibility of rapid response during the slightest pauses. Timeplan helps to control internal production processes and manage customer expectations. On the Gantt chart, all “milestones” and activities to coordinate work with the client, including “business testing”, “content provision”, “content”, etc., must be marked. Grouping of tasks on timing should correspond to modules from Intervals and binding to columns on a kanban / scrum board in Jira or Trello (project xml-file with grouping by modules is generated automatically).
When compiling the timings, it is necessary to take into account the correct setting of the production calendar (to exclude RF-specific weekends and holidays) and suitable days of the week for control points (for example, the release should never be performed on Friday). Information about the necessary resources (already locally, as opposed to a roadmap, indicating specific specialists, and not departments) and the actual cost of resources are recorded for timing. It is important to consider the correct setting of the status of activities on the plan.
We mainly use Merlin to prepare the timings, some employees practice OmniPlan and MSProject . Merlin is easy to use, and most importantly, allows you to export Gantt charts to HTML.
So that all project participants (both from the developers and the customer) see the current time plan and track the project progress, we organized an external platform. So the project manager can connect to the server and update the timing with the help of any ftp-client (in Merlin you can set up export directly to an ftp-server). Timings are usually placed in html format, but pdf and png are also allowed. If necessary, you can add http-authorization for access to "timing": to do this, you need to create a file .htaccess and .htpasswd, register in it a login and password through a colon in base64.
Example:
www.agima.ru/demo/RBS
In general, try new tools and constantly optimize the planning process, because this is the basis of commercial production. Well, do not forget: "If you do not manage the project, the project controls you!".
PS In the next article in this series, we will examine in more detail the course of the project and the features of each of the stages.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/302820/
All Articles