Binocular vision and stereopsis
I want to write about what I do in Tech. University of Tampere .
Stereopsis (stereo effect) - a sense of the length of space and relief, arising from the observation of real objects, viewing stereo pairs, stereo photographs, stereo images and holograms. Often referred to as “depth perception”.
As you know (in any case, most of us have heard something about it), the image visible by the left eye is slightly different from the image obtained by the right eye. Due to which our brain is able to restore the “depth” of the observed scene. However, how exactly he does it, and how far it is possible that far from many people know.
In 1838, English scientist Charles Wheatstone discovered (more precisely, explained) the nature of 3-dimensional vision.
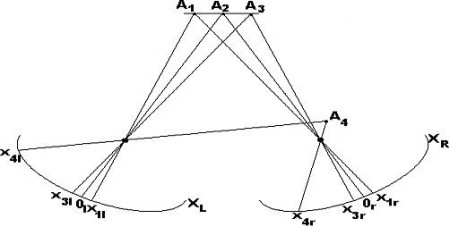
If we imagine the optical system of a person from two eyes with more or less parallel optical axes (parallax), it turns out that the difference in images (disparity) is determined by the depth. To be more precise, disparity (or disparity ) is inversely proportional to the depth (distance), i.e. for example, an infinitely remote point will be projected equally on both retinas (disparity = 0), and a close-lying point will be projected to completely different places of the retina (large disparity). This is roughly depicted in the picture worn out with the Russian Wikipedia. (For more details, see Disparity )
Despite the long history of stereo technology, there has been a surge in popularity for stereo-vision insome scientific circles in the past few years. With the invention and improvement of computers, it became possible to measure the depth of scenes with the help of machines equipped with digital photo / video cameras. It can be argued that in the last decade the number of scientific publications on stereo-vision has increased exponentially. Very noticeable progress in the creation of algorithms to restore the depth of a given stereo pair.
')
Naturally, where there are two cameras (stereo), it’s not difficult for a computer to add another twenty-two to improve the quality of depth recovery (as many 3-D scanners do), but from a scientific point of view, stereo vision is the most fundamental (and hence an interesting) task since any multi-camera approaches can be viewed as a set of several stereo cameras, and process them independently.
Moreover, it is believed that the human brain copes with the task of restoring the depth in two pictures (actually a very controversial statement), then computer programs (stereo-matching, dense depth estimation) should restore the depth with quite a good result.
In the scientific community there is a special site where different groups of scientists compare the achieved results (in depth assessment) with each other: vision.middlebury.edu/stereo/eval
So progress in this area is very well tracked by the results table, which has accumulated over several years. Here are a couple of results:
These are the results of the algorithm Scanline optimization (1D optimization using horizontal smoothness terms), 2002


These are the results of the Double Belief Propagation algorithm, published in 2007. As they say feel the difference.


(Source: vision.middlebury.edu/stereo/eval )
(Note 1: These ground truths and test picture frames, from which depth estimates are obtained, can be viewed on the same page)
(Note 2: Since this framework evaluates disparity, and not distance, the bright areas in the picture correspond to nearby objects, the dark areas correspond to distant ones)
As you can see, over the past 5 years, the quality of the restoration of the depth of the scene based on the stereo pair has almost reached the maximum possible. Nevertheless, there are still many places in this area where researchers need to make efforts. Which is likely to be done in the coming years. Scene Understanding could become a further development of this area, when a computer not only "sees", but also "understands" what objects are in front of it.
If the readers of this blog like the new topic, then I am ready to continue to raise topics on Digital Image Processing. In particular, I would like to highlight the topic of the theory (and maybe about practice) Image Denoising, Image Deblurring / focusing, etc.
What to read next:
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stereopsis
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Binocular_disparity
ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/%D0%94%D0%B8%D1%81%D0%BF%D0%B0%D1%80%D0%B0%D1%82%D0%BD%D0%BE%D1 % 81% D1% 82% D1% 8C
vision.middlebury.edu/stereo
www.stereoscopy.com
scholar.google.fi/scholar?q=Stereo+matching&hl=en&lr=&btnG=Search
Wheatstone Charles, Contributions to the Physiology of Vision. Part the First. On some remarkable, and hitherto unobserved, Phenomena of Binocular Vision.
Stereopsis (stereo effect) - a sense of the length of space and relief, arising from the observation of real objects, viewing stereo pairs, stereo photographs, stereo images and holograms. Often referred to as “depth perception”.
As you know (in any case, most of us have heard something about it), the image visible by the left eye is slightly different from the image obtained by the right eye. Due to which our brain is able to restore the “depth” of the observed scene. However, how exactly he does it, and how far it is possible that far from many people know.
In 1838, English scientist Charles Wheatstone discovered (more precisely, explained) the nature of 3-dimensional vision.
If we imagine the optical system of a person from two eyes with more or less parallel optical axes (parallax), it turns out that the difference in images (disparity) is determined by the depth. To be more precise, disparity (or disparity ) is inversely proportional to the depth (distance), i.e. for example, an infinitely remote point will be projected equally on both retinas (disparity = 0), and a close-lying point will be projected to completely different places of the retina (large disparity). This is roughly depicted in the picture worn out with the Russian Wikipedia. (For more details, see Disparity )

Despite the long history of stereo technology, there has been a surge in popularity for stereo-vision in
')
Naturally, where there are two cameras (stereo), it’s not difficult for a computer to add another twenty-two to improve the quality of depth recovery (as many 3-D scanners do), but from a scientific point of view, stereo vision is the most fundamental (and hence an interesting) task since any multi-camera approaches can be viewed as a set of several stereo cameras, and process them independently.
Moreover, it is believed that the human brain copes with the task of restoring the depth in two pictures (actually a very controversial statement), then computer programs (stereo-matching, dense depth estimation) should restore the depth with quite a good result.
In the scientific community there is a special site where different groups of scientists compare the achieved results (in depth assessment) with each other: vision.middlebury.edu/stereo/eval
So progress in this area is very well tracked by the results table, which has accumulated over several years. Here are a couple of results:
These are the results of the algorithm Scanline optimization (1D optimization using horizontal smoothness terms), 2002


These are the results of the Double Belief Propagation algorithm, published in 2007. As they say feel the difference.


(Source: vision.middlebury.edu/stereo/eval )
(Note 1: These ground truths and test picture frames, from which depth estimates are obtained, can be viewed on the same page)
(Note 2: Since this framework evaluates disparity, and not distance, the bright areas in the picture correspond to nearby objects, the dark areas correspond to distant ones)
As you can see, over the past 5 years, the quality of the restoration of the depth of the scene based on the stereo pair has almost reached the maximum possible. Nevertheless, there are still many places in this area where researchers need to make efforts. Which is likely to be done in the coming years. Scene Understanding could become a further development of this area, when a computer not only "sees", but also "understands" what objects are in front of it.
If the readers of this blog like the new topic, then I am ready to continue to raise topics on Digital Image Processing. In particular, I would like to highlight the topic of the theory (and maybe about practice) Image Denoising, Image Deblurring / focusing, etc.
What to read next:
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stereopsis
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Binocular_disparity
ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/%D0%94%D0%B8%D1%81%D0%BF%D0%B0%D1%80%D0%B0%D1%82%D0%BD%D0%BE%D1 % 81% D1% 82% D1% 8C
vision.middlebury.edu/stereo
www.stereoscopy.com
scholar.google.fi/scholar?q=Stereo+matching&hl=en&lr=&btnG=Search
Wheatstone Charles, Contributions to the Physiology of Vision. Part the First. On some remarkable, and hitherto unobserved, Phenomena of Binocular Vision.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/30282/
All Articles