About the new features of SQL Server 2016
Databases are the heart of any company that ensures the literal performance of every line of business. But what is the place of the database in modern realities? After all, they did not appear today. They were created at a time when we could not even imagine that the world of technology would be as it is now. Traditional databases were intended solely for recording and retrieving transactions, such as orders and payments. Their task was to ensure reliable and secure operation of applications in a small or medium scale local data center.
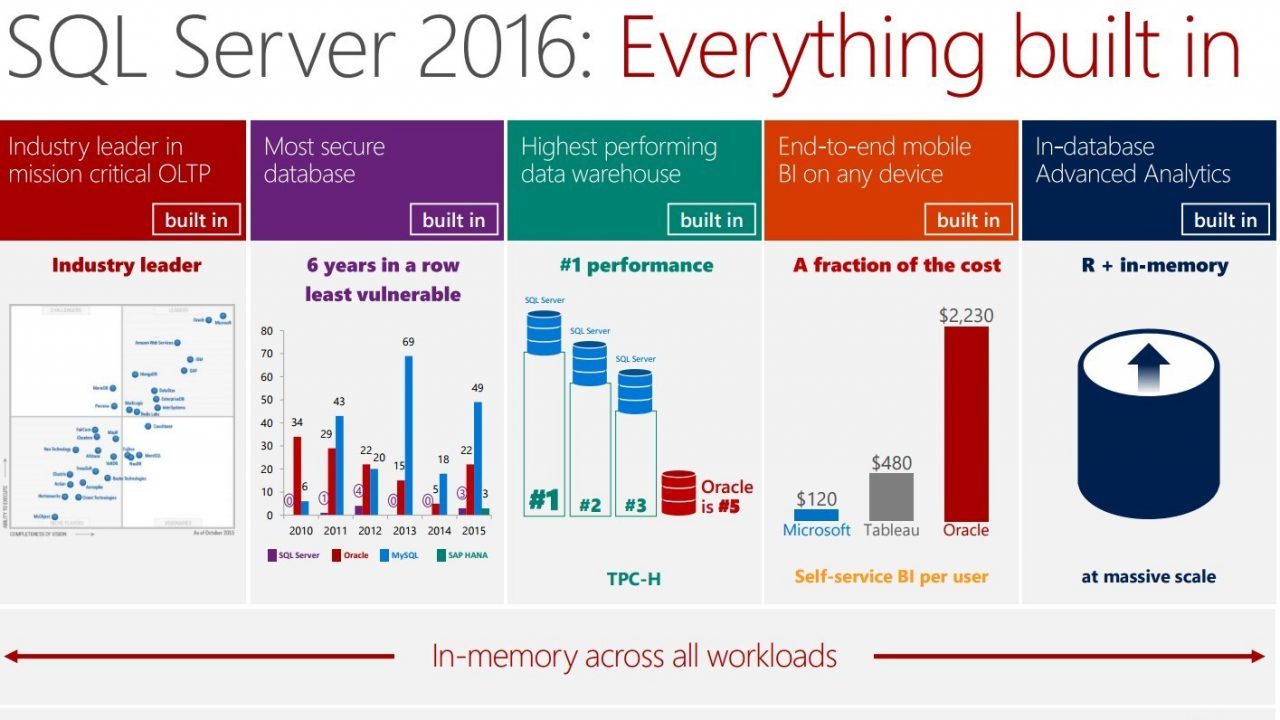
Our product - SQL Server 2016 - helps to realize the full potential of the latest technological trends. It supports hybrid transaction processing, advanced analytics and machine learning, mobile business analytics, data integration, encryption request processing, and in-memory transaction processing. Apparently, this is a one-of-a-kind relational database originally intended for the cloud. Most of its functions were originally developed and tested in Azure, in 22 data centers scattered throughout the world, with a load of several billion queries per day. She has already managed to demonstrate excellent results in practice. Many of our clients successfully use this database.
You can learn more and more on our virtual forum .
The R programming language is widely used as data analysis and prediction software. It is free, open source, and supported by a large community. You can use several thousand packages for various tasks. At your service are standard functions of statistics and data management, graphical interfaces and advanced machine learning algorithms. Language R is chosen by scientists and companies who want to innovate using modern analytical methods.
')
SQL Server R Services is a new component in SQL Server 2016. You can still take advantage of the R language, an ever-growing set of packages and a large community of users, but now you can also use SQL Server features and the familiar Transact-SQL interface.
SQL Server R Services is a unique data analysis solution using the R language, which provides scaling, allows integration with applications in an industrial environment and does not require large cash outlays.
Where to begin?
Here is a list of resources to help you get started with R Services:
Over the past 10 years, the world of information technology has changed beyond recognition. The Internet of Things, the technology of processing unstructured data and the reduction in prices for IT equipment - all this has led to a real boom in Big Data. There are solutions (such as Hadoop and HDFS) that allow processing huge arrays of semi-structured data without requiring the purchase of expensive specialized hardware. All this opened up new opportunities for business to make a profit; however, the “reverse side of the coin” was the growing complexity of corporate platforms for working with data. In addition, data sources have become much more diverse. Often, companies have to deal with several separate data sets: relational in SQL Server and non-relational in HDFS. If the analyst needs to combine analysis of semi-structured and structured data, then he will have to first copy it from one environment to another, which takes a lot of time and effort.
But everything in the world is changing for the better! The PolyBase solution in SQL Server 2016 eliminates the problem of the separation of relational and semi-structured data. Using PolyBase and T-SQL allows users to send queries to HDFS data as if they were stored on a local SQL Server, which opens up a lot of new possibilities for analysis.

Examples of using
PolyBase offers three scripts for accessing data in SQL Server and Hadoop:
When sending requests to data in Hadoop, PolyBase strives to make the most efficient use of the computing resources of this platform. In particular, PolyBase can decide to transfer the computational load to Hadoop by creating MapReduce jobs, which ensures the most efficient processing of requests.
Additional resources
Are you interested in the features offered by PolyBase for SQL Server 2016? Below you will find links to useful resources, as well as a video that tells how PolyBase allows you to send queries to HDFS data using T-SQL directly from SQL Server.
The Stretch Database technology, which is part of SQL Server 2016, makes it possible to store any amount of data as long as necessary, without violating the business service level agreement and the high costs of acquiring enterprise-level storage systems. Unlike the usual solutions used to store “cold” data, the Stretch Database provides constant access to your data by using the inexhaustible Azure cloud resources, and also does not require modification of most applications. Database administrators only need to activate the storage of "cold" data in the cloud.
Key Scenarios
Benefits
Azure SQL Stretch Database allows you to use Azure on your terms.
Recall once again that you do not need to make changes to the code for most applications to use Stretch Database.
We are pleased to invite you to the key event of the year in the data world - Microsoft Virtual Forum “Data. Technology. SQL Server 2016 ” to be held on June 8, 2016.
The main program of the forum consists of three parallel technology sessions:
A detailed program is available on the event website.
The space of the Virtual Forum is organized in such a way that you can feel like a participant in a real conference.
And that's not all - you can see technology in action during the day by taking part in a test drive of the platform with the help of online laboratory work under the guidance of a trainer.
Participation in the forum is free. Pre-registration is required .
We suggest you to pay attention to the blog of Sergey Olontsev , where you can find a lot of materials on SQL Server 2016.
Pay attention to the cool program with meta tags - which we have specially prepared for technical specialists (with the possibility of filtering by interests) http://www.sql2016.ru/schedule

Our product - SQL Server 2016 - helps to realize the full potential of the latest technological trends. It supports hybrid transaction processing, advanced analytics and machine learning, mobile business analytics, data integration, encryption request processing, and in-memory transaction processing. Apparently, this is a one-of-a-kind relational database originally intended for the cloud. Most of its functions were originally developed and tested in Azure, in 22 data centers scattered throughout the world, with a load of several billion queries per day. She has already managed to demonstrate excellent results in practice. Many of our clients successfully use this database.
We are pleased to invite you to the key event of the year in the data world - Microsoft Virtual Forum “Data. Technology. SQL Server 2016 ” to be held on June 8, 2016.Below are details on some of the new features in SQL Server 2016 - R Services, PolyBase, Stretch Database.
You can learn more and more on our virtual forum .
Analysis inside the database using the R language
The R programming language is widely used as data analysis and prediction software. It is free, open source, and supported by a large community. You can use several thousand packages for various tasks. At your service are standard functions of statistics and data management, graphical interfaces and advanced machine learning algorithms. Language R is chosen by scientists and companies who want to innovate using modern analytical methods.
')
SQL Server R Services is a new component in SQL Server 2016. You can still take advantage of the R language, an ever-growing set of packages and a large community of users, but now you can also use SQL Server features and the familiar Transact-SQL interface.
- R Services allows you to perform analysis within the database. You can store data in SQL Server 2016, and applications call R scripts through a T-SQL stored procedure. This makes it easy to integrate applications with the R language. The R scripts run on the same machine where the data is stored, so you don’t need to worry about security: the R code cannot access the Internet or other processes running on SQL Server.
- R Services users can use the ScaleR algorithm library — a set of functions that offers equivalents for everyday tasks performed in R. However, unlike CRAN-R analogs, ScaleR functions are scalable to handle hundreds of millions and billions of rows through parallel computing. This provides performance that cannot be achieved using common open source packages. The ScaleR APIs were developed by Revolution Analytics. After Microsoft acquired this company, the APIs were integrated into SQL Server. They are cross-platform, that is, they support not only SQL Server, but also other platforms.
- SQL Server also offers existing features and mechanisms for integration and performance improvements. For example, it is possible to use ColumnStore indexes together with the R language in order to perform analytical queries faster. The built-in control mechanism allows you to control resources allocated to the R runtime environment. And SQL Server Integration Services (SSIS) provides seamless integration with ETL and scheduling scheduled tasks through a stored procedure interface.
- Another important feature of R Services is that users can work with familiar tools:
- Specialists involved in the study of data, have the opportunity to use the usual R IDE. They can work with R Studio, with the recently announced R Tools for Visual Studio tools, or with any IDE at their discretion. Instead of transferring data to the local machine, you can use the ScaleR tool for remote execution directly from the IDE. Using the tools of SQL Server 2016 for analysis within the database allows you to speed up the analysis of large data sets.
- Server administrators are familiar with the SQL Server Management Studio software for managing R Services, monitoring resources, and assigning access rights.
- Application developers can access T-SQL APIs. They can create SQL Server Reporting Services reports or Power BI dashboards with estimates, forecasts and graphics from R without having to learn the R language itself.
- Data engineers can combine R with existing ETL streams and plan routine tasks using SQL Server Integration Services.
- Specialists involved in the study of data, have the opportunity to use the usual R IDE. They can work with R Studio, with the recently announced R Tools for Visual Studio tools, or with any IDE at their discretion. Instead of transferring data to the local machine, you can use the ScaleR tool for remote execution directly from the IDE. Using the tools of SQL Server 2016 for analysis within the database allows you to speed up the analysis of large data sets.
SQL Server R Services is a unique data analysis solution using the R language, which provides scaling, allows integration with applications in an industrial environment and does not require large cash outlays.
Where to begin?
Here is a list of resources to help you get started with R Services:
- Product Documentation on MSDN
- A Data Driven video covering how SQL Server R Services helps you create intelligent applications, perform predictive analysis, and extract valuable information from data. For more videos on R Services, see the Data Driven playlist and on Channel9 .
- MSDN manuals
- Solution templates on the Cortana Analytics Gallery website, sample data and code on GitHub.
- If you don’t know anything about the R language, take our online courses, for example on the Datacamp website, where you can also find advanced ScaleR API courses.
Introducing PolyBase
Over the past 10 years, the world of information technology has changed beyond recognition. The Internet of Things, the technology of processing unstructured data and the reduction in prices for IT equipment - all this has led to a real boom in Big Data. There are solutions (such as Hadoop and HDFS) that allow processing huge arrays of semi-structured data without requiring the purchase of expensive specialized hardware. All this opened up new opportunities for business to make a profit; however, the “reverse side of the coin” was the growing complexity of corporate platforms for working with data. In addition, data sources have become much more diverse. Often, companies have to deal with several separate data sets: relational in SQL Server and non-relational in HDFS. If the analyst needs to combine analysis of semi-structured and structured data, then he will have to first copy it from one environment to another, which takes a lot of time and effort.
But everything in the world is changing for the better! The PolyBase solution in SQL Server 2016 eliminates the problem of the separation of relational and semi-structured data. Using PolyBase and T-SQL allows users to send queries to HDFS data as if they were stored on a local SQL Server, which opens up a lot of new possibilities for analysis.

Examples of using
PolyBase offers three scripts for accessing data in SQL Server and Hadoop:
- one-time requests to Hadoop and SQL Server 2016 using T-SQL;
- Import data from Hadoop or Azure blob storage into SQL Server 2016
- Exporting "cold" relational data to Hadoop or Azure blob storage while maintaining the ability to send requests at the same time.
When sending requests to data in Hadoop, PolyBase strives to make the most efficient use of the computing resources of this platform. In particular, PolyBase can decide to transfer the computational load to Hadoop by creating MapReduce jobs, which ensures the most efficient processing of requests.
Additional resources
Are you interested in the features offered by PolyBase for SQL Server 2016? Below you will find links to useful resources, as well as a video that tells how PolyBase allows you to send queries to HDFS data using T-SQL directly from SQL Server.
- Getting started with PolyBase
- PolyBase groups for scale-out computation
- PolyBase troubleshooting with dynamic management views
Unlimited data storage with Stretch Database technology
The Stretch Database technology, which is part of SQL Server 2016, makes it possible to store any amount of data as long as necessary, without violating the business service level agreement and the high costs of acquiring enterprise-level storage systems. Unlike the usual solutions used to store “cold” data, the Stretch Database provides constant access to your data by using the inexhaustible Azure cloud resources, and also does not require modification of most applications. Database administrators only need to activate the storage of "cold" data in the cloud.
Key Scenarios
- Transfer to the cloud of the entire table: the existing dedicated table for the “cold” data can be transferred as a whole. Suppose you have the Order_details and Order_details_history tables, the last of which contains only the “cold” data transferred from the first.
- Migrating “cold” rows: if there are both “hot” and “cold” data in the same table, only “cold” data can be transferred to Azure. To do this, it is enough to specify exactly which lines are (usually this is determined by date or state), and SQL Server will take care of the transfer.
Benefits
Azure SQL Stretch Database allows you to use Azure on your terms.
- Get enterprise-class storage space — how much and when you need it. Automated backup and geo-replication are enabled by default.
- If necessary, scale computing resources and storage space to meet the requirements of the work task and pay only for the amount used.
- Using the built-in security mechanism, centrally manage access for customers who have joined the local Active Directory with the Azure Active Directory.
- Use existing knowledge and tools, such as SQL Server Management Studio, SQL Server Data Tools, T-SQL and PowerShell, and expand the available features through the Azure portal.
Recall once again that you do not need to make changes to the code for most applications to use Stretch Database.
Virtual Forum
We are pleased to invite you to the key event of the year in the data world - Microsoft Virtual Forum “Data. Technology. SQL Server 2016 ” to be held on June 8, 2016.
The main program of the forum consists of three parallel technology sessions:
- SQL Server 2016: New Standards in the Transaction World;
- Business Analytics: SQL, Power BI, R, Mobile;
- Azure: a new generation of analytics solutions and Big Data.
A detailed program is available on the event website.
The space of the Virtual Forum is organized in such a way that you can feel like a participant in a real conference.
- Each participant will be able to visit the exhibition of partner solutions.
- Chat with MVP technology experts , ask questions.
- Ask questions to the speakers .
- Get all the necessary materials and presentations.
- And even win prizes - the most active will receive one of 30 certificates for passing exams in SQL Server 2016.
And that's not all - you can see technology in action during the day by taking part in a test drive of the platform with the help of online laboratory work under the guidance of a trainer.
Participation in the forum is free. Pre-registration is required .
Additionally
We suggest you to pay attention to the blog of Sergey Olontsev , where you can find a lot of materials on SQL Server 2016.
Pay attention to the cool program with meta tags - which we have specially prepared for technical specialists (with the possibility of filtering by interests) http://www.sql2016.ru/schedule
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/302770/
All Articles