Attackers use the Burger King theme to send spam to WhatsApp
Our specialists have discovered a fraudulent email campaign that uses the theme of discount coupons from the Burger King fast food chain. A message comes to the user from one of the contacts or group in the WhatsApp messenger. His text prompts the user to receive a discount coupon from Burger King for a certain amount. We recorded messages in the following languages: English, German, Spanish, Portuguese, Italian.

The fraudulent campaign of intruders is a good example of social engineering that can be used as a means to achieve a goal in marketing or cyber attacks. Social engineering, then, is a way of persuading a person to perform an action. In our example we are talking about buying fake coupons for which a discount is offered.
')
After clicking on the link, the user is redirected to a special survey containing several questions.
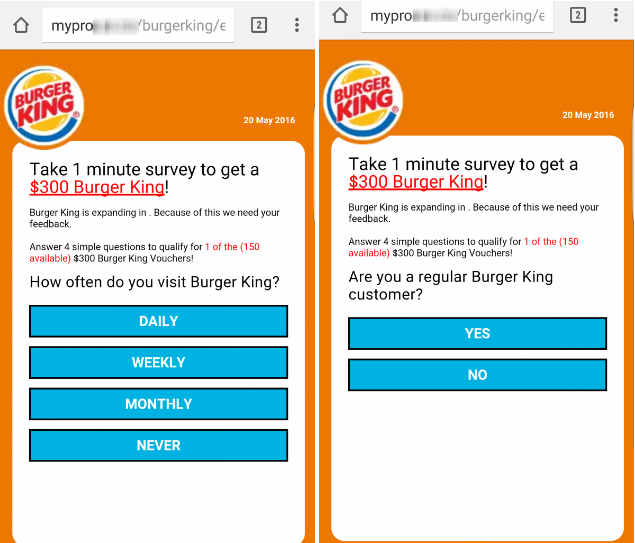
Fig. A survey that is used to divert the user's attention.
The expression “only 150 coupons left” is an example of social engineering practice to encourage the user to quickly follow the link.
It is interesting to note that the attackers have added a special line to the code of the phishing web page to prevent Google search engines and Bing from indexing its content. To do this, use the function "noindex". Thus, the attackers hope to leave their campaign invisible as long as possible. The content itself will be visible only to users who have received a link to it.
In addition, cyber campaign is relevant only for viewing a web page from a mobile web browser, i.e. when accessing it from a tablet or smartphone. If you try to open the link from the computer, an error message will be displayed. This feature is an update to the code of a malicious campaign, since its previous versions did not have this feature, that is, they made a web page accessible to all systems.
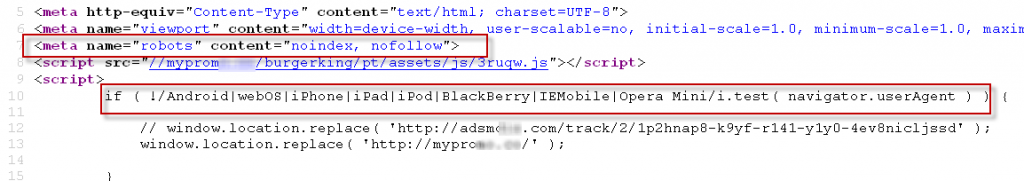
Fig. The parameter "noindex" is used to prohibit indexation by search engines. Also on the screenshot you can see the condition for checking the user’s use of the web browser.
For a coupon, scammers offer the user to share this message with ten friends or publish it in three WhatsApp groups. This notification is equipped with a special countdown counter, which counts 225 seconds “during which the message is valid”. Below is the source code that is responsible for the implementation of this part of the malicious campaign. He is responsible for implementing the further distribution of the message and redirecting the user to the desired resource.
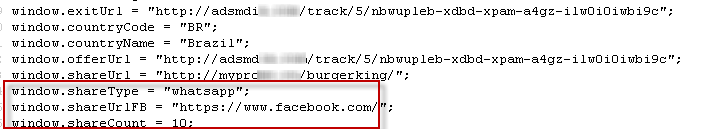
Fig. URLs to redirect the user.
It should be noted that similar malicious campaigns (without the block of code that is highlighted in the screenshot above) can be extended to facebook.
After performing these actions, scammers indicate to the user that he could not win the discount and he needs to try next time. “Thank you for participating. You did not win; try again and good luck. ”

Fig. The last stage of fraud with the proposal of new "coupons".
An essential detail is the ability for attackers to automatically change the language of messages and currency depending on the user's IP address and the language settings of the web browser.
Ultimately, the user will be redirected to one of the websites on which the attackers earn. This can be a simple redirect (click), for which the authors of a malicious campaign will receive a few cents or register on any site where payment is made for registering new subscribers.

Fig. Services and websites to which the user is redirected.
Protection measures
Improving user literacy and awareness is the best way to protect against this kind of fraud, which uses social engineering techniques. Although there was nothing new in this fraudulent campaign, it is still relevant to attackers. Unfortunately, many WhatsApp users still fall victim to it.
In order not to become a victim if you receive a fraudulent message in WhatsApp, you should follow these simple rules.

The fraudulent campaign of intruders is a good example of social engineering that can be used as a means to achieve a goal in marketing or cyber attacks. Social engineering, then, is a way of persuading a person to perform an action. In our example we are talking about buying fake coupons for which a discount is offered.
')
After clicking on the link, the user is redirected to a special survey containing several questions.

Fig. A survey that is used to divert the user's attention.
The expression “only 150 coupons left” is an example of social engineering practice to encourage the user to quickly follow the link.
It is interesting to note that the attackers have added a special line to the code of the phishing web page to prevent Google search engines and Bing from indexing its content. To do this, use the function "noindex". Thus, the attackers hope to leave their campaign invisible as long as possible. The content itself will be visible only to users who have received a link to it.
In addition, cyber campaign is relevant only for viewing a web page from a mobile web browser, i.e. when accessing it from a tablet or smartphone. If you try to open the link from the computer, an error message will be displayed. This feature is an update to the code of a malicious campaign, since its previous versions did not have this feature, that is, they made a web page accessible to all systems.

Fig. The parameter "noindex" is used to prohibit indexation by search engines. Also on the screenshot you can see the condition for checking the user’s use of the web browser.
For a coupon, scammers offer the user to share this message with ten friends or publish it in three WhatsApp groups. This notification is equipped with a special countdown counter, which counts 225 seconds “during which the message is valid”. Below is the source code that is responsible for the implementation of this part of the malicious campaign. He is responsible for implementing the further distribution of the message and redirecting the user to the desired resource.

Fig. URLs to redirect the user.
It should be noted that similar malicious campaigns (without the block of code that is highlighted in the screenshot above) can be extended to facebook.
After performing these actions, scammers indicate to the user that he could not win the discount and he needs to try next time. “Thank you for participating. You did not win; try again and good luck. ”

Fig. The last stage of fraud with the proposal of new "coupons".
An essential detail is the ability for attackers to automatically change the language of messages and currency depending on the user's IP address and the language settings of the web browser.
Ultimately, the user will be redirected to one of the websites on which the attackers earn. This can be a simple redirect (click), for which the authors of a malicious campaign will receive a few cents or register on any site where payment is made for registering new subscribers.

Fig. Services and websites to which the user is redirected.
Protection measures
Improving user literacy and awareness is the best way to protect against this kind of fraud, which uses social engineering techniques. Although there was nothing new in this fraudulent campaign, it is still relevant to attackers. Unfortunately, many WhatsApp users still fall victim to it.
In order not to become a victim if you receive a fraudulent message in WhatsApp, you should follow these simple rules.
- Do not follow suspicious links in incoming WhatsApp text messages or other instant messengers, as well as social services.
- Avoid publishing your personal information in a reply message if the source of the original message is unknown or unreliable.
- Do not install applications on smartphones from third-party sources. For example, to install applications, you should use the Google Play and Apple App Store.
- Do not share suspicious messages with your friends and contacts.
- Use anti-virus software that protects malicious and fraudulent activity, including malicious websites, to protect it.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/302310/
All Articles