Measurement collection system using a weather station
 It would seem that everyone who masters arduino, first of all designs or repeats an instrument for measuring temperature and (or) other environmental parameters. Only the majority of such structures, unfortunately, are of little use in the household - as a workout will fit, but there is no benefit. Let's try to fix this flaw. In the article I will talk about the creation of a complex for measuring and storing any data using the example of collecting readings from sensors for temperature, air humidity and atmospheric pressure. I will begin with the requirements for the device and the description of the exchange protocol, I will end with a web-service for receiving data from the database. Detailed calculations and walkthroughs will not be, but there will be a little theory and a lot of code.
It would seem that everyone who masters arduino, first of all designs or repeats an instrument for measuring temperature and (or) other environmental parameters. Only the majority of such structures, unfortunately, are of little use in the household - as a workout will fit, but there is no benefit. Let's try to fix this flaw. In the article I will talk about the creation of a complex for measuring and storing any data using the example of collecting readings from sensors for temperature, air humidity and atmospheric pressure. I will begin with the requirements for the device and the description of the exchange protocol, I will end with a web-service for receiving data from the database. Detailed calculations and walkthroughs will not be, but there will be a little theory and a lot of code.This story began one day when the wire of the remote sensor of the home weather station was bitten by one of the pets. I repaired the wire, but after that incident the device began to periodically show a lie. There is a lack of analog measurement, when a small impact is enough to completely distort the data. This case and pushed me to make their own similar complex.
After thinking about the problem, we got the following specification:
- Sensors must be digital, with acceptable accuracy. Temperature - DS1820, humidity - DHT22, air pressure - BMP085. The choice of sensors was due to their presence “in the bins”. By the way, the temperature measurement function is in all these three types, but we will use the DS1820, since they can be switched on in parallel.
- These sensors should be connected on the fly, i.e. do not require operator intervention.
- The controller to which the sensors must be connected must be accessible. My choice fell on the Arduino, because it is inexpensive and has a minimum level of entry.
- The controller must be connected to the computer via the serial port. We will use a USB2Serial adapter as a common and inexpensive solution.
- Since the controller may be located at some distance from the computer, and there may be several controllers on one port, the protocol of the exchange must provide protection against data corruption and the possibility of addressing devices.
- The complex must store in the database the history of all measurements. My choice is SQLite.
- All programs for working with the controller must be portable. work equally on different platforms without major improvements. My choice is Python 2.7.
Description of the exchange protocol between the computer and the controller
Since the data exchange with the controller will be asynchronous, with packets of a previously unknown length, the SLIP was taken as the basis of the channel protocol. This is a protocol in which data is transmitted using SLIP frames. The borders of the SLIP frame is the END (0xC0) flag. If the frame contains byte 0xC0, it is replaced by the escape sequence 0xDB, 0xDC, and if the byte is encountered ESC (0xDB), it is replaced by the sequence (0xDB, 0xDD). The inverse transform is symmetric.
')
In SLIP frames, we will wrap messages with a pre-calculated checksum.
To calculate the checksum, the CRC16 algorithm with the polynomial 0xA001 (modbus) was applied:
- The 16-bit register (CRC) is loaded 0xFFFF.
- The first byte of the message is added by EXCLUSIVE OR with the contents of the CRC register. The result is placed in the CRC register.
- The CRC register is shifted to the right by 1 bit, the most significant bit is filled with 0.
- (If the low-order bit is 1): The content of the CRC is added to the EXCLUSIVE OR with the polynomial number 0xA001.
- Steps 3 and 4 are repeated eight times.
- Steps 2-5 are repeated for all subsequent bytes of the package.
- The final content of the CRC register is the checksum.
The CRC is added to the end of the message in the format of the low byte first, then the high byte.
Application Exchange Protocol
The format of the request to the device
instrument_address (1 byte) class (1 byte) [method (1 byte)] [data (N byte)]
Device response format:
instrument_address (1 byte) data (N bytes)class 0 (PING)
returns 0x55 0xAA 0x55 0xAA
class 1 (INFO)
methods
0 - request for the number of temperature sensors
returns: (unsigned char) number
1 - request readings and serial numbers from temperature sensors
returns: ((float) temperature (8 bytes) sernum) * number of sensors
2 - request readings from the pressure sensor
returns: (int32_t) pressure (char) sernum
3 - request readings from the humidity sensor
returns: (float) moisture (byte) sernum
There are only two classes, but the reader, if he wishes, will be able, in an image and likeness, to expand the protocol with the required parameters.
Example
Request
Device Address - 00
Class - 00 (PING)
Checksum - 01 B0
Final package - C0 00 00 B0 01 C0
Answer
Device response - C0 00 55 AA 55 AA C3 AA C0
Device Address - 00
Checksum - AA C3
Message - 55 AA 55 AA (PING response)
Device layout
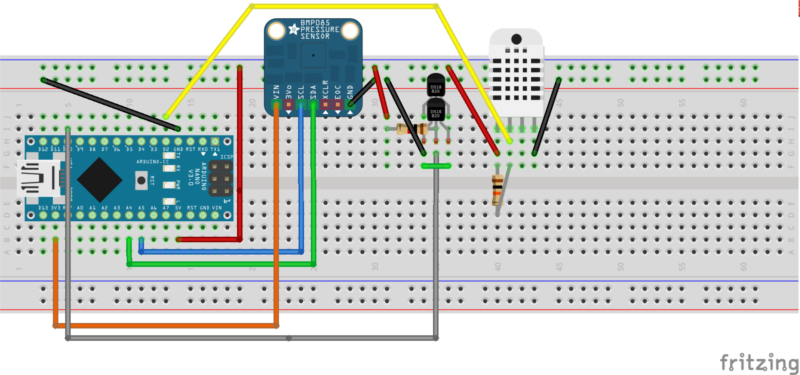
Photo layout

Here is a photo of the intermediate version with the support of the screen from Nokia (the code is in the repository by the link at the end of the article).
Photos of the finished product


Source:
Sketch for Arduino
#include <DallasTemperature.h> #include <Adafruit_BMP085.h> #include <OneWire.h> #include <DHT.h> #define ONE_WIRE_BUS 10 #define TEMPERATURE_PRECISION 9 #define DHTPIN 2 #define DHTTYPE DHT22 OneWire oneWire(ONE_WIRE_BUS); DallasTemperature sensors(&oneWire); Adafruit_BMP085 bmp; const unsigned char MAXNUMBERS = 10; DeviceAddress addresses[MAXNUMBERS]; unsigned char numbers; DHT dht(DHTPIN, DHTTYPE); char readbuf[50]; char writebuf[130]; char tmpbuf[50]; int msglen = 0; const int bufLength = 8; const char SLIP_END = '\xC0'; const char SLIP_ESC = '\xDB'; const char SLIP_ESC_END = '\xDC'; const char SLIP_ESC_ESC = '\xDD'; const char CS_PING = '\x00'; const char CS_INFO = '\x01'; const char LOC_ADR = '\x00'; int transferData(char *buf, unsigned char cnt) { Serial.print(SLIP_END); for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) { switch (buf[i]) { case SLIP_END: Serial.print(SLIP_ESC); Serial.print(SLIP_ESC_END); break; case SLIP_ESC: Serial.print(SLIP_ESC); Serial.print(SLIP_ESC_ESC); break; default: Serial.print(buf[i]); break; } } Serial.print(SLIP_END); } unsigned short getCRC(char *buf, unsigned char cnt) { unsigned short temp, temp2, flag; temp = 0xFFFF; for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) { temp ^= (unsigned char) buf[i]; for (int j = 1; j <= 8; j++) { flag = temp & 0x0001; temp >>= 1; if (flag) temp ^= 0xA001; } } temp2 = temp >> 8; temp = (temp << 8) | temp2; temp &= 0xFFFF; return temp; } int addCRC(char *buf, unsigned char cnt) { unsigned short crc = getCRC(buf, cnt); memcpy(&buf[cnt], &crc, 2); return cnt + 2; } void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); bmp.begin(); sensors.begin(); dht.begin(); } void loop() { float humidity = dht.readHumidity(); int32_t pressure = (int32_t)(bmp.readPressure() / 133.3224); numbers = 0; for (int i = 0; i < MAXNUMBERS; i++) { if (!sensors.getAddress(addresses[i], i)) break; numbers++; } for (unsigned char i = 0; i < numbers; i++) { sensors.setResolution(addresses[i], TEMPERATURE_PRECISION); } sensors.requestTemperatures(); if (msglen) { unsigned short msgcrc; memcpy(&msgcrc, &readbuf[msglen-2], 2); unsigned short crc = getCRC(readbuf, msglen-2); if (crc == msgcrc) { char adr = readbuf[0]; char cs = readbuf[1]; char mtd = readbuf[2]; int len; unsigned char n; float temp; if (adr == LOC_ADR) { switch (cs) { case CS_PING: writebuf[0] = LOC_ADR; writebuf[1] = '\x55'; writebuf[2] = '\xAA'; writebuf[3] = '\x55'; writebuf[4] = '\xAA'; len = addCRC(writebuf, 5); delay(100); transferData(writebuf, len); break; case CS_INFO: switch (mtd) { case 0: writebuf[0] = LOC_ADR; writebuf[1] = numbers; len = addCRC(writebuf, 2); delay(100); transferData(writebuf, len); break; case 1: writebuf[0] = LOC_ADR; writebuf[1] = numbers; for (int i=0; i < numbers; i++) { temp = sensors.getTempC(addresses[i]); memcpy(&writebuf[i*12+2], &temp, 4); memcpy(&writebuf[i*12+6], &addresses[i], 8); } len = addCRC(writebuf, numbers*12+2); delay(100); transferData(writebuf, len); break; case 2: writebuf[0] = LOC_ADR; memcpy(&writebuf[1], &pressure, 4); writebuf[5] = 0; len = addCRC(writebuf, 6); delay(100); transferData(writebuf, len); break; case 3: writebuf[0] = LOC_ADR; memcpy(&writebuf[1], &humidity, 4); writebuf[5] = 0; len = addCRC(writebuf, 6); delay(100); transferData(writebuf, len); break; } break; } } } msglen = 0; } } void serialEvent() { msglen = readCommand(readbuf); } int readCommand(char *buf) { int i = 0; bool escaped = false; char c = (char) Serial.read(); if (c == SLIP_END) { bool beginflag = true; while (beginflag) { char c1 = (char) Serial.read(); switch (c1) { case SLIP_END: return i; break; case SLIP_ESC: escaped = true; break; case SLIP_ESC_END: if (escaped) { buf[i] = SLIP_END; escaped = false; } else buf[i] = c1; i++; break; case SLIP_ESC_ESC: if (escaped) { buf[i] = SLIP_ESC; escaped = false; } else buf[i] = c1; i++; break; default: if (escaped) { return 0; } else buf[i] = c1; i++; break; } } } return i; } Class slip.py
class SlipConv: def __init__(self): self.started = False self.escaped = False self.packet = '' self.SLIP_END = '\xc0' self.SLIP_ESC = '\xdb' self.SLIP_ESC_END = '\xdc' self.SLIP_ESC_ESC = '\xdd' self.serialComm = None def __getcrc(self, buf): temp = 0xffff for c in buf: i = ord(c) temp ^= i j = 1 while j <= 8: flag = temp & 0x0001 temp >>= 1 if flag > 0: temp ^= 0xa001 j += 1 temp2 = temp >> 8 temp = (temp << 8) | temp2 temp &= 0xffff return temp def addcrc(self, packet): crc = self.__getcrc(packet) return packet + chr(crc & 0xff) + chr(crc >> 8) def checkcrc(self, packet): tmpcrc = self.__getcrc(self.getmsgpart(packet)) msgcrc = self.getcrcpart(packet) return (chr(tmpcrc & 0xff) + chr(tmpcrc >> 8)) == msgcrc def getcrcpart(self, packet): return packet[len(packet)-2:len(packet)] def getmsgpart(self, packet): return packet[0:len(packet)-2] def unslip(self, stream): packetlist = '' for char in stream: if char == self.SLIP_END: if self.started: packetlist += self.packet else: self.started = True self.packet = '' elif char == self.SLIP_ESC: self.escaped = True elif char == self.SLIP_ESC_END: if self.escaped: self.packet += self.SLIP_END self.escaped = False else: self.packet += char elif char == self.SLIP_ESC_ESC: if self.escaped: self.packet += self.SLIP_ESC self.escaped = False else: self.packet += char else: if self.escaped: self.packet = '' self.escaped = False return '' else: self.packet += char self.started = True self.started = False return packetlist def slip(self, packet): encoded = self.SLIP_END for char in packet: if char == self.SLIP_END: encoded += self.SLIP_ESC + self.SLIP_ESC_END elif char == self.SLIP_ESC: encoded += self.SLIP_ESC + self.SLIP_ESC_ESC else: encoded += char encoded += self.SLIP_END return encoded Class protocol.py
# - *- coding: utf- 8 - *- import sys import serial import time import math from slip import SlipConv import struct class Protocol: def __init__(self, port, baudrate, logon): self.log = logon self.slipC = SlipConv() self.SLIP_END = '\xc0' self.ser = serial.Serial() self.ser.port = port self.ser.baudrate = baudrate self.ser.timeout = 5 try: self.ser.open() except serial.SerialException as e: print ('Oops! IO Error. Check ' + port + ' at ' + str(baudrate) + '.') sys.exit(1) if self.log: print ('Opened ' + port + ' at ' + str(baudrate) + '.') time.sleep(2) def printPacket(self, packet): print ' '.join("%X" % ord(c) if ord(c) > 0x0f else '0' + "%X" % ord(c) for c in packet) def sendCommand(self, packet): crcPack = self.slipC.addcrc(packet) out = self.slipC.slip(crcPack) self.ser.write(out) if self.log: print ('Sent ' + str(len(out)) + ' bytes: '), self.printPacket(out) def receiveAnswer(self): packet = '' char = '' firsttime = time.time() while (time.time() - firsttime) < self.ser.timeout: char = self.ser.read(1) if char == self.SLIP_END: break if char != self.SLIP_END: print 'Timeout error!!! Check the connections' sys.exit(1) packet += char beginflag = True while beginflag: c = self.ser.read(1) packet += c if c == self.SLIP_END: beginflag = False if self.log: print ('Received ' + str(len(packet)) + ' bytes: '), self.printPacket(packet) unsliped = self.slipC.unslip(packet) if self.slipC.checkcrc(unsliped): if self.log: print ('CRC - OK') return self.slipC.getmsgpart(unsliped) else: if self.log: print ('BAD CRC,'), print 'received ', self.printPacket(packet) return '' def ping(self, adr): if self.log: print ('Ping adr=' + str(adr)) self.sendCommand(chr(adr) + chr(0)) if self.receiveAnswer() == ((chr(0) + chr(0x55) + chr(0xAA) + chr(0x55) + chr(0xAA))): if self.log: print ('Ping to adr=' + str(adr) + ' - OK') return True else: return False def getTemp(self, adr): if self.log: print ('Get a temperature from sensors.') self.sendCommand(chr(adr) + chr(1) + chr(1)) res = self.receiveAnswer() num = ord(res[1]) values = [] for i in range(0, num): temp, = struct.unpack('<f', res[i*12+2:i*12+6]) sernum = res[i*12+6:i*12+14] values.append((temp, sernum)) if self.log: print 'It has ' + str(num) + ' temperature sensors:' print ("%.1f" % temp + 'C on the sensor with the serial number'), self.printPacket(sernum) return values def getPressure(self, adr): if self.log: print ('Get the atmospheric pressure.') self.sendCommand(chr(adr) + chr(1) + chr(2)) res = self.receiveAnswer() pressure, = struct.unpack('<i', res[1:5]) sernum = res[5] if self.log: if 10 < pressure < 1000: print (str(pressure) + ' mmHg on the sensor with the serial number'), self.printPacket(sernum) else: print 'The pressure sensor doesn\'t exist' return pressure, sernum def getHumidity(self, adr): if self.log: print ('Get a humidity.') self.sendCommand(chr(adr) + chr(1) + chr(3)) res = self.receiveAnswer() humidity, = struct.unpack('<f', res[1:5]) sernum = res[5] if self.log: if math.isnan(humidity): print 'The humidity sensor doesn\'t exist' else: print (str(humidity) + '% on the sensor with the serial number'), self.printPacket(sernum) return humidity, sernum def close(self): self.ser.close() A bit about the host computer
Absolutely any computer with installed Python 2.7 and SQLite can be used as a host. To work you need to install the library pyserial .The choice fell on the already quite old Asus WL-500gp router.
I installed OpenWrt on it, mounted USB-flash, installed Python, SQLite and libraries.
A test script can be used to check the device’s performance.
Tst.py script
#!/usr/bin/python import math from protocol import Protocol deviceAddress = 0 serialPort = '/dev/ttyUSB0' baudRate = 9600 logEnabled = True device = Protocol(serialPort, baudRate, logEnabled) if device.ping(deviceAddress): pressure, sernumP = device.getPressure(deviceAddress) if 10 < pressure < 1000: print ('Pressure - ' + str(pressure) + ' mmHg') humidity, sernumH = device.getHumidity(deviceAddress) if not math.isnan(humidity): print ('Humidity - ' + str(humidity) + '%') values = device.getTemp(deviceAddress) i = 1 for (temperature, sn) in values: print ('T' + str(i) + ' - ' + "%.1f" % temperature + ' C, sensor'), device.printPacket(sn) i += 1 device.close() If everything works fine, the output will be something like this:
Opened /dev/ttyUSB0 at 9600. Ping adr=0 Sent 6 bytes: C0 00 00 B0 01 C0 Received 9 bytes: C0 00 55 AA 55 AA C3 AA C0 CRC - OK Ping to adr=0 - OK Get the atmospheric pressure. Sent 7 bytes: C0 00 01 02 91 F1 C0 Received 10 bytes: C0 00 EB 02 00 00 00 B4 25 C0 CRC - OK 747 mmHg on the sensor with the serial number 00 Pressure - 747 mmHg Get a humidity. Sent 7 bytes: C0 00 01 03 51 30 C0 Received 10 bytes: C0 00 9A 99 33 42 00 34 B6 C0 CRC - OK 44.9000015259% on the sensor with the serial number 00 Humidity - 44.9000015259% Get a temperature from sensors. Sent 7 bytes: C0 00 01 01 90 B1 C0 Received 19 bytes: C0 00 01 00 80 BD 41 10 60 3B 4F 00 08 00 DB DC 21 1B C0 CRC - OK It has 1 temperature sensors: 23.7C on the sensor with the serial number 10 60 3B 4F 00 08 00 C0 T1 - 23.7 C, sensor 10 60 3B 4F 00 08 00 C0 Now you need to save the measurement results in the database.
We create the following structure: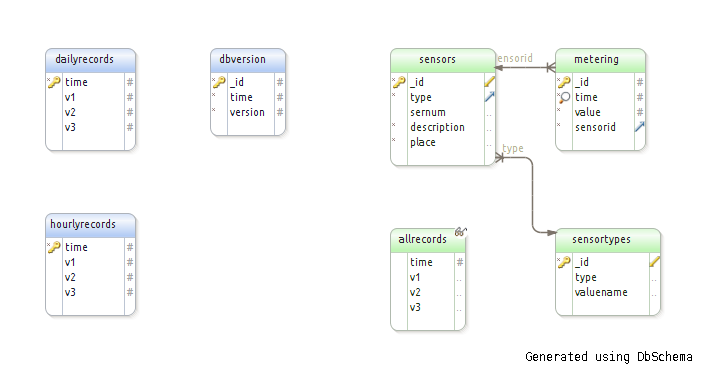
The base contains three main tables - sensortypes, sensors and metering (types, sensors, measurements) and one allrecords view (flat measurement table).
The hourlyrecords and dailyrecords tables contain hourly and daily average data.
In the dbversion table, the database version.
Immediately make a reservation - I did not use any built-in SQLite features that go beyond the limits of SQL-92, which appeared in recent versions, since I had 3.8.2 SQLite and had no reason to update it. But there is a plus, this code can be used from any database with minimal changes.
A small class was written to work with the database:
Class dbhelper.py
# - *- coding: utf- 8 - *- import sqlite3 import time from datetime import datetime class DBHelper: dbconnect = None cursor = None version = 1 def __init__(self, fileName): self.dbconnect = sqlite3.connect(fileName) self.dbconnect.text_factory = str self.cursor = self.dbconnect.cursor() self.cursor.execute('CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS dbversion' + '(_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT NOT NULL,' + 'time INTEGER NOT NULL,' + 'version INTEGER NOT NULL)') self.cursor.execute('SELECT version FROM dbversion') if len(self.cursor.fetchall()) == 0: self.cursor.execute('INSERT INTO dbversion (time, version) VALUES (?,?)', (int(time.time()), self.version)) self.cursor.execute('CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS sensortypes' + '(_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT NOT NULL,' + 'type TEXT,' + 'valuename TEXT)') self.cursor.execute('SELECT type FROM sensortypes') if len(self.cursor.fetchall()) == 0: self.cursor.execute('INSERT INTO sensortypes (type, valuename) VALUES (?,?)', ('', '. ')) self.cursor.execute('INSERT INTO sensortypes (type, valuename) VALUES (?,?)', ('', ' . .')) self.cursor.execute('INSERT INTO sensortypes (type, valuename) VALUES (?,?)', ('', '%')) self.cursor.execute('CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS sensors' + '(_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT NOT NULL,' + 'type INTEGER NOT NULL,' + 'sernum TEXT,' + 'description TEXT NOT NULL,' + 'place TEXT NOT NULL,' + 'FOREIGN KEY (type) REFERENCES sensortypes(_id))') self.cursor.execute('CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS metering' + '(_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT NOT NULL,' + 'time INTEGER NOT NULL,' + 'value REAL NOT NULL,' + 'sensorid INTEGER NOT NULL,' + 'FOREIGN KEY (sensorid) REFERENCES sensors(_id))') self.cursor.execute('CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS hourlyrecords' + '(time INTEGER PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL)') self.cursor.execute('CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS dailyrecords' + '(time INTEGER PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL)') self.cursor.execute('CREATE UNIQUE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS "avgday" on dailyrecords (time ASC)') self.cursor.execute('CREATE UNIQUE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS "avghour" on hourlyrecords (time ASC)') self.cursor.execute('CREATE UNIQUE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS "mid" on metering (_id ASC)') self.cursor.execute('CREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS "time" on metering (time ASC)') self.cursor.execute('CREATE UNIQUE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS "sid" on sensors (_id ASC)') self.cursor.execute('CREATE UNIQUE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS "stid" on sensortypes (_id ASC)') def updateAvgTables(self): self.cursor.execute('SELECT MAX(_id) FROM sensors') number = self.cursor.fetchone()[0] self.cursor.execute('SELECT * FROM hourlyrecords ORDER BY ROWID ASC LIMIT 1') columnnamelist = [tuple[0] for tuple in self.cursor.description] if number > (len(columnnamelist)-1): for i in range(len(columnnamelist), number+1): self.cursor.execute('ALTER TABLE hourlyrecords ADD COLUMN v%s REAL' % str(i)) self.cursor.execute('ALTER TABLE dailyrecords ADD COLUMN v%s REAL' % str(i)) self.cursor.execute('SELECT MIN(time) FROM metering') minrealtime = self.cursor.fetchone()[0] if minrealtime is not None: self.cursor.execute('SELECT MAX(time) FROM metering') maxrealtime = self.cursor.fetchone()[0] self.cursor.execute('SELECT MAX(time) FROM hourlyrecords') maxhourlyavgtime = self.cursor.fetchone()[0] self.cursor.execute('SELECT MAX(time) FROM dailyrecords') maxdailyavgtime = self.cursor.fetchone()[0] firsthourtime = 3600 firstdaytime = 86400 if maxhourlyavgtime is None: maxhourlyavgtime = minrealtime firsthourtime = 0 if maxdailyavgtime is None: maxdailyavgtime = minrealtime firstdaytime = 0 begintimestamp = datetime.fromtimestamp(float(maxhourlyavgtime)) endtimestamp = datetime.fromtimestamp(float(maxrealtime)) firstedge = datetime(begintimestamp.year, begintimestamp.month, begintimestamp.day, begintimestamp.hour) secondedge = datetime(endtimestamp.year, endtimestamp.month, endtimestamp.day, endtimestamp.hour) begin = int(time.mktime(firstedge.timetuple())) + firsthourtime end = int(time.mktime(secondedge.timetuple()))-1 for i in range(begin, end, 3600): self.cursor.execute('SELECT AVG(time) FROM metering WHERE time >= %s AND time <= %s' % (str(i), str(i+3599))) if self.cursor.fetchone()[0] is None: continue insert = 'INSERT INTO hourlyrecords (time' select = 'SELECT CAST(AVG(time) AS INTEGER)' for v in range(1, number+1): insert += ', v%s' % str(v) select += ', AVG(CASE WHEN sensorid=%s THEN value ELSE NULL END)' % str(v) insert += ') ' select += ' FROM metering WHERE time >= %s AND time <= %s' % (str(i), str(i+3599)) self.cursor.execute(insert + select) begintimestamp = datetime.fromtimestamp(float(maxdailyavgtime)) endtimestamp = datetime.fromtimestamp(float(maxrealtime)) firstedge = datetime(begintimestamp.year, begintimestamp.month, begintimestamp.day) secondedge = datetime(endtimestamp.year, endtimestamp.month, endtimestamp.day) begin = int(time.mktime(firstedge.timetuple())) + firstdaytime end = int(time.mktime(secondedge.timetuple()))-1 for i in range(begin, end, 86400): self.cursor.execute('SELECT AVG(time) FROM metering WHERE time >= %s AND time <= %s' % (str(i), str(i+85399))) if self.cursor.fetchone()[0] is None: continue insert = 'INSERT INTO dailyrecords (time' select = 'SELECT CAST(AVG(time) AS INTEGER)' for v in range(1, number+1): insert += ', v%s' % str(v) select += ', AVG(CASE WHEN sensorid=%s THEN value ELSE NULL END)' % str(v) insert += ') ' select += ' FROM metering WHERE time >= %s AND time <= %s' % (str(i), str(i+85399)) query = insert + select self.cursor.execute(query) def __makeDict(self, raw): res = {'time': raw[0]} for i in range(2, len(raw)+1): res[str(i-1)] = raw[i - 1] return res def getSensorId(self, sensorType, sernum): self.cursor.execute('SELECT _id FROM sensors WHERE sernum=? AND type=?', (sernum, sensorType)) selres = self.cursor.fetchall() if len(selres) > 0: sensorId = selres[0][0] else: self.cursor.execute('INSERT INTO sensors (type, sernum, description, place) VALUES (?,?,?,?)', (sensorType, sernum, '', '')) self.cursor.execute('SELECT _id FROM sensors WHERE sernum=? AND type=?', (sernum, sensorType)) sensorId = self.cursor.fetchone()[0] return sensorId def storeValue(self, time, value, sensorId): self.cursor.execute('INSERT INTO metering (time, value, sensorid) VALUES (?,?,?)', (int(time), value, sensorId)) def getLast(self): self.cursor.execute('SELECT MAX(_id) FROM sensors') number = self.cursor.fetchone()[0] query = 'SELECT time' for i in range(1, number+1): query += ', (SELECT value FROM metering WHERE sensorid=%s AND time=m.time)' % str(i) query += ' FROM metering m WHERE time=(SELECT MAX(time) FROM metering) GROUP BY time' self.cursor.execute(query) return [self.__makeDict(self.cursor.fetchone()), ] def getInterval(self, minTime = None, maxTime = None): self.cursor.execute('SELECT MAX(_id) FROM sensors') number = self.cursor.fetchone()[0] query = 'SELECT time' for i in range(1, number+1): query += ', (SELECT value FROM metering WHERE sensorid=%s AND time=m.time)' % str(i) if minTime is not None and maxTime is not None: query += ' FROM metering m WHERE (time >= ? AND time <= ?) GROUP BY time' self.cursor.execute(query, (minTime, maxTime)) else: query += ' FROM metering m GROUP BY time ORDER BY time' self.cursor.execute(query) return [self.__makeDict(raw) for raw in self.cursor.fetchall()] def updateAllRecordsView(self): self.cursor.execute('SELECT MAX(_id) FROM sensors') number = self.cursor.fetchone()[0] self.cursor.execute('DROP VIEW IF EXISTS allrecords') query = 'CREATE VIEW allrecords AS SELECT time time' for i in range(1, number+1): query += ', max(CASE WHEN sensorid=%s THEN value ELSE NULL END) v%s' % (str(i), str(i)) query += ' FROM metering GROUP BY time ORDER BY time' self.cursor.execute(query) return def getAll(self): return self.getInterval() def getSensors(self): self.cursor.execute('SELECT s._id, st.type, s.sernum, s.description, s.place, st.valuename FROM sensors s, sensortypes st WHERE s.type=st._id ORDER BY s._id') res = [] for raw in self.cursor.fetchall(): res.append({'id': raw[0], 'type': raw[1], 'sernum': ' '.join("%X" % ord(c) if ord(c) > 0x0f else '0' + "%X" % ord(c) for c in raw[2]), 'description': raw[3], 'place': raw[4], 'valuename': raw[5]}) return res def updateSensor(self, sensorid, description, place): self.cursor.execute('UPDATE sensors SET description = ?, place = ? WHERE _id = ?', (description, place, sensorid)) def getDBVersion(self): self.cursor.execute('SELECT version FROM dbversion WHERE _id=(SELECT MAX(_id) FROM dbversion)') return self.cursor.fetchone()[0] def close(self): self.dbconnect.commit() The next step is to combine the poll of sensors with saving in the database
Getweather.py poll script
#!/usr/bin/python # - *- coding: utf- 8 - *- import math from protocol import Protocol import sys import time import os from dbhelper import DBHelper deviceAddress = 0 serialPort = '/dev/ttyUSB0' baudRate = 9600 logEnabled = True dbFileName = 'weatherstation.db' # modulePath = os.path.abspath('/home/weather') + '/' # dbFileName = modulePath + 'weatherstation.db' termSensorType = 1 pressureSensorType = 2 humiditySensorType = 3 if len(sys.argv) == 3: serialPort = sys.argv[1] baudRate = sys.argv[2] deviceAddress = sys.argv[3] logEnabled = sys.argv[4] elif len(sys.argv) == 1: print ('Command line: getweather.py serial_port serial_speed') print ('Trying with serial_port = ' + serialPort + ' and serial_speed = ' + str(baudRate)) else: print ('Command line: getweather.py serial_port serial_speed') sys.exit(1) currenttime = time.time() db = DBHelper(dbFileName) device = Protocol(serialPort, baudRate, logEnabled) if device.ping(deviceAddress): pressure, sernumP = device.getPressure(deviceAddress) if 10 < pressure < 1000: print ('Pressure - ' + str(pressure) + ' mmHg') pressureSensorId = db.getSensorId(pressureSensorType, sernumP) db.storeValue(currenttime, pressure, pressureSensorId) humidity, sernumH = device.getHumidity(deviceAddress) if not math.isnan(humidity): print ('Humidity - ' + str(humidity) + '%') humiditySensorID = db.getSensorId(humiditySensorType, sernumH) db.storeValue(currenttime, humidity, humiditySensorID) values = device.getTemp(deviceAddress) i = 1 for (temperature, sn) in values: print ('T' + str(i) + ' - ' + "%.1f" % temperature + ' C, sensor'), device.printPacket(sn) i += 1 termSensorId = db.getSensorId(termSensorType, sn) db.storeValue(currenttime, temperature, termSensorId) device.close() db.updateAvgTables() db.updateAllRecordsView() db.close() Next, copy the files to our host computer, add a task to the scheduler to run getweater.py every 5 minutes, and leave our device to collect statistics.
Now you need to get this data somehow. Develop API:
/ws.py will return the html page with the last entry from the database.
/ws.py?mtd=last - the last entry in the database in json-string format.
/ws.py?mtd=intervalmin=XXmax=YY - the range of records between the dates min and max in the format of a json string.
/ws.py?mtd=all - all entries in json string format.
/ws.py?mtd=version - database version in json-string format.
/sensors.py - html-page with a list of sensors.
To do this, we write a simple web-service and editor of sensors.
Ws.py script
#!/usr/bin/python # - *- coding: utf- 8 - *- import sys import os import json import cgi import time modulePath = os.path.dirname(__file__) + '/../../' # modulePath = os.path.abspath('/home/weather') + '/' sys.path.append(modulePath) from dbhelper import DBHelper method = 'mtd' version = 'version' minThr = 'min' maxThr = 'max' dbFileName = modulePath + 'weatherstation.db' # dbFileName = modulePath + 'genweather.db' db = DBHelper(dbFileName) def makeJSON(records): return json.JSONEncoder().encode({'sensors': db.getSensors(), 'records': records}) args = cgi.FieldStorage() if len(args) == 0: sensors = db.getSensors() records = db.getLast() print 'Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8' print defaulthtml = """ <title></title> <h1></h1> <hr>""" defaulthtml += '<P>' + time.strftime("%d.%m.%Y %H:%M", time.localtime(records[0]['time'])) + '</P>' defaulthtml += '<table border=0>' for i in range(1, len(sensors) + 1): if records[0][str(i)] is not None: defaulthtml += '<tr>' defaulthtml += '<td>' + str(sensors[i - 1]['id']) + '</td>' defaulthtml += '<td>' + sensors[i - 1]['type'] + '</td>' defaulthtml += '<td>' + sensors[i - 1]['description'] + '</td>' defaulthtml += '<td>' + sensors[i - 1]['place'] + '</td>' defaulthtml += '<td>' + "%.1f" % records[0][str(i)] + '</td>' defaulthtml += '<td>' + sensors[i - 1]['valuename'] + '</td>' defaulthtml += '</tr>' defaulthtml += '<p><a href="sensors.py"></a></p>' print defaulthtml elif method in args: if args[method].value == 'last': print "Content-type: application/json" print print (makeJSON(db.getLast())) elif args[method].value == 'all': print "Content-type: application/json" print print (makeJSON(db.getAll())) elif args[method].value == 'interval': if minThr in args: if maxThr in args: print "Content-type: application/json" print print (makeJSON(db.getInterval(args[minThr].value, args[maxThr].value))) elif args[method].value == version: print "Content-type: application/json" print print (json.JSONEncoder().encode({version: db.getDBVersion()})) db.close() Script sensors.py
#!/usr/bin/python # - *- coding: utf- 8 - *- import sys import os import cgi modulePath = os.path.dirname(__file__) + '/../../' # modulePath = os.path.abspath('/home/weather') + '/' sys.path.append(modulePath) from dbhelper import DBHelper method = 'mtd' sensorNumber = 'sensornumber' dbFileName = modulePath + 'weatherstation.db' db = DBHelper(dbFileName) args = cgi.FieldStorage() if len(args) == 0: sensors = db.getSensors() print 'Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8' print sensorshtml = """ <title></title> <h1></h1> <hr> <table border=0> <tr> <td> № </td> <td></td> <td> s/n </td> <td></td> <td> </td> <td>. </td> </tr>""" url = 'sensors.py?mtd=sensor&' for s in sensors: sensorshtml += '<tr>' sensorshtml += '<td>' + '<a href="' + url + sensorNumber + '=' + str(s['id']) + '">' + str(s['id']) + '</a></td>' sensorshtml += '<td>' + '<a href="' + url + sensorNumber + '=' + str(s['id']) + '">' + s['type'] + '</a></td>' sensorshtml += '<td>' + '<a href="' + url + sensorNumber + '=' + str(s['id']) + '">' + s['sernum'] + '</a></td>' sensorshtml += '<td>' + '<a href="' + url + sensorNumber + '=' + str(s['id']) + '">' + s['description'] + '</a></td>' sensorshtml += '<td>' + '<a href="' + url + sensorNumber + '=' + str(s['id']) + '">' + s['place'] + '</a></td>' sensorshtml += '<td>' + '<a href="' + url + sensorNumber + '=' + str(s['id']) + '">' + s['valuename'] + '</a></td>' sensorshtml += '</tr>' print sensorshtml elif method in args: if args[method].value == 'sensor': if sensorNumber in args: numstr = args[sensorNumber].value if numstr.isdigit(): num = int(numstr) - 1 sensors = db.getSensors() if 0 <= num <= len(sensors): sensor = sensors[num] sensorshtml = """<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> </head> <body> <H1> </H1> <hr> <form method=POST action="sensors.py"> <B> № %s</B> <input type=text name=id value="%s" hidden> <B></B> <input type=text name=type value="%s" disabled> <B> s/n </B> <input type=text name=sernum value="%s" disabled> <B></B> <input type=text name=description value="%s"> <B> </B> <input type=text name=place value="%s"> <B>. </B> <input type=text name=valuename value="%s" disabled> <input type=submit name="save" value=""> </form> </body> </html>""" % (sensor['id'], sensor['id'], sensor['type'], sensor['sernum'], sensor['description'], sensor['place'], sensor['valuename']) print 'Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8' print print sensorshtml elif 'save' in args: description = cgi.escape(args['description'].value) if 'description' in args else '' place = cgi.escape(args['place'].value) if 'place' in args else '' sensorid = int(args['id'].value) print 'Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8' print db.updateSensor(sensorid, description, place) savehtml = """<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="refresh" content="1;url=sensors.py"> <title></title> </head>""" print savehtml db.close() These two scripts need to be placed in the cgi-bin directory of the web server (in my case, this is / www / cgi-bin), make them executable and give permissions to execute:
chmod -R 755 /www/cgi-bin chmod -R +x /www/cgi-bin For those who do not wish to allocate a separate computer for weather data collection and (or) do not want to install a full-fledged web server on their only one, I can recommend this script:
Webserver.py script
#!/usr/bin/python # - *- coding: utf- 8 - *- import BaseHTTPServer import CGIHTTPServer import cgitb cgitb.enable() server = BaseHTTPServer.HTTPServer handler = CGIHTTPServer.CGIHTTPRequestHandler server_address = ("", 8000) handler.cgi_directories = ["/cgi-bin"] httpd = server(server_address, handler) httpd.serve_forever() By running it on the command line, you will get a web server that allows you to debug cgi-scripts and simple pages. As a result, the following should turn out:
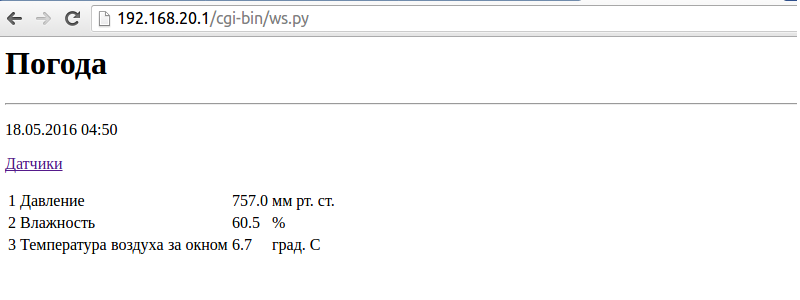
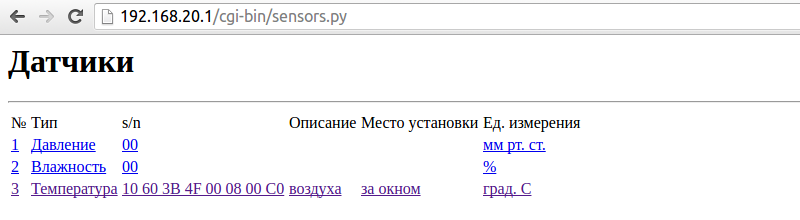
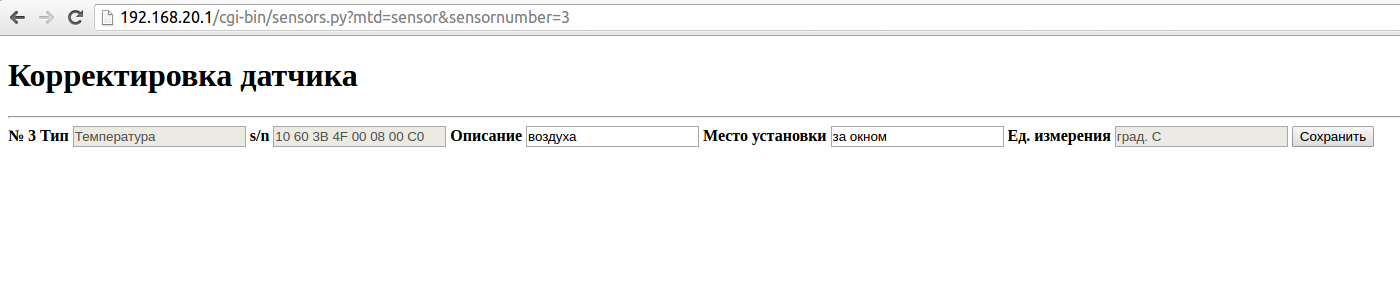
All code is available on github .
Conclusion
I described the problem of collecting weather data as an example of how to build a system for fixing any measurable processes — how to build an exchange protocol, how to protect data from distortion during transmission, and how to store it in a database. The reader, if desired, will be able to adapt this project to fit their needs.
You can write a separate article on how to use this data later, for example, how to make a remote control from an old abandoned Android tablet to display the observation diary.
Thank you for your attention, I hope it was interesting.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/302164/
All Articles