Local positioning methods
Our company “RTL-Service” develops and promotes local positioning solutions, in connection with which we have already introduced our readers to a variety of local positioning technologies. In today's article we will try to elaborate on local positioning methods based on the use of radio waves.
So, all methods can be divided into 3 groups, depending on the method of determining the location of the object (mobile device, MU):
')
I. Method based on the use of triangulation.
AoA (angle of arrival) is based on determining the direction to the signal source. For this purpose, base stations (BS) are used, equipped with several antennas, a rotating antenna or a phased antenna array. Having received the direction to the signal source from the BS, you can determine its location. The greater the number of BS, the more accurately you can determine this zone.
+ simple algorithms for determining the location of the mobile device;
+ the ability to work on various physical principles;
+ long range;
- the complexity of the antenna;
- low accuracy of determining the location of the mobile device.
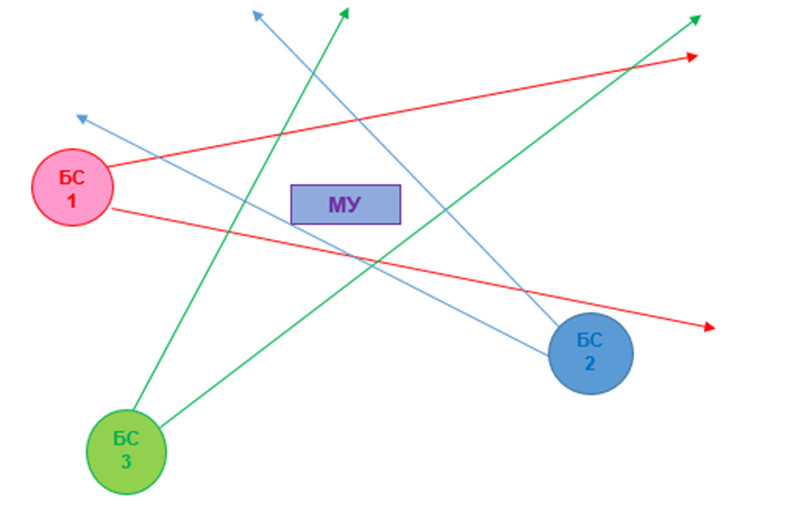
Ii. Methods based on the use of trilateration.

The ToA method (time of arrival) is based on measuring the propagation delay of a radio signal between a mobile device and a BS. The minimum number of measurements to determine the location of MU is three. The mobile device sends a signal at a time exactly known to the BS. The BS measures the time interval between sending a signal to a mobile device and receiving it. The distance is determined by the formula S = t * c (where t is time and c is the speed of light).
+ low power consumption by mobile device;
+ high accuracy of determining the location of the mobile device;
+ long range;
- the need for time synchronization on all BS and MU;
- complex algorithms for determining the location of the mobile device.
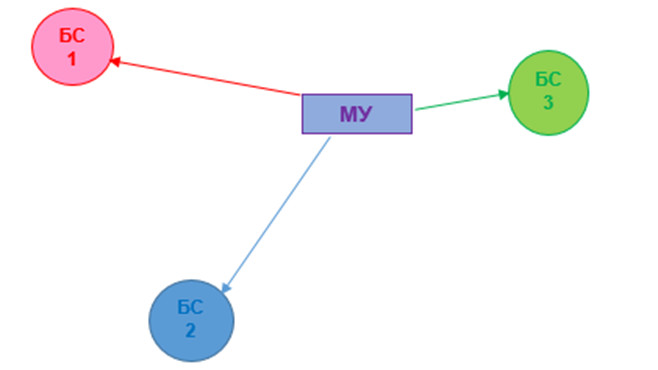
The TDoA method (time difference of arrival) is based on measuring the difference in time of signal transmission from a mobile device to a BS, with a synchronized clock and a known location. Knowing the difference in time to receive a signal using mathematical processing, you can get the distance from the mobile device to the base stations.
+ low power consumption by mobile device;
+ high accuracy of determining the location of the mobile device;
+ long range;
- the need for time synchronization between all mobile devices;
- complex algorithms for determining the location of the mobile device.
The ToF (time of flight) method is based on measuring the time that an electromagnetic wave spends on bridging the distance between a BS to a mobile device and returning to a BS after it is reflected from the ME. After receiving this time and knowing the speed of the wave, you can calculate the distance from the mobile device to the BS. S = t * c / 2.
+ mobile device - passive (does not consume energy);
+ high accuracy of determining the location of the mobile device;
+ long range;
+ no need for synchronization between devices;
- MU should reflect the electromagnetic wave in the direction of the BS;
- it is impossible to separate mobile devices.

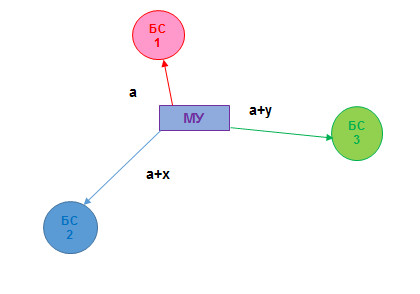
The TWR (two-way ranging) method is as follows: The BS records the signal departure time (T1), the mobile device records the signal acquisition time (t1), as well as the signal departure time back to the BS (t2). In the signal from the mobile node to the base station, the times t1 and t2 are transmitted. The BS receives the signal from the mobile device and records the time it was received. The distance is calculated using the formula S = ((T2-T1) - (t2-t1)) * c / 2. The initiator of the measurement can be a mobile device according to a similar algorithm.
There is also the SDS-TWR method (symmetrical double-sided two-way ranging) , which is based on repeating this procedure in the opposite direction, which can serve to verify the correctness of the calculation.
+ high accuracy of determining the location of the mobile device;
+ long range;
+ no need for synchronization between devices;
- high energy consumption MU.

NFER, near-field electromagnetic ranging is a method of measuring the distance in a near electromagnetic field, where there is a phase shift between the electric and magnetic components of an electromagnetic wave. BS emits an electromagnetic wave of a given frequency. A mobile device with the help of two antennas measures the amplitude of the separate magnetic and electrical components of the wave and calculates the phase shift between them. Knowing the wavelength and phase difference between them (this difference varies from 90 ° near the BS to zero at a distance equal to half the wavelength), one can calculate the distance from the BS to the device.
+ high accuracy of determining the location of the mobile device;
+ the ability to work in enclosed spaces;
- small radius of action;
- complex antennas;
- complex algorithms for determining the location of the mobile device.
Iii. Method based on measuring signal strength.
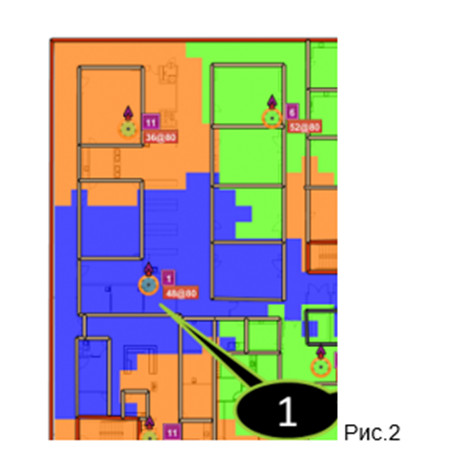
The RSSI, received signal strength indicator is an indicator of the power level of the received signal. This method allows you to determine the location of the device based on the strength of the signal received by the BS or vice versa. To use this method, either the signal power level is converted into a distance, or in accordance with the coverage maps (Fig. 2).
+ low power consumption by mobile device;
+ low cost;
- low accuracy of determining the location of the mobile device;
- complex algorithms for determining the location of MU.

It should be noted that for determining the location, most systems use a combination of methods, since This approach eliminates the disadvantages of one method by adding the properties of another. In addition, different systems set different tasks for themselves, which may also require different methods. The method of measuring the distance depends on the available equipment and the presence of synchronization between the BS and the mobile device.
For example, RTL-Service's RealTrac system locates using IMU inertial positioning technology and a combination of ToF and RSSI methods. As the main problem inherent in all inertial positioning systems is an error that accumulates over time, the use of ToF and RSSI methods in addition to this This problem can be eliminated by periodically associating the trajectory with local coordinates.
So, all methods can be divided into 3 groups, depending on the method of determining the location of the object (mobile device, MU):
- A method based on the use of triangulation (determining the location of a mobile device at angles relative to base stations).
- A method based on the use of trilateration (determining the location of a mobile device by distance from base stations).
- Method based on measuring signal strength.
')
I. Method based on the use of triangulation.
AoA (angle of arrival) is based on determining the direction to the signal source. For this purpose, base stations (BS) are used, equipped with several antennas, a rotating antenna or a phased antenna array. Having received the direction to the signal source from the BS, you can determine its location. The greater the number of BS, the more accurately you can determine this zone.
+ simple algorithms for determining the location of the mobile device;
+ the ability to work on various physical principles;
+ long range;
- the complexity of the antenna;
- low accuracy of determining the location of the mobile device.

Ii. Methods based on the use of trilateration.

The ToA method (time of arrival) is based on measuring the propagation delay of a radio signal between a mobile device and a BS. The minimum number of measurements to determine the location of MU is three. The mobile device sends a signal at a time exactly known to the BS. The BS measures the time interval between sending a signal to a mobile device and receiving it. The distance is determined by the formula S = t * c (where t is time and c is the speed of light).
+ low power consumption by mobile device;
+ high accuracy of determining the location of the mobile device;
+ long range;
- the need for time synchronization on all BS and MU;
- complex algorithms for determining the location of the mobile device.

The TDoA method (time difference of arrival) is based on measuring the difference in time of signal transmission from a mobile device to a BS, with a synchronized clock and a known location. Knowing the difference in time to receive a signal using mathematical processing, you can get the distance from the mobile device to the base stations.
+ low power consumption by mobile device;
+ high accuracy of determining the location of the mobile device;
+ long range;
- the need for time synchronization between all mobile devices;
- complex algorithms for determining the location of the mobile device.

The ToF (time of flight) method is based on measuring the time that an electromagnetic wave spends on bridging the distance between a BS to a mobile device and returning to a BS after it is reflected from the ME. After receiving this time and knowing the speed of the wave, you can calculate the distance from the mobile device to the BS. S = t * c / 2.
+ mobile device - passive (does not consume energy);
+ high accuracy of determining the location of the mobile device;
+ long range;
+ no need for synchronization between devices;
- MU should reflect the electromagnetic wave in the direction of the BS;
- it is impossible to separate mobile devices.

The TWR (two-way ranging) method is as follows: The BS records the signal departure time (T1), the mobile device records the signal acquisition time (t1), as well as the signal departure time back to the BS (t2). In the signal from the mobile node to the base station, the times t1 and t2 are transmitted. The BS receives the signal from the mobile device and records the time it was received. The distance is calculated using the formula S = ((T2-T1) - (t2-t1)) * c / 2. The initiator of the measurement can be a mobile device according to a similar algorithm.
There is also the SDS-TWR method (symmetrical double-sided two-way ranging) , which is based on repeating this procedure in the opposite direction, which can serve to verify the correctness of the calculation.
+ high accuracy of determining the location of the mobile device;
+ long range;
+ no need for synchronization between devices;
- high energy consumption MU.

NFER, near-field electromagnetic ranging is a method of measuring the distance in a near electromagnetic field, where there is a phase shift between the electric and magnetic components of an electromagnetic wave. BS emits an electromagnetic wave of a given frequency. A mobile device with the help of two antennas measures the amplitude of the separate magnetic and electrical components of the wave and calculates the phase shift between them. Knowing the wavelength and phase difference between them (this difference varies from 90 ° near the BS to zero at a distance equal to half the wavelength), one can calculate the distance from the BS to the device.
+ high accuracy of determining the location of the mobile device;
+ the ability to work in enclosed spaces;
- small radius of action;
- complex antennas;
- complex algorithms for determining the location of the mobile device.
Iii. Method based on measuring signal strength.
The RSSI, received signal strength indicator is an indicator of the power level of the received signal. This method allows you to determine the location of the device based on the strength of the signal received by the BS or vice versa. To use this method, either the signal power level is converted into a distance, or in accordance with the coverage maps (Fig. 2).
+ low power consumption by mobile device;
+ low cost;
- low accuracy of determining the location of the mobile device;
- complex algorithms for determining the location of MU.


It should be noted that for determining the location, most systems use a combination of methods, since This approach eliminates the disadvantages of one method by adding the properties of another. In addition, different systems set different tasks for themselves, which may also require different methods. The method of measuring the distance depends on the available equipment and the presence of synchronization between the BS and the mobile device.
For example, RTL-Service's RealTrac system locates using IMU inertial positioning technology and a combination of ToF and RSSI methods. As the main problem inherent in all inertial positioning systems is an error that accumulates over time, the use of ToF and RSSI methods in addition to this This problem can be eliminated by periodically associating the trajectory with local coordinates.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/301706/
All Articles