Running NodeJS-application on Android
No doubt you will enjoy running NodeJS on your Android device. Thanks to the terminal emulator and Linux environment for Android, the development of web applications on a smartphone will no longer be a problem for you.

Termux is a free application that can be installed directly from the Google Play store. Requires Android 5.0 or later. Does not require root rights.
When you open Termux, you are welcomed by the command line interface. It is recommended to check for updates immediately after installing Termux. Type the following command and press Enter:
Termux comes in minimal basic configuration, so you should install coreutils to fully use command line commands such as mv, ls, etc.

Termux stores data in its own data warehouse, i.e. The $ HOME folder is inside the private area of Termux, like a regular Android application. Deleting Termux will cause the loss of this data. If you are going to store important files there, then use termux-setup-storage to ensure that data is stored in external storage (for example, on an SD card).
')
So, let's create a folder for our application and go to this directory:
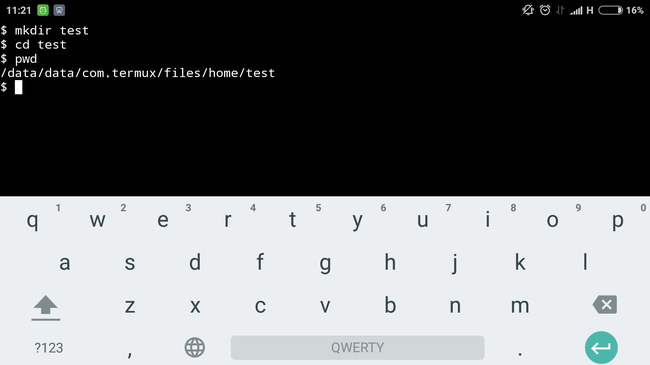
At this point, you will most likely feel some problems when working in the console with a standard keyboard. To get around them, I installed a hacker keyboard from Google play . This is a touch keyboard, which has everything you need to write code - Esc, Tab and the arrow keys.

For writing code, we need any text editor available in the console. You can install Emacs or Vim, but for simplicity, you can use nano. Install it:
Create an app.js file and open it in the editor:
Let's write some simple NodeJS code to check:
To exit nano, press Ctrl + X, write 'yes' and press Enter.
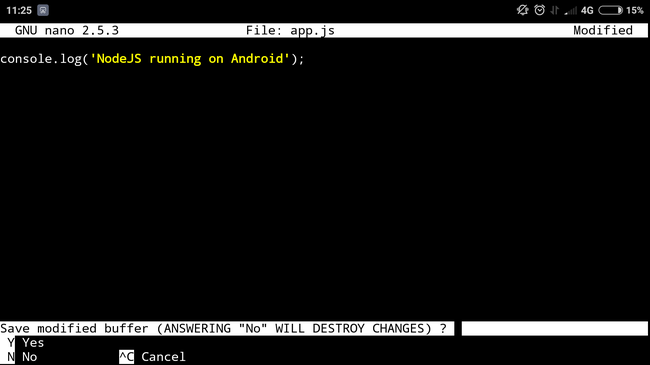
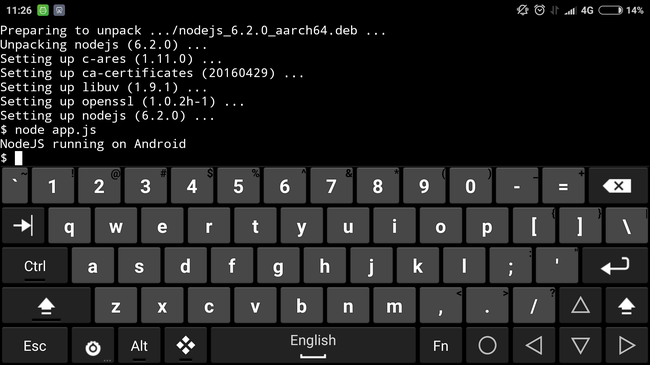
Now it's time to install NodeJS. This is very easy to do:
Now we can finally run our script:
Together with NodeJS, the npm package manager is available. Let's use it:
Open app.js and write / copy-paste the following code there:

This should display the port number on which the server responds to the console. If you open http: // localhost: 8080 / in a browser, you will see the following text on the page:

To avoid manually rebooting the server every time the app.js file changes, we can install nodemon. Nodemon is a utility that will track changes in your code and automatically restart the server.
Now you can start the server using the nodemon command instead of node:
Even with a hacker keyboard, writing code on the touchscreen is not very convenient. Most likely, you write your code in much more convenient places and store it in the repository. Install git:
Now you can run git commands like git push, git pull, etc. without any errors.
Unfortunately, I could not run the MongoDB server on Android. Alternatively, you can use cloud services, such as MongoLab, or be content with something like NeDB .
Building a Node.js application on Android
Termux is the ONE for Android

Termux
Termux is a free application that can be installed directly from the Google Play store. Requires Android 5.0 or later. Does not require root rights.
When you open Termux, you are welcomed by the command line interface. It is recommended to check for updates immediately after installing Termux. Type the following command and press Enter:
$ apt update Termux comes in minimal basic configuration, so you should install coreutils to fully use command line commands such as mv, ls, etc.
$ apt install coreutils 
Termux stores data in its own data warehouse, i.e. The $ HOME folder is inside the private area of Termux, like a regular Android application. Deleting Termux will cause the loss of this data. If you are going to store important files there, then use termux-setup-storage to ensure that data is stored in external storage (for example, on an SD card).
')
So, let's create a folder for our application and go to this directory:

Keyboard
At this point, you will most likely feel some problems when working in the console with a standard keyboard. To get around them, I installed a hacker keyboard from Google play . This is a touch keyboard, which has everything you need to write code - Esc, Tab and the arrow keys.

Nano
For writing code, we need any text editor available in the console. You can install Emacs or Vim, but for simplicity, you can use nano. Install it:
$ apt install nano Create an app.js file and open it in the editor:
$ touch app.js $ nano app.js Let's write some simple NodeJS code to check:
console.log('NodeJS running on Android'); To exit nano, press Ctrl + X, write 'yes' and press Enter.

Nodejs
Now it's time to install NodeJS. This is very easy to do:
$ apt install nodejs Now we can finally run our script:
$ node app.js 
Express
Together with NodeJS, the npm package manager is available. Let's use it:
$ npm init $ npm install express --save $ nano app.js Open app.js and write / copy-paste the following code there:
var express = require('express'), app = express(), port = Number(process.env.PORT || 8080); app.get('/', function(req, res) { res.send('Express is working'); }); app.listen(port, function() { console.log('Listening on port ' + port); }); 
$ node app.js This should display the port number on which the server responds to the console. If you open http: // localhost: 8080 / in a browser, you will see the following text on the page:

Nodemon
To avoid manually rebooting the server every time the app.js file changes, we can install nodemon. Nodemon is a utility that will track changes in your code and automatically restart the server.
$ npm install nodemon --save-dev Now you can start the server using the nodemon command instead of node:
$ nodemon app.js Git
Even with a hacker keyboard, writing code on the touchscreen is not very convenient. Most likely, you write your code in much more convenient places and store it in the repository. Install git:
$ apt install git Now you can run git commands like git push, git pull, etc. without any errors.
MongoDB
Unfortunately, I could not run the MongoDB server on Android. Alternatively, you can use cloud services, such as MongoLab, or be content with something like NeDB .
See also:
Building a Node.js application on Android
Termux is the ONE for Android
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/301442/
All Articles