Process approach to management: a tribute to fashion or success?
System theory regards a process as a change of system. Indeed, any activity is an action aimed at achieving a result, which is expressed in the fact that the system acquires a new state. We encounter processes in engineering, engineering, chemistry, and even sociology. However, each of us is a daily participant in workflows. As experience shows, often the leaders of companies avoid automation and formalization of processes, it seems to them not quite democratic “crackdown”. And in vain. Proper construction and management of processes in a company of any profile helps to ensure adequate interaction between employees, due to responsibility and attention to deadlines. The process approach is not dead - it lies at the heart of many fashionable theories of managing development, company, personnel. Today we will tell where the processes are found, how to manage them and whether you need them in principle.

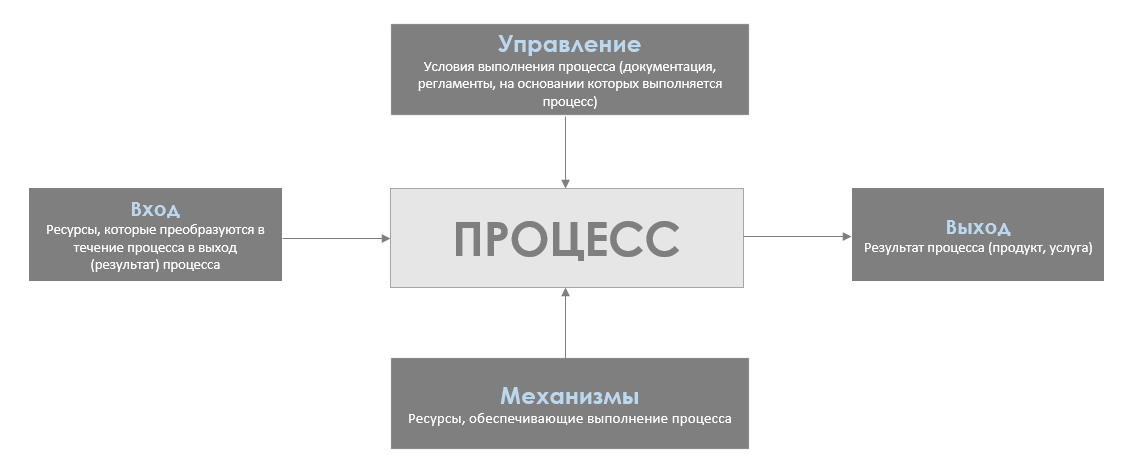
The theory of processes defines a process as a model of behavior that consists in the execution of actions. As a rule, the process is not aware of the details of the implementation of each of the actions (the behavior of the system to which it belongs). For example, in the process of agreeing a document in a company, the terms and procedure for agreeing are laid down, but the process does not care from which device and in which geographical point the document will be agreed. Another important feature of the process is its controllability, the ability to undergo changes from the outside.
Generally, speaking of CRM and ERP, everyone is accustomed to hearing the concept of “business process” and often the discussions boil down to how the business process differs from the process. There is a version that the term is tracing from the English “business process” (business process) and the business term does not bear any burden, apart from isolating the processes taking place in companies from numerous processes (technical, chemical, biological, etc.). Actually, it is easy to agree with this version, remembering how, for example, a trial is called simply a process, having discarded the sign.
We in Ruli24 have accumulated considerable expertise in the processes - in fact, our entire system is a process management system, so it was very important for us to decide what we are working with: processes or fashionable business processes. And yet, as it seems to us, between these two concepts there is a thin line that lies outside of cybernetics, but is described by organization theory: a process is a set of actions repeated in time with a given periodicity, having a starting point and a point of achieving the result, the goal of which is value creation for internal and external customers. And here we rest on the concept of external and internal client and the line becomes noticeable.
')
Business is an economic activity aimed at making a profit from the production and sale of goods, rendering services and works. But after all, not every process is profitable (research, charity, assistance to social institutions). Yes, there is a result (satisfaction of need), but not profit. It means that in our system not only business processes are described.
For example, for the purposes of building the logic of the Rule24 process control system, we used the separation of processes into 4 main types. We have already mentioned them in a post about business processes , but now we will look at them from the point of view of processes not in business, but in any company. However, consider the processes on the example closest to us - the company-developer. That is actually on our real case.
The research process focuses on sourcing and discussion. The result of this process is not predetermined, but upon reaching it forms the basis of the strategy. That is, this is actually a concept. For example, a developer company (vendor) begins to look for ideas for new features and solutions for the market: desk research, polls are held, information is collected, meetings and brainstorming begin. No one knows in advance what the team decides to include in the new release. However, at the end of the research process, the concept of a specific development appears - this is also the entry point of the project process.
The project process is the organization of work in accordance with the network schedule (as variations, this is a Gantt chart, Scrum board, etc.). At this stage KPI, man-hours are calculated, total work is taken into account. The result is determined - this is a product. In our case, the development team and designers proceed to implement the development, strictly following the steps and deadlines. In case of a shift in the deadline of one of the subtasks, the deadlines for the entire project are shifted.
The production process is a kind of branch after research. It can be executed along with the project or outside of it. It includes business processes with predetermined routes. This is more "conveyor" model. For example, when developing each new functionality or product, it passes standard testing: regression, functional, load, and usability. It is rather a production process.
Information process - a process parallel to the previous three. This is work with documents, coordination, notification of personnel and so on. It serves all the stages of creating good.
These processes are present in any organization and require resources and management. They can be sequential, parallel, have points of intersection. It is important to debug processes in a company in order to achieve several important goals:
Ultimately, process management reduces the cost of the final product, provides savings on the release and redistribution of resources, makes the company transparent, but retains flexibility - you can always make changes to the process.
In ISO 9000 quality system certification standards, one of the most important components of achieving quality is the principle of the process approach to the performance of any work. Here is what the standard GOST R ISO 9001-2008 means:
“This standard advocates the application of the“ process approach ”principle in the design, implementation and improvement of the effectiveness of the quality management system in order to increase customer satisfaction by fulfilling their requirements.
For successful operation, an organization must define and manage multiple interrelated activities. An activity that uses resources and is managed to transform inputs into outputs can be considered as a process. Often the output of one process directly forms the input of the next.
The application of a system of processes in an organization along with their identification and interaction, as well as the management of processes aimed at obtaining the desired result, can be defined as a “process approach”.
The advantage of the process approach is the continuity of management, which it provides at the junction of individual processes within their system, as well as their combination and interaction.
When used in a quality management system, this approach emphasizes the importance of:
a) understanding and fulfilling the requirements;
b) the need to consider processes in terms of the value they add;
(c) Achievement of the planned results of the implementation of processes and ensuring their effectiveness;
d) continuous improvement of processes based on objective measurement.
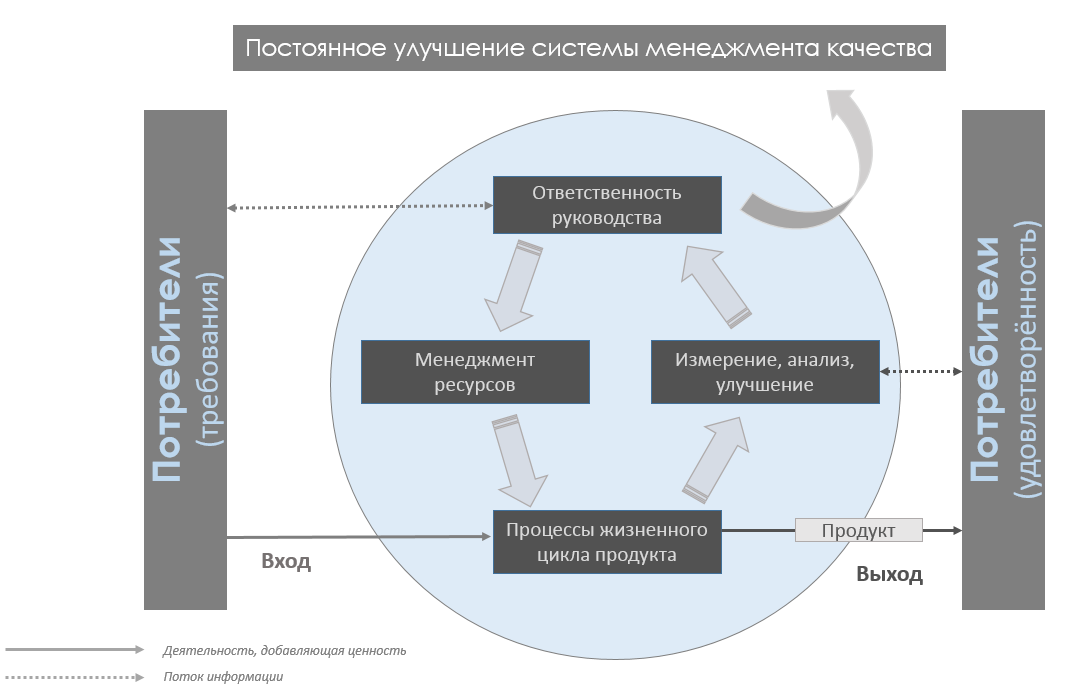
The quality management system model shown in the figure, based on the process approach, illustrates the connections between processes (organizations - author's note). This model shows that consumers play a significant role in setting the requirements considered as inputs. Monitoring customer satisfaction requires an assessment of information about how consumers are satisfied with their requirements. The model shown in the figure covers all the basic requirements of this standard, but does not show processes at a detailed level. ”
Thus, the standard recommends that the organization identify all major activities and learn how to manage them. In turn, an activity that uses resources, has a goal and a result is already considered as a process. And often the result of one process serves as an entry point for another. The standard GOST R ISO 9001: 2008 itself refers to the significant activities of the company: planning, management, management review, resource management (including personnel and infrastructure), product life cycle management, design and development, measurement, analysis and improvement.
“Everything is a process” - it was from this position that we proceeded when designing the Rulee system24. In the post about the growth of companies there were schemes, which reflected the three main groups of processes in any company, regardless of its structure, commercialization and legal form.
This is how the document approval process in Rule24 looks like: each of the chain receives an alert about the action and electronically coordinates the document. At the same time, the human factor is minimized: the owner of the process can at any moment see who has stalled and take action. By the way, such processes are set up in BPMN notation in Rulers, and we do not abandon the user alone with the designer, but design the processes precisely, quickly, and for the client.
All analytics is built in reports: the user can make the necessary samples and analyze the slices with the help of filters, graphical, tabular and chess views.
To implement these processes requires an entire arsenal: this CRM, and planners, and calendars, and Gantt chart. The actions of several units should be coordinated and focused on the ultimate goal.
The supporting processes are numerous and it is important to adjust them so as to exclude the same human factor as in the leading processes. For this, the complex automation of the company is used, taking into account the interrelationship of the processes.
In addition to this division, there is a division, which is mentioned above: into research, design, production and information processes. They are not only interrelated, but also act on any object or part of it.
In Rule24, the process control mechanism includes the organization of work regarding the four specified types of processes. Each process has its own order of execution, form of management and the expected result. The input and output of the process are work.
The system contains several forms of work management. The use of one form or another is due both to the specifics of various types of activity and to organizational aspects. Work with information processes is carried out using the forms of management:
Work with research and search processes is carried out through the forms of management:
Work with project processes is carried out through the forms of management:
Work on production processes are recorded using the forms of management:
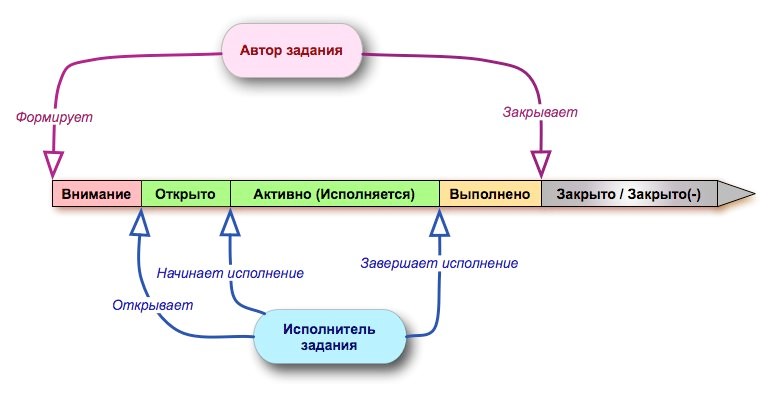
As we have said, the input and output of each process is work. Each job has its own life cycle:
In the course of work, the following functions are performed:
If you turn to the Russian development (and the development of their CIS), you can find several classic CRM with embedded business processes, but none of them treats the process as a component of each level of management and production. We in Ruli24 were repelled precisely by focusing on the process approach, and did not implement processes as a separate module or fashionable functionality.
If you do not read the post for the sake of interest in the process approach, but choose a CRM or a suitable automation system for all components of your business, look under the spoiler - the implementation of the processes in the Rule interface is clearly presented there.
By convention, all the processes within the organization lie between the requirements and customer satisfaction. And this is precisely the main process of producing goods (goods, works, services). Consider the example of our client. There is a bank, Ruli24 stands in it, as we joke, in the luxury package. The bank has two types of customers: legal entities and individuals. They make demands on products: open accounts, conduct operations, make deposits. They impose requirements on the level of service, they wish to have a client-bank, a mobile version, mailings, etc. The bank satisfies the requirements, and all processes take place within the Ruli24 system: from accounting to analytics of the product portfolio and the system of internal tickets. At the same time, all processes are interconnected, which reduces the average service time and simplifies the collection of business information, on the basis of which new product offers are formed.
However, the process control system in a company is needed not only for such frailies as banks, but also practically any company. For a deeper understanding of the process approach, you can use the so-called Deming-Shewhart cycle "Plan - Do - Check - Act" (PDCA). This is "planning - action - checking - improving action." Using this cycle allows you to continuously implement continuous improvement processes, aimed at improving the efficiency of the organization. This concept was deeply reflected in the development of the Ruli xRM .This is the volume control model that underlies the idea of the whole system. If you imagine the model to be interactive, the relationships and intersections of all components become clear.
The process description form below resembles a PERT diagram, i.e. network schedule. The difference is that not all work can be carried out in a specific implementation of the production process, depending on the conditions of the "intersection". In addition, each work can be defined (in some of its attributes) depending on the conditions in the process description. But, as we remember, the process is not aware of the implementation of the procedures and instructions within it.
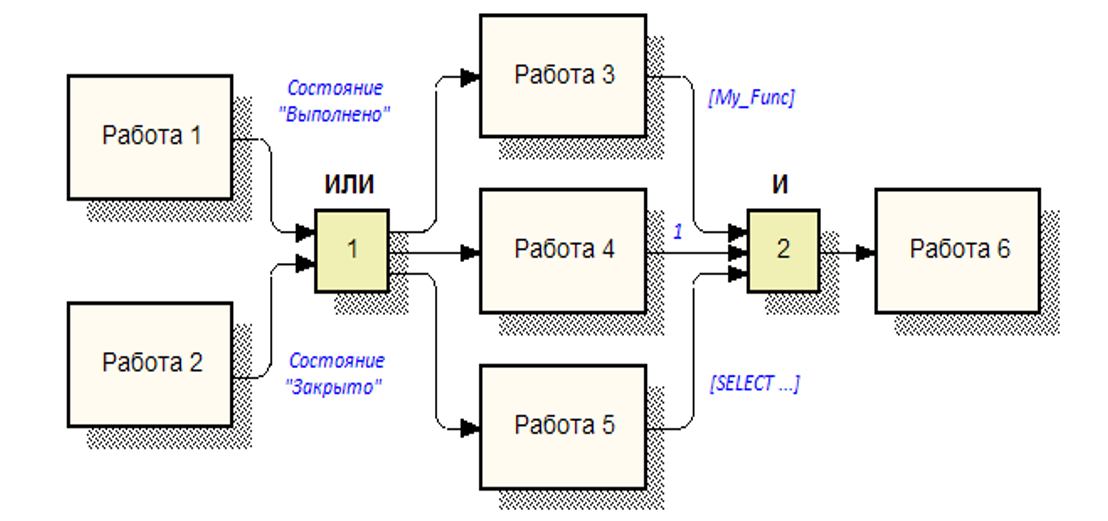
So, we decided on the model and draw up a sample checklist for managing the processes in your company.
“To whom are you telling it now? I have a small business, guys in the palm of my hand, what processes! ”- some of Habr's readers will probably think so. We assure you, you are wrong. Company management does not begin with the first day of its existence, but with the birth of the very idea of creating such. And it is at this stage that the first processes are formed. Start small — automate primary connections and actions, then increase automation along with control growth. When the company grows and the flow of calls or customers becomes noticeable, you will not have a mess and the need for its automation. After all, as crm-schiki colleagues repeatedly joked here, the automated mess remains a mess.

Process approach: from cybernetics to management
The theory of processes defines a process as a model of behavior that consists in the execution of actions. As a rule, the process is not aware of the details of the implementation of each of the actions (the behavior of the system to which it belongs). For example, in the process of agreeing a document in a company, the terms and procedure for agreeing are laid down, but the process does not care from which device and in which geographical point the document will be agreed. Another important feature of the process is its controllability, the ability to undergo changes from the outside.
Generally, speaking of CRM and ERP, everyone is accustomed to hearing the concept of “business process” and often the discussions boil down to how the business process differs from the process. There is a version that the term is tracing from the English “business process” (business process) and the business term does not bear any burden, apart from isolating the processes taking place in companies from numerous processes (technical, chemical, biological, etc.). Actually, it is easy to agree with this version, remembering how, for example, a trial is called simply a process, having discarded the sign.
We in Ruli24 have accumulated considerable expertise in the processes - in fact, our entire system is a process management system, so it was very important for us to decide what we are working with: processes or fashionable business processes. And yet, as it seems to us, between these two concepts there is a thin line that lies outside of cybernetics, but is described by organization theory: a process is a set of actions repeated in time with a given periodicity, having a starting point and a point of achieving the result, the goal of which is value creation for internal and external customers. And here we rest on the concept of external and internal client and the line becomes noticeable.
')

Business is an economic activity aimed at making a profit from the production and sale of goods, rendering services and works. But after all, not every process is profitable (research, charity, assistance to social institutions). Yes, there is a result (satisfaction of need), but not profit. It means that in our system not only business processes are described.
For example, for the purposes of building the logic of the Rule24 process control system, we used the separation of processes into 4 main types. We have already mentioned them in a post about business processes , but now we will look at them from the point of view of processes not in business, but in any company. However, consider the processes on the example closest to us - the company-developer. That is actually on our real case.
The research process focuses on sourcing and discussion. The result of this process is not predetermined, but upon reaching it forms the basis of the strategy. That is, this is actually a concept. For example, a developer company (vendor) begins to look for ideas for new features and solutions for the market: desk research, polls are held, information is collected, meetings and brainstorming begin. No one knows in advance what the team decides to include in the new release. However, at the end of the research process, the concept of a specific development appears - this is also the entry point of the project process.
The project process is the organization of work in accordance with the network schedule (as variations, this is a Gantt chart, Scrum board, etc.). At this stage KPI, man-hours are calculated, total work is taken into account. The result is determined - this is a product. In our case, the development team and designers proceed to implement the development, strictly following the steps and deadlines. In case of a shift in the deadline of one of the subtasks, the deadlines for the entire project are shifted.
The production process is a kind of branch after research. It can be executed along with the project or outside of it. It includes business processes with predetermined routes. This is more "conveyor" model. For example, when developing each new functionality or product, it passes standard testing: regression, functional, load, and usability. It is rather a production process.
Information process - a process parallel to the previous three. This is work with documents, coordination, notification of personnel and so on. It serves all the stages of creating good.
These processes are present in any organization and require resources and management. They can be sequential, parallel, have points of intersection. It is important to debug processes in a company in order to achieve several important goals:
- increase the accuracy and speed of execution of routine tasks due to automation and reminder system
- growth of responsibility at each stage and minimization of the human factor due to the designation of process owners, performers and transparency of control over the process execution process (clearly seen in the ACS, for example, our Rule24 )
- predictability of the final result due to the accumulation of a knowledge base and resource management within the project
- continuous quality control and creation of improvements due to continuous optimization of processes and their separation
- involvement of all elements of the infrastructure and all employees due to competent planning based on the result of previous results.
Ultimately, process management reduces the cost of the final product, provides savings on the release and redistribution of resources, makes the company transparent, but retains flexibility - you can always make changes to the process.
An important digression: the place of the process in the quality management system (ISO 9001)
In ISO 9000 quality system certification standards, one of the most important components of achieving quality is the principle of the process approach to the performance of any work. Here is what the standard GOST R ISO 9001-2008 means:
“This standard advocates the application of the“ process approach ”principle in the design, implementation and improvement of the effectiveness of the quality management system in order to increase customer satisfaction by fulfilling their requirements.
For successful operation, an organization must define and manage multiple interrelated activities. An activity that uses resources and is managed to transform inputs into outputs can be considered as a process. Often the output of one process directly forms the input of the next.
The application of a system of processes in an organization along with their identification and interaction, as well as the management of processes aimed at obtaining the desired result, can be defined as a “process approach”.
The advantage of the process approach is the continuity of management, which it provides at the junction of individual processes within their system, as well as their combination and interaction.
When used in a quality management system, this approach emphasizes the importance of:
a) understanding and fulfilling the requirements;
b) the need to consider processes in terms of the value they add;
(c) Achievement of the planned results of the implementation of processes and ensuring their effectiveness;
d) continuous improvement of processes based on objective measurement.

The quality management system model shown in the figure, based on the process approach, illustrates the connections between processes (organizations - author's note). This model shows that consumers play a significant role in setting the requirements considered as inputs. Monitoring customer satisfaction requires an assessment of information about how consumers are satisfied with their requirements. The model shown in the figure covers all the basic requirements of this standard, but does not show processes at a detailed level. ”
Thus, the standard recommends that the organization identify all major activities and learn how to manage them. In turn, an activity that uses resources, has a goal and a result is already considered as a process. And often the result of one process serves as an entry point for another. The standard GOST R ISO 9001: 2008 itself refers to the significant activities of the company: planning, management, management review, resource management (including personnel and infrastructure), product life cycle management, design and development, measurement, analysis and improvement.
Ruli24 processes - how to steer correctly
“Everything is a process” - it was from this position that we proceeded when designing the Rulee system24. In the post about the growth of companies there were schemes, which reflected the three main groups of processes in any company, regardless of its structure, commercialization and legal form.
- Leading processes. They boil down to three components: organization, leadership, management. For these processes, it is important to softly lay down a competent process of coordination, analysis and data collection.
This is how the document approval process in Rule24 looks like: each of the chain receives an alert about the action and electronically coordinates the document. At the same time, the human factor is minimized: the owner of the process can at any moment see who has stalled and take action. By the way, such processes are set up in BPMN notation in Rulers, and we do not abandon the user alone with the designer, but design the processes precisely, quickly, and for the client.
All analytics is built in reports: the user can make the necessary samples and analyze the slices with the help of filters, graphical, tabular and chess views.
- The main processes. Strongly dependent on the type of activity of the company, but almost always include marketing, procurement, promotion.
To implement these processes requires an entire arsenal: this CRM, and planners, and calendars, and Gantt chart. The actions of several units should be coordinated and focused on the ultimate goal.
- Supporting processes are elements of direct production and support of the main activity. This includes personnel management, financial management, security, IT infrastructure, accounting, and so on.
The supporting processes are numerous and it is important to adjust them so as to exclude the same human factor as in the leading processes. For this, the complex automation of the company is used, taking into account the interrelationship of the processes.
In addition to this division, there is a division, which is mentioned above: into research, design, production and information processes. They are not only interrelated, but also act on any object or part of it.
In Rule24, the process control mechanism includes the organization of work regarding the four specified types of processes. Each process has its own order of execution, form of management and the expected result. The input and output of the process are work.
The system contains several forms of work management. The use of one form or another is due both to the specifics of various types of activity and to organizational aspects. Work with information processes is carried out using the forms of management:
- “Incoming Document” - registration of external incoming documents;
- “Outgoing document” - registration of documents sent to external organizations;
- “Request” is a universal mechanism for official correspondence, regardless of the administrative hierarchy of relationships.
Work with research and search processes is carried out through the forms of management:
- “Forum” - registration of teamwork, distribution of internal documents, discussion mechanism;
- A “meeting” is a meeting scheduling mechanism.
Work with project processes is carried out through the forms of management:
- "Theme" - the form is used to highlight work in certain areas;
- “Project” - the form is used to group work on specific projects;
- "Total work" - registration of work of a general nature, which includes works assigned to specific performers.
- “Project Task” - registration of a specific task to the project executor.
Work on production processes are recorded using the forms of management:
- "Business process" - the basis of the form is the description of the sequence of work to achieve a certain result.
- “Task” is the form by which the organization of work and the control of execution are carried out, depending on the hierarchy of service relationships
As we have said, the input and output of each process is work. Each job has its own life cycle:

In the course of work, the following functions are performed:
- Creating a new job - as a result, a record is created in the system describing the work in the “Attention” state.
- Acquaintance with work - the work is transferred to the “Open” state.
- Work performance - the work is transferred to the “Active” state.
- Registration of the fact of execution - enter the date of completion of the work and report on the work performed. The work is transferred to the “Completed” state.
- Closing the work - the author of the work checks the fact of the work execution and translates it into the “Closed” state. If the result of the work performed was unsatisfactory, the author transfers the work to the “Closed (-)” state.
If you turn to the Russian development (and the development of their CIS), you can find several classic CRM with embedded business processes, but none of them treats the process as a component of each level of management and production. We in Ruli24 were repelled precisely by focusing on the process approach, and did not implement processes as a separate module or fashionable functionality.
If you do not read the post for the sake of interest in the process approach, but choose a CRM or a suitable automation system for all components of your business, look under the spoiler - the implementation of the processes in the Rule interface is clearly presented there.
Slides, slides!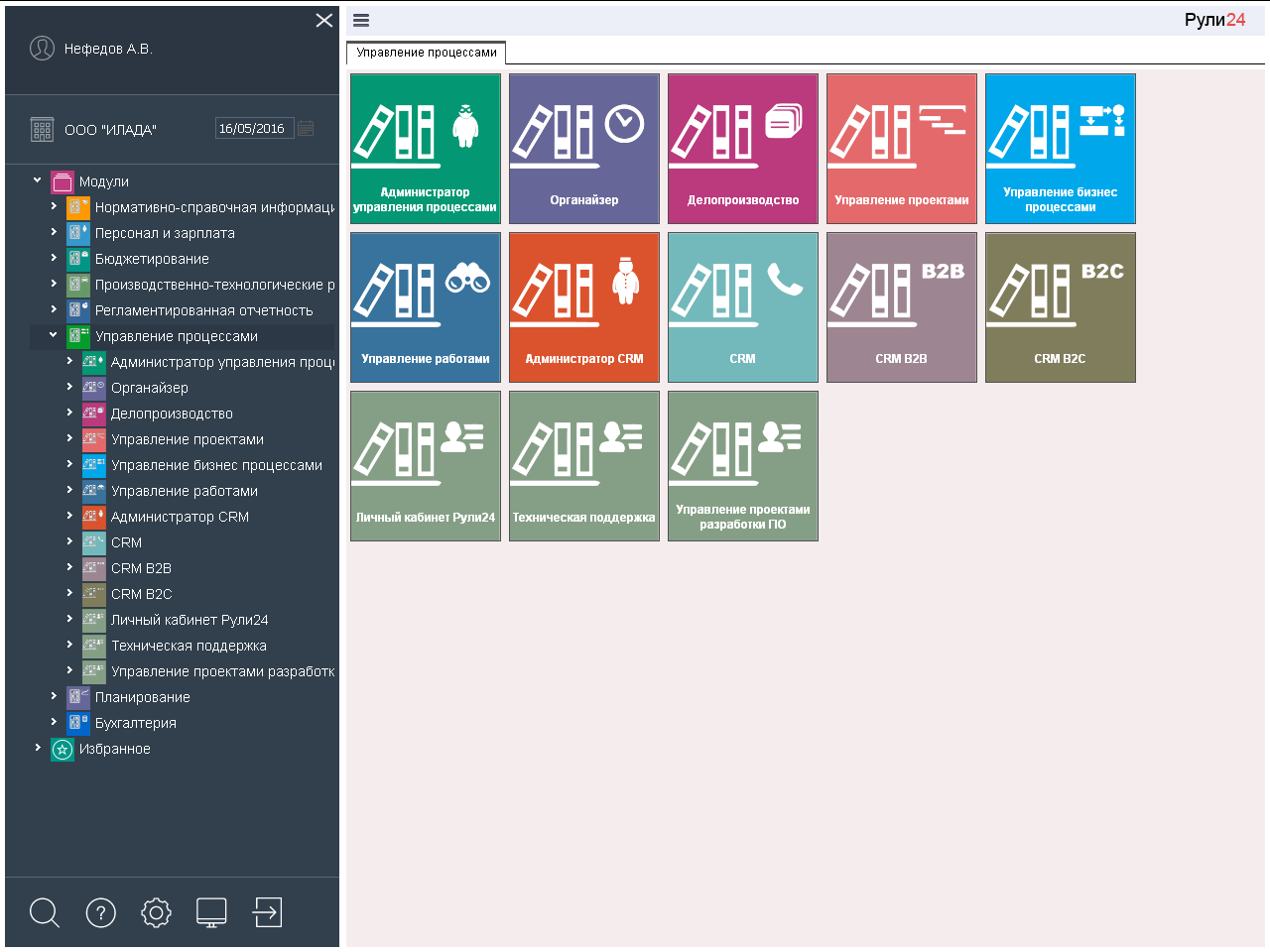
Rule24 Process Management - includes 13 tasks.
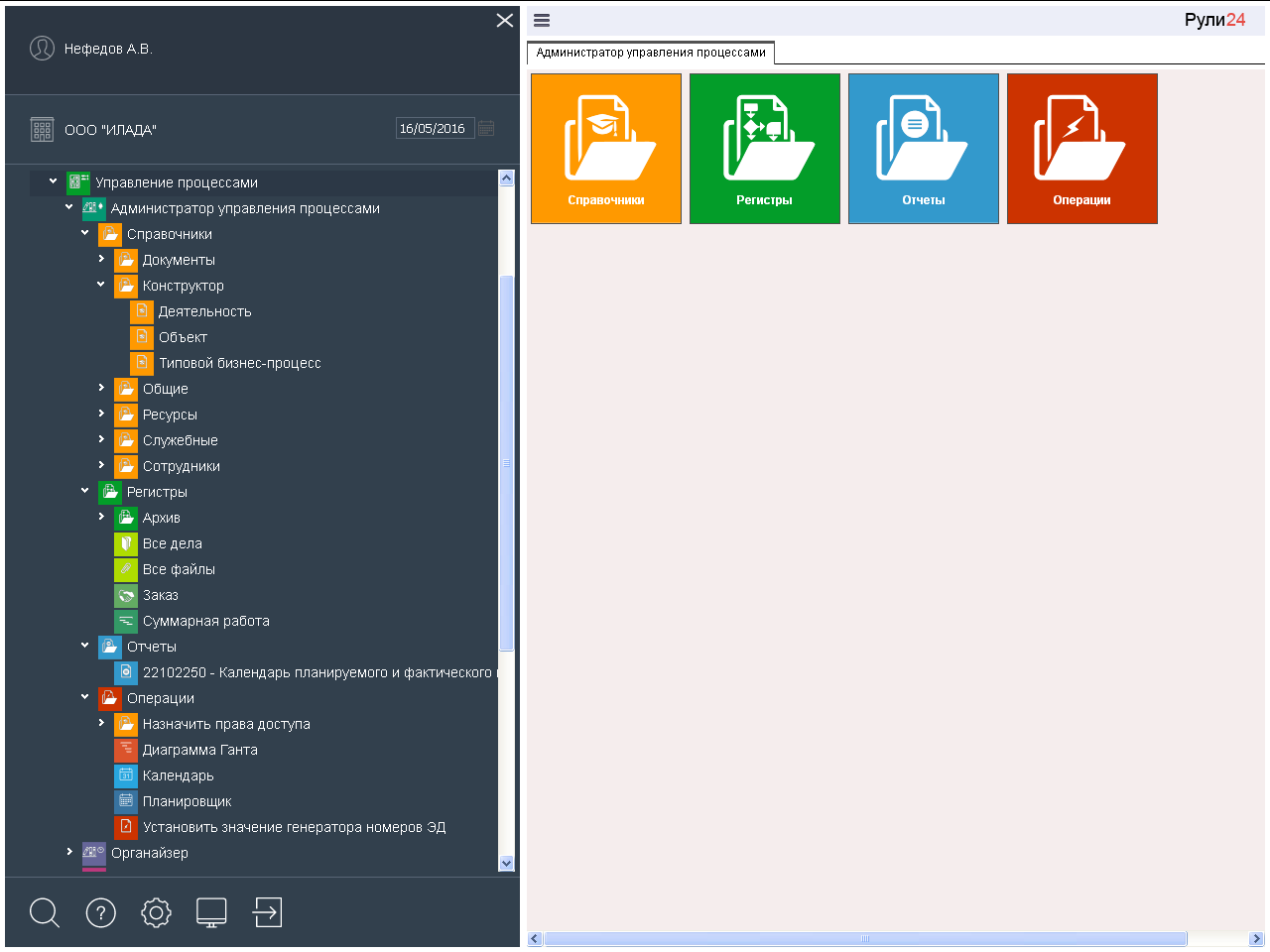
Rule24 Process Management Administrator - allows you to customize activities, objects and user rights.
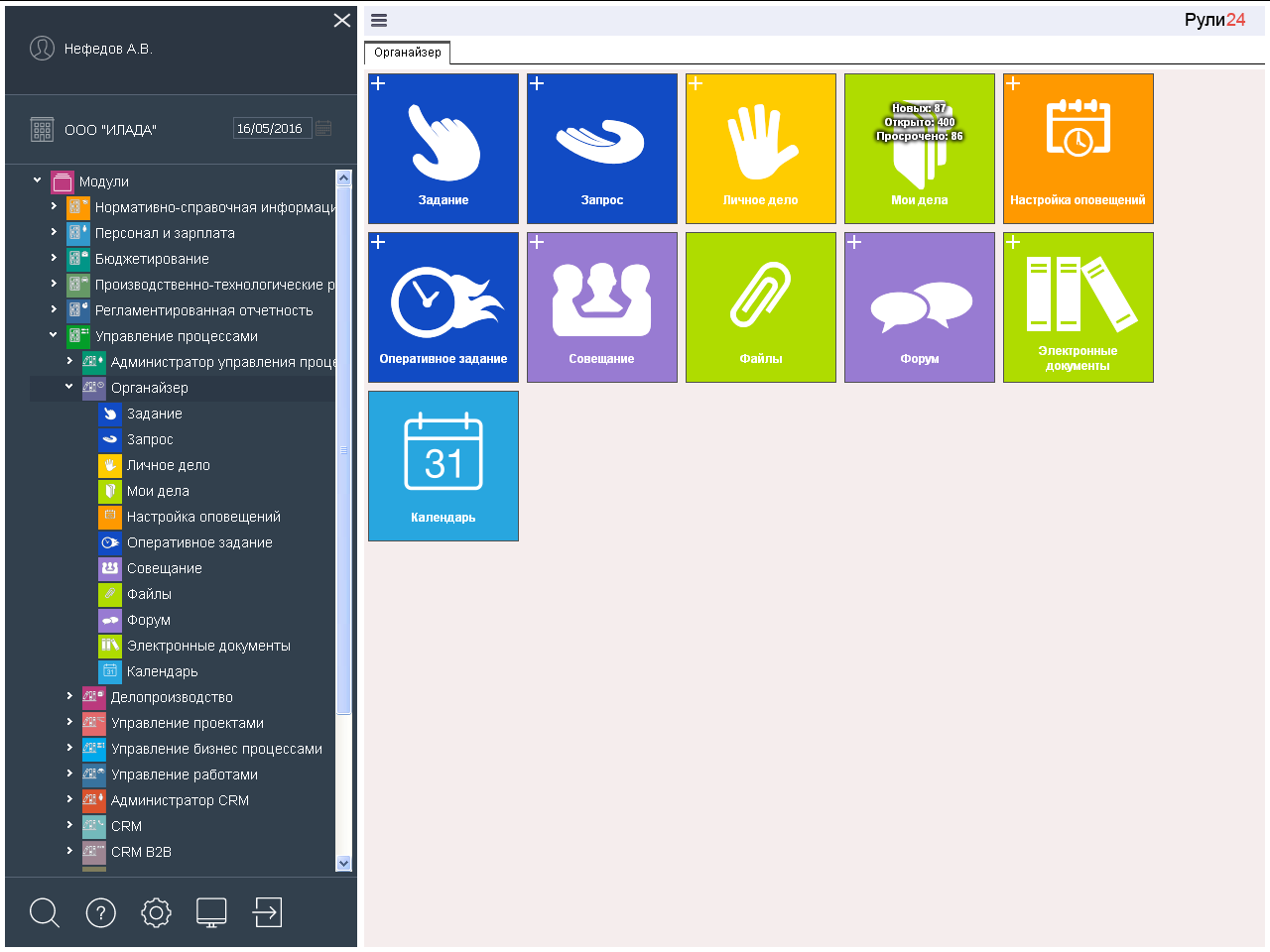
Rule24 Organizer allows you to conduct both personal and collective time management. Here are planned and controlled personal affairs, simple production (tasks, requests, operational tasks) and research work (meetings and forums). Planning can be done through your calendar or through an employee calendar. Various files and electronic documents are also available here. All types of work are available in the “My Affairs” folder, in which widgets reflect new, open and expired affairs.
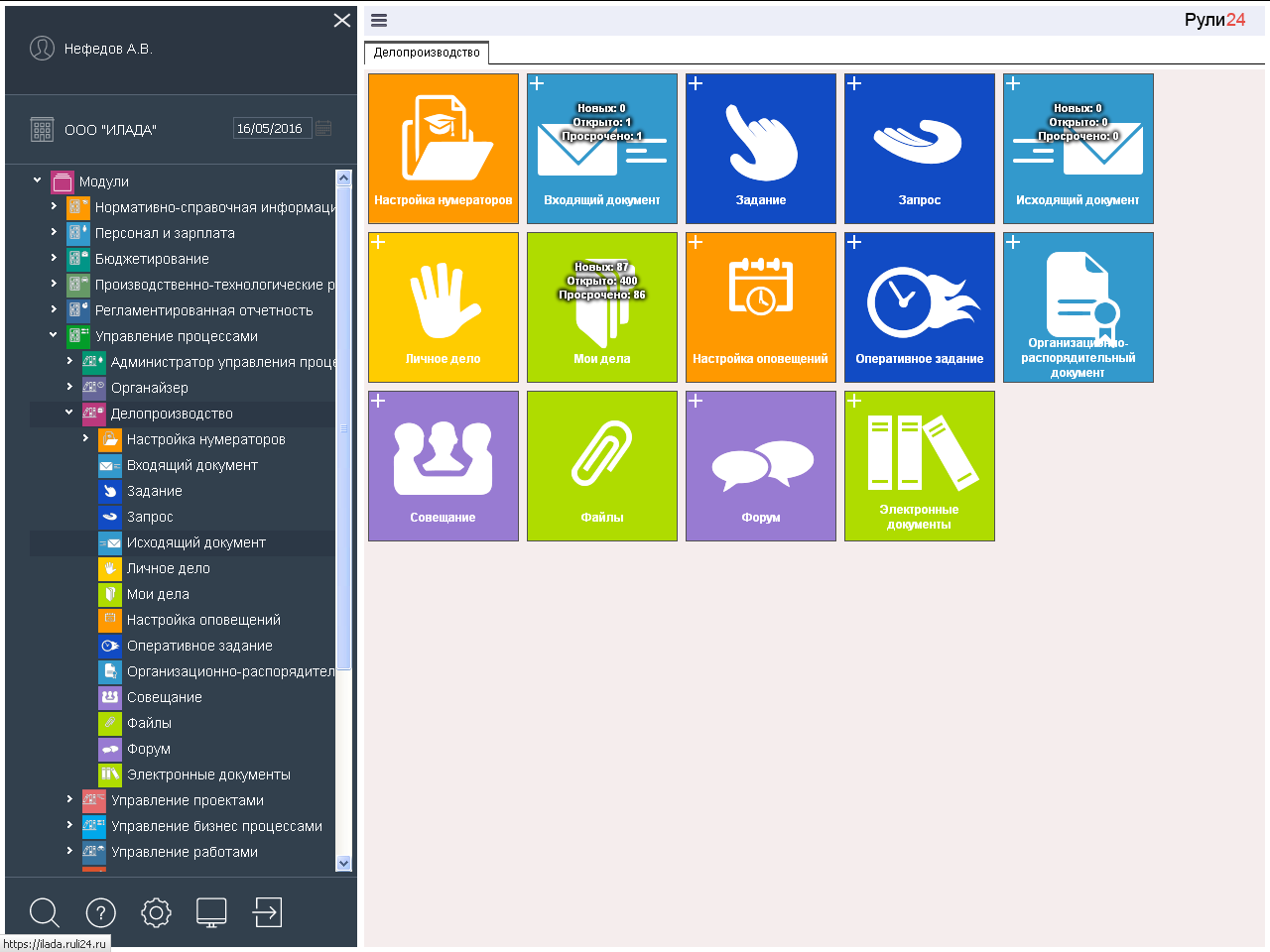
In the task Rule24 Record keeping , Inbox, Outgoing and Distribution documents are added to the Organizer objects. Now in the folder "My affairs" and these documents are available.
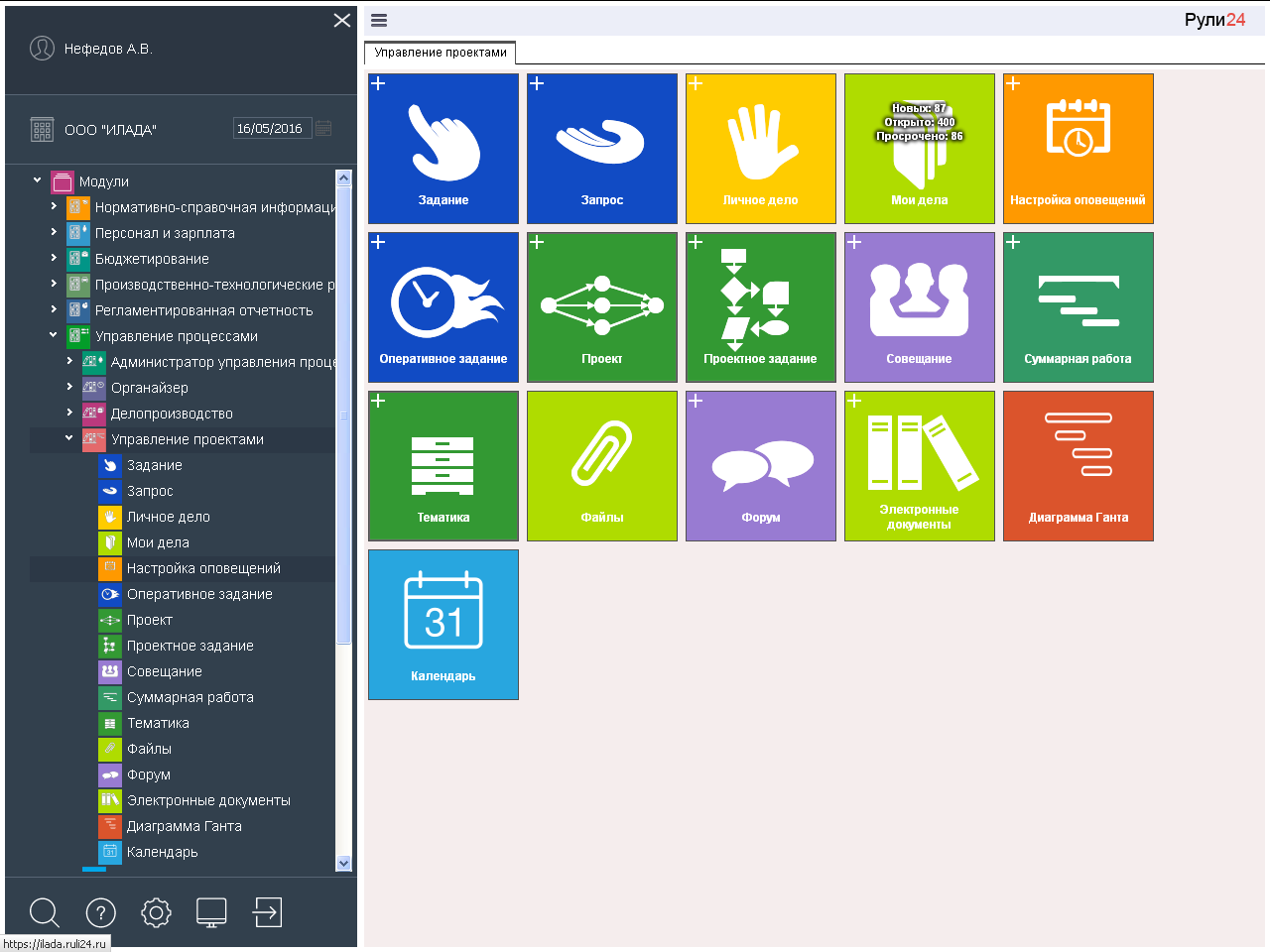
In the task Rule24 Project Management the Subject, Project, Summary work, Project task are added to the Organizer objects. All these works can be seen not only in the Calendar, but also on the Gantt chart and in the Scheduler. Now in the folder "My affairs" available and these works.
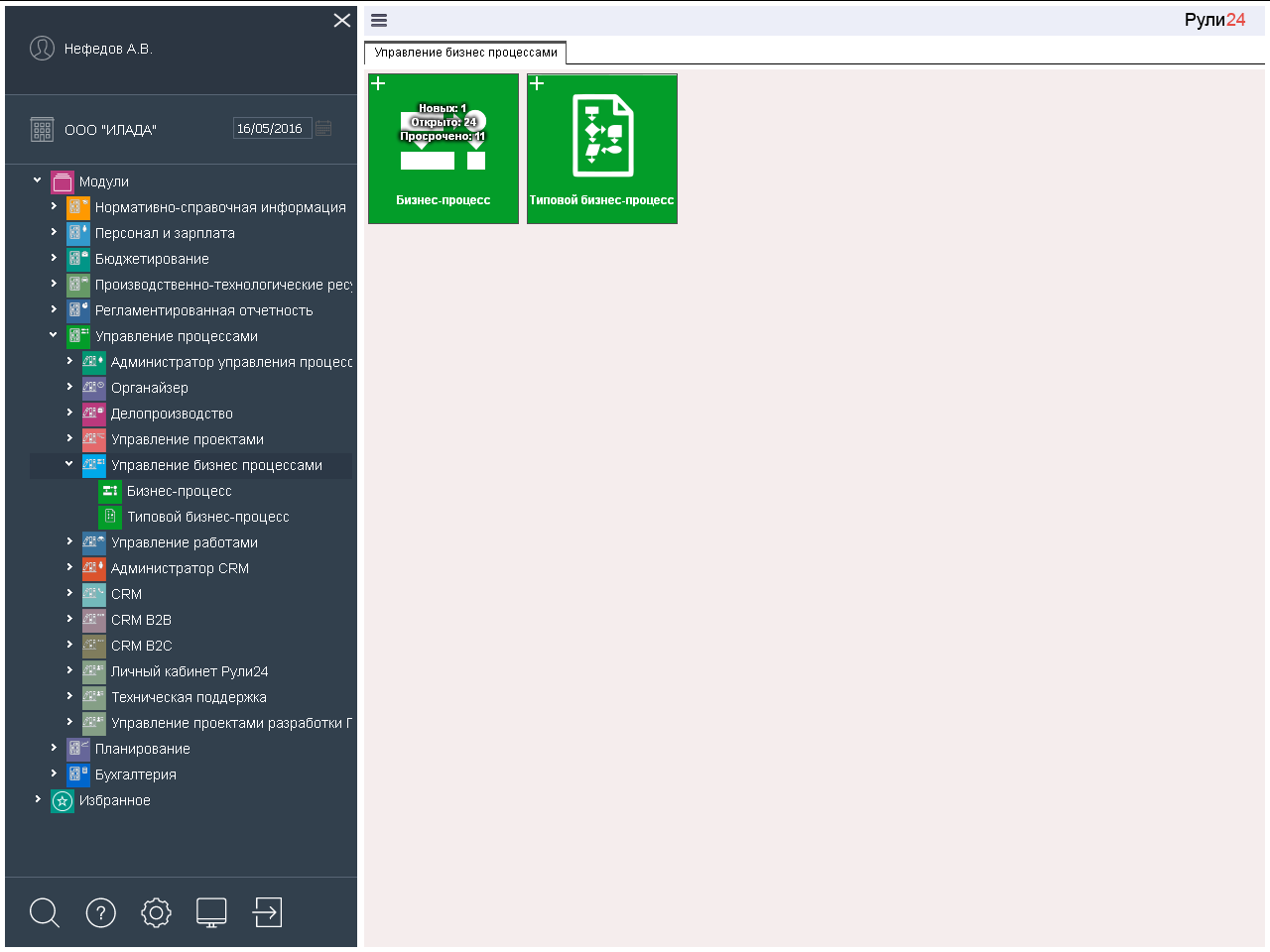
In Task 24 of Business Process Management, you can create typical business processes and start and monitor instances of business processes.
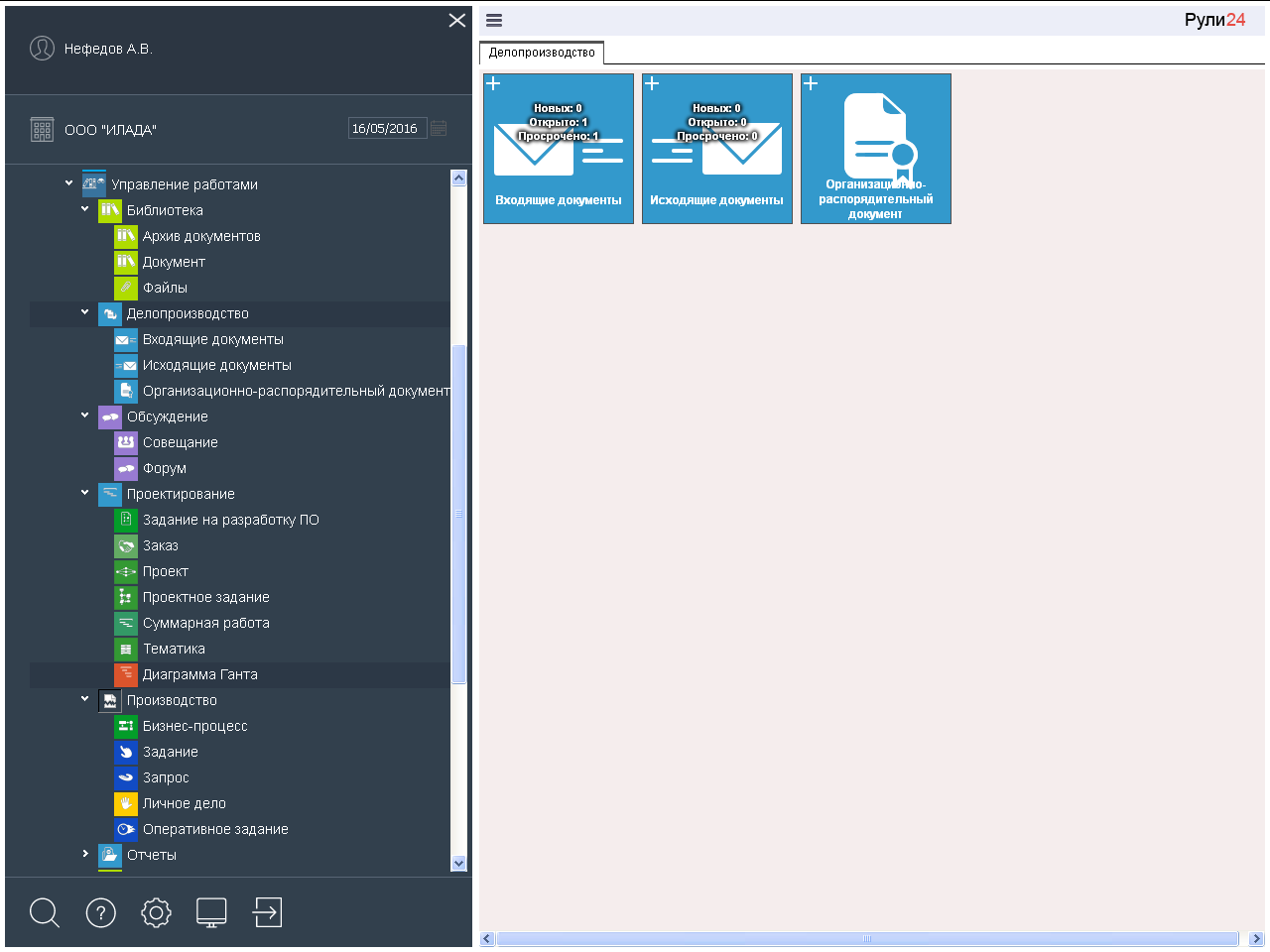
In task Rule24 Work management , all work from the research process (discussion), from the information process (office work), the project process (design) and the production process (production) are collected. Now in the folder "My affairs" are available all the work of these processes.

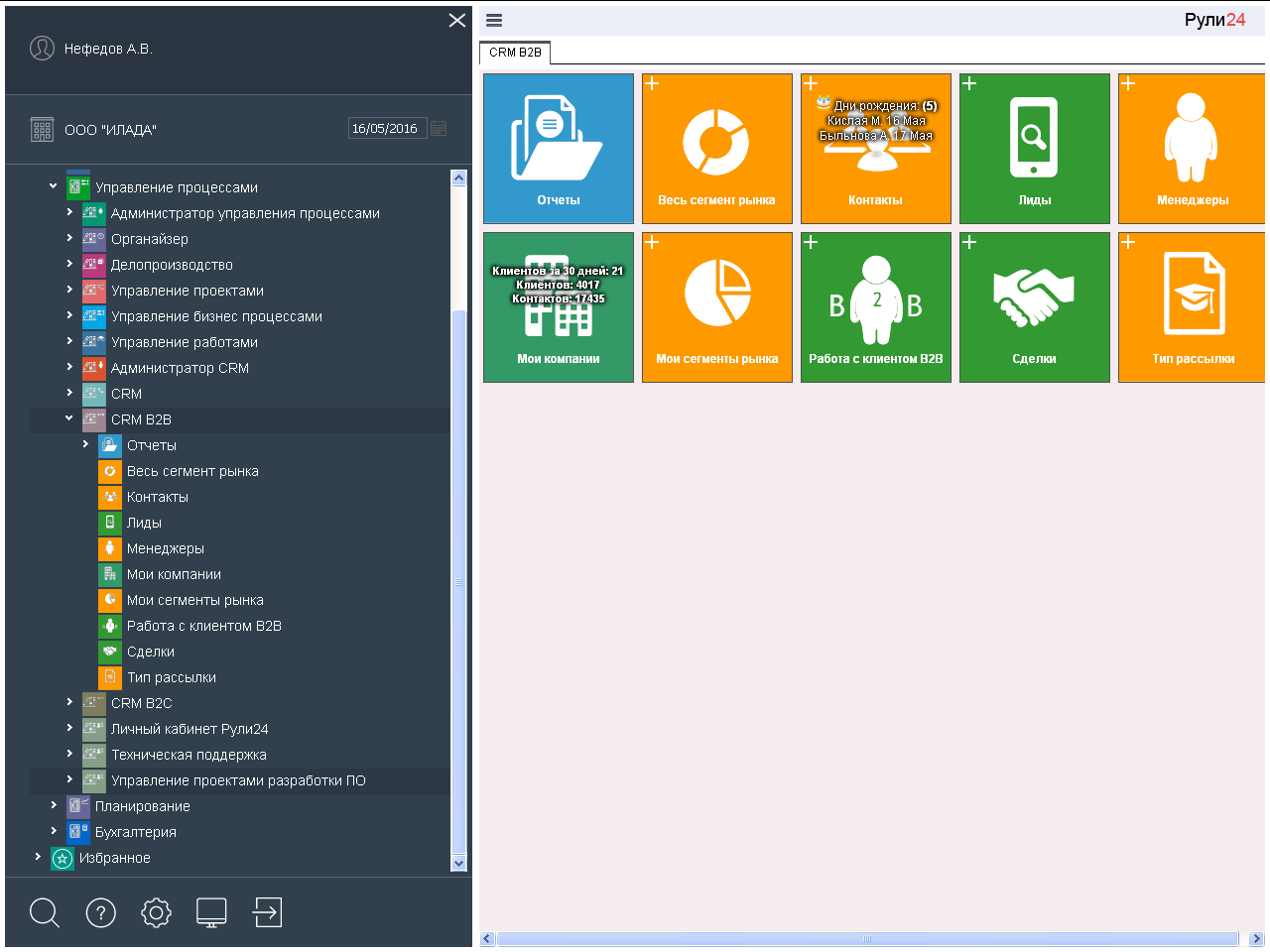
In the task Rule24 Administrator CRM , CRM, CRM B2B, CRM B2C are added Lida, Transactions, Work with B2B clients, Work with B2C clients. Now in the folder "My affairs" available and work from the CRM.

Rule24 Process Management - includes 13 tasks.

Rule24 Process Management Administrator - allows you to customize activities, objects and user rights.

Rule24 Organizer allows you to conduct both personal and collective time management. Here are planned and controlled personal affairs, simple production (tasks, requests, operational tasks) and research work (meetings and forums). Planning can be done through your calendar or through an employee calendar. Various files and electronic documents are also available here. All types of work are available in the “My Affairs” folder, in which widgets reflect new, open and expired affairs.

In the task Rule24 Record keeping , Inbox, Outgoing and Distribution documents are added to the Organizer objects. Now in the folder "My affairs" and these documents are available.

In the task Rule24 Project Management the Subject, Project, Summary work, Project task are added to the Organizer objects. All these works can be seen not only in the Calendar, but also on the Gantt chart and in the Scheduler. Now in the folder "My affairs" available and these works.

In Task 24 of Business Process Management, you can create typical business processes and start and monitor instances of business processes.

In task Rule24 Work management , all work from the research process (discussion), from the information process (office work), the project process (design) and the production process (production) are collected. Now in the folder "My affairs" are available all the work of these processes.


In the task Rule24 Administrator CRM , CRM, CRM B2B, CRM B2C are added Lida, Transactions, Work with B2B clients, Work with B2C clients. Now in the folder "My affairs" available and work from the CRM.
By convention, all the processes within the organization lie between the requirements and customer satisfaction. And this is precisely the main process of producing goods (goods, works, services). Consider the example of our client. There is a bank, Ruli24 stands in it, as we joke, in the luxury package. The bank has two types of customers: legal entities and individuals. They make demands on products: open accounts, conduct operations, make deposits. They impose requirements on the level of service, they wish to have a client-bank, a mobile version, mailings, etc. The bank satisfies the requirements, and all processes take place within the Ruli24 system: from accounting to analytics of the product portfolio and the system of internal tickets. At the same time, all processes are interconnected, which reduces the average service time and simplifies the collection of business information, on the basis of which new product offers are formed.
However, the process control system in a company is needed not only for such frailies as banks, but also practically any company. For a deeper understanding of the process approach, you can use the so-called Deming-Shewhart cycle "Plan - Do - Check - Act" (PDCA). This is "planning - action - checking - improving action." Using this cycle allows you to continuously implement continuous improvement processes, aimed at improving the efficiency of the organization. This concept was deeply reflected in the development of the Ruli xRM .This is the volume control model that underlies the idea of the whole system. If you imagine the model to be interactive, the relationships and intersections of all components become clear.

The process description form below resembles a PERT diagram, i.e. network schedule. The difference is that not all work can be carried out in a specific implementation of the production process, depending on the conditions of the "intersection". In addition, each work can be defined (in some of its attributes) depending on the conditions in the process description. But, as we remember, the process is not aware of the implementation of the procedures and instructions within it.

So, we decided on the model and draw up a sample checklist for managing the processes in your company.
- . , . , , , . .
- . , , , , . / . — , «»: , .
- — . , , , .
- (, , , ). .
- , . , 24, . , , . —«», .
- , , , . , . ( 24 ) , . , , .
- , , . , .
“To whom are you telling it now? I have a small business, guys in the palm of my hand, what processes! ”- some of Habr's readers will probably think so. We assure you, you are wrong. Company management does not begin with the first day of its existence, but with the birth of the very idea of creating such. And it is at this stage that the first processes are formed. Start small — automate primary connections and actions, then increase automation along with control growth. When the company grows and the flow of calls or customers becomes noticeable, you will not have a mess and the need for its automation. After all, as crm-schiki colleagues repeatedly joked here, the automated mess remains a mess.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/300994/
All Articles