Why need HTTP / 2 for sites

In the near future, the Internet is waiting for the transition to the new HTTP / 2 protocol, which accelerates the loading of sites. We understand how this will affect web development, search promotion, site security and other aspects, as well as what you need to know to connect HTTP / 2 and how to check its support.
What is HTTP / 2 and why is it needed?
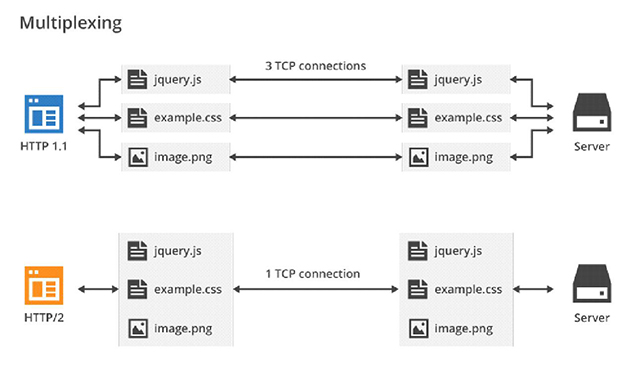
The HTTP / 1.1 protocol has been used since 1999, and over time it has found one significant problem. Modern websites, unlike the sites of the last century, use a variety of different elements: Javascript scripts, CSS styles, fonts, videos, and sometimes flash animation. When you transfer all this stuff between the browser and the server, several connections are created.
')
The HTTP / 2 protocol significantly speeds up the opening of sites due to the following features:
- connections: multiple requests can be sent through a single TCP connection, and responses can be received in any order. There is no need to keep multiple TCP connections;
- thread priorities: the client can set priorities for the server — what type of resources are more important to it than others;
header compression: the size of the HTTP header can be reduced; - push-sending data from the server: the server can send data to the client that it has not yet requested, for example, based on what page users are opening.
The development of the HTTP / 2 protocol was based on another SPDY protocol, which was developed by Google , but Google has already announced that it will refuse further support for SPDY in favor of more promising HTTP / 2.
Is HTTP / 2 really faster?
Experts from HttpWatch conducted several tests and found a serious acceleration from using HTTP / 2.
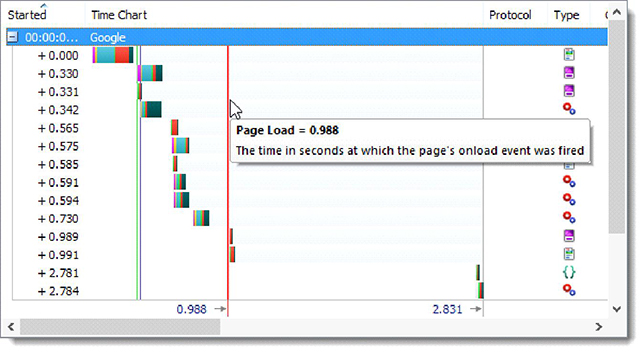
The screenshot below shows the page loading speed using HTTP / 1.1:
And on this screenshot - the result using HTTP / 2:
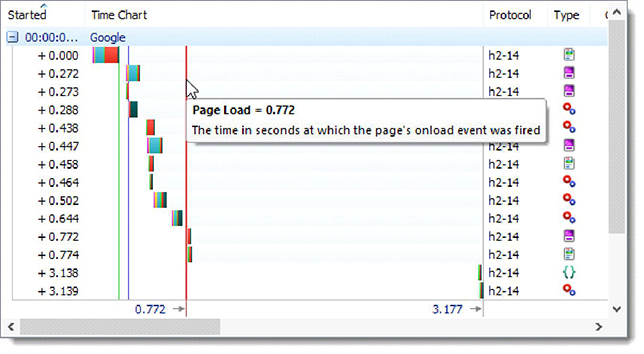
Download speed increased by 23%. HttpWatch experts also note that the technology is not yet fully optimized, and they expect a real acceleration of around 30%.
There are several other services that offer demo or provide an opportunity to check the speed difference on a live site: HTTPvsHTTPS and LoadImpact .
Airy.rf specialists also conducted testing in January-February 2016 to find out how much a real (small or medium) website can win after being transferred to the HTTPS + HTTP / 2 protocol. On average, several sites that have already been pre-optimized for speed (file compression and merging, network optimization), client download speeds increased by 13-18% only due to the inclusion of HTTP / 2.
It is worth mentioning that not all experiments were so unambiguous. On Habré, an experiment has already been described by the Yandex.Mail team . The SPDY protocol was tested, but recall that HTTP / 2 was developed on the basis of SPDY and is very close to it in terms of the methods used.
The Yandex.Mail team, after testing SPDY on some of its real users, found that the average load time changed only by 0.6% and did not exceed the statistical error. However, Yandex.Mail specialists found, nevertheless, a positive moment from using SPDY. Since the number of server connections has decreased (this is a key feature of SPDY and HTTP / 2), the load on the servers has noticeably decreased).
Why is it important to look for opportunities to speed up the loading of site pages?
John Muller, an analyst at the Google Webmaster Trends team, wrote on his Google+ blog that the presence of HTTP / 2 support on the site is not a direct ranking factor in Google. At the same time, download speed is in itself a significant ranking factor, so it makes sense to start using HTTP / 2 for SEO promotion.
He added that in itself the acceleration of the site should have a positive effect on the ranking due to behavioral factors. A more “quick” page has a lower bounce rate — most likely, more users will do something on such a page, and this will affect the ranking in the search.
John Muller also said that Googlebot will soon support HTTP / 2. And who knows - maybe in the future the presence of HTTP / 2 on the site will become a ranking factor. After all, search engines are constantly changing algorithms.
Which browsers already support HTTP / 2?
According to CanIUse.com, these are the following browsers:
IE 11 in Windows 10;
Edge 12 and 13;
Firefox 36 - 45;
Chrome 41 - 49;
Safari 9;
Opera 28 - 34;
Safari for iOS 9.1;
Opera 30 for Android;
Chrome 46 for Android;
Firefox 41 for Android.
According to CanIUse.com, this represents about 70% of the traffic .
It is clear that the traffic to their website may differ from the average on the Internet, but the data suggests that a sufficiently large proportion of users can use browsers that support HTTP / 2.
Security sites
Switching to HTTP / 2 (now) automatically means switching to HTTPS (protected mode of the site), other modes are not supported by browsers. HTTPS encrypts all site traffic and requires an installed certificate (a normal DV certificate can be obtained absolutely free of charge, for example, via WoSign or Let's Encrypt ).
Encrypting the site will not only help HTTP / 2. Google has already announced that site encryption is a positive sign of ranking .
Does HTTP / 2 give something to web developers?
Yes! HTTP / 2 allows you to get rid of a whole wagon of old tricks designed to speed up the loading of pages without HTTP / 2. We list them:
- domain-sharding or the use of multiple related domains for downloading files to allow more TCP connections to be established;
- image sprites - merge images into one file to reduce the number of requests. However, such a file must first be loaded completely, before at least one picture is displayed. In addition, processing large files eats more memory;
- combining CSS and Javascript files , which is also done to reduce the number of requests, and also increases the memory usage (and potentially, the amount of data loaded);
- inline inclusion or placement of CSS and Javascript, and sometimes even images inside an HTML file, to reduce the number of connections (for example, via base64). At the same time, it causes the page not to be shown until the entire file is loaded;
- non-cookie domains : download images, CSS and Javascript from another domain where cookies are not used.
How to connect HTTP / 2
The HTTP / 2 era is very close: many browsers already support this protocol . Its implementation does not require any changes in the site itself: you do not need to change the URL of the pages, you do not need to change the links, put redirects, add or change some markup, or provide additional data for Google Search Console or Yandex.Webmaster. HTTPS is used). If your site does not use protected mode yet, then to use HTTP / 2 you will need to enable HTTPS (with all related actions).
The implementation of HTTP / 2 takes place on that part of the server that gives pages to users, that is, on hosting. If you use an external hosting service, it is possible that your pages are already being sent to HTTP / 2 for all supported browsers.
If you use your own virtual or dedicated server, then HTTP / 2 support is added at the module level to nginx (in addition, you will need to install an SSL certificate and key on the server): on Habré already published a good instruction here .
You can check the HTTP / 2 support either through browser extensions for Firefox or Chrome , or through a speed check on the Iri.rf website: in the case of HTTP / 2 support, the test results will have a green [HTTP / 2.0] plate.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/300794/
All Articles