Internet of things for business objects (part 6)
How to integrate business into the Internet of things.
Information technologies are increasingly influencing the existence and nature of companies. Lined and formed functional and organizational business structures are intensively complemented by information systems in various areas and areas of activity. In all this interaction of information and personnel, business must learn to understand. And it is desirable not just to learn to understand , but to learn to extract the maximum beneficial effect from it.

')
The involvement of an object or thing in a business and its inclusion in the existing functionality is its linking with the business, to one degree or another according to one technology or another. At the same time, it is important to effectively link in a stable model both business objects from the real economic environment and things from the Internet.
Internet of things for business objects - all parts:
High performance of the company should give active use of the potential of the Internet of things. Integration of things from IoT with other objects that a business includes and involves in its processes can be organized as part of a coherent, evolving management network of interaction. At the core of this integration are three key principles :
Based on the above principles, one should speak about the possibility of a special level of qualified integration of things from the Internet within the framework of a single business organization model - we conditionally denote such a model as IoT'bo ( Internet of things for business objects ).
The business model in which traditional elements of economic activity are combined in executable processes, innovative business objects and things from the Internet is a built-up system of interacting units whose goal is to accomplish a selected mission, to execute a formalized strategy or to achieve a main goal. The model organizes and combines all used by the business independent or dependent units (resources, tasks, methods, technologies, tools, solutions, etc.). Management within the framework of such a model is carried out primarily not only by personnel and processes, but also by related goals (tasks), knowledge, data, relationships within the business, external communications, other information-dependent parties of the economic and market existence of the company.
The model, conventionally referred to as IoT'bo, is formed within the framework of the actual business activities of a business with the active involvement of things from the Internet and their inclusion in its functionality. Thus, a business is consolidated into a separate multi-purpose structure, through which interacting objects and things realize their unique competitive mission, strategy or main goal.
Business according to the IoT'bo model is an entrepreneurial economic system at the information and technological level, which is a purposefully designed and managed network of objects .
The basic sustainability and success of a business according to the IoT'bo model will depend on:
... unifying relationships based on a generally accepted mission, strategy or goal (a consequence of the principle of a unifying mission, strategy or goal);
... the quality of the objects and things involved in the business (a consequence of the principle of a common technological interaction platform);
... the quality of the connections between objects and things designed and operating in business (a consequence of the principle of a common technological interaction platform);
... qualification level of business management and quality of tools used for management (a consequence of the principle of dynamic information management).
The involvement of an object or thing in a business and its inclusion in the existing functionality is its linking with the business, to one degree or another according to one technology or another. At the same time, it is important to effectively link in the IoT'bo model both business objects from the real economic environment and things from the Internet.
The considered integrated model is much more complicated than managing a traditional company or project on the Internet of Things. And this follows, including from a number of features arising at the level of the junction of two networks of interacting units of different nature. The juxtaposition of the elements that make up the real business with the physical and logical things from the global information network has many features both in theoretical and in practical terms. Because of this, there is a need to pay special attention in IoT'bo to knowledge, methods, technologies, practices and standards of effective integrated management. To the forefront: innovative developments, intensive and objective analytics, continuous non-stop training, information development, building communications, protection from risks. Thus, they fade into the background, but are not excluded from the zone of attention and responsibility: the formalization of processes, an increase in fixed assets, price manipulations, sales logistics, hierarchical and vertical alignment of the organizational structure, bureaucratic regulation. Direct, and sometimes manual, management is replaced by the delegation of goals and capabilities with regulation based on standards and regulations.
IoT'bo-style business managers should be assisted by powerful and productive tools that enable them to respond quickly and flexibly to changes in the internal and external environment. With weak process connections, tools for experts who are able to practically combine various and sometimes multidirectional business processes or their blocks play a special role. Business develops important, practically significant competitive practices, patterns, situational decisions, algorithms, projects, and forecast plans. In this case, everything will have to ensure in a special way the stability and security of the built business model. The management will not be able to ignore risk management tools and technologies for a long time. Moreover, the IoT'bo model richly offers new comprehensive effective tools and technologies for a variety of subject areas of management.
Deep integration of real business with the Internet of things is very tempting and promising in terms of possible competitive advantages. The problem is how to implement this network integration holistically and harmoniously for the business itself and for its partners, contractors, competitors, customers, potential consumers.
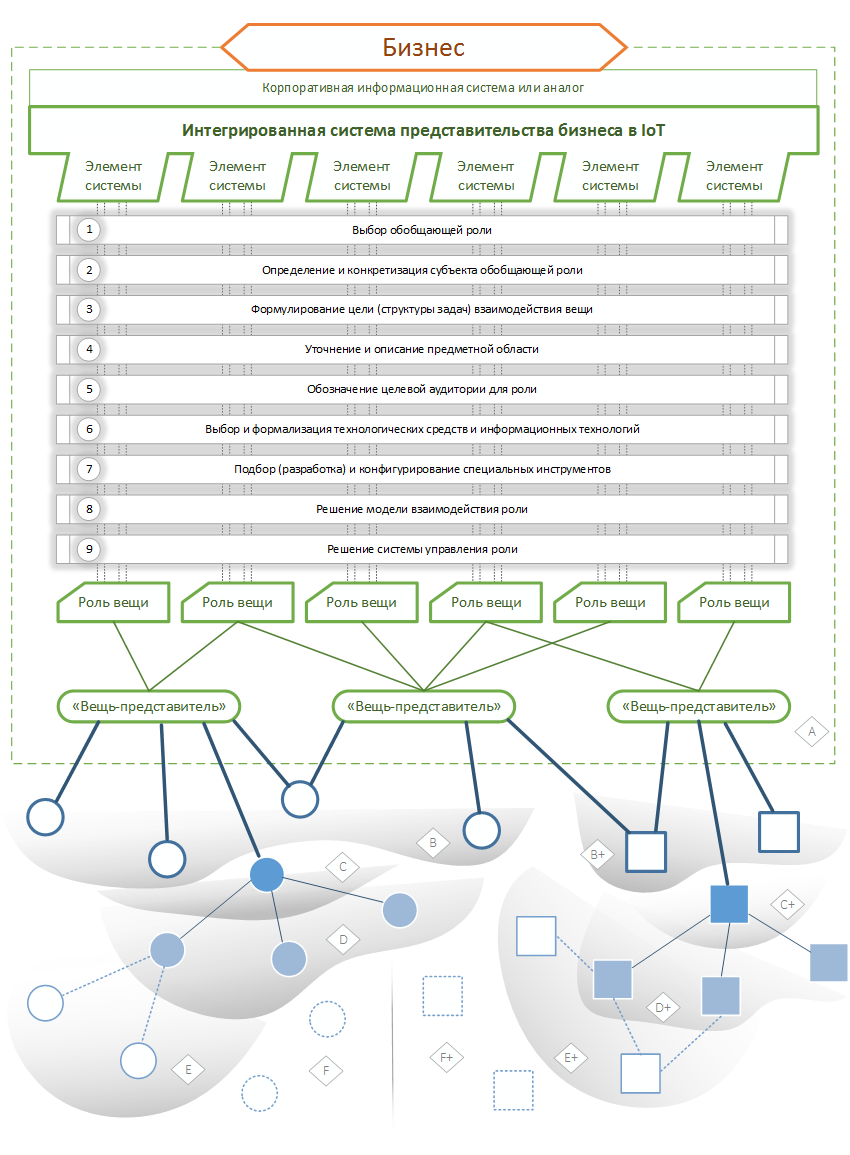
It is clear that business can be built into the information communication processes of the global network, by analogy with embedding the “ordinary thing”. But after all, an economic subject is not just a physical thing, but its state and functionality are very wide and changeable. It will be necessary to represent business as a kind of interrelated structure of several things of the Internet with certain attributes and functions. In a real implementation, a business should be represented on the network as a set of related “representative things” (connectedness or independence of things determines the marketing strategy). Each such thing represents a complete interface of state and functions for interaction within the framework of IoT, accessible to external users and things. A set of such representative things as a whole, representing and implementing a business on the network, should be systematically linked in a single managed model at the level of the business itself, and most likely will be integrated into the corporate information system (or its equivalent).
We introduce such a classification of the roles of representative things that can represent a business in the global network. Moreover, this classification is a functional-target definition of role elements that can be performed by a thing representing a business in a network.

Note to the table: a resource as a subject of a generalizing role is divided into information (non-material resource) and a material resource, due to the fact that information is the most important part of the global information network, which is the focus of this publication.
Integration of business with the Internet of Things through the representation in the form of a system of representative things is realized on the basis of special software and telecommunication means and technologies. These can be both holistic, custom-developed systems, and sets of specialized information management tools. For practical implementation, all the power of modern information technologies can be used, which are available within the open and closed (corporate) segment of the global information network, including: hypertext systems, Web services, Web applications (platform applications), cloud storages, servers data "issued on request", etc.
The thing that represents a business in IoT consists of a set of implemented roles that are connected by resources, tasks and functionality. The construction of each of these roles can be carried out within the framework of a typical scheme that details the parameters and helps to determine the initial conditions for the development specification.
A typical scheme for constructing the role of a representative item includes nine necessary steps:
For the correct construction of the role, it is necessary to consider and consistently decide on each of the indicated steps of the typical scheme. A specific business will eventually be forced to choose and form its own more detailed and practically meaningful, competitive scheme for constructing its representative things in the global information network. However, in one form or another, he will have to answer general questions from a typical scheme.
Optimal for business is the creation of a single, but rather complex subsystem, which, within the framework of the general policy of information interaction and IT development strategy, formulate tasks, develop, test, run for execution, monitor, adjust and analyze the result regarding IoT representatives. in general and for their individual role components.
(continuation - Part 7. Business objects: new technologies - Advantages. Perspectives.)
Information technologies are increasingly influencing the existence and nature of companies. Lined and formed functional and organizational business structures are intensively complemented by information systems in various areas and areas of activity. In all this interaction of information and personnel, business must learn to understand. And it is desirable not just to learn to understand , but to learn to extract the maximum beneficial effect from it.

')
The involvement of an object or thing in a business and its inclusion in the existing functionality is its linking with the business, to one degree or another according to one technology or another. At the same time, it is important to effectively link in a stable model both business objects from the real economic environment and things from the Internet.
Internet of things for business objects - all parts:
- Part 1. Internet of things: new features - Network. Factors.
- Part 2. The Internet of Things: New Features - Things. Purpose.
- Part 3. The Internet of Things: New Opportunities - Potential.
- Part 4. Business objects: new technologies - Model.
- Part 5. Business objects: new technologies - Factors. Objects
- Part 6. Business facilities: new technologies - IoT'bo. Integration.
- Part 7. Business objects: new technologies - Advantages. Perspectives.
BUSINESS OBJECTS: NEW TECHNOLOGIES
4. IoT'bo
High performance of the company should give active use of the potential of the Internet of things. Integration of things from IoT with other objects that a business includes and involves in its processes can be organized as part of a coherent, evolving management network of interaction. At the core of this integration are three key principles :
- The principle of a unifying mission (strategy or main goal) is to link various elements (objects, things) within a business on the basis of a mission uniting and shared by them (explaining the reason for the existence of a business) strategy (which forms an approach to achieving common goals for the realization of which business) or goals (determining the overall end result for which the business exists).
- The principle of a common technological platform of interaction is the organization and execution of the interaction of elements involved in the business, based on a unified system of interrelated methods, technologies, standards, protocols, procedures and rules.
- The principle of dynamic information management consists in the integrated management of a system of elements that are combined into business interaction on the basis of an information-oriented approach, an expanded productive set of tools, continuous development and training.
Based on the above principles, one should speak about the possibility of a special level of qualified integration of things from the Internet within the framework of a single business organization model - we conditionally denote such a model as IoT'bo ( Internet of things for business objects ).
The business model in which traditional elements of economic activity are combined in executable processes, innovative business objects and things from the Internet is a built-up system of interacting units whose goal is to accomplish a selected mission, to execute a formalized strategy or to achieve a main goal. The model organizes and combines all used by the business independent or dependent units (resources, tasks, methods, technologies, tools, solutions, etc.). Management within the framework of such a model is carried out primarily not only by personnel and processes, but also by related goals (tasks), knowledge, data, relationships within the business, external communications, other information-dependent parties of the economic and market existence of the company.
The model, conventionally referred to as IoT'bo, is formed within the framework of the actual business activities of a business with the active involvement of things from the Internet and their inclusion in its functionality. Thus, a business is consolidated into a separate multi-purpose structure, through which interacting objects and things realize their unique competitive mission, strategy or main goal.
Business according to the IoT'bo model is an entrepreneurial economic system at the information and technological level, which is a purposefully designed and managed network of objects .
The basic sustainability and success of a business according to the IoT'bo model will depend on:
... unifying relationships based on a generally accepted mission, strategy or goal (a consequence of the principle of a unifying mission, strategy or goal);
... the quality of the objects and things involved in the business (a consequence of the principle of a common technological interaction platform);
... the quality of the connections between objects and things designed and operating in business (a consequence of the principle of a common technological interaction platform);
... qualification level of business management and quality of tools used for management (a consequence of the principle of dynamic information management).
The involvement of an object or thing in a business and its inclusion in the existing functionality is its linking with the business, to one degree or another according to one technology or another. At the same time, it is important to effectively link in the IoT'bo model both business objects from the real economic environment and things from the Internet.
The considered integrated model is much more complicated than managing a traditional company or project on the Internet of Things. And this follows, including from a number of features arising at the level of the junction of two networks of interacting units of different nature. The juxtaposition of the elements that make up the real business with the physical and logical things from the global information network has many features both in theoretical and in practical terms. Because of this, there is a need to pay special attention in IoT'bo to knowledge, methods, technologies, practices and standards of effective integrated management. To the forefront: innovative developments, intensive and objective analytics, continuous non-stop training, information development, building communications, protection from risks. Thus, they fade into the background, but are not excluded from the zone of attention and responsibility: the formalization of processes, an increase in fixed assets, price manipulations, sales logistics, hierarchical and vertical alignment of the organizational structure, bureaucratic regulation. Direct, and sometimes manual, management is replaced by the delegation of goals and capabilities with regulation based on standards and regulations.
IoT'bo-style business managers should be assisted by powerful and productive tools that enable them to respond quickly and flexibly to changes in the internal and external environment. With weak process connections, tools for experts who are able to practically combine various and sometimes multidirectional business processes or their blocks play a special role. Business develops important, practically significant competitive practices, patterns, situational decisions, algorithms, projects, and forecast plans. In this case, everything will have to ensure in a special way the stability and security of the built business model. The management will not be able to ignore risk management tools and technologies for a long time. Moreover, the IoT'bo model richly offers new comprehensive effective tools and technologies for a variety of subject areas of management.
5. Integration
Deep integration of real business with the Internet of things is very tempting and promising in terms of possible competitive advantages. The problem is how to implement this network integration holistically and harmoniously for the business itself and for its partners, contractors, competitors, customers, potential consumers.
It is clear that business can be built into the information communication processes of the global network, by analogy with embedding the “ordinary thing”. But after all, an economic subject is not just a physical thing, but its state and functionality are very wide and changeable. It will be necessary to represent business as a kind of interrelated structure of several things of the Internet with certain attributes and functions. In a real implementation, a business should be represented on the network as a set of related “representative things” (connectedness or independence of things determines the marketing strategy). Each such thing represents a complete interface of state and functions for interaction within the framework of IoT, accessible to external users and things. A set of such representative things as a whole, representing and implementing a business on the network, should be systematically linked in a single managed model at the level of the business itself, and most likely will be integrated into the corporate information system (or its equivalent).
We introduce such a classification of the roles of representative things that can represent a business in the global network. Moreover, this classification is a functional-target definition of role elements that can be performed by a thing representing a business in a network.

Note to the table: a resource as a subject of a generalizing role is divided into information (non-material resource) and a material resource, due to the fact that information is the most important part of the global information network, which is the focus of this publication.
Integration of business with the Internet of Things through the representation in the form of a system of representative things is realized on the basis of special software and telecommunication means and technologies. These can be both holistic, custom-developed systems, and sets of specialized information management tools. For practical implementation, all the power of modern information technologies can be used, which are available within the open and closed (corporate) segment of the global information network, including: hypertext systems, Web services, Web applications (platform applications), cloud storages, servers data "issued on request", etc.
The thing that represents a business in IoT consists of a set of implemented roles that are connected by resources, tasks and functionality. The construction of each of these roles can be carried out within the framework of a typical scheme that details the parameters and helps to determine the initial conditions for the development specification.
A typical scheme for constructing the role of a representative item includes nine necessary steps:
- The choice of the generalizing role of business in a network (supplier, consumer, regulator)
- Definition and specification of the subject of a generalizing role (class of information, type of material resource, category of goal or task, type of functional)
- The formulation of the goal (structure of tasks) of the interaction of the thing representing the business in the network, which is realized through the role being developed
- Refinement and description of the subject area (issues) in which the role is being developed
- Designation of the target audience for the role , i.e. of things in IoT on which a business is oriented in terms of interaction through the developed role of a representative thing
- Selection and formalization of technical means and information (communication) technologies that the constructed role will use
- Selection (development) and configuration of special tools that will ensure the execution of the role being developed
- Solution of the role interaction model with its counterparties (including: the state and interface of the role, the transaction algorithm, the event model)
- The solution of a role management system , the task of which is to monitor the state of the role, its regulation, safety, and fit into the overall model being developed of a representative thing
For the correct construction of the role, it is necessary to consider and consistently decide on each of the indicated steps of the typical scheme. A specific business will eventually be forced to choose and form its own more detailed and practically meaningful, competitive scheme for constructing its representative things in the global information network. However, in one form or another, he will have to answer general questions from a typical scheme.
Optimal for business is the creation of a single, but rather complex subsystem, which, within the framework of the general policy of information interaction and IT development strategy, formulate tasks, develop, test, run for execution, monitor, adjust and analyze the result regarding IoT representatives. in general and for their individual role components.

(continuation - Part 7. Business objects: new technologies - Advantages. Perspectives.)
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/300168/
All Articles