How to improve the world?
Not the strongest, but the fastest survives in the modern world, and despite the fact that software today is the basis of almost any business, a company that can more quickly and others create and market products and services based on high-quality reliable programs gets a chance to improve how the world is overall, and their well-being, in particular. But how to do it in a large corporation, where you can only dream of speed, and not a startup from several programmers, where any crazy idea is good, because tomorrow it can turn the market around?

Today IT is not something single, always working according to the same rules, but at least two-speed education:
- traditional IT, with priorities in security and risk minimization;
- flexible IT, which should be responsive to new market requirements.
Realizing the importance of speed, such companies as Amazon, Facebook and Google, support the release of a significant number of versions of systems per day without compromising the reliability of the main functionality, which allows, in particular, they remain leaders in their fields. But how do they manage to organize the activities of developers so that, with unchanged quality, they can quickly release new versions? The answer interests not only IT companies, but also the industry, whose activity depends on software.
')
For organizing development processes, traditional approaches have long been invented and used, for example, a cascade development model, as well as flexible models, Scrum, for example, the most popular agile development technique in the world. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages. The agile development technique, in particular, Scrum, allows us to receive feedback earlier and detect errors, correct them, quickly release a version with implementation of customer-critical functionality, discarding minor features for the time being. However, for projects involving more than nine people in a team, approaches in the Agile style work poorly: teams for purely psychological reasons “fall apart” into subgroups of interest, difficulties arise in general communication. As a result, many, including Russian companies operating in the banking and telecom industry, are faced with the inability to bring together disparate teams that can offer users better quality, convenience and adaptability to any changing requirements.
Perhaps, Waterfall, Scrum and in general Agile methods are simply outdated, not suitable for large-scale projects, and they need to be replaced with something else? Is the waterfall model out of date? No, because such fundamental business systems as billing and processing systems of the bank change slowly, but the disruption of their work threatens to destroy the business. To achieve maximum stability of such systems, a waterfall model is applied. Systems of competitive advantage, forming the average level of the company's IT landscape, can be built on both classical and flexible approaches (Scrum). Finally, innovation systems, such as a mobile bank or a subscriber’s personal account, are constantly changing, directly interacting with end users, and Agile and DevOps are used to develop them.
When solving large-scale tasks, different approaches will inevitably be required, provided that the company's policies are mandatory and that they are prepared to change one or several approaches in response to external demands. But how can a large company scale Kanban, Waterfall, Scrum to synchronize all levels of development and ensure the coordinated work of teams from hundreds of programmers, testers, designers and architects?
HPE's research and development departments have existed for decades and, in particular, their task includes continuous improvement of internal development processes. Waterfall has been used for a long time and everywhere, its problems are understandable, in the past few years, some developers switched to Scrum, but none of them individually allows us to support large development and quickly and scalably - some kind of unifying idea, methodology was required. The SAFe ( Scaled Agile Framework ) framework on the platform from the pool of its own automation tools has become such a methodology for supporting the implementation of internal projects in the company. As a result, today, thanks to HPE Codar, Jenkins, HPE ALM, HPE Agile Manager, HPE UFT, and so on, the entire process of building, deploying and testing is automatic.
SAFe is a knowledge base, framework that allows scaling a flexible approach to the size of very large enterprises using Lean-Agile synergy.
As you know, Scrum aims to organize the process of approaching the project goal by conducting iteration cycles with adjustments to follow-up, based on analyzing the results of previous ones, and if Scrum is a tool for increasing functionality cyclically and adjusting the development course across a small group of programmers, then SAFe is a scale tool corporations. Classic and flexible approaches to development with the addition of new quality are integrated into SAFe: the methods of building teams of developers able to solve individual subtasks are taken from Scrum; the rules of fast creation of high-quality program code are taken from “extreme programming” (XP); Kanban introduces in particular the idea that teams and employees should have a limited amount of ongoing work. A distinctive feature of SAFe is Lean (Lean), which helps minimize costs by removing any obstacles to the release of new versions.
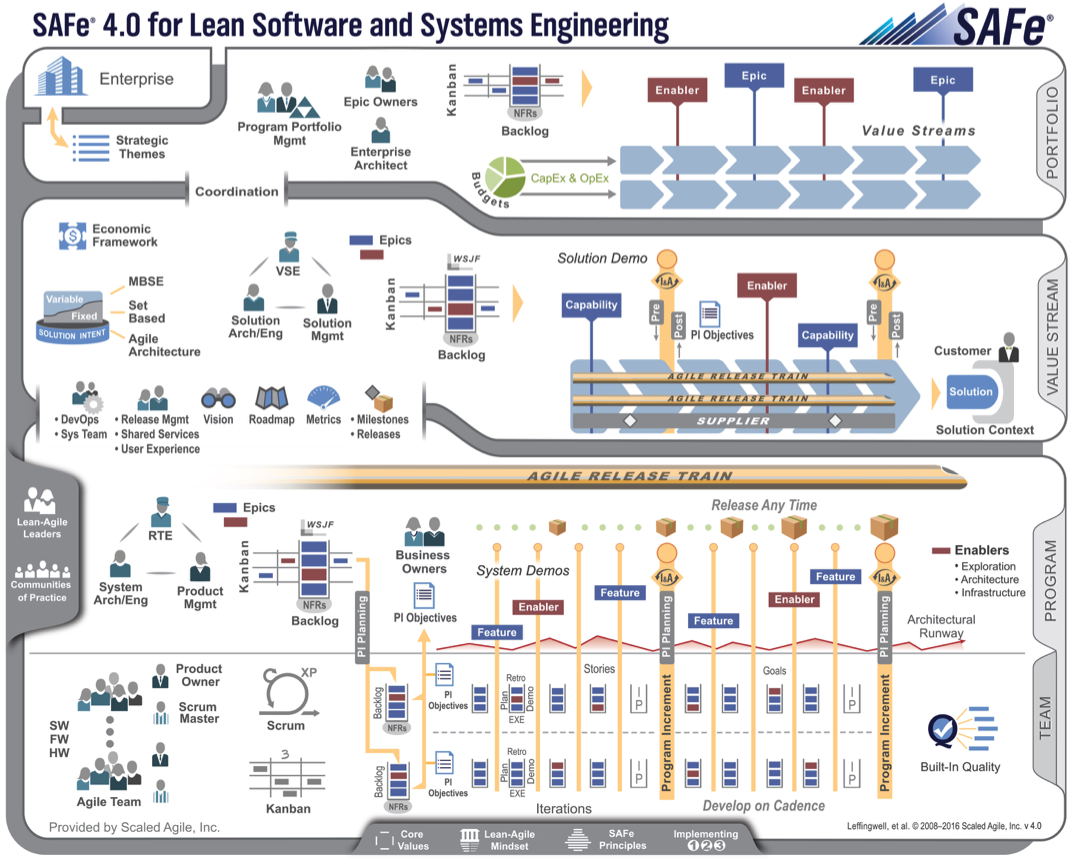
SAFe architecture
The main advantage of SAFe is support for large-scale development, in other words, the work of a large team goes not only through sprints (two-week cycles), as in Scrum, but with an additional iteration of planning (program increment) lasting ten weeks. At the same time, not one small team participates in planning, but a group of hundreds of developers involved in one project. It is important that within ten weeks versions of a product can be released, i.e. releases to the plan are not tied, the plan is needed only to set the tact for the development of a large system, which distinguishes SAFe from the waterfall model, in which the budget is allocated to the project plan, and not to the constantly financed program of all activities.
In SAFe, work is organized as a permanent process in a single step, without a schedule of release versions, but with a clear preservation of architectural integrity: the next version is released exactly at the moment when the business required it, and not when it was planned by someone in advance. In SAFe, the idea of a “locomotive of releases” is implemented, which is well integrated into the ideology of any large company while preserving the principles of flexible approaches when scaling and with a detailed description of the interaction processes. At the same time, any automation tools available to companies can be used in SAFe — the SAFe methodology is invariant with respect to automation tools.
SAFe facilitates the solution of one of the main problems of traditional development methodologies - the transfer of a large group of developers of knowledge from business, explaining the task of the next iteration. In traditional methodologies, communication usually breaks down and agile development principles are violated — you cannot control every developer at any time, but if he knows how his contribution fits into the big picture, he can make decisions and be responsible for his actions.
It is argued that SAFe allows developers to increase developer productivity by 20–50%, the quality of the solution by 50%, and the time taken to bring the product to light by 30–50%. Thanks to SAFe, satisfaction of the project of all its subjects is increased, and the project no longer risks turning into a “black hole” of the budget, but quickly begins to produce results. As a result, today more than 60% of Fortune 100 companies already have SAFe-certified specialists in their staff who help create a single “IT for IT” picture in which software development, engineering solutions, and operational management are consistent.
Why is all this made possible?
- SAFe sets the tact of movement not only to developers, but also to all the services of a corporation: marketing, planning department, service units, etc.
- SAFe eliminates the bottleneck: if product managers are involved in all the details of the development, participating in each decision, they become a bottleneck. Delegation of authority to teams allows this to be avoided.
- SAFe not only allows communication between individual developers, but also encourages the interaction of teams and departments and integrates well with the DevOps approach.
To this can be added transparency of development and reduction of risks of making wrong decisions only on the basis that the leader of a team shouts the loudest about its problems: any solution is aimed at achieving a common, not a private goal.
Many domestic companies that are familiar with the Kanban, Scrum and Lean methodologies and have obtained the first successful results with their help, want to improve the world today, but now they are faced with the issue of scaling. There are already quite a few large organizations in Russia that are interested in flexible project management techniques for development, but they lack experience in scaling to large teams and SAFe can help here.

Today IT is not something single, always working according to the same rules, but at least two-speed education:
- traditional IT, with priorities in security and risk minimization;
- flexible IT, which should be responsive to new market requirements.
Realizing the importance of speed, such companies as Amazon, Facebook and Google, support the release of a significant number of versions of systems per day without compromising the reliability of the main functionality, which allows, in particular, they remain leaders in their fields. But how do they manage to organize the activities of developers so that, with unchanged quality, they can quickly release new versions? The answer interests not only IT companies, but also the industry, whose activity depends on software.
')
For organizing development processes, traditional approaches have long been invented and used, for example, a cascade development model, as well as flexible models, Scrum, for example, the most popular agile development technique in the world. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages. The agile development technique, in particular, Scrum, allows us to receive feedback earlier and detect errors, correct them, quickly release a version with implementation of customer-critical functionality, discarding minor features for the time being. However, for projects involving more than nine people in a team, approaches in the Agile style work poorly: teams for purely psychological reasons “fall apart” into subgroups of interest, difficulties arise in general communication. As a result, many, including Russian companies operating in the banking and telecom industry, are faced with the inability to bring together disparate teams that can offer users better quality, convenience and adaptability to any changing requirements.
Perhaps, Waterfall, Scrum and in general Agile methods are simply outdated, not suitable for large-scale projects, and they need to be replaced with something else? Is the waterfall model out of date? No, because such fundamental business systems as billing and processing systems of the bank change slowly, but the disruption of their work threatens to destroy the business. To achieve maximum stability of such systems, a waterfall model is applied. Systems of competitive advantage, forming the average level of the company's IT landscape, can be built on both classical and flexible approaches (Scrum). Finally, innovation systems, such as a mobile bank or a subscriber’s personal account, are constantly changing, directly interacting with end users, and Agile and DevOps are used to develop them.
When solving large-scale tasks, different approaches will inevitably be required, provided that the company's policies are mandatory and that they are prepared to change one or several approaches in response to external demands. But how can a large company scale Kanban, Waterfall, Scrum to synchronize all levels of development and ensure the coordinated work of teams from hundreds of programmers, testers, designers and architects?
HPE's research and development departments have existed for decades and, in particular, their task includes continuous improvement of internal development processes. Waterfall has been used for a long time and everywhere, its problems are understandable, in the past few years, some developers switched to Scrum, but none of them individually allows us to support large development and quickly and scalably - some kind of unifying idea, methodology was required. The SAFe ( Scaled Agile Framework ) framework on the platform from the pool of its own automation tools has become such a methodology for supporting the implementation of internal projects in the company. As a result, today, thanks to HPE Codar, Jenkins, HPE ALM, HPE Agile Manager, HPE UFT, and so on, the entire process of building, deploying and testing is automatic.
SAFe is a knowledge base, framework that allows scaling a flexible approach to the size of very large enterprises using Lean-Agile synergy.
As you know, Scrum aims to organize the process of approaching the project goal by conducting iteration cycles with adjustments to follow-up, based on analyzing the results of previous ones, and if Scrum is a tool for increasing functionality cyclically and adjusting the development course across a small group of programmers, then SAFe is a scale tool corporations. Classic and flexible approaches to development with the addition of new quality are integrated into SAFe: the methods of building teams of developers able to solve individual subtasks are taken from Scrum; the rules of fast creation of high-quality program code are taken from “extreme programming” (XP); Kanban introduces in particular the idea that teams and employees should have a limited amount of ongoing work. A distinctive feature of SAFe is Lean (Lean), which helps minimize costs by removing any obstacles to the release of new versions.

SAFe architecture
The main advantage of SAFe is support for large-scale development, in other words, the work of a large team goes not only through sprints (two-week cycles), as in Scrum, but with an additional iteration of planning (program increment) lasting ten weeks. At the same time, not one small team participates in planning, but a group of hundreds of developers involved in one project. It is important that within ten weeks versions of a product can be released, i.e. releases to the plan are not tied, the plan is needed only to set the tact for the development of a large system, which distinguishes SAFe from the waterfall model, in which the budget is allocated to the project plan, and not to the constantly financed program of all activities.
In SAFe, work is organized as a permanent process in a single step, without a schedule of release versions, but with a clear preservation of architectural integrity: the next version is released exactly at the moment when the business required it, and not when it was planned by someone in advance. In SAFe, the idea of a “locomotive of releases” is implemented, which is well integrated into the ideology of any large company while preserving the principles of flexible approaches when scaling and with a detailed description of the interaction processes. At the same time, any automation tools available to companies can be used in SAFe — the SAFe methodology is invariant with respect to automation tools.
SAFe facilitates the solution of one of the main problems of traditional development methodologies - the transfer of a large group of developers of knowledge from business, explaining the task of the next iteration. In traditional methodologies, communication usually breaks down and agile development principles are violated — you cannot control every developer at any time, but if he knows how his contribution fits into the big picture, he can make decisions and be responsible for his actions.
It is argued that SAFe allows developers to increase developer productivity by 20–50%, the quality of the solution by 50%, and the time taken to bring the product to light by 30–50%. Thanks to SAFe, satisfaction of the project of all its subjects is increased, and the project no longer risks turning into a “black hole” of the budget, but quickly begins to produce results. As a result, today more than 60% of Fortune 100 companies already have SAFe-certified specialists in their staff who help create a single “IT for IT” picture in which software development, engineering solutions, and operational management are consistent.
Why is all this made possible?
- SAFe sets the tact of movement not only to developers, but also to all the services of a corporation: marketing, planning department, service units, etc.
- SAFe eliminates the bottleneck: if product managers are involved in all the details of the development, participating in each decision, they become a bottleneck. Delegation of authority to teams allows this to be avoided.
- SAFe not only allows communication between individual developers, but also encourages the interaction of teams and departments and integrates well with the DevOps approach.
To this can be added transparency of development and reduction of risks of making wrong decisions only on the basis that the leader of a team shouts the loudest about its problems: any solution is aimed at achieving a common, not a private goal.
Many domestic companies that are familiar with the Kanban, Scrum and Lean methodologies and have obtained the first successful results with their help, want to improve the world today, but now they are faced with the issue of scaling. There are already quite a few large organizations in Russia that are interested in flexible project management techniques for development, but they lack experience in scaling to large teams and SAFe can help here.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/299872/
All Articles