Lecture 1 out of 10. Experiment and grow. How Twitter and FB Grows

Growth Hacking is already a science and it claims that the key to multiple growth is within the team.
The hopox hypothesis testing service in 10 lectures systematizes knowledge about multiple growth based on experiments, hypotheses and analytics. Here is the content of the lecture course:
- Experiment and grow
- 7 types of hypotheses
- Work Growth Team
- Attraction Hypotheses and Values
- Work based on data
- Activation hypotheses
- Retention hypotheses
- Viral hypotheses
- Hypothesis Guidance Note
- What I hid.
Lecture 1. Experiment and grow
What is the secret of the rapid growth of Twitter, Facebook, Amazon?
Perhaps they originally had a brilliant idea? Or crazy investments allowed to hire expensive marketers? Perhaps just lucky?
I’ll say the answer right away: in fact, they were not afraid to experiment, make mistakes, and did it often and quickly. The location of buttons on Facebook, the mechanics of keeping users on Twitter, forcing to buy on Amazon or Booking through a chain of letters, retargeting or discounts, all this is the result of a huge number of experiments.
')

All big companies do it. Facebook’s mobile app constantly needs to be updated, Amazon changes the code on the site on average every 11 seconds, and Twitter’s vice president admitted that significant growth began when ten hypotheses were tested in
a week, not one in two weeks.
The number of experiments per week = the growth rate of the company.
Any marketing actions, even changing the code on the site, can be interpreted as an experiment. But feel the difference between “just selling” on the phone, or selling a lot, if the processes are built, the staff is trained, the CRM system is implemented. The difference, as between craft and production, is not it?
Use this material from 10 lectures and a service for hopox marketers so that growth in your company ceases to be a spontaneous phenomenon. Now growth is a streamlined, manageable process that can be measured and influenced.
The described growth technology is perfect if you already have a product in which users feel happy and pay for it. In this case, multiple growth is achieved by continuously searching for bottlenecks, reducing costs, and increasing the number of clients through fast, data-based experiments.
Who came up with these marketing experiments?
In the book “Business from scratch,” Eric Rees described the scientific approach to bringing new products and services to the market with minimal resources using constant experiments and feedback from customers. Here are some key principles you need to use to systematize the process of experimentation:
- Any marketing initiatives should be taken only as assumptions. To quickly test the assumptions - formulate them in the form of a hypothesis indicating the predicted effect in numbers.
That is, now all the tasks are formulated as hypotheses:
“If <action>, then <result in numbers>”
- Any new functionality can be tested by creating a Minimum Sustainable Product (MVP) to get feedback from the client and understand what functionality is really needed. This statement applies to everything.
- You can not build long-term plans. Having a long-term vision, divide the plan into short iterations for a period of one to two weeks and do only what you can quickly get a response from the client.
- Start the process of continuous learning in the Build-Measure-Learn cycle. This cycle connects the experiment, the receipt of feedback from the client in numbers and the awareness of the experiment results into a single process.
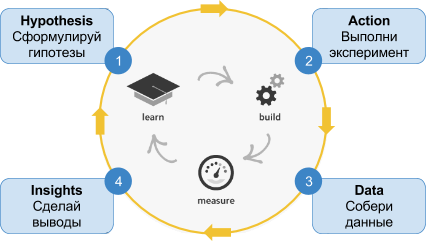
What does the Build-Measure-Learn cycle do?
1. Objective development based on data.
No feelings, emotions, speculation. The cycle allows you to measure performance immediately, as something done. In fact, the cycle instills a work-based work culture.
2. Continuous learning.
It is important to understand that each product is unique, each audience is capricious, and what works in one company may not work in another. Multiple advantage is possible when you do not copy someone else's model, but create your own, unique one.
The cycle allows you to accumulate unique knowledge within the team. Each new hypothesis contains the accumulated experience of all
tested
In hopox, the HADI cycle is used (Hypothesis - Action - Data - Insights) - this is the simplest algorithm for cyclically testing ideas - from hypothesis, through action, to data and conclusions.
The management cycle begins with the formulation of a hypothesis (Hypothesis) according to the principle “if ... then ...”. At the second stage, it is necessary to carry out a series of works to launch an experiment (Action), then collect data for a given period (Data) and finally make an unambiguous conclusion whether the hypothesis was successful, what can be improved by running the next Insights cycle.
Homework:
1. Create a project in hopox
2. Add the whole team to the project
3. Create one simple experiment in hopox, which is easy to check in one week. Just take one task that you already wanted to do this week, only now do it in the form of a hypothesis indicating the result in numbers.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/299582/
All Articles