The organization of the warehouse. Description. BPMN diagrams are attached
The barcode was invented in 1951 and, it would seem, has already firmly entered our lives, however, as my practice shows, many users do not know what it is, even many IT specialists do not know what a barcode scanner and data collection terminal are. . And it seems that all this is difficult to understand and implement, but in fact it is quite simple. And one of the goals of this article is to show how easy it is to work with bar-coding, to clarify the logic and sequence of operations in an automated warehouse.
This article does not claim to be true: on some projects, the issue of automation is solved differently than the option given in the article. There were about 30 such projects where it was necessary to bring the warehouse to an efficient, working condition. And I developed a scheme of work that has become for me the standard for warehouse automation. On the one hand, it is simple, on the other - it meets the basic requirements.
The scheme of work of the warehouse given in the article is scalable, but the essence in any case remains the same. Such a scheme of work is suitable for both reseller companies and manufacturing companies that have a warehouse and keep records of goods or materials.
')
We will talk about warehouse accounting with the use of special equipment, software and hardware. I will tell you what devices are used, at what point, how to act in certain situations.
This article is intended primarily for IT-specialists, for programmers and for those who possess at least some technical skills. First, the article uses terms that are often not understandable to ordinary users. Secondly, there are still BPMN notations with a description of business processes that will be understandable to the specialist, but not to the user. In addition, lately, it was IT specialists who approached me three or four times, who opened their stores or advised their customers. If you are going to open your business, which requires a warehouse, or provide advice on the implementation of programs and equipment, this article will be useful to you.
So, let's begin.
Why do we need warehouse automation?
Nowadays, my company quite often is approached by customers regarding the implementation of a CRM system, sales increase, process optimization, etc.
But at the analysis stage I, as a rule, also look at how the work of the warehouse is built (usually in companies there is always a warehouse). And if I see some kind of “failures” in the work of the warehouse, I will certainly inform the management of the company.
What is the point of introducing a CRM-system and a system of increasing sales, if the accounting of goods is incorrect If a client with whom you worked so thoroughly, applying innovations, will you order in the end a product that will be in short supply or re-grading, and is not in stock? So, you have done vain work?
Therefore, I always recommend to start to establish a system of storage and accounting of goods and automate the work of the warehouse.
Usually, the warehouse of small and medium enterprises is at the most primitive level. Keeping inventory is conducted manually. The accuracy of the accounting leaves much to be desired. Based on my experience, I would say that keeping stock control by the manual method costs the company much more than its automation. With the manual method of collecting and entering data, the information that is needed is often unreliable. And the increase in the cost of servicing the goods leads to an increase in the cost of the product itself.
Warehouse automation is a relatively simple technology, the implementation of which does not require expensive equipment or software. Thus, automation, if not directly affecting the increase in profits and sales, then reduces the running costs of an enterprise for sure.
Barcode goods
In accounting systems it is necessary to enter data on the barcodes of the item. Otherwise, your accounting system does not recognize the product, and you will not receive a full account. When filling out information about the new position of the item, there are two options for forming a bar code:
- barcode input using a scanner - this option is relevant for companies selling when they receive a product that has its own barcode
- automatic formation of a barcode in the accounting system - this option is relevant for companies producing goods and reseller companies in case the goods from the supplier are received without a barcode
Equipment for inventory accounting
To automate the work of the warehouse requires special equipment. You will need:
- barcode scanners for receiving, assembling and shipping goods;
- data collection terminals for inventory;
- label printers for printing when you need your own labeling of goods
Consider each of these types of equipment in more detail.
1. Barcode scanner
Barcode scanner is a compact device, the main function of which is to read information from the product label and transfer it to the accounting system. Barcode scanner is used when assembling goods, when goods are received and sales of goods to the client.
Scanners are different in their technical characteristics: single-plane, multi-plane, etc. They differ in quality, speed, reading range and other indicators.
Barcode scanners are wired and wireless. I recommend using wireless in order not to limit employee mobility and not be tied to a place. Yes, they are many times more expensive, but it is very convenient.
2. Terminal data collection
Data collection terminals are a specialized device that is a portable computer with a built-in barcode scanner.
The terminal is intended primarily for the rapid collection, processing and transmission of information about the product during the inventory, but can also be used when goods are received and goods are assembled for shipment to the customer.
The data collection terminal has a beam for scanning; a monitor on which we can see which product is scanned; and a keypad for entering information about the quantity of goods and for executing various commands.
With the help of TSD, you can both scan the entire product in a row, or read the barcode of a specific position and manually enter the quantity of this product.
The terminal, unlike the scanner, not only reads a barcode, but also accumulates information about scanned barcodes in its memory. Naturally, there are more expensive devices that can communicate with the database and give information about the rest of the goods, etc. But we consider the simplest version of the TSD, when we just need to take an inventory.
TSD are different, their cost varies from 25 thousand rubles to exorbitant numbers (I saw the TSD for 250 thousand). The effectiveness of the TSD in this case does not depend on the price. Which one do i recommend using tsd? I recommend the simplest one that performs scanning, storing and transferring data to the accounting system. All new-fangled systems on android, with color display and other advanced functionality require skilled professionals, thoughtful work with this equipment and good software. Yes, such functions are not needed, since they do not affect the final result. Therefore, the simpler - the better.
Also, when buying a TSD, components such as a stand and a spare battery are needed. TSD is such equipment which is quickly removed from production. You bought it, and then you may not find components on it, and you will have to either look for them or buy a new one. Therefore, I recommend immediately stock up on batteries.
Why do I need a stand? It is connected with the accounting system itself, through which data is transferred from the TSD to the system. In addition, bundled with the equipment is usually no USB cable to connect the stand with a computer, it also needs to be purchased.
Another important nuance that must be considered when buying a TSD: you can buy one or two stands on four or five terminals. Why? The terminal itself is constantly used during the inventory, the stand is used for a short period of time to upload and download data from your system to the terminal data into your accounting system. You can wait, because the unloading itself takes 10-15 seconds, depending on the speed of the terminal. I recommend that customers purchase 2 coasters and 5 TSDs for one medium-sized warehouse for a quick inventory.
In addition, TSD can be used for admission or implementation. You can scan all incoming goods by the terminal, and load the data into the receipt document in the accounting system.
3. label printer
A label printer is a device with which a barcode image is applied to a label. In the accounting system is formed a label, which is then printed on the printer.
Barcode labels must be printed, as I wrote above, on a product that does not have a barcode. This happens if you are a manufacturer of a product, or you received a product from a supplier that does not have a barcode.
What to buy label printer? I recommend buying not the most expensive, but not the cheapest label printer.
What you should pay attention to when buying:
- performance
- label width. If you have a large product and you want to print a large label, then you should choose a printer that can print that width.
- conditions in which the device can function. Quite often it happens that warehouses are in an unheated room, and equipment is bought for an office, naturally, it will quickly fail due to temperature, humidity, etc. Therefore, if you have an unheated warehouse, always take into account the conditions in which it can function device.
It is necessary to say a few words about the labels themselves. Labels are specialized paper for marking a product, with the possibility of applying graphic information, and not just a bar code. Labels can be of different sizes and from different materials. The sizes are presented the most different and it makes no sense to describe them. I just dwell on the material - there are two types:
- thermal transfer labels - printing is possible only with ink ribbon, mainly black
- thermal labels - printing on thermal labels is carried out by direct heating of selected points of the moving label with the thermal head of the printer or weights
The article would not be complete if I did not say about the cost of equipment. Yes, the equipment on the market presents a different cost of it varies greatly, but I will give a list of the equipment chosen by me for a real project.
| Item number | Name | Price | Qty | Amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| one | Thermotransfer label printer Citizen CL-S 621 (black) | 33014 | one | 33014 |
| 2 | Self-adhesive label tape 30x20 (2000 pcs.) Semi-gloss | 76 | 2 | 152 |
| 3 | BlueTooth Laser Barcode Scanner Honeywell / Metrologic 1202g, Voyager, BT, USB, with stand (black) | 27411 | 2 | 54822 |
| four | USB interface cable (AB) | 242 | one | 242 |
| five | Terminal OPH-1005 (complete) 4Mb flash, 64Mb RAM | 38293 | 2 | 76586 |
| Total: | 164816 | |||
Now, when the goods are scanned, the data on the compliance of the nomenclature and barcode have been entered into the accounting system, the equipment has been purchased, we can carry out automated work of the warehouse. Consider in detail how this happens.
Automation of warehouse processes
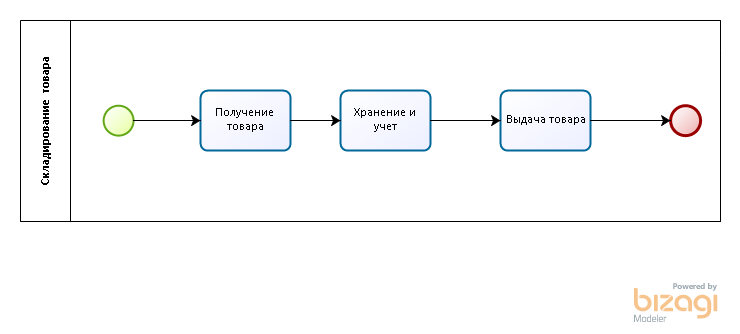
Conventionally, the work of the warehouse can be divided into three processes:
- Receipt of goods - includes the following operations: capitalization of surplus, receipt of goods from the supplier, receipt of goods from production.
- Storage and accounting of goods - involves carrying out inventories of goods, the movement of goods between warehouses and premises.
- Delivery of goods - includes various operations of the expenditure of goods: write-off for internal needs, write-off of damage to goods, shipment to the client.
Let us consider, in order, what work takes place in the warehouse at each of these processes using the example of specific operations. For the convenience of perception of your and your customers, at the beginning of each of the three sections, I provide a description of business processes in BPMN 2.0 notation
Receipt of goods from the supplier.
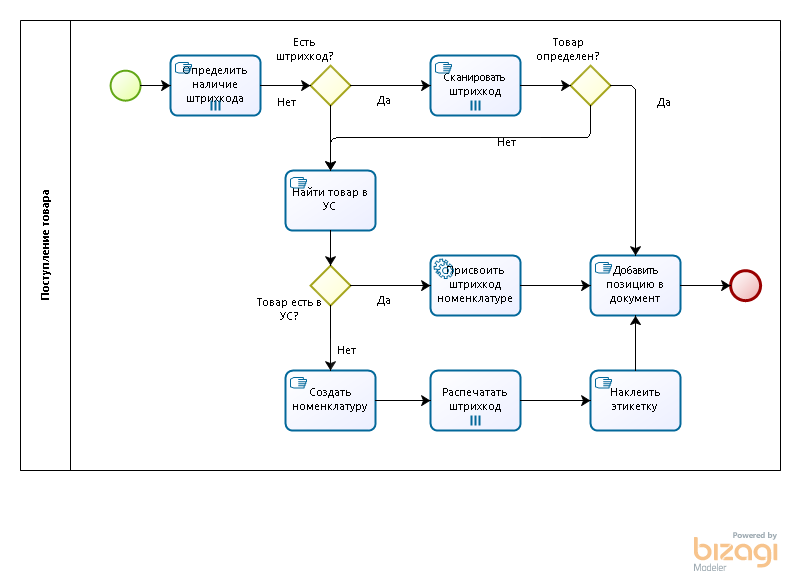
How does the operation of receiving goods from the supplier?
- We create an order to the supplier, in which we indicate the goods we need.
- The supplier brings the goods.
- We read one after another barcodes of goods by a scanner, and enter them into the database in the document Goods Receipt.
The question immediately arises: what if the goods arrived without a barcode?
We have already talked about this above, but for now let's take a closer look at the procedure itself. If the goods came without a barcode, then there are two options for the development of events:
- If we have time and we know what kind of goods will be without a barcode, we can prepare in advance or print the required number of labels during the reception, paste them on the goods, and then transfer them to the warehouse by scanning.
- If we quickly need to credit the goods in order to have information on the balances in the database and immediately begin to reserve the goods for customers - we credit the goods by quantity, but without carrying it through a scanner. That is, employees consider the goods and manually enter the data into the accounting system.
When the goods receipt document is carried out in the system, employees can safely barcode the goods: print labels with a barcode and glue them onto the goods.
If the products are expensive - I do not recommend using the second option of receiving goods. Still, in this case, you first need to scan the goods, take it, and then start selling.
We must remember the rule: if a product arrives without a barcode, if we have little time and the product is not very valuable, we can first credit it by quantity, not spend it through a barcode scanner, and then barcode and paste labels.
When labeling barcode labels on a product, there is one useful trick. It is very simple, but greatly facilitates the work:
If you made an order to the supplier, and you know what quantity of goods will come, you print the labels in advance. It so happens that the product is either not all shaded-coded, or it is known which product will not have a barcode - you generate barcodes for such a product in the accounting system in advance and print all the labels on the product of the future receipt. The number of labels must match the number of expected goods.
Then when you receive the goods from the supplier, you can not counting it, just stick labels. If there are no labels left and no glued goods, then the quantity of goods corresponds to what you ordered. If there are extra labels left (this happens), it means that the goods are not delivered. If the labels were not enough, it means that they brought a surplus or there was some sort of re-grading (perhaps they stuck a barcode on the wrong product). In this case, you must immediately find out where you made a mistake, or what the supplier did not bring.
So, for the posting of goods from the supplier or any other posting you need a barcode scanner and label printer. It is also possible to make a receipt by the data collection terminal: we read all bar codes by the terminal, and then we load all the information in a lump sum or in parts into the goods receipt document in the accounting system.
Once the product is labeled, you lay it out. About address storage, when your warehouse is divided into sections, and in a certain section you put a certain product and mark it in the system - I will not say here. To use or not to use the address warehouse - everyone decides for himself. But I do not recommend it to be used in small and medium-sized enterprises, as employees begin to make mistakes, they cannot calculate the size and volume of their warehouse and the like. Therefore, this article will not consider such an option as address storage, serial accounting and the like. This scaling, complication of the system, but it does not affect the essence of the work.
After we have received the goods, it is stored with us, we must control the goods, keep records of them, make a so-called inventory and, if necessary, arrange the movement of goods.
Storage and accounting of goods in stock

Storage and accounting of goods involves the conduct of inventories and the movement of goods between warehouses and premises. Moving goods occurs by reading bar codes - here I will not delve into the description. The Transfer document is the simultaneous delivery of goods from one source warehouse and receipt at the receiving warehouse. You open the Move goods document and scan the necessary goods into it.
Let's take a closer look at the inventory. How is she going? What equipment is needed for this?
Inventory is the verification of the availability of goods on a certain date by comparing the actual data with the accounting system.
From my experience I will say that it is wrong to do the inventory on your own. Many companies make an inventory on their own, arguing that their employees know the product very well, unlike third-party specialists. But this is wrong, as it turns out that the warehouse worker checks himself.
Ideally, if third-party companies (auditors or 1c-nicknames) are involved in the inventory, or if there is no such possibility, involve employees of their own company, but from other departments that are not related to work in a warehouse. Why is this necessary? Because, I repeat, it is impossible for a person to check himself.
There were such cases when the inventory (especially if it was the first inventory) was a reason to write off all its flaws, theft, etc. etc. Especially if a person works for a long time. If according to the results of the inventory - everything came together, this should make you suspicious, most likely the case is not clear, there is a deception of the system by the employee.
When I was such a case that the warehousekeeper "found" the product after identifying shortages as a result of inventory. It looked extremely suspicious.
Also I remind you that the inventory must be carried out on weekends or during off-hours, in order to avoid the movement of goods. Many companies neglect this, and then they are looking for where the shortage came from.
How is the inventory going? An employee or several employees (if several employees - the warehouse is divided into sections) read the goods on the racks one by one using the data collection terminal. Each employee goes and scans the goods that he comes across in his section. Then the TSD is installed on the stand and the data is loaded into the accounting system.
Information from the TSD comes in the form of a document inventory or recalculation of goods with information about what product was scanned during this work. Then you need to delete data from the terminal, after which you can scan the next portion of data until the entire product has been scanned.
What nuances need to be considered in the automated inventory of goods? If you scan a product in several passes, there is such a problem: when loading data from the terminal into the accounting system, the previous data from the Inventory document is deleted.
How do we usually act in such cases? It creates several documents of the Data Inventory, where it is recorded, who scanned, and which rack. Then we take and combine the data from several documents into one by copying.
What should the system do next when we have all the data in one document? The system compares the results of the Inventory document with the credentials and provides information about surpluses and shortages. In order for the system to have up-to-date information on the residues of goods in warehouses, according to the results of the inventory, the following should be done:
- write off shortages
- deposit surplus
Then, the financially responsible person for the warehouse can be penalized for the difference between the write-off and the posting.
To summarize, during the inventory, the following actions are performed:
- scan goods
- load this data into the Inventory document,
- the system automatically compares the credentials with the actual, and gives us information about the need to create documents of cancellation and / or posting of goods.
Delivery of goods
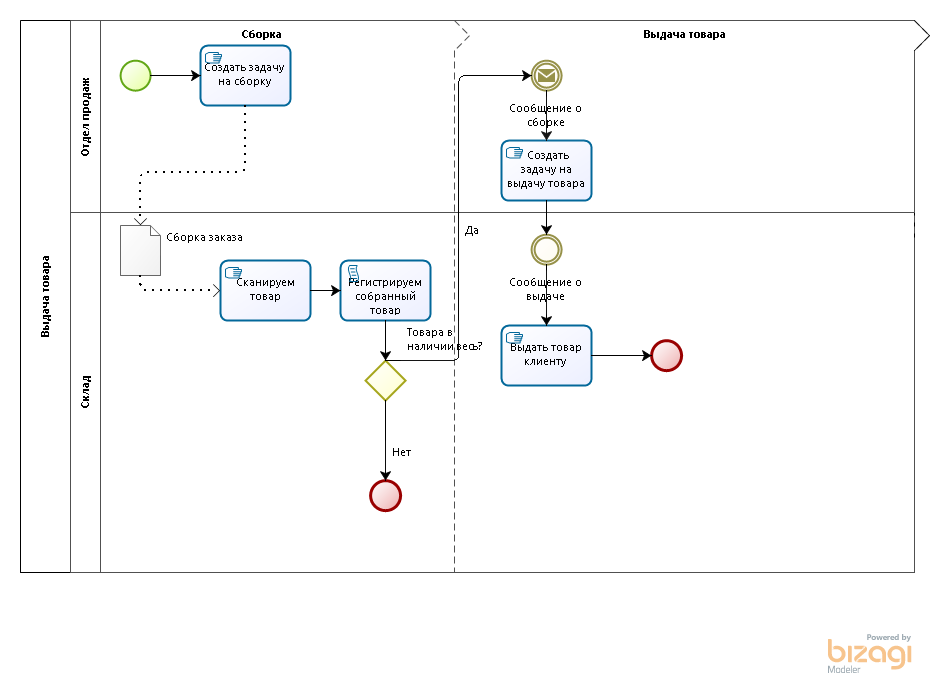
Now consider the option of shipment of goods to the client. Usually the scheme of selling goods to the client looks like this:
- sales manager places a customer order
- after payment of the goods (or meringing it, if the company releases the goods on credit) the manager draws up a document for the sale of goods
- the warehouse collects and releases the goods ordered by the customer
But here it is necessary to understand the problems of the Russian discipline. For example, you have 50 units of goods in the database, and there are 49 of them in stock. If we create a realization and carry it out, and only then we collect the goods, conflicts may arise with a client who has already paid 50 pieces and counted on 50.
And with such a scheme of work, the storekeeper informs the manager about the shortage of goods after the fact.
How can this be solved? I recommend to introduce between the registration of the customer’s order and the implementation of the implementation procedure for the assembly of goods:
- the manager reserves the goods as requested by the client
- the manager gives the warehouse a task to collect an order
- the warehouse on the basis of the order draws up the document Assembly of the order, where it holds the necessary data about the product collected for the order.
The product assembly document consists of information that needs to be collected and how much has already been collected. The warehouse worker collects the goods, scans it, if the goods are scanned, the data in the column of the collected goods increase.
If we scan more than the required number, then the system issues a list of redundant positions. If we scan a smaller amount, we will not be able to close the work on the order until all the goods have been assembled. If in the assembly the quantity of the assembled goods coincides with the quantity to the assembly - on the basis of this assembly the realization of goods and services is created.
If the product is not enough, this is reported to the manager, the manager is already communicating with the customer about the order, but this is another business process.
Why do I need to assemble the goods? If we create an implementation right away, this is wrong, because then our financial obligations to the client occur. But in fact, as long as we do not see all the goods on stock as ordered by the client, until we have collected them, we cannot tell the buyer that the goods really are in stock.
You can arrange the assembly of goods not only with the help of a scanner, but also with the help of a data collection terminal. In this case, all the collected goods are scanned at a time, and the data is loaded into the Goods Assembling document.
Often the question arises at the enterprises: What to do with the weight goods that we sell by the piece?
It happens that the goods are credited by weight, and sold by the piece. For example, bolts. Bolts come in kilograms, and you sell them piece. How to be here? Very simple. The system starts two units of measurement of the item - pcs and kg, indicates the ratio of how many pieces are contained in a kilogram. When selling and assembling goods, the employee scans the barcode of this product and enters the quantity of goods sold. At the same time labels with bar codes do not need to stick on each unit of goods. The storekeeper has a piece of goods with bar codes on which the bar code cannot be pasted, he scans and drives in the number of bolts.
When writing off, the amount is debited both in units and in kilograms. Then the inventory is carried out by kilograms, the goods are weighed, and the actual weight is checked with the accounting. Due to the coefficient you can always know how many pieces are contained in a kilogram, how much one piece weighs. And if 50 kg of bolts arrived, and 1000 units were sold at 50 grams - we should have a quantity of 0. If nothing is left, then everything is in order: 50 kg of bolts arrived, 50 kg was gone.
Conclusion
I hope the information provided will be enough to design and automate the work of the warehouse in your company or your client.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/296718/
All Articles
