New auction in Yandex Direct: 3 changes and how to use them

In late August, Yandex Direct moves to a new type of auction VCG. The current “second price” scheme will remain in the past. For some it is an apocalypse, but for someone a bright future. What is the essence of the changes, what the new rules will bring and how to use them with the maximum benefit - read in this article.
As it was before: second price auction
')
Here advertisers pay for each click a downstream competitor’s bid plus bidding increments (1 cent or 30 kopecks). Thus, in the block of special placement, for positions in which advertisers fight, whoever pays more, he is higher. Hence the effect of “overheating” of the auction and the failure for those who evaluate the effectiveness of the advertising campaign for the recoupment of traffic.
Here is how it looks in an example:
Suppose you have two competitors with a similar product. Marginality and conversion rates are all the same:
The purchase price of one unit of goods - 10 000 rubles;
Retail cost - 13 000 rubles;
Margin - 3,000 rubles;
Landing page conversion - 3%;
Conversion of the sales department (calls and orders for sales) - 50%.
The maximum bid you are willing to pay is calculated as the product of the margin, site conversion and sales force conversion. The result is:
Maximum bid = 3,000 rubles. x 3% x 50% = 45 rubles.
If the rate is above 45 rubles, advertising does not pay off.
Suppose you set the maximum allowable rate of 45 rubles. with a CTR of 10%. The second competitor puts 30 rubles. with a CTR of 15% and the third - 20 rubles. with a CTR of 20%. At the same time, the minimum threshold for entering the special accommodation is 25 rubles, therefore the last competitor is “in the span”.
Positions are distributed as follows:

Cool: we rank first due to the highest bid. But what does this mean in terms of efficiency?
According to Yandex statistics, the first place in the special placement collects 100% of clicks, the second - 85% and the third - 75%.
Revenue is defined as the product of the number of clicks, conversions and margins. And profit as the difference between revenue and advertising costs. And what picture we get:
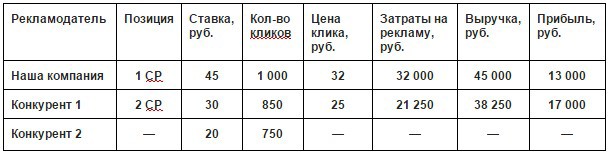
As you can see, the second position has a higher return on investment (ROI) due to lower traffic prices. That is why many advertisers have used the “Show in block at minimum price” strategy.
New VCG system
Here it is assumed that the cost per click depends on the traffic: the more traffic you collect, the more you pay. Specifically, the payment will go for additional clicks that our competitors have received less (the same 15% and 25% for the second and third places in the special placement).
Advertising budget = Costs of competitors if we are not in the auction - Costs of competitors when we participate in the auction
If we were not there, the 1st competitor would receive 100% clicks for 30 rubles, and the 2nd competitor 85% of clicks for 20 rubles. Accordingly, their costs would be 30,000 and 17,000 rubles. Total - 47 000 rubles.
Our budget = 47 000 - 17 850 = 29 150 rubles.
The cost of a click on the 1st place in special placement = 29 150/1 000 = 29.15 rubles.
The price of a click under new conditions decreases (in the first case, it was equal to 32 rubles.) Of course, while competitors maintain their rates.
VCG does not protect against rate hikes and, most likely, in the near future we will again encounter an “overheating auction”. This is already established psychology. However, ideally, the VCG system prompts you to set a true bet if all participants behave rationally. Some experts call this type of auction “sincere” because it is the most optimal for both Yandex and advertisers.
By the way, VCG (by the names of American economists Vickrey, Clark, Groves) has long been used by Google and Facebook, so Yandex in this regard is drawing on the best practice of auctions in online advertising.
Yes, there are still bets on the Yandex.Direct interface for entering a specific position and the ability to set your own bets. At the same time you will see the actual price for each position: the system will become more transparent.
That's not all: except for the new auction, Yandex abolishes discounts and amends the ranking of ads in the blocks. What does this mean?
Cancel discounts
This is a blow to large advertisers who bought large amounts of traffic and received a discount from Direct. Such a system had a negative impact on the ranking and the price of a click: for example, with a 10% discount, the advertiser could use it to overestimate the rates by the same 10%. The new auction establishes uniform rules of the game, without price odds for anyone. Traffic in the first positions should be cheaper, due to which Yandex intends to compensate for the damage to the "monsters" of the market.
New ranking rules
Now sorting in blocks will depend on three factors: CTR, rates and quality factor. Recall that, until now, only the rate affects it. As a result, the last place in the special placement was the ad with the highest CTR.
Interesting data leads in the book "Optimization of contextual advertising" Andrei Belousov. This is the probability that the position of the best ad in the block:
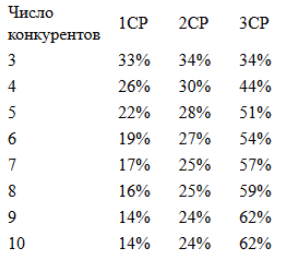
The worse the CTR, the greater the chances of first place. Here is such a strange logic)
Yandex declares that more attractive ads for users will get more benefits. Okay, everything is clear with CTR and rates, but what does the quality factor mean? As usual, its formula is unknown to mere mortals, but from the available information we can assume the following.
Yandex approximates the Yandex.Direct scheme to search results algorithms. And in the first place here is the rule of relevance: how relevant are the request, the announcement and the landing page. This is where the fun begins. If directors got the hang of copying the request into the headline and ad text, then the landing pages are in trouble.
As a rule, traffic goes on one page. In the extreme case, several landing pages for different types of services. For example, Tinkoff Bank has a credit card, a special credit program and a debit card. Only three pages for 1,350 unique ads!
It is a bit easier for online stores, where there are a lot of product pages, but even they are not able to fully ensure that the content of the page matches all user requests.
A common example is when an ad promises one thing:

A user lands in a completely unfamiliar place:

Where are the Samsung tablets at a super-advantageous price? Even if the store has a separate page for a specific brand, users have dozens of various query options: in terms of memory size, screen diagonal, color, functionality, not to mention the conditions of purchase and service. And they all get on the same page: those who are looking for a "Tablet with Windows", and those who are looking for a "Tablet with delivery."
Leading context experts say that behavioral factors will influence the ranking. That quality factor is directly correlated with the bounce rate and viewing time. And if users "run away" at breakneck speed from the landing page, they don’t see top positions for advertisers, even at high rates and good CTR. Thus, Yandex introduces a rule of efficiency based on the logical chain “Request - Announcement - Landing”.
What to do
1. Adjust traffic to relevant landing pages.
First of all it concerns online stores. With an exact request (for example, “Samsung Galaxy Tab 4 tablet”), users are not sent to a category, but to a page of a specific product or sample. Yes, this is a more labor-intensive process, but it is worth it: otherwise, the bounce rate will go off-scale (remember the previous example of the discrepancy between the ad and the product page).
The fact is that contextual advertising competes with organic matter, where, in the overwhelming majority of cases, the principle of relevance is observed. And Yandex simply does not have the advantage of rolling commercial ads "past the box office." To save long-term profit, he will be forced to reduce the number of ads in special allocation (to two, for example).
For example, the official website of Samsung, the request "Samsung Galaxy Tab 4 tablet."
Advertising (1 CP) leads to this page:

And link from organic here:
Backfill question: Which of the two options will the user choose?
2. Disable non-targeted traffic
Everything is simple here: you need to "shovel" the semantics and exclude the homonyms that sound the same with your product, but mean something completely different. For example, in the Tinkoff Bank's advertising campaign, we found the query “sanatorium card”. And there are a lot of such examples.
Working with additional relevant phrases and auto-expansion is a delicate process. If you want to capture the so-called one-cent traffic, you need to carefully work out the offer for each such keyword. As a rule, directors do not bother with this and merge 10-20% of the budget to nowhere.
3. Increase the uniqueness of ads
Compliance with the text of the request remains a key condition, while you can even more unique ad: to expand the mode of operation, create additional benefits, as well as use quick links-triggers.
4. Increase the relevance of landing pages
Real truth: the user must immediately find the necessary information, see the correspondence to his query. At the same time, we showed how things are in practice.
Dynamic content allows to create an exact correspondence of a site to user requests from contextual advertising. With the help of the Yagla service , you specify which elements you want to substitute for requests. We recommend the most conversion ones, on which the execution of the target action directly depends: title, subtitle, CTA button, signatures for lead forms.
The simplest option is an exact match “Request = Title”, as in Direct. For example, one of our customers, a pawnshop, has two types of services: buying and exchanging cars. On request “Car exchange”, the user sees in the title the sentence “We will exchange your car with mileage”. And at the request of “Purchase of cars” - “We will buy your used car”. This already gives an increase in conversion in the application by at least 15-18% in different niches.
But for a tangible increase in conversion, you need to create not just a match, but an attractive offer (selling proposition). For example, “We will redeem your car with a mileage of up to 90% of the market value / Evaluation within 60 minutes. The whole amount on the same day. The “Headline + Subtitle” scheme is more cumbersome, and at the same time contains several triggers at once. In this case, by successive tests, you can achieve an increase in conversion by several times. Record - 960%.
For details on how dynamic content works, how to implement it and what it gives on specific examples in different niches, see this article .
PS Everything goes to the approximation of contextual advertising to the principles of ranking organic traffic. Some experts even predict a mix of advertisements with search results in 1-2 years. And at the head of the corner is user experience, the quality of which depends on the compliance of needs (requests) with the offer on the site (landing page). In other words, give the user what he is looking for and give it immediately.
With respect to you and your business, the founder of the service Yagla.ru Alexander Alimov
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/293554/
All Articles