Case: how to accelerate the development of the project

In May 2015, representatives of FRIA together with Ilya Krasinsky and Carrot Quest conducted an unusual workshop, whose main task was to improve the unit economy of 5 startups. What did and how improved, read on.
The lead speaker of the event was Ilya Krasinsky (expert and trainer of the Accelerator of IIDF, the founder of AppCraft, mentor, coach and entrepreneur in Magic Ink).
The economy of startups has been raised through the use of an integrated approach that has been worked out in the Accelerator of IIDF for more than 150 startups. An important role in this methodology is played by HADI – cycles. We want to talk about them in this article, written on the basis of the material of the workshop.
')

This technique can be applied in any sphere, but first of all, it will be useful if you are an internet marketer or founder of a startup.
HADI cycles
HADI cycles are one of the tools of the methodology with which help IOs startups successfully in the Accelerator. The essence of HADI is very simple. Almost any action has an impact on a particular metric. If the changes are “screwed” to the indicators in advance (formulate hypotheses), then the whole process of changes will be controlled. In short, you will understand how your actions influenced the result , and you can quickly test ideas, discarding non-working ones.
This is what the HADI loop looks like:
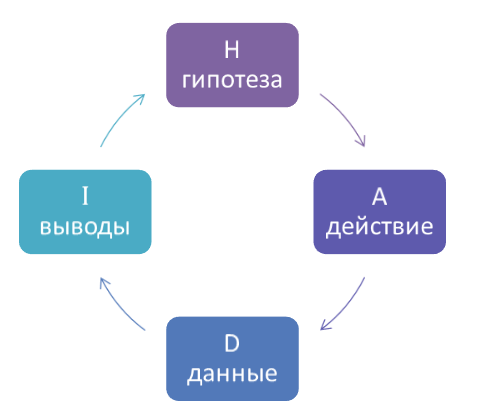
1. Hypothesis .
We write down hypotheses, that is, changes (your actions) that can improve the performance of your economy.
For example: “changing the title will increase the conversion to landing page registration by 5%”.
First of all, it is necessary to generate hypotheses for those indicators, the change of which is important in the near future. This means that if there is a problem with conversion to registration, then it is necessary to generate those ideas that directly affect this indicator.
2. Action .
At the beginning of each cycle (we have this every week) we take several hypotheses and begin to put them into practice. For example, we rewrite the headers, and add customer benefits there.
The main formula is to do it quickly. If the change is beneficial, it will not be difficult to improve it and scale it. The main thing in HADI is operational testing.
3. Data collection .
We start collecting data on indicators that will be affected by the change. In our example, this is the conversion to registration.
In order for the indicators to reflect real changes, the sample (the number of visitors during testing) must be representative. More on this later.
4. Conclusions ( Insights ).
We analyze whether the hypothesis worked. If yes, then we plan to improve it, scale it.
Not all hypotheses will be confirmed. In order not to waste time on weak hypotheses, you can use a special ranking algorithm, which we will discuss below.
Do not simultaneously test several hypotheses that affect one metric, since you will not understand which particular hypothesis worked, which changed the indicator. For example, they changed the product description on the site and made another payment system. The number of purchases fell, why? The answer to this question will be difficult to find.
About the event and practice HADI
5 startups actively participated in the workshop:
- Carrot Quest (a service for communication and user management based on their behavior, this is us);
- LPmotor (entrepreneur's office with Landing Designer, built-in CRM-system and sales funnel);
- SkyparkCDN (CDN, content delivery service, speed up content loading);
- PlayKey (cloud gaming service that allows you to run modern games on any device);
- Capsidea (data visualization service).
- In the process, several more teams connected.
Ilya Krasinsky and I analyzed the landing pages of all startups, which we will write about in a separate article. After the analysis, each startup already knew its problem areas and understood in which direction to begin work.
Brainstorming teams recorded a number of hypotheses, which were later added to a special table.
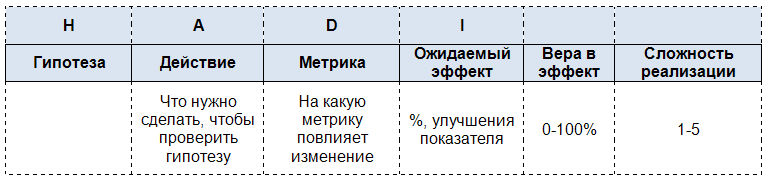
Belief in effect shows how much the team believes in this hypothesis. The complexity of implementation reflects how much resources will be required to test the hypothesis (1 is simple, 5 is difficult).
Here is an example of several hypotheses from different teams:
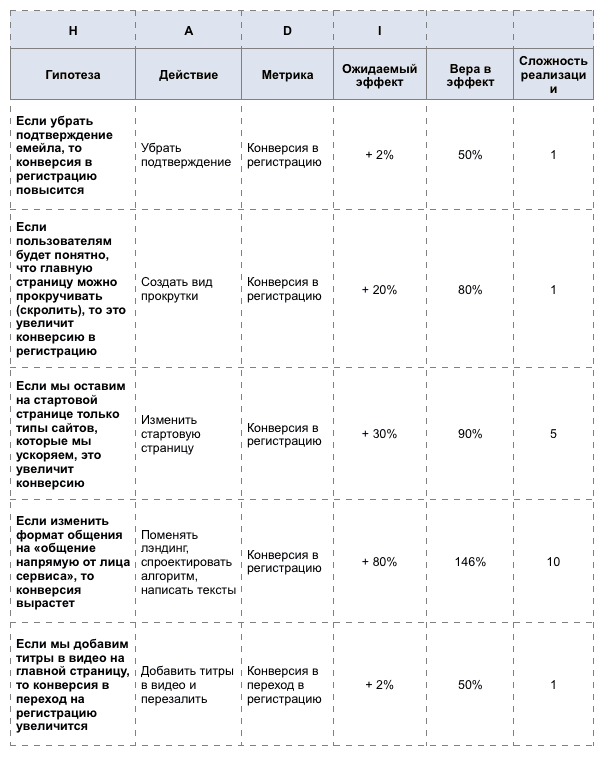
Each team has formulated 10 different hypotheses.
To continue the work, you need to build a hypothesis on priority. The list should be headed by the most significant hypotheses, and the weak should be discarded (so as not to waste precious time on checking them). If the belief in the effect is low, and the complexity of implementation is high, then it is worth postponing such a task.
Next, startups tested their hypotheses for a week (approximately 2-3 hypotheses for each team). For the objectivity of the tests, all projects were given the task: to attract 3000 visitors per week. With such attendance, the confidence interval (error) is about 1%, which means that if the conversion increases or decreases by more than 1%, then the reason for this is our change. If less than 1%, then this is just an error: the changes have affected slightly.
For most teams, this was the first experience with HADI cycles. Someone checked 2-3 hypotheses, someone managed only 1. A number of hypotheses were confirmed, and some, on the contrary, led to the opposite result (indicators worsened).
Week is the best time for short iterations, teams in the Accelerator analyze their HADI cycles once a week at the Saturday traction rally, and they also plan on testing hypotheses for the next week, this helps them focus. The main value for a startup is that each team quickly checks several ideas and sees which ones work. The team also receives feedback if it shows its results to experts and other teams in Accelerator or a similar workshop.
An example of working with hypotheses from Carrot Quest
A small box about us so that you understand our specifics.
Carrot Quest is a service for communicating and managing users based on their behavior. A service in which you know about the actions of each of your visitors and use this knowledge to retain and involve him in the purchase. We have combined the very best tools of Internet marketing: eCRM, online chat, pop-ups, email newsletters and web analytics. Our target audience is SaaS services, online stores and online projects.
The main task for us was to increase the conversion to registration, so we built our hypotheses for this indicator.
Here is the work on one of the hypotheses:

As it was:
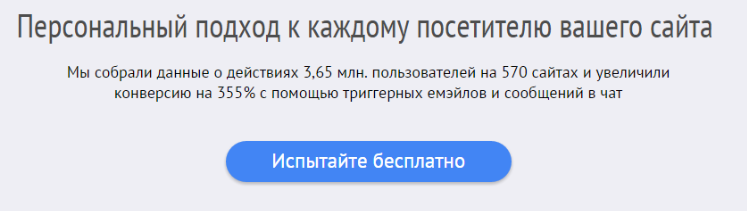
We decided to show that leaders in various market segments are already using marketing automation and personal communications in their projects. Found those companies that accurately automate marketing, and used their names in the title.
As it became:

In this title, the names of the companies changed (Ikea, Kaspersky, Intel, etc.). We also changed the rest of the headings and buttons on the page.
As a result, the growth of conversion in this regard, we have not seen. Therefore, we are already testing the following hypotheses. If you are interested in, what results were obtained in the following tests - write in the comments, we will tell.
PS
Read the article on the CPU, how we manage the HADI cycle in our team: How to organize work on the SaaS projects in Trello . The technique is excellent, with its help we have already saved a lot of time and made a number of remarkable changes.
Successful work with HADI – cycles and large conversions. If you already have experience - share it in the comments, discuss together. If you have any questions, ask.
With pleasure, the Carrot Quest team.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/291700/
All Articles