Why do you need a business process model?
We are often forgotten to ask why we love business processes so much and what tasks we solve with the help of process management. In this pilot article of our blog, we will consider how using one model of one business process we can solve several practical problems from the life of a business of any size.
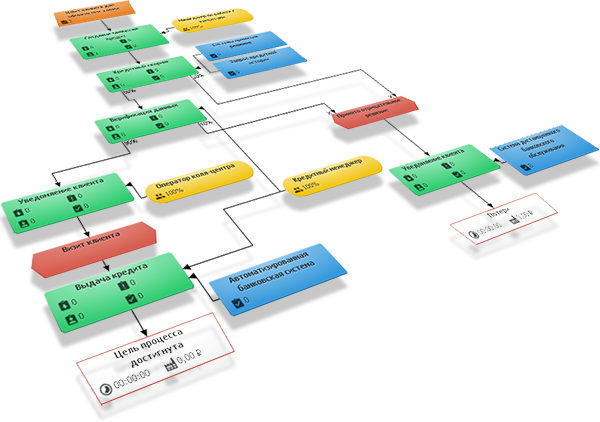
For example, let's create if not a federal bank, then at least a sales department of a new company for the planned sale of N units of product per month. For the department needs staff and head. How many and which employees and supervisors are needed to sell such a volume of products? It's not clear yet, you have to jot down a model. Before the BPM Simulator BPM service, this had to be done on beach sand, on walls and other available platforms.
')
This is enough for manual or automatic generation:
And if you create a model of organizational structure and competency model, then you can immediately form and:
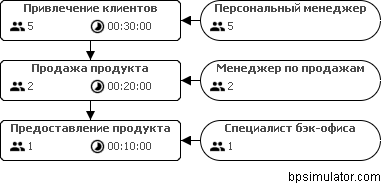
We have prepared the resources, you need to think about the tool - the software. A project manager from the IT department will be happy if, instead of a series of conflicting interviews, you give him a more detailed model of the future business process. So here it is, we added the inputs / outputs and resources to perform the functions:

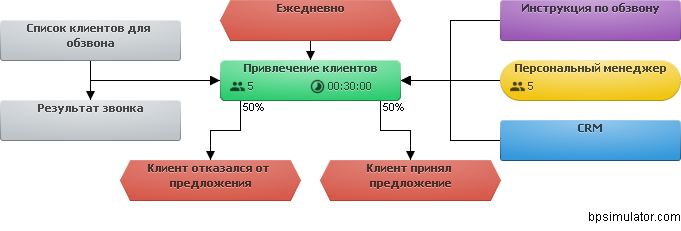
The requirements can be described in more detail the sequence of functions, for example, "Attracting customers":
Based on such requirements, it is possible to evaluate the possibility of introducing software.
With capital expenditures on software licenses decided, and what about operating? It is necessary to conduct a cost analysis of the share of costs for the cost of the product. We will supplement our model with the cost of resources (or we will connect the organizational model created earlier with data from software on payroll).

So simple? Now, yes, but earlier for such an analysis it was necessary to involve operators, productologists, technologists, financiers and personnel managers. If in the process of creating the cost driver the process itself was changed, then you had to start the whole calculation all over again.
It would seem that it would be easier for the formation of the rules for the execution of the business process to assign the aunt in a shawl (methodologist), explain, pray and wait several months before the born Rules appear in the throes. Maybe if you remember that both the model and the regulations are different forms of the same entity. Take our model and finger or cursor from top to bottom:
We get:
All, current and complete regulations, understandable for the performer and for the controller is ready, carry on the signature.
Experiments in combat conditions are very expensive. How to find out how the process will behave, if on Friday to make the working day shorter, on Wednesday the chief specialist will unexpectedly go on maternity leave and how much will the florists physically sell on March 8? To do this, we need to place the model of our process in an imitation environment as close as possible to the real one.
In addition to the business process model, you will need an external environment model, but it just needs to know how often an instance of the process and events are launched that affect its execution. For example, in the afternoon the call center receives an incoming call on average every 5 minutes.
The simulator will run tasks in the business process model in the quantity and as long as necessary. And upon completion you will have the results of simulation modeling necessary for making a decision, as if the process actually worked for the right time.
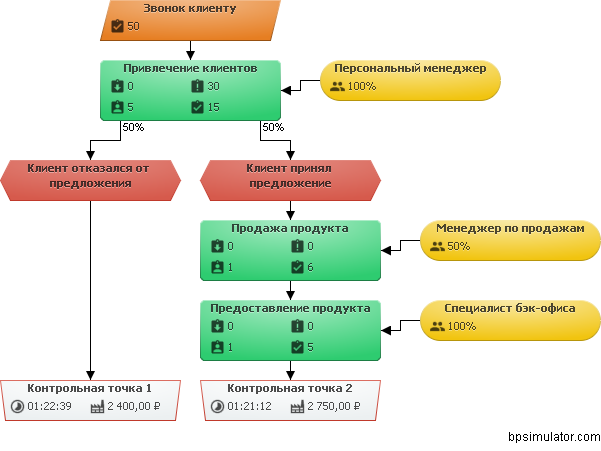
Unlike the static model, the simulation results show that employees do not work for more than 8 hours, their tasks are transferred and wait for their turn to execute or available resources, bringing the calculated performance data to the actual ones.
All the examples of the application of the model described above are real, often applicable and accessible. In addition, with the help of the BP model, less trivial tasks are also simply solved: creating a risk map, analyzing quality management circuits and sources of defects for lean manufacturing. Having a model of only one process for the formation of the listed results saves a lot of man-hours, in case of a change in the process, the results are also easily updated by making changes to the model. We are too lazy to spend time on a routine, which is why we love processes and, we hope, will love you too.
Subscribe to our blog here and you might find out:
In the meantime, we are waiting for you at our BP Simulator business process optimization service .

Organizational structure
For example, let's create if not a federal bank, then at least a sales department of a new company for the planned sale of N units of product per month. For the department needs staff and head. How many and which employees and supervisors are needed to sell such a volume of products? It's not clear yet, you have to jot down a model. Before the BPM Simulator BPM service, this had to be done on beach sand, on walls and other available platforms.

')
This is enough for manual or automatic generation:
- Regulations on the division "Sales Department"
- Employee Recruitment Plan (9 posts)
- Job descriptions of employees:
- Head of Department
- Personal manager
- Sales Manager
- Back Office Specialist
And if you create a model of organizational structure and competency model, then you can immediately form and:
- Job search vacancies (4 roles)
- Training plan (9 employees for 4 roles)
Formation of business requirements for software implementation
We have prepared the resources, you need to think about the tool - the software. A project manager from the IT department will be happy if, instead of a series of conflicting interviews, you give him a more detailed model of the future business process. So here it is, we added the inputs / outputs and resources to perform the functions:

The requirements can be described in more detail the sequence of functions, for example, "Attracting customers":
- Import customer list
- Prioritization of the list of customers for calling
- Automatic customer dialing
- Fixing contact result
Based on such requirements, it is possible to evaluate the possibility of introducing software.
Operating expenses
With capital expenditures on software licenses decided, and what about operating? It is necessary to conduct a cost analysis of the share of costs for the cost of the product. We will supplement our model with the cost of resources (or we will connect the organizational model created earlier with data from software on payroll).

So simple? Now, yes, but earlier for such an analysis it was necessary to involve operators, productologists, technologists, financiers and personnel managers. If in the process of creating the cost driver the process itself was changed, then you had to start the whole calculation all over again.
Execution schedule
It would seem that it would be easier for the formation of the rules for the execution of the business process to assign the aunt in a shawl (methodologist), explain, pray and wait several months before the born Rules appear in the throes. Maybe if you remember that both the model and the regulations are different forms of the same entity. Take our model and finger or cursor from top to bottom:

We get:
Every day, when receiving the document “List of customers for calling”, the Personal Manager performs the function “Attracting customers” according to the normative-regulating document “Instructions for Calling” using the CRM software. As a result of the function, the “Result of the call” document should be filled out. The standard time for the “Customer Attraction” function is 00:30:00.
If, as a result of the “Customer Attraction” function, the event “Customer accepted the offer” occurred ... etc.
All, current and complete regulations, understandable for the performer and for the controller is ready, carry on the signature.
Conducting experiments
Experiments in combat conditions are very expensive. How to find out how the process will behave, if on Friday to make the working day shorter, on Wednesday the chief specialist will unexpectedly go on maternity leave and how much will the florists physically sell on March 8? To do this, we need to place the model of our process in an imitation environment as close as possible to the real one.
In addition to the business process model, you will need an external environment model, but it just needs to know how often an instance of the process and events are launched that affect its execution. For example, in the afternoon the call center receives an incoming call on average every 5 minutes.
The simulator will run tasks in the business process model in the quantity and as long as necessary. And upon completion you will have the results of simulation modeling necessary for making a decision, as if the process actually worked for the right time.

Unlike the static model, the simulation results show that employees do not work for more than 8 hours, their tasks are transferred and wait for their turn to execute or available resources, bringing the calculated performance data to the actual ones.
Conclusion
All the examples of the application of the model described above are real, often applicable and accessible. In addition, with the help of the BP model, less trivial tasks are also simply solved: creating a risk map, analyzing quality management circuits and sources of defects for lean manufacturing. Having a model of only one process for the formation of the listed results saves a lot of man-hours, in case of a change in the process, the results are also easily updated by making changes to the model. We are too lazy to spend time on a routine, which is why we love processes and, we hope, will love you too.
Subscribe to our blog here and you might find out:
- How to correctly identify business processes so that project boundaries do not increase
- What to do if the simulated process has time to change by the time the simulation ends
- The reverse engineering of the process is not difficult and legal, the hunt for models and much more.
In the meantime, we are waiting for you at our BP Simulator business process optimization service .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/289918/
All Articles