21st century media. Part 6. New journalists for new information flows.
Information is changing. The news industry was born at a time when information was scarce. The law of supply and demand clearly shows that this is what made the information valuable. But the past 30 years, the deficit has somehow eroded. It’s not just that the obstacles to publishing have disappeared, computers have made broadcasting and distribution easier, not only in satellite, digital and Internet technologies, but also that the whole PR industry has grown, which now itself prepares and delivers “cheap” news in the media.
Information is changing. Increasingly, we are not looking for information, but she finds us. In short supply is not information, but our time, which is required for its processing, awareness, action based on it.
Information is changing. So that journalists, too, should. In the previous parts of the article, I showed how the news production process can change , how to engage old audiences , what can happen after news is published , how journalists and readers distribute content , and what business models use new media . In this part, I want to look at the staff of a media company and show how you can move away from the usual division into “correspondents”, “editors”, “chief editors” to a more flat structure of the distribution of responsibilities based on the type of information.
Until now, many news media enter the changed media environment simply by increasing the volume of work of their journalists. They require you to make podcasts, take photos, blog, follow social networks, forums and video hosting, get an audience, involve it in production. Some have introduced special posts for community editors, flash developers, and even “data delivery editors.” But such vacancies are still relatively few, and there are even fewer specialists with the necessary skills.
I singled out 6 roles for journalists , depending on the 3 key sources of information they deal with in the network environment. Maybe you offer your roles or types of information. This is by no means an exhaustive list.
')
Editor-aggregator
In traditional newsrooms, editors are the intermediate link between the work of a journalist and the reader. The media of the 21st century is the opposite. In the world of information overload, the skills of the editor are aimed at gathering information (aggregation), selecting useful and relevant material (filtering), publishing (social bookmarks and blogs), and avoiding conflicts with legislation.
In other words, the editor has been doing what bloggers have been doing for many years - they get interesting information and publish it. Therefore, you can hire an intelligent blogger for this position, pay him on an hourly basis, or for using his content. And yet - it is advisable, after all, to snipe it in advance in the necessary topic.
In addition, the editor-aggregator can be useful in that it prompts useful topics to journalists or will fill widgets with high-quality collections of feeds. A good example of this is the Jemima Kiss's Newsbucket Bouquet .
Mobile Journalist (MoJo)
As news media increasingly seeks to efficiently use their resources, it is sometimes very difficult for reporters to prove the viability of their work outside the office. The editors are increasingly relying not on the live testimony of witnesses to the event, but on press releases and telephone comments.
It's funny that new technologies (3G / Wi-fi) at the same time allow the journalist to fully carry out their work just outside the office. From this it follows that the mobile journalist must be constantly on the road, posting news on Twitter, broadcast video directly from the phone, publish unedited audio from the scene of action. Their mission is to get people and news that you cannot get online. Reuters experimented in this area , and Gannett too , and Trinity Mirror equips its N96 reporters (obviously, this is about Nokia N96 phones - translator's note ) and wi-fi laptops. As Chuck Myron says : “This is a smarter way of doing business. Instead of sitting in the office and waiting for the call, I am in the field, in the center of events. And at the same time I do not miss important calls, as if I had gone to the copier in the office, because my mobile is in my pocket. Technology has made people more mobile, journalism must respond. ”
Data retriever
The journalist-analyst of the 21st century is the one who knows how to work with databases and tables, catching interesting patterns, processing huge data arrays, understanding the quirks of statistics. The ChicagoCrime.org Adrian Holovaty website has already become a classic example in this area , and the New York Times has launched its own Visualization Lab . Among the new names are Stefan Gray, Heather Brooke, Luis Ekford and Dominic Casciani ( Stephen Gray, Heather Brooke, Louise Acford , Dominic Casciani ).
If you are wondering what exactly is the responsibility of the data retriever, then you can see what the Chicago Tribune newspaper asked the applicants for this position and what the Roanoke Times was waiting for . If you are interested in looking at the results of the data retrievers, then look at my bookmarks on this topic .
Multimedia Producer
Despite all the controversies about quality and quantity, there is nothing worse when a journalist is a master of all trades (in fact, this is exactly what the editor should be). Depending on which media you use for the news, you will make decisions about how you submit it and how you will collect information. Multimedia producer thinks in this way and is able to work with audio, video, graphics, blogs, use databases, maps and mix XML data (mashup). Perhaps not all the work they do themselves. For example, programmers will develop a Flash application for working with a database, and a mobile journalist will bring the necessary piece of video. But multimedia producers have a vision. They have an internal picture of what can be done at all.
Here is a description of the work in the Roanoke Times , here is another one from The Day , and here is an interview with Regina McComb of the Star Tribune newspaper about her role as a multimedia producer.
Network Specialist
It is a specialized 21st century reporter. To do this, it is not enough to be an expert in your field and know the basic names. To do this, you need to shine in this area, keep a blog, video blog, share social bookmarks, comment on your topic throughout the blogosphere.
Such successful blogs like Mashable, TechCrunch, Daily Kos, Boing Boing, TPM are vivid examples of this sphere. They not only inform about what is happening, but also involve, contribute to the spread and interaction, they are like regulated road intersections.
Community editor
I said earlier that new technologies put communication with society on a new basis and on a new scale. Sources became collaborators, collaborators, and distributors, and the role of a community editor is to build a community, help start and support discussion, keep from being rude, answer questions, explain, help them in individual projects.
There are already a lot of such journalists. For example, Shane Richmond in the Telegraph, Joanna Geary in the Birmingham Post and Mail, and Andrew Rogers in the Reed Business Information. I have a whole series of interviews with them.
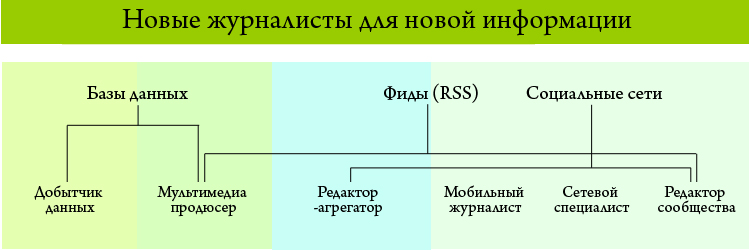
As you can see, different roles mean using different sources of information. Databases are used purposefully by data producers and multimedia producers, feeds are used by everyone except data producers (this is not particularly important for them, although they can be used as a tool, for example, for retrieving data from Google Spreadsheet), but social networks are important in their work. community editor, network specialist and mobile journalist.
The classification proposed by me is not final.
Paul Bradshaw
December 4, 2008.
From the translator:
The article was translated with the personal permission of the author. At his request, I indicate the address of the article directly in the text:
http://onlinejournalismblog.com/2008/12/04/model-for-the-21st-century-newsroom-pt6-new-journalists-for-new-information-flows/
I hope the administration of Habr will take into account the request of the author and forgive me a forced violation of the format.
Other parts of this article:
Part 1. Diamond news.
Part 2. Distributed journalism.
Part 3. Six questions after.
Part 4. Distribution of content in the new media environment.
Part 5. How to make money on journalism? Business models for new media.
Information is changing. Increasingly, we are not looking for information, but she finds us. In short supply is not information, but our time, which is required for its processing, awareness, action based on it.
Information is changing. So that journalists, too, should. In the previous parts of the article, I showed how the news production process can change , how to engage old audiences , what can happen after news is published , how journalists and readers distribute content , and what business models use new media . In this part, I want to look at the staff of a media company and show how you can move away from the usual division into “correspondents”, “editors”, “chief editors” to a more flat structure of the distribution of responsibilities based on the type of information.
Quality vs. quantity
Until now, many news media enter the changed media environment simply by increasing the volume of work of their journalists. They require you to make podcasts, take photos, blog, follow social networks, forums and video hosting, get an audience, involve it in production. Some have introduced special posts for community editors, flash developers, and even “data delivery editors.” But such vacancies are still relatively few, and there are even fewer specialists with the necessary skills.
I singled out 6 roles for journalists , depending on the 3 key sources of information they deal with in the network environment. Maybe you offer your roles or types of information. This is by no means an exhaustive list.
')
Three sources of information:
- feeds (RSS) - not only specific sites and blogs, but in principle. In this post you can read more about the passive-aggressive news gathering .
- social networks - online and in real life. You may have called them “my sources” before, but now the online tools take them to a new level. And here's why: now your sources should look for you no less than before you were looking for them.
- databases - those that are in the public domain, and their own.
Six roles for journalists:
Editor-aggregator
In traditional newsrooms, editors are the intermediate link between the work of a journalist and the reader. The media of the 21st century is the opposite. In the world of information overload, the skills of the editor are aimed at gathering information (aggregation), selecting useful and relevant material (filtering), publishing (social bookmarks and blogs), and avoiding conflicts with legislation.
In other words, the editor has been doing what bloggers have been doing for many years - they get interesting information and publish it. Therefore, you can hire an intelligent blogger for this position, pay him on an hourly basis, or for using his content. And yet - it is advisable, after all, to snipe it in advance in the necessary topic.
In addition, the editor-aggregator can be useful in that it prompts useful topics to journalists or will fill widgets with high-quality collections of feeds. A good example of this is the Jemima Kiss's Newsbucket Bouquet .
Mobile Journalist (MoJo)
As news media increasingly seeks to efficiently use their resources, it is sometimes very difficult for reporters to prove the viability of their work outside the office. The editors are increasingly relying not on the live testimony of witnesses to the event, but on press releases and telephone comments.
It's funny that new technologies (3G / Wi-fi) at the same time allow the journalist to fully carry out their work just outside the office. From this it follows that the mobile journalist must be constantly on the road, posting news on Twitter, broadcast video directly from the phone, publish unedited audio from the scene of action. Their mission is to get people and news that you cannot get online. Reuters experimented in this area , and Gannett too , and Trinity Mirror equips its N96 reporters (obviously, this is about Nokia N96 phones - translator's note ) and wi-fi laptops. As Chuck Myron says : “This is a smarter way of doing business. Instead of sitting in the office and waiting for the call, I am in the field, in the center of events. And at the same time I do not miss important calls, as if I had gone to the copier in the office, because my mobile is in my pocket. Technology has made people more mobile, journalism must respond. ”
Data retriever
The journalist-analyst of the 21st century is the one who knows how to work with databases and tables, catching interesting patterns, processing huge data arrays, understanding the quirks of statistics. The ChicagoCrime.org Adrian Holovaty website has already become a classic example in this area , and the New York Times has launched its own Visualization Lab . Among the new names are Stefan Gray, Heather Brooke, Luis Ekford and Dominic Casciani ( Stephen Gray, Heather Brooke, Louise Acford , Dominic Casciani ).
If you are wondering what exactly is the responsibility of the data retriever, then you can see what the Chicago Tribune newspaper asked the applicants for this position and what the Roanoke Times was waiting for . If you are interested in looking at the results of the data retrievers, then look at my bookmarks on this topic .
Multimedia Producer
Despite all the controversies about quality and quantity, there is nothing worse when a journalist is a master of all trades (in fact, this is exactly what the editor should be). Depending on which media you use for the news, you will make decisions about how you submit it and how you will collect information. Multimedia producer thinks in this way and is able to work with audio, video, graphics, blogs, use databases, maps and mix XML data (mashup). Perhaps not all the work they do themselves. For example, programmers will develop a Flash application for working with a database, and a mobile journalist will bring the necessary piece of video. But multimedia producers have a vision. They have an internal picture of what can be done at all.
Here is a description of the work in the Roanoke Times , here is another one from The Day , and here is an interview with Regina McComb of the Star Tribune newspaper about her role as a multimedia producer.
Network Specialist
It is a specialized 21st century reporter. To do this, it is not enough to be an expert in your field and know the basic names. To do this, you need to shine in this area, keep a blog, video blog, share social bookmarks, comment on your topic throughout the blogosphere.
Such successful blogs like Mashable, TechCrunch, Daily Kos, Boing Boing, TPM are vivid examples of this sphere. They not only inform about what is happening, but also involve, contribute to the spread and interaction, they are like regulated road intersections.
Community editor
I said earlier that new technologies put communication with society on a new basis and on a new scale. Sources became collaborators, collaborators, and distributors, and the role of a community editor is to build a community, help start and support discussion, keep from being rude, answer questions, explain, help them in individual projects.
There are already a lot of such journalists. For example, Shane Richmond in the Telegraph, Joanna Geary in the Birmingham Post and Mail, and Andrew Rogers in the Reed Business Information. I have a whole series of interviews with them.
Official separation of the roles of journalists and sources of information

As you can see, different roles mean using different sources of information. Databases are used purposefully by data producers and multimedia producers, feeds are used by everyone except data producers (this is not particularly important for them, although they can be used as a tool, for example, for retrieving data from Google Spreadsheet), but social networks are important in their work. community editor, network specialist and mobile journalist.
The classification proposed by me is not final.
Paul Bradshaw
December 4, 2008.
From the translator:
The article was translated with the personal permission of the author. At his request, I indicate the address of the article directly in the text:
http://onlinejournalismblog.com/2008/12/04/model-for-the-21st-century-newsroom-pt6-new-journalists-for-new-information-flows/
I hope the administration of Habr will take into account the request of the author and forgive me a forced violation of the format.
Other parts of this article:
Part 1. Diamond news.
Part 2. Distributed journalism.
Part 3. Six questions after.
Part 4. Distribution of content in the new media environment.
Part 5. How to make money on journalism? Business models for new media.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/288766/
All Articles