Optimization of foreign patenting route
The development of several routes for foreign patenting of inventions allows us to choose between economy and flexibility in making decisions about patenting in a particular group of countries.
The described routes of foreign patenting are applicable for Russian companies with a high-tech product of the B2B sector, planning to enter the international market. Patenting countries are countries with target markets. In this example, 37 foreign countries are considered, which is quite typical for the B2B sector (the geography of patenting usually covers 30-40 countries). They are divided into four groups in accordance with the priority determined by the marketing division. The cost of patenting is determined for a typical patent application - 30 pages, 15 claims, of which two are independent. The forecast of the cost of patenting by year for the first ten years includes the cost of preparing one patent application, obtaining and maintaining one patent family in force, including fees and fees for representatives (patent agents or lawyers) in US dollars.
Route number 1 involves the filing of a national (priority) application to Rospatent, a petition for the immediate commencement of substantive examination, then the filing of an international application through Rospatent with its subsequent transfer to the national or regional phase. At the same time, from 37 countries the international application in 17 countries is transferred to the regional phase through the European Patent Organization, in 4 countries is transferred to the regional phase through the Eurasian Patent Organization, in the remaining 16 countries the international application is transferred to the national phase. The total cost of patenting on route 1 is $ 274,800.
Route 2 involves the submission of a national (priority) application to Rospatent, a petition for immediate commencement of substantive examination, then a simultaneous (more precisely, within approximately one year) submission of national and regional applications in countries of category 1, or in countries of categories 1 and 2, or in countries of categories 1, 2 and 3, or in countries of categories 1, 2, 3 and 4. Of the 37 countries, category 1 includes 5 countries, category 2 includes 6 countries, category 3 includes 7 individual countries and 3 countries of the Eurasian Patent Organization, category 4 includes 5 ndividualnyh countries and 11 countries of the European Patent Organization. The total cost of patenting on route 2 for countries of category 1 is $ 65,300, for countries of categories 1 + 2 - $ 139,200, for countries of categories 1 + 2 + 3 - $ 238,100, for countries of categories 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 - 350 600 dollars.
Route number 3 involves the filing of a national (priority) application to Rospatent, a petition for the immediate commencement of substantive examination, then the filing of an international application through Rospatent with its subsequent transfer to the national and regional phase within two years. The distribution of countries is similar to route 2, but entry into the national and regional phase for countries of category 3 and 4 is shifted to the end of the grace period of international patenting (that is, approximately one year later). The total cost of patenting on route 3 for countries of category 1 is $ 68,300, for countries of categories 1 + 2 - 142,200 dollars, for countries of categories 1 + 2 + 3 - 237,400 dollars, for countries of categories 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 - 342,400 dollars.
')
The difference in the cost of patenting and in the distribution of the costs of patenting by year is illustrated in figures 1 and 2.
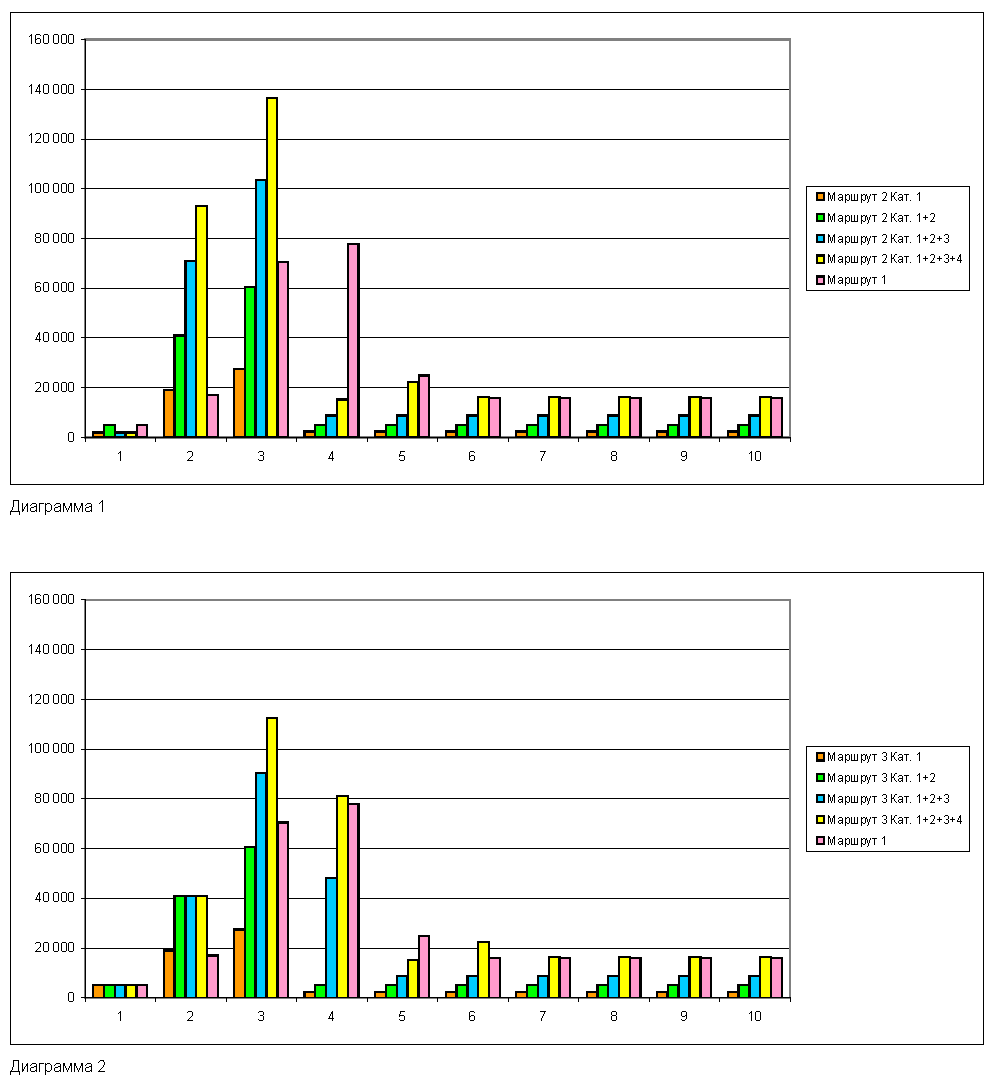
Route 1 is selected as a base for comparison, chart 1 contains a comparison of routes 1 and 2, chart 2 - routes 1 and 3. Using route 1 allows you to most evenly distribute expenses over time (the maximum falls on the third and fourth years) and provides the minimum total amount but requires strict adherence to the financing schedule in order to ensure the desired result and so that expenses already incurred are not worthless. Using route 2 allows you to make a decision on patenting in each category of countries, but the total amount for all countries is higher and there is a sharp increase in costs in the second and third years. Using route 3 also allows deciding on patenting in each category of countries, but at a cost close to the cost of route 2, it makes it possible to obtain a somewhat smoother distribution of costs over time, although in this case there is a noticeable surge in the third and fourth years.
Thus, the development of several foreign patenting routes allows us to choose between economy and flexibility in making decisions for one country or another, and also to take into account the preferred schedule for financing the program of patenting.
Initial data
The described routes of foreign patenting are applicable for Russian companies with a high-tech product of the B2B sector, planning to enter the international market. Patenting countries are countries with target markets. In this example, 37 foreign countries are considered, which is quite typical for the B2B sector (the geography of patenting usually covers 30-40 countries). They are divided into four groups in accordance with the priority determined by the marketing division. The cost of patenting is determined for a typical patent application - 30 pages, 15 claims, of which two are independent. The forecast of the cost of patenting by year for the first ten years includes the cost of preparing one patent application, obtaining and maintaining one patent family in force, including fees and fees for representatives (patent agents or lawyers) in US dollars.
Patenting Routes
Route number 1 involves the filing of a national (priority) application to Rospatent, a petition for the immediate commencement of substantive examination, then the filing of an international application through Rospatent with its subsequent transfer to the national or regional phase. At the same time, from 37 countries the international application in 17 countries is transferred to the regional phase through the European Patent Organization, in 4 countries is transferred to the regional phase through the Eurasian Patent Organization, in the remaining 16 countries the international application is transferred to the national phase. The total cost of patenting on route 1 is $ 274,800.
Route 2 involves the submission of a national (priority) application to Rospatent, a petition for immediate commencement of substantive examination, then a simultaneous (more precisely, within approximately one year) submission of national and regional applications in countries of category 1, or in countries of categories 1 and 2, or in countries of categories 1, 2 and 3, or in countries of categories 1, 2, 3 and 4. Of the 37 countries, category 1 includes 5 countries, category 2 includes 6 countries, category 3 includes 7 individual countries and 3 countries of the Eurasian Patent Organization, category 4 includes 5 ndividualnyh countries and 11 countries of the European Patent Organization. The total cost of patenting on route 2 for countries of category 1 is $ 65,300, for countries of categories 1 + 2 - $ 139,200, for countries of categories 1 + 2 + 3 - $ 238,100, for countries of categories 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 - 350 600 dollars.
Route number 3 involves the filing of a national (priority) application to Rospatent, a petition for the immediate commencement of substantive examination, then the filing of an international application through Rospatent with its subsequent transfer to the national and regional phase within two years. The distribution of countries is similar to route 2, but entry into the national and regional phase for countries of category 3 and 4 is shifted to the end of the grace period of international patenting (that is, approximately one year later). The total cost of patenting on route 3 for countries of category 1 is $ 68,300, for countries of categories 1 + 2 - 142,200 dollars, for countries of categories 1 + 2 + 3 - 237,400 dollars, for countries of categories 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 - 342,400 dollars.
')
Comparison of the cost of patenting
The difference in the cost of patenting and in the distribution of the costs of patenting by year is illustrated in figures 1 and 2.

Route 1 is selected as a base for comparison, chart 1 contains a comparison of routes 1 and 2, chart 2 - routes 1 and 3. Using route 1 allows you to most evenly distribute expenses over time (the maximum falls on the third and fourth years) and provides the minimum total amount but requires strict adherence to the financing schedule in order to ensure the desired result and so that expenses already incurred are not worthless. Using route 2 allows you to make a decision on patenting in each category of countries, but the total amount for all countries is higher and there is a sharp increase in costs in the second and third years. Using route 3 also allows deciding on patenting in each category of countries, but at a cost close to the cost of route 2, it makes it possible to obtain a somewhat smoother distribution of costs over time, although in this case there is a noticeable surge in the third and fourth years.
Thus, the development of several foreign patenting routes allows us to choose between economy and flexibility in making decisions for one country or another, and also to take into account the preferred schedule for financing the program of patenting.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/288394/
All Articles