Why do most Russians become victims of cyber fraud?
For several years now we have been constantly confronted with unpleasant stories of cyber fraud. Some of them we learn from the news, some happened to our friends, and some, unfortunately, we know firsthand. According to a recent study by Neilsen and Mail.ru Group, more than 64% of Runet users were victims of cyber fraud.
There are no uniform rules of behavior that would allow to avoid such situations in 100% of cases. After all, the attackers are constantly coming up with new methods of fraud, using the latest technology and attract outstanding specialists to this.
As the study shows, Russians become “easy prey” for cyber frauds because of their carelessness or banal laziness. Every fifth research participant has never changed the password from his main mailbox. In social networks, the password is changed even less often: 38% do it no more than once a year, and 18% do not change it at all. But frequent password changes are one of the easiest and most effective measures to protect against cyber fraud.
')
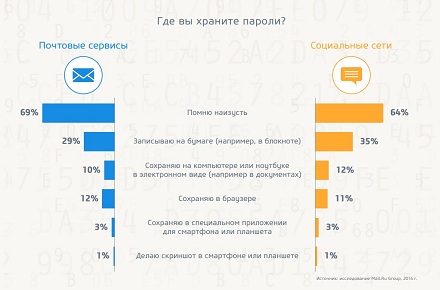
Worse, 25% of respondents use their email password on other resources: in social networks, online stores and other services. Therefore, if the password and account information fall into the hands of intruders, they can take possession of not only your confidential information, but also your money.
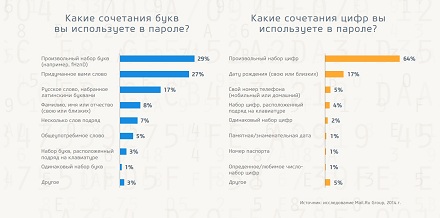
Of course, the complexity of the password itself is also important. Most users create very simple passwords: from letters and numbers only. 37% of respondents create passwords only from lowercase letters. 43% have passwords with a length of 6 to 8 characters. If passwords use numbers, then 17% of respondents prefer to enter their date of birth there, and 5% - a phone number, which is also unsafe. And we are no longer talking here about special password storage applications that only 3% of users use.
Inattention of users manifests itself even in such a simple situation as checking the installation of a secure connection on the site when entering personal data.
“HTTPS is almost the golden standard for protecting services that users trust confidential information, such as mail, for example. However, we decided to additionally protect users from potential malicious attacks: now HTTPS works on all content projects. Our task is to take care of protecting users even in those moments when they do not think about it, ”said Anatoly Rozhkov, director of media projects at Mail.Ru Group.
The company uses 3 main ways to protect personal data: HTTP only cookie, Secure cookie and sharing sessions when working with different services.
However, according to research by the antivirus company ESET, users with cybercriminals are also victims of a higher than average level - gamers. It turns out that 40% of them at least once were subjected to attacks by intruders. In most cases, these attacks represent the theft of well-pumped game accounts.
A common example is hacking and stealing accounts from World of Tanks players, who themselves are substituted, trying to download cheats or other dubious additions to the game. Ways to protect against such attacks, in general, are also reduced to simple precautions: use a strong password, high-quality antivirus, be careful and do not climb on the rampage.
Cyber fraudsters can appear anywhere, use any service for their own purposes in the most unexpected way. So, from the middle of 2014, attacks by cybercriminals began to spread via Skype.
According to MegaFon, fraudsters hack Skype user accounts and send messages on their behalf requesting money to be transferred to mobile numbers.
Therefore, only attention to detail and common sense will help determine from whom the messages actually come and for what purpose.
But the fantasy of cyber frauds knows no bounds: another wave of cyber threats has swept through the online services of travel services. So, in early February , tourists who bought non-existent tickets on the website broniruem-online.ru became victims of deception. They were attracted by low prices and discounts. They were calculated using a bank card, then they received confirmation of payment, but they could not get the tickets themselves. To solve the problem, the deceived customers called the number that was listed on the site, but got into a foreign travel agency that never sold any air tickets.
Of all these stories you can make a whole book. Maybe this number of precedents is due to the lack of computer literacy of Russians, and in a few years the situation will change for the better. Most likely, solving a problem at the global level comes down to combining the efforts of users and developers. Users should try to be more attentive, competent, responsible. The task of the developers is to ensure the most secure exchange of data. This is of particular relevance now, in the period of intensive development of web-technologies and cloud computing.
There are no uniform rules of behavior that would allow to avoid such situations in 100% of cases. After all, the attackers are constantly coming up with new methods of fraud, using the latest technology and attract outstanding specialists to this.
As the study shows, Russians become “easy prey” for cyber frauds because of their carelessness or banal laziness. Every fifth research participant has never changed the password from his main mailbox. In social networks, the password is changed even less often: 38% do it no more than once a year, and 18% do not change it at all. But frequent password changes are one of the easiest and most effective measures to protect against cyber fraud.
')

Worse, 25% of respondents use their email password on other resources: in social networks, online stores and other services. Therefore, if the password and account information fall into the hands of intruders, they can take possession of not only your confidential information, but also your money.
Of course, the complexity of the password itself is also important. Most users create very simple passwords: from letters and numbers only. 37% of respondents create passwords only from lowercase letters. 43% have passwords with a length of 6 to 8 characters. If passwords use numbers, then 17% of respondents prefer to enter their date of birth there, and 5% - a phone number, which is also unsafe. And we are no longer talking here about special password storage applications that only 3% of users use.

Inattention of users manifests itself even in such a simple situation as checking the installation of a secure connection on the site when entering personal data.
“HTTPS is almost the golden standard for protecting services that users trust confidential information, such as mail, for example. However, we decided to additionally protect users from potential malicious attacks: now HTTPS works on all content projects. Our task is to take care of protecting users even in those moments when they do not think about it, ”said Anatoly Rozhkov, director of media projects at Mail.Ru Group.
The company uses 3 main ways to protect personal data: HTTP only cookie, Secure cookie and sharing sessions when working with different services.
However, according to research by the antivirus company ESET, users with cybercriminals are also victims of a higher than average level - gamers. It turns out that 40% of them at least once were subjected to attacks by intruders. In most cases, these attacks represent the theft of well-pumped game accounts.
A common example is hacking and stealing accounts from World of Tanks players, who themselves are substituted, trying to download cheats or other dubious additions to the game. Ways to protect against such attacks, in general, are also reduced to simple precautions: use a strong password, high-quality antivirus, be careful and do not climb on the rampage.
Cyber fraudsters can appear anywhere, use any service for their own purposes in the most unexpected way. So, from the middle of 2014, attacks by cybercriminals began to spread via Skype.
According to MegaFon, fraudsters hack Skype user accounts and send messages on their behalf requesting money to be transferred to mobile numbers.
Therefore, only attention to detail and common sense will help determine from whom the messages actually come and for what purpose.
But the fantasy of cyber frauds knows no bounds: another wave of cyber threats has swept through the online services of travel services. So, in early February , tourists who bought non-existent tickets on the website broniruem-online.ru became victims of deception. They were attracted by low prices and discounts. They were calculated using a bank card, then they received confirmation of payment, but they could not get the tickets themselves. To solve the problem, the deceived customers called the number that was listed on the site, but got into a foreign travel agency that never sold any air tickets.
Of all these stories you can make a whole book. Maybe this number of precedents is due to the lack of computer literacy of Russians, and in a few years the situation will change for the better. Most likely, solving a problem at the global level comes down to combining the efforts of users and developers. Users should try to be more attentive, competent, responsible. The task of the developers is to ensure the most secure exchange of data. This is of particular relevance now, in the period of intensive development of web-technologies and cloud computing.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/286386/
All Articles