See you in court: Why do startups need trademarks?

Anyone who is interested in the topic of technology development and Internet business has repeatedly heard stories about the wars of companies with “patent trolls”, battles with cybersquatters for the return of important domain names and other unpleasant things for any organization.
To prepare our today's topic, we invited experts from the Online Patent project to use their help to consider the topic of the importance of registering trademarks and list the main ways to protect our intellectual rights, which start-ups can use.
')
What is a trademark
Article 1477 of Part 1 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation proposes the following definition of the concept of a “trademark”:
Trademark - a designation that serves to individualize the goods of legal entities or individual entrepreneurs.
There is also an important concept of “service mark” (Civil Code of the Russian Federation, Part 2 of Art. 1477):
A service mark is a designation used to individualize the work performed by legal entities or individual entrepreneurs, or the services they provide.
There are verbal, pictorial, combined and three-dimensional trademarks. In addition, other categories of trademarks are allowed (although rarely found in the real world):
- sonic (Metro Goldwyn Mayer growl of a lion)
- olfactory (smell of grass from Senta tennis balls)
- only from flowers (red color Ferrari)
With the concept itself, everything became clearer, but why do we need trademarks? And especially, why do startups need them?
Why do we need trademarks
Contrary to popular belief, trademarks are registered not only to protect themselves from copying products and business decisions by competitors. Despite the fact that in the event of a conflict related to such violations, the fact of registration of a trademark will help in court proceedings, according to the law, only those “copyicates” whom the right holder finds himself — cannot be brought to court — neither FAS nor Rospatent is required to do so and will not.
The second reason for registering a trademark is to avoid the risk of becoming a violator of other intellectual property rights - if a company creates a product that has analogues, it is likely that its competitors could register their own trademark - this may lead to the fact that the young startup team is completely not wanting to violate other people's exclusive rights, using, say, to the extent of confusion with a competing product, the packaging design or name (for example, LOUIS RUITTON and LOUIS VUITTON).
All this can lead to claims and fines - in accordance with Art. 1515 of the Civil Code, compensation to the copyright holder in such cases can reach up to 5 million rubles (rarely which startup can afford such expenses).
In addition to all the above, registration of a trademark is not only a means of defense or attack, but also a means of extracting profit through the legitimate sale of an intangible asset of a company. These include commercial concession agreements, license agreements, various forms of agreements with dealers or retailers. Without protecting a trademark, you do not have the ability to legally correctly exercise your rights to it.
Cafe and geolocation social network with photo sharing: what is the difference?
There are a number of reasons why registering a trademark for a technological Internet startup is more important than for companies doing more traditional business.
Growth problems
If a conditional one-of-a-kind existing cafe can be called anything in a certain area (in Moscow or in different cities of the Moscow region there may be many Flamingo cafes belonging to different owners), then a startup planning expansion across Russia and abroad will surely face with copyright holders of similar products, both at home and at the global level.
And these are just bona fide competitors, and in fact there are so-called trademark squatters (similar to patent trolls or cybersquatters for the trademark sphere). It is important to understand that in many countries (including, for example, Russia and China) the principle of “first to file” is used in determining the right to register a trademark and the fact of using the designation in commercial circulation is not taken into account. Even large companies are not always able to prove their case in disputes with trademark squatters, and the legal costs that arise are simply incomparable with start-up budgets.
Thrifty startup easy to copy
As a rule, startups at the first stage of their existence test the advanced market hypotheses and test the minimally viable version of the product. In such circumstances, competitors can very easily copy the idea of the project, find a similar name and create a similar design.
It is possible and unpleasant situation in which the start-up team creates a name for the company, which is initially defenseless for copying due to its wording - for example, if it is formulated as descriptive for this business, consists of obviously unprotected elements (for example, contains the name of a famous character, literary name works or well-known element - “.ru”, “www”, etc.). In this case, even a trial will not always help.
Domain Security
Domain names in Russian law are not recognized as means of individualization. In practice, this means that:
- Before selling a domain name, no one has ever checked for similarity (or identity) with trademarks registered in the territory of the Russian Federation (or marks valid in the Russian Federation on the basis of international agreements);
- The legal right holder of a registered trademark at any time may request to stop using a domain name that is identical or confusingly similar to its trademark in relation to similar goods / services;
- actions to register a domain name may be recognized as an act of unfair competition, and a claim may be made to the domain name administrator for compensation for the unlawful use of a trademark.
Compensation for such violations can be as not very large (Resolution of the Ninth Arbitration Court of Appeal No. 09-4173/2009- dated April 13, 2009 in case number A40-42348 / 08-15-353, domain avtovaz.ru, compensation of 10 thousand rubles.), and very significant, reaching millions of rubles (Resolution of the Fifth Arbitration Court of Appeal No. 05AP-6335/2011 dated 10.19.2011 in case number A51-5935 / 2011, domain "onegagipertonik.ru" , compensation of 5 million rubles.).

Obviously, the protection of a domain name is important for technology companies, since it can not only be a means of promotion (as in an offline business like a bakery), but also an object, without which the direct activity of the company is impossible.
It is hardly necessary to explain why reliable legal protection of a domain name is important for a web service: after all, if you are engaged in the production of equipment or confectionery, the site is a means for you to promote a company, but for a startup, the site is the main source of income. It should be noted that the number of cases reviewed for canceling the registration of domain names is increasing annually by at least 30%.
How to register a trademark
Coined logo, approved the name, it would seem, everything is ready to start the registration procedure. The first question that arises at this stage is, and what, exactly, are we going to register? Logo? The name of the service? Both together? And the name - we will register in Russian or English version? Is it possible to somehow register a sign in 3-5 options at once? And what to do with the domain?
In the general case, a company wishing to register a trademark must go through several stages - either literally (by visiting relevant departments), or - that will be closer to readers - virtually through the Online Patent website .
Selection of designation for registration
The trademark is protected in the form in which it was registered, and does not accept the concept of "options". That is why the registration should be exactly the designation that you will use most often. Otherwise, you may well later face unfair attempts to revoke a trademark registration certificate you received.
In practice, one trademark is obviously insufficient to ensure the full protection of the rights of the company. As one example of a serious approach to the legal protection of means of individualization among the IT services of the Runet, one can cite dnevnik.ru, which owns seven trademarks at once:
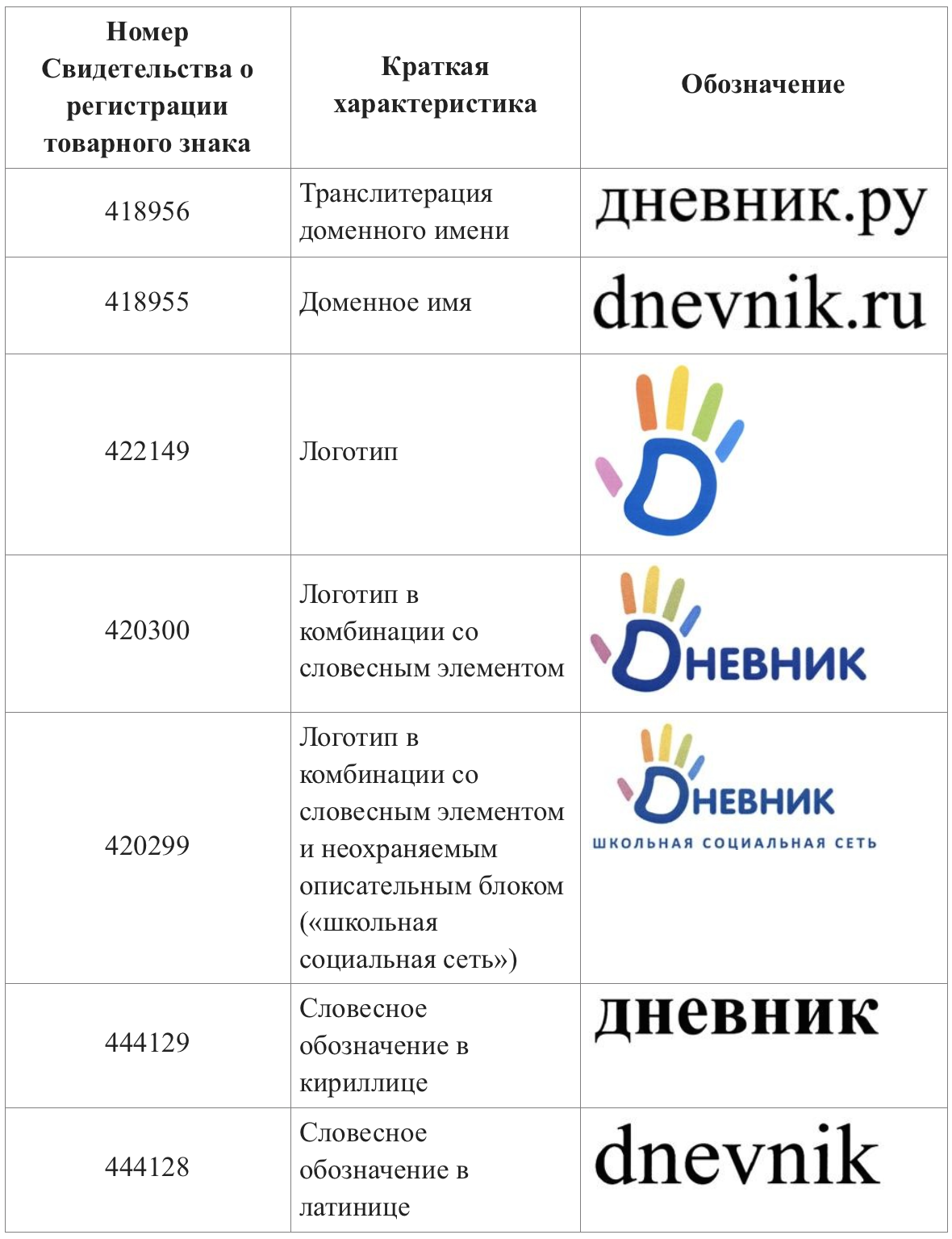
At the same time, it is important to understand that the legal protection of a trademark is granted in relation to pre-selected goods and services classified in accordance with the International Classification of Goods and Services (ICGS). It contains 45 classes describing groups of goods (classes 1-34) and services (classes 35-45). Thus, it is possible to simultaneously register similar trademarks of companies operating in different areas of business.
Classification of ICGS
Having decided on the registered designation, the next step is to select the goods and services that will be provided by the company and which must be protected. For this, you can use the WIPO Product and Service Manager or the TMClass search system.
The choice of the designation and classes of the MKTU are two main steps that are necessary to form an application for registration of a trademark. Actually, after it is already quite possible to contact Rospatent (the application form can be viewed here ), but this approach carries certain risks.
Firstly, the application has not yet been checked for trademark non-protection (for example, the word Taxi for class 39 services), moreover, the trademark you have chosen may be confusingly similar to the one already registered (register the Audi trademark by 12 MKTU class for obvious reasons will not work). Few people will want after 1-1.5 years of examination at Rospatent to receive a refusal for such “stupid” reasons (and to waste money on fees).
The second risk is that the application should be checked for violations of the legal rights and interests of third parties. By applying to Rospatent and continuing to use the mark, without carrying out such a check, the company cannot be completely sure that the same designation does not belong to another organization. In this case, there may be a situation where a startup spends money on advertising and brand promotion (essentially someone else's), and then its true owner will sue and demand compensation. Therefore, it is necessary to do more and check your application for registration of a trademark.
Check
The verification of the application does not guarantee its successful satisfaction in the future. Firstly, there is a delay in the publication of the application documents of Rospatent, which takes about two weeks from the moment they are received by the Office. In other words, the company cannot receive information on applications submitted at this time, and among them there may be confusingly similar signs, and they will have priority due to earlier filing of the application.
In addition, there are territorial restrictions on the search for similar applications. Russia is a party to the Madrid Agreement and Protocol, which means that if a trademark was registered in a conditional Germany for up to 6 months, after a similar registration in Russia, a German company can expand to Russia and try to take rights to itself (the likelihood of such a development, however, it is extremely small).
Also, no one has canceled the subjectivity of consideration of the application at Rospatent - and the concepts of “degree of confusion” and “misleading the consumer” leave room for different interpretations. (Whether the use of English letters in the logo is misleading - buyers may have the impression that the company is foreign).
According to the results of the inspection, you receive a report containing conclusions about the protectability of the claimed designation. As a rule, in the event of a negative response on the prospects for registration, the document will also contain recommendations for eliminating the weak points of the application. However, after such changes have been made, the verification needs to be carried out anew, since changes can provoke the appearance of new legal risks that should be taken into account. If the answer is yes, then the company can, with a clear conscience, apply to Rospatent.
Consideration of the application
Consideration of an application for registration of a trademark takes on average 10-14 months, and there is simply no way to speed up this process.
The first stage of the examination is a formal examination, which lasts for 1 month. During this period, the content of the application submitted for examination is verified, it is confirmed that all the necessary documents are in it, as well as their compliance with the established requirements. According to the results of the formal examination, the application is accepted for consideration or a decision is taken to refuse to accept it for consideration.
Suppose you receive a Notice of acceptance of the application for consideration. This means that your application has moved to the next stage of the examination and now there will be a verification of the patentability of the designation you have applied for. It is based on the results of this stage of examination that the decision on registration of a trademark or on refusal of its registration is made.
In the ideal case, based on the results of the examination, a decision is made on the registration of a trademark, and all you need to do is to receive a certificate of registration of a trademark by paying the appropriate fee. If the events do not develop so successfully, then first the applicant may be issued a "preliminary refusal" - a notification of the results of the verification of the conformity of the claimed designation to the established requirements for protection. Having received such a refusal, the applicant, within six months from the date of its receipt, can prepare and send to the patent office a reasoned response containing arguments on the merits of the examination objections.
If, however, the arguments of a reasoned response do not convince the examination of the patentability of the claimed designation, then the application will nevertheless decide to refuse to register the trademark. Objections to this decision may be filed within three months from the date of its receipt with the Chamber for Patent Disputes.
How much does it all cost
In the "Online Patent" they say that trademark registration is objectively not the cheapest event. Preparation and filing of an application for registration of a trademark for one class of ICGS through a patent attorney will cost 5-7 thousand rubles. All fees for consideration of the application by Rospatent will be at least 30 thousand rubles.
The price of preliminary verification of the application before filing with the Office may be different. It largely depends on what type of designation you are applying for registration. The most common are the three types of symbols (we will use the previously considered example of Dnevnik.ru to illustrate them):

Preparing responses to the “preliminary failures” of Rospatent also costs 15–20 thousand rubles, but in some cases, for example, if a specialized sociological survey is needed, the total cost of the work can reach up to 150–200 thousand rubles.
Today everything, in our next material of the “legal” series, we will talk about the procedure for filing an international application for registration of a trademark and its specificity in the most popular countries of registration.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/285900/
All Articles