Trend Analysis in Mobile Broadband Access (MBB)
We live in an era of rapid mobile broadband (MBB) development. Modern subscribers have become accustomed to the availability of all types of information on their mobile phones. Never before has MBB technology been so close and accessible to people.
After analyzing the statistics on the use of mobile services, trends in the development of mobile terminals and the prospects for mobile services following the results of 2015, Huawei has made eight key conclusions, which we describe below.
• Use of mobile services: in 2020, it is expected that 70% of all mobile data traffic will be accounted for by video services. Subscribers will become more accustomed to watching videos on their mobile phones anytime, anywhere. At the same time, Voice over LTE (VoLTE) voice service will provide 4G subscribers with a new level of audiovisual quality.
')
• Terminals: in 2015, more than 70% of mobile phones were equipped with displays, according to the PPI value, corresponding to entry-level Retina requirements. With the increase in the capacity of mobile phone batteries, the duration of their work does not increase in the same proportion. Increasing battery life can be achieved by optimizing mobile applications.
• Future services: to support virtual reality (VR) with retina-level resolution, the data transfer rate should reach the Gb / s level. With the development of the Internet of Things (IoT), more and more devices will consume data traffic automatically in accordance with specific usage scenarios.
The most important observations
1. The widespread availability of mobile video
According to the analysis of worldwide data traffic generated by mobile applications, traffic from countries with a high level of MBB development, for example, from Japan and South Korea, accounts for about 50% of the total. In emerging markets, the share of mobile video traffic is increasing rapidly. It can be said that in the reporting period, most often, MBB services were used specifically for viewing mobile video (“at any time and in any place”). We also found out that the 4G network more strongly stimulates the consumption of video in HD format compared to the traditional 3G network.

The world average monthly amount of traffic consumed by the user is 500 MB. However, in some countries with a high level of development of MBB networks, this figure exceeds 4 GB per month. Consequently, the need for people to view mobile video is to some extent suppressed. One of the main reasons for this is the high cost of traffic for the user.
2. Measuring user-perceived video quality
With the rapid development of mobile Internet technologies, viewing video programs on mobile terminals has become a widespread form of entertainment.
To measure the user-perceived quality of viewing online video programs, Huawei, in conjunction with the Peking University School of New Media, conducted research covering more than 3,000 consumers from more than 30 cities in the world. The results of these studies show that user perception is determined by the following main factors: the amount of consumed mobile data, the duration of video delays, pre-buffering, and the level of image resolution. The last three factors depend on the data throughput in the mobile network.
Assessing these factors allows you to assess the ability to support online video specific mobile network. In collaboration with the leading human factor and ergonomic research lab, Huawei measures user-perceived video quality using gaze tracking devices and recording physiological parameters. After evaluating these three factors, Huawei performs the analysis and modeling, and then formulates the result based on the mobile video MOS (vMOS) standard for user experience perception .
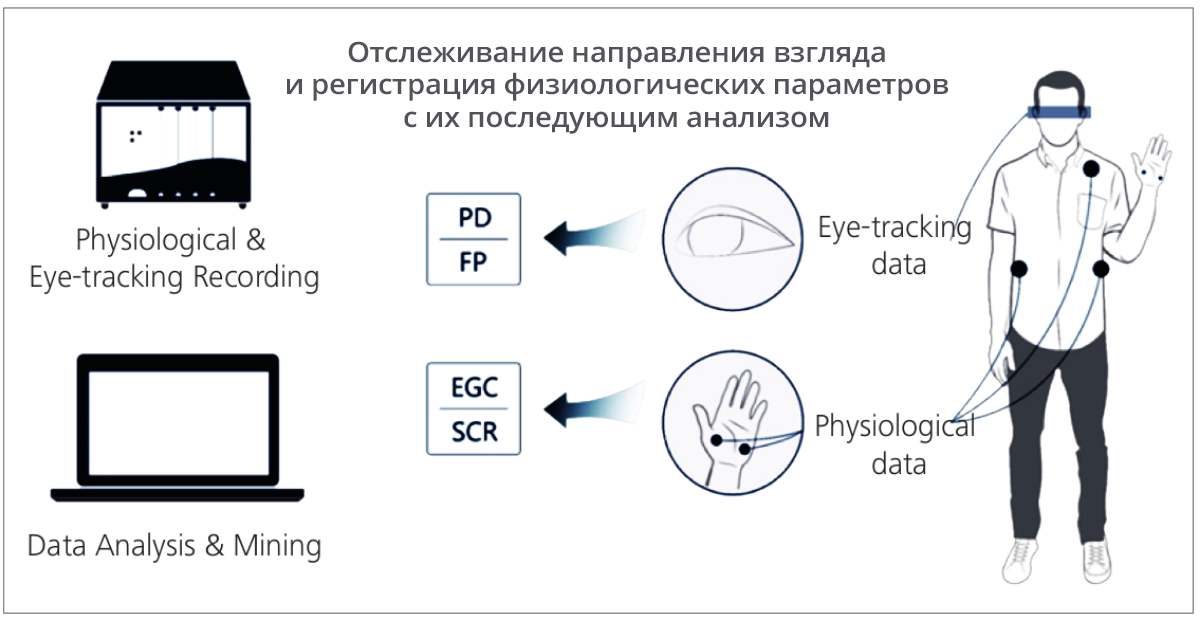
The vMOS standard is created on the basis of the MOS (Mean Opinion Score) expert evaluation, a widely recognized industry standard for quality assessment. The vMOS score is calculated based on factors that influence the user's perception: video quality, pre-buffering time and playout delays. The vMOS method allows you to assess the quality of the video from the point of view of the mobile network user. For testing using the vMOS method, you can download and install SpeedVideo - a Huawei-developed vMOS-based test application.
3. Wideband sound (HD Voice) with a presence effect
Observant users probably noticed that sometimes while making a call, the 4G icon suddenly disappears. This is because the sound on the 4G network is not well supported, and smartphones have to switch to a 2G or 3G network in order to provide voice services. With the growing popularity of VoLTE, the 4G network will be available anywhere you want to make a call or use data services. According to Huawei, VoLTE technology will provide users with a completely new level of sound quality.
Quick connection when calling
Compared with the forced switching to a 2G or 3G network, the delay in establishing a connection through a VoLTE network is much lower (approximately 1 second). At the same time, in traditional 2G networks the connection establishment delay for a voice call is about 6 seconds.
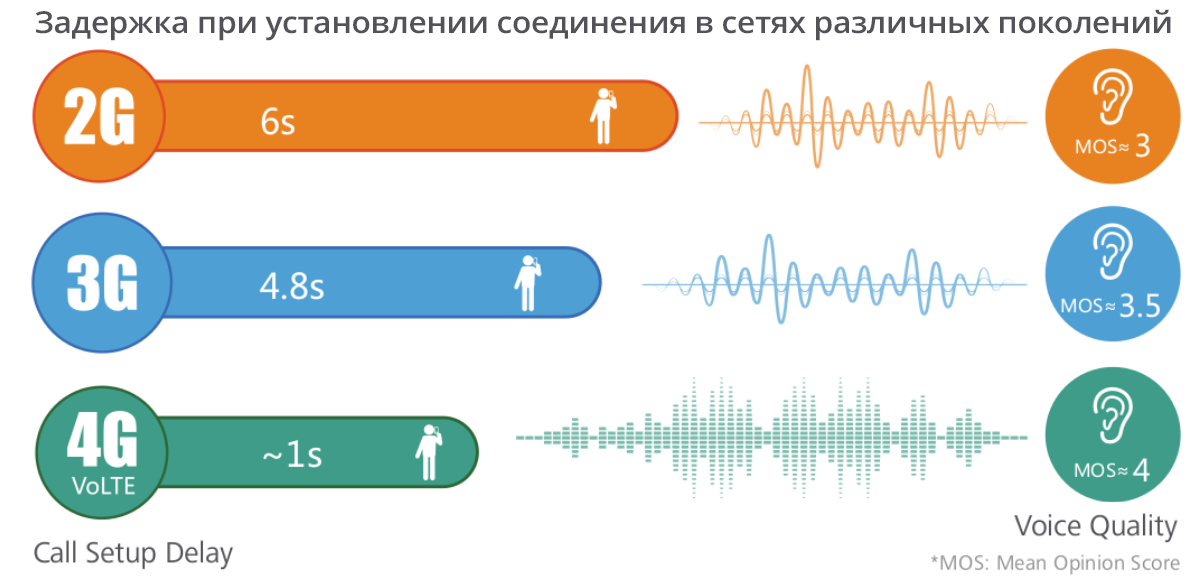
Crystal clear sound
Traditional 2G and 3G voice services are focused on the standards of a conventional wired telephone network, the width of the voice range in which ranges from 300 to 3400 Hz. However, the human ear is able to perceive frequencies in the range from 20 to 20 000 Hz and easily notice any sound distortion. In VoLTE networks, the audio frequency range is from 50 to 7000 Hz. The wider the frequency range, the more comfortable and more natural the sound is perceived by the human ear.
Video call 720P + with high quality
VoLTE easily supports video chat. We found out that in the same network environment, video calls on a VoLTE network are more clean and stable than in most video chat applications.
Simultaneous use of voice and data services
VoLTE technology has already been commercialized in South Korea. The South Korean telecommunications operator launched Uwa, VoLTE technology-based services, which ensure that calls are received at mobile terminals without interrupting data services. The launch of Uwa services has increased both the duration of voice calls and the volume of data traffic. These services also stimulate subscribers' desire to use the connection, as they allow chatting without interrupting the work of data transmission services.
4. The trade off between latency and throughput
The 4G network provides significantly better transmission performance over the air interface compared to the 3G network. In other words, the bandwidth of this network is much higher. However, the user perceived video quality is not always higher in the same proportion. The research results show that the available bandwidth has a negative correlation with end-to-end network latency. Therefore, the subjectively perceived user data rate can be increased by reducing the end-to-end delay.
The network bandwidth depends on which operator subscribers will choose. Optimizing latency requires the combined efforts of telecommunications operators and service providers. Currently, there are two main ways to optimize end-to-end delay.
1. Reducing the total length of the transmission path: the path length can be reduced by placing content as close as possible to subscribers. Among the most commonly used solutions are placing CDN nodes as close as possible to subscribers and deploying caching nodes.
2. Optimization of transmission resources: the delay in transmission lines can be optimized by the preferential use of fiber-optic resources in order to reduce the number of re-reception sites.
In terms of technological and architectural evolution, it is expected that the 5G network will support the download speed of traffic of 10 Gbit / s with a through delay of no more than 1 ms. At this point, “zero expectation” will become the standard of quality for mobile services.
5. Battery capacity: always be in touch
Battery life is still a bottleneck limiting the capabilities of mobile phone users. It depends on a number of factors: battery capacity, screen size, user habits and the availability of applications on your smartphone that require a constant connection to the Internet (for example, social networks).
In recent years, steady growth in battery capacity continues in response to an increase in screen sizes. According to the analysis of information about the 18 largest global manufacturers of smartphones, 54.5% of devices released in 2014 had a screen with a diagonal of 5 inches or more. In 2015, this ratio was already 76%, with most smartphones having a screen size of 5 or 6 inches. In 2014, 29.7% of new smartphones had a battery with a capacity of at least 3000 mAh. 36.2% of smartphones are equipped with a battery with capacity from 3000 to 4000 mAh.
However, the growth of battery capacity does not compensate for the increase in the duration of using devices and the volume of mobile data traffic. Analysis of user habits in recent years shows that they spend most of their time on applications that require constant access to the Internet, for example, Facebook and WeChat. Therefore, optimization is needed that would take into account the specifics of using such applications.
An effective means of extending battery life is the Unified Heartbeat mechanism used in some brands of smartphones. Heartbeat messages inform devices at the opposite end of the line about online status to make better use of the channel. However, different applications send these messages at different frequencies. Heartbeat messages and push messages sent by applications constantly consume battery life. The Unified Heartbeat mechanism reduces the amount of signaling messages exchanged by sending unified Heartbeat messages to the device at the opposite end not permanently, but according to a predetermined schedule. This saves battery life.
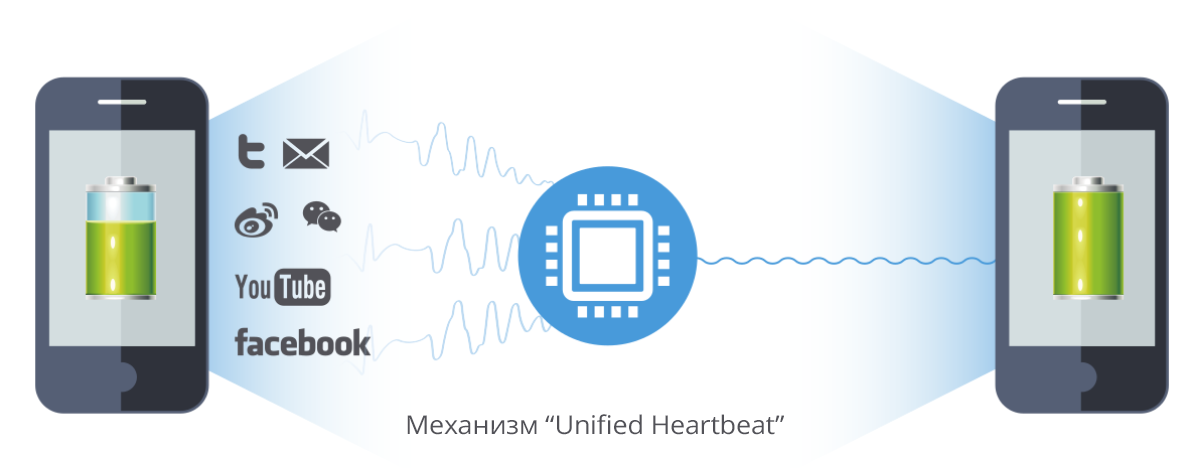
You can also increase battery life by using the latest 4G voice services (Voice over LTE; voice over LTE). Using intermittent reception (discontinuous reception; DRX) with long cycles, users of certain models of smartphones spend less on battery capacity compared to using traditional 2G / 3G services.
6. Overcoming the limitations of the resolution of Retina-displays
As the hardware of smartphones improves, the resolution of their displays increases. All major smartphone makers are looking to use higher resolution displays in their next-generation flagship models. Analyzing data from 18 manufacturers of smartphones from different countries shows a significant increase in the share of terminals with high-resolution displays. The percentage of terminals with a resolution of at least 1080p increased from 25% in 2014 to 36.4% in 2015. By the second half of 2015, 85 models of terminals with a resolution of 2K were launched in the series, among which 51 models are tablets and smartphones. Sony has released the world's first 4K smartphone - Sony Xperia Z5 Premium.
Huawei believes that tablets with a diagonal of 7–10 inches will soon appear, meeting the requirements for retina-resolution limit (above 4K), which will provide an unrivaled quality of 2D-video viewing with the naked eye. As for virtual reality (VR) applications, they use the principle of splitting an image with a distance between the eyes and a display on the order of several centimeters to create virtual images. If a 2K smartphone is used to view VR video, the effect will be the same as when watching a 360p video on it. Thus, the pursuit of higher-resolution smartphones will never stop.
7. “Stealthy” data traffic
Usually, users understand that when they browse websites or online video, certain data traffic is generated. However, in some cases, the consumption of such traffic remains unnoticed by users, for example, when sending health data from their devices or uploading photos to the cloud storage. It is safe to predict that with the development of the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence, the blurring of boundaries between the physical and digital world will accelerate. People are gradually becoming "network nodes." In such a “computerized” life, each of us will have special agents (that is, things) for different scenarios. These agents will autonomously download data for their owners (i.e., people) according to the requirements of the specific scenario. For example, when you turn on the mobile office mode in your car, email will be automatically downloaded. As our life becomes more computerized, the imperceptible traffic will become commonplace.
Some applications preload data. Basically it is necessary to watch the video, because it allows you to reduce the time of initial waiting and increase the subjectively perceived level of quality. The amount of such preloaded data is usually from 100 to 500 KB. As shown by the results of testing video viewing on Facebook, playback starts after tapping the screen with almost zero latency.
Huawei also found that the default 4are session (default bearer) remains active even when the data transfer is off. This is determined by the requirements of the standard and has nothing to do with the operating system. On some terminals, signal traffic may be generated during state confirmation procedures. Therefore, in order to prevent the generation of such traffic, in addition to disabling data transfer, it is recommended to disable 4G mode.
8. The “Gigabit World” makes virtual reality universally accessible.
VR technology takes us to the virtual world. Oculus Rift DK2, Sony Project Morpheus and Samsung Gear VR can be attributed to virtual reality devices that provide satisfactory perception quality. Virtual reality head units are divided into glasses (connected to smartphones), helmets (connected to personal computers), and self-contained all-in-one devices (used independently). Nowadays, VR devices connected to personal computers are popular among video game enthusiasts. Huawei believes that self-sufficient mobile consumer VR devices will become the most common, since they better meet the requirements of virtual reality and do not suffer from technical problems inherent in smartphones.
VR content on smartphones or computers is downloaded in advance, and not downloaded from the server after changing the viewpoint. Therefore, the delay in the transmission channel is not the main factor determining the amount of "delay in the output of moving objects" (motion-to-photon; MTP). Due to the insufficient level of development of gaming devices for shooting in virtual space and video synthesis technologies, video sources with a 4K resolution (less than or equal to 4K and not meeting the PPI requirements for retina-resolution of the initial level) will gain popularity. Increasing the computational capabilities of terminals is not the main trend of VR development. Due to the increase in transmission speeds in mobile networks, computations can be performed in the cloud with the delivery of results directly to the terminals.
It takes time for high-resolution recording technologies to emerge and strengthen. Therefore, in the coming years, 4K video will be used for virtual reality services. The introduction of VR-Video on Demand (VoD) will require high bandwidth. The transfer rate of 1 Gbps will accelerate the commercialization of high-quality VR services.
www.vk.com/huaweirussiaofficial
www.facebook.com/huaweirus
www.linkedin.com/company/huawei-russia
www.twitter.com/huaweirus
After analyzing the statistics on the use of mobile services, trends in the development of mobile terminals and the prospects for mobile services following the results of 2015, Huawei has made eight key conclusions, which we describe below.
• Use of mobile services: in 2020, it is expected that 70% of all mobile data traffic will be accounted for by video services. Subscribers will become more accustomed to watching videos on their mobile phones anytime, anywhere. At the same time, Voice over LTE (VoLTE) voice service will provide 4G subscribers with a new level of audiovisual quality.
')
• Terminals: in 2015, more than 70% of mobile phones were equipped with displays, according to the PPI value, corresponding to entry-level Retina requirements. With the increase in the capacity of mobile phone batteries, the duration of their work does not increase in the same proportion. Increasing battery life can be achieved by optimizing mobile applications.
• Future services: to support virtual reality (VR) with retina-level resolution, the data transfer rate should reach the Gb / s level. With the development of the Internet of Things (IoT), more and more devices will consume data traffic automatically in accordance with specific usage scenarios.
The most important observations
1. The widespread availability of mobile video
According to the analysis of worldwide data traffic generated by mobile applications, traffic from countries with a high level of MBB development, for example, from Japan and South Korea, accounts for about 50% of the total. In emerging markets, the share of mobile video traffic is increasing rapidly. It can be said that in the reporting period, most often, MBB services were used specifically for viewing mobile video (“at any time and in any place”). We also found out that the 4G network more strongly stimulates the consumption of video in HD format compared to the traditional 3G network.

The world average monthly amount of traffic consumed by the user is 500 MB. However, in some countries with a high level of development of MBB networks, this figure exceeds 4 GB per month. Consequently, the need for people to view mobile video is to some extent suppressed. One of the main reasons for this is the high cost of traffic for the user.
2. Measuring user-perceived video quality
With the rapid development of mobile Internet technologies, viewing video programs on mobile terminals has become a widespread form of entertainment.
To measure the user-perceived quality of viewing online video programs, Huawei, in conjunction with the Peking University School of New Media, conducted research covering more than 3,000 consumers from more than 30 cities in the world. The results of these studies show that user perception is determined by the following main factors: the amount of consumed mobile data, the duration of video delays, pre-buffering, and the level of image resolution. The last three factors depend on the data throughput in the mobile network.
Assessing these factors allows you to assess the ability to support online video specific mobile network. In collaboration with the leading human factor and ergonomic research lab, Huawei measures user-perceived video quality using gaze tracking devices and recording physiological parameters. After evaluating these three factors, Huawei performs the analysis and modeling, and then formulates the result based on the mobile video MOS (vMOS) standard for user experience perception .

The vMOS standard is created on the basis of the MOS (Mean Opinion Score) expert evaluation, a widely recognized industry standard for quality assessment. The vMOS score is calculated based on factors that influence the user's perception: video quality, pre-buffering time and playout delays. The vMOS method allows you to assess the quality of the video from the point of view of the mobile network user. For testing using the vMOS method, you can download and install SpeedVideo - a Huawei-developed vMOS-based test application.
3. Wideband sound (HD Voice) with a presence effect
Observant users probably noticed that sometimes while making a call, the 4G icon suddenly disappears. This is because the sound on the 4G network is not well supported, and smartphones have to switch to a 2G or 3G network in order to provide voice services. With the growing popularity of VoLTE, the 4G network will be available anywhere you want to make a call or use data services. According to Huawei, VoLTE technology will provide users with a completely new level of sound quality.
Quick connection when calling
Compared with the forced switching to a 2G or 3G network, the delay in establishing a connection through a VoLTE network is much lower (approximately 1 second). At the same time, in traditional 2G networks the connection establishment delay for a voice call is about 6 seconds.

Crystal clear sound
Traditional 2G and 3G voice services are focused on the standards of a conventional wired telephone network, the width of the voice range in which ranges from 300 to 3400 Hz. However, the human ear is able to perceive frequencies in the range from 20 to 20 000 Hz and easily notice any sound distortion. In VoLTE networks, the audio frequency range is from 50 to 7000 Hz. The wider the frequency range, the more comfortable and more natural the sound is perceived by the human ear.
Video call 720P + with high quality
VoLTE easily supports video chat. We found out that in the same network environment, video calls on a VoLTE network are more clean and stable than in most video chat applications.
Simultaneous use of voice and data services
VoLTE technology has already been commercialized in South Korea. The South Korean telecommunications operator launched Uwa, VoLTE technology-based services, which ensure that calls are received at mobile terminals without interrupting data services. The launch of Uwa services has increased both the duration of voice calls and the volume of data traffic. These services also stimulate subscribers' desire to use the connection, as they allow chatting without interrupting the work of data transmission services.
4. The trade off between latency and throughput
The 4G network provides significantly better transmission performance over the air interface compared to the 3G network. In other words, the bandwidth of this network is much higher. However, the user perceived video quality is not always higher in the same proportion. The research results show that the available bandwidth has a negative correlation with end-to-end network latency. Therefore, the subjectively perceived user data rate can be increased by reducing the end-to-end delay.
The network bandwidth depends on which operator subscribers will choose. Optimizing latency requires the combined efforts of telecommunications operators and service providers. Currently, there are two main ways to optimize end-to-end delay.
1. Reducing the total length of the transmission path: the path length can be reduced by placing content as close as possible to subscribers. Among the most commonly used solutions are placing CDN nodes as close as possible to subscribers and deploying caching nodes.
2. Optimization of transmission resources: the delay in transmission lines can be optimized by the preferential use of fiber-optic resources in order to reduce the number of re-reception sites.
In terms of technological and architectural evolution, it is expected that the 5G network will support the download speed of traffic of 10 Gbit / s with a through delay of no more than 1 ms. At this point, “zero expectation” will become the standard of quality for mobile services.
5. Battery capacity: always be in touch
Battery life is still a bottleneck limiting the capabilities of mobile phone users. It depends on a number of factors: battery capacity, screen size, user habits and the availability of applications on your smartphone that require a constant connection to the Internet (for example, social networks).
In recent years, steady growth in battery capacity continues in response to an increase in screen sizes. According to the analysis of information about the 18 largest global manufacturers of smartphones, 54.5% of devices released in 2014 had a screen with a diagonal of 5 inches or more. In 2015, this ratio was already 76%, with most smartphones having a screen size of 5 or 6 inches. In 2014, 29.7% of new smartphones had a battery with a capacity of at least 3000 mAh. 36.2% of smartphones are equipped with a battery with capacity from 3000 to 4000 mAh.
However, the growth of battery capacity does not compensate for the increase in the duration of using devices and the volume of mobile data traffic. Analysis of user habits in recent years shows that they spend most of their time on applications that require constant access to the Internet, for example, Facebook and WeChat. Therefore, optimization is needed that would take into account the specifics of using such applications.
An effective means of extending battery life is the Unified Heartbeat mechanism used in some brands of smartphones. Heartbeat messages inform devices at the opposite end of the line about online status to make better use of the channel. However, different applications send these messages at different frequencies. Heartbeat messages and push messages sent by applications constantly consume battery life. The Unified Heartbeat mechanism reduces the amount of signaling messages exchanged by sending unified Heartbeat messages to the device at the opposite end not permanently, but according to a predetermined schedule. This saves battery life.

You can also increase battery life by using the latest 4G voice services (Voice over LTE; voice over LTE). Using intermittent reception (discontinuous reception; DRX) with long cycles, users of certain models of smartphones spend less on battery capacity compared to using traditional 2G / 3G services.
6. Overcoming the limitations of the resolution of Retina-displays
As the hardware of smartphones improves, the resolution of their displays increases. All major smartphone makers are looking to use higher resolution displays in their next-generation flagship models. Analyzing data from 18 manufacturers of smartphones from different countries shows a significant increase in the share of terminals with high-resolution displays. The percentage of terminals with a resolution of at least 1080p increased from 25% in 2014 to 36.4% in 2015. By the second half of 2015, 85 models of terminals with a resolution of 2K were launched in the series, among which 51 models are tablets and smartphones. Sony has released the world's first 4K smartphone - Sony Xperia Z5 Premium.
Huawei believes that tablets with a diagonal of 7–10 inches will soon appear, meeting the requirements for retina-resolution limit (above 4K), which will provide an unrivaled quality of 2D-video viewing with the naked eye. As for virtual reality (VR) applications, they use the principle of splitting an image with a distance between the eyes and a display on the order of several centimeters to create virtual images. If a 2K smartphone is used to view VR video, the effect will be the same as when watching a 360p video on it. Thus, the pursuit of higher-resolution smartphones will never stop.
7. “Stealthy” data traffic
Usually, users understand that when they browse websites or online video, certain data traffic is generated. However, in some cases, the consumption of such traffic remains unnoticed by users, for example, when sending health data from their devices or uploading photos to the cloud storage. It is safe to predict that with the development of the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence, the blurring of boundaries between the physical and digital world will accelerate. People are gradually becoming "network nodes." In such a “computerized” life, each of us will have special agents (that is, things) for different scenarios. These agents will autonomously download data for their owners (i.e., people) according to the requirements of the specific scenario. For example, when you turn on the mobile office mode in your car, email will be automatically downloaded. As our life becomes more computerized, the imperceptible traffic will become commonplace.
Some applications preload data. Basically it is necessary to watch the video, because it allows you to reduce the time of initial waiting and increase the subjectively perceived level of quality. The amount of such preloaded data is usually from 100 to 500 KB. As shown by the results of testing video viewing on Facebook, playback starts after tapping the screen with almost zero latency.
Huawei also found that the default 4are session (default bearer) remains active even when the data transfer is off. This is determined by the requirements of the standard and has nothing to do with the operating system. On some terminals, signal traffic may be generated during state confirmation procedures. Therefore, in order to prevent the generation of such traffic, in addition to disabling data transfer, it is recommended to disable 4G mode.
8. The “Gigabit World” makes virtual reality universally accessible.
VR technology takes us to the virtual world. Oculus Rift DK2, Sony Project Morpheus and Samsung Gear VR can be attributed to virtual reality devices that provide satisfactory perception quality. Virtual reality head units are divided into glasses (connected to smartphones), helmets (connected to personal computers), and self-contained all-in-one devices (used independently). Nowadays, VR devices connected to personal computers are popular among video game enthusiasts. Huawei believes that self-sufficient mobile consumer VR devices will become the most common, since they better meet the requirements of virtual reality and do not suffer from technical problems inherent in smartphones.
VR content on smartphones or computers is downloaded in advance, and not downloaded from the server after changing the viewpoint. Therefore, the delay in the transmission channel is not the main factor determining the amount of "delay in the output of moving objects" (motion-to-photon; MTP). Due to the insufficient level of development of gaming devices for shooting in virtual space and video synthesis technologies, video sources with a 4K resolution (less than or equal to 4K and not meeting the PPI requirements for retina-resolution of the initial level) will gain popularity. Increasing the computational capabilities of terminals is not the main trend of VR development. Due to the increase in transmission speeds in mobile networks, computations can be performed in the cloud with the delivery of results directly to the terminals.
It takes time for high-resolution recording technologies to emerge and strengthen. Therefore, in the coming years, 4K video will be used for virtual reality services. The introduction of VR-Video on Demand (VoD) will require high bandwidth. The transfer rate of 1 Gbps will accelerate the commercialization of high-quality VR services.
www.vk.com/huaweirussiaofficial
www.facebook.com/huaweirus
www.linkedin.com/company/huawei-russia
www.twitter.com/huaweirus
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/283256/
All Articles