Hackers and exchanges: The consequences of attacks on financial companies

In our blog on Habré we write about various aspects related to work on the stock exchange . And information security issues are the most relevant of them. Unscrupulous traders and employees of financial companies often cannot resist the temptation to use insider information for their own benefit — sometimes original tools like gaming chats are used to transfer it.
However, the big money that "live" in the financial markets attract not only unprepared criminals, but also entire hacker criminal groups using high-tech means of attack. Today we will talk about the consequences of their actions, and how to defend the simple participants of exchange trading.
')
Trojan Corkow: a jump in the exchange rate of the ruble and 244 million loss
In late February last year, hackers caused a panic on the Moscow Stock Exchange. For fifteen minutes, the dollar exchange rate "jumped" in a very large range for the usual course of trading. An unknown trader first sold dollars at 55 rubles, and then bought, but already at 65. Suddenly, the resulting volatility allowed, for example, to make a deal to buy dollars at the rate of 59.0560 and in 51 seconds to sell them at the rate of 62.3490.
The culprit of the incident was originally called Kazan Energobank, on whose behalf non-market bids were made - totaling more than $ 500 million. In just 15 minutes, the damage to the bank amounted to 244 million rubles. Initially, bidders and regulators put forward various versions that were not related to hackers. For example, the first deputy chairman of the Central Bank, Sergey Shvetsov, accused the Kazan bank of deliberately manipulating currency. Some financiers decided that this is how the representatives of “Energobank” withdraw money.
When the bank demanded that all transactions be canceled and the funds be returned, the participants in these transactions recognized the transactions as legal - as a result, the bank sued brokers whose clients became counterparties of committed hackers were ruinous non-market transactions.
Later, the Ministry of Internal Affairs turned to the company Group-IB, which is engaged in cyber-investigations. It was her experts who published a report in which they told that a group of hackers was worth the financial manipulations.
In fact, they used Corkow , a Trojan known from the beginning of the 2010s, who were infected with a terminal for remote management of bank transactions. What is interesting, according to media reports, at the end of March 2015, the Moscow Exchange Currency Market Committee recommended the exchange board to exclude the financial institution from the bidders of the foreign exchange market due to insufficient security of the information security system.
The trojan used for the attack can open a remote control channel on the infected computer through legitimate looking sites or files. As a result, hackers are able to remotely control. Corkow is constantly updated to bypass antivirus programs. According to information security experts, the Trojan has already infected 250,000 computers all over the world, and also has penetrated into the systems of more than a hundred financial companies. In all the banks where this malware was detected, the antivirus was installed and worked correctly, which did not prevent Corkow in some cases from going unnoticed for more than six months.
At the moment, it is unknown whether the hackers managed to really steal money during unauthorized transactions. Who exactly managed to earn - these are ordinary stock traders who could find their time and were able to buy or sell currency at a rate that was extremely profitable for themselves and unprofitable for the bank. The only way to get this money back is to collect it from those who have injected malware into the bank’s system. There is a version that a former employee of the bank who decided to avenge his dismissal could contribute to hackers.
However, there are still no final conclusions, the investigation continues, the final recipient of 250 million is still not found.
Foreign financiers suffer from Russian hackers
The report of the US Securities Commission, published in February last year, reported that 88% of brokers, in one way or another, face hacker attacks in their work. According to statistics, attempts to penetrate the network of America's largest banks occur every 34 seconds. Often foreign hackers are behind these cyber attacks - often Russians.
So a group of supposedly Russian hackers in October last year successfully attacked the servers of the financial data provider company and the publisher of the specialized media Dow Jones, stealing information that could be sold to exchange traders. A week before this incident, about 3,500 customers were abducted from the company. The FBI did not manage to find out whether these attacks against Dow Jones are related.
In October 2010, hackers (again Russians) committed a daring cyber attack on the Nasdaq exchange. The FBI received an alert from the exchange that a virus was in the system. Moreover, after studying it in the bureau, they came to the conclusion that the malware was introduced not by simple hackers, but by enemy security services. Journalists from many Western publications tried to find out what the consequences of this attack were, but none of the experts answered the question. But it was this incident that showed the American special services, and the whole world, how vulnerable the stock exchange, banks, and also infrastructure objects are to vulnerable cyber attacks.
The attacks on Dow Jones and Nasdaq are far from the only attempts of Russian-speaking hackers to seize financial information. In August 2015, the US authorities carried out arrests of Russian-speaking hackers who hacked into the PRNewswire, Marketwired and Businesswire news terminal systems in order to obtain insider information for trading on the stock exchange. Allegedly, the criminal group for several years of its existence was able to earn in this way more than $ 100 million dollars.
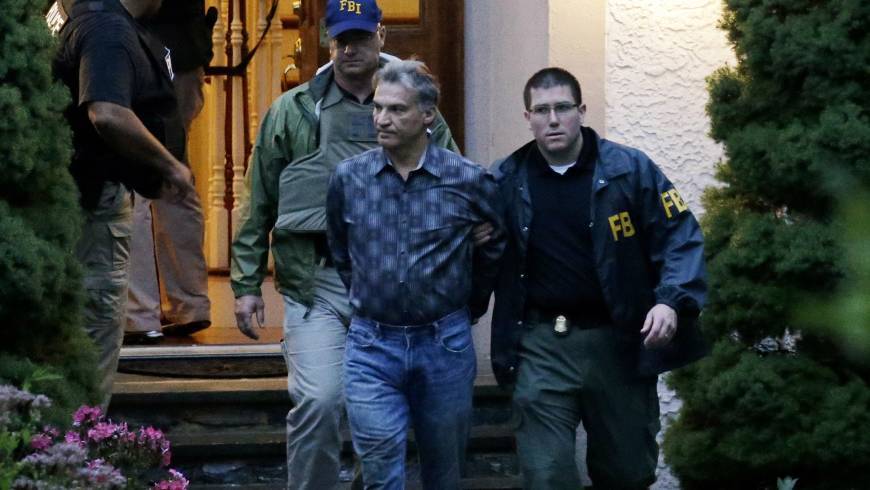

The arrest of one of the accused Vitaly Korchevsky
However, financial companies and stock exchanges are attacking not only hackers from our country. So in July last year, an attack was made on the New York Stock Exchange, as a result of which its work stopped for several hours. Despite the fact that the representatives of the exchange said about "technical problems", many commentators did not believe in this version - the reason for this was a suspicious tweet in the Twitter account of Anonymous, published 12 hours before the crash.
I wonder if something bad will happen for Wall Street tomorrow ... you can only hope for it.
In addition, the creator of McAfee antivirus, John McAfee, in his column for the British edition of IBTimes, said that the hackers' actions like Anonymous could be the cause of the stock market crash. Allegedly, McAfee studied the hacker dialogues in the shadow part of the Internet (dark web), in which they congratulated each other on "successful work on Wall Street." Journalists have suggested that the reason for the possible attack could be widespread press coverage of the stock crisis in China.
How to protect
On modern stock exchanges, there are rules that allow you to minimize the consequences of sudden and strong price movements. Usually, before the start of trading, a corridor is established within which the price may change during the trading session. When going beyond its limits, trading stops - this helps prevent situations where, if a panic arises in the market, the price of any financial instruments can fall by tens of percent per day.
In addition, disruptions can occur for reasons unrelated to the activities of cybercriminals. In any case, stopping the bidding is not the only possible problem. Errors in the work of the exchange system can lead to incorrect display of trading data or incorrect calculation of the collateral to hold the position (an error can even lead to premature closing of the transaction)
In order to minimize possible damage, brokerage companies are developing various systems to protect customers. How this protection is implemented in the ITinvest MatriX trading system can be found here .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/282489/
All Articles