SpyEye authors were given 24 years for two
Two years ago we wrote about the arrest of the main author SpyEye, who is known under the pseudonym Gribodemon (Alexander Panin). All this time, a native of Tver was awaiting trial and sentencing in an American prison. Famous American security journalist Brian Krebs points out in his blog that Panin and his “business partner” Algerian Hamza Bendelladj (Bx1) got 24 years for two. Panin received nine and a half years, and Bx1 fifteen. If the former was the creator of the Trojan itself, then the latter specialized in selling it.

SpyEye has already been written about quite a lot, so there is no sense in repeating it again. It is worth noting that before the so-called. full-featured crimeware toolkits were still rare, Zeus and SpyEye defined the format of this business as such. The client was selling a ready-made tool to create a botnet and centrally siphon money from victims who had been compromised by stealing online banking data. Further, the stolen funds were distributed in different portions to the accounts of the intruders and were also cashed out in portions using the so-called. money mules.
')

Bx1 not only specialized in selling this malicious tool to other cybercriminals, but also helped Panin improve SpyEye. In addition, Bx1 has created its own botnet, which has helped its operator collect data from 200 thousand bank cards of victims of SpyEye. According to experts, the cybercriminal received a profit of $ 100 million from this botnet.
In November 2010, Panin received the source texts of another well-known banking Trojan called Zeus from a cybercriminal under the pseudonym Slavik (Bogachev). After this, SpyEye acquired many of the malicious features of Zeus. Unlike Panin, Bogachev is still at large, although he is one of the most wanted cybercriminals in the world.

Fig. Orientation to Bogachev from fbi.gov.
A typical scheme of fraud (fraud) work using SpyEye is shown below. Behind a large botnet based on a malicious program is the organizer who coordinates the cybercrime links of the common chain, including distributors of Trojan droppers, hackers who service the infrastructure and lead mules who specialize in cash-outs of stolen funds.
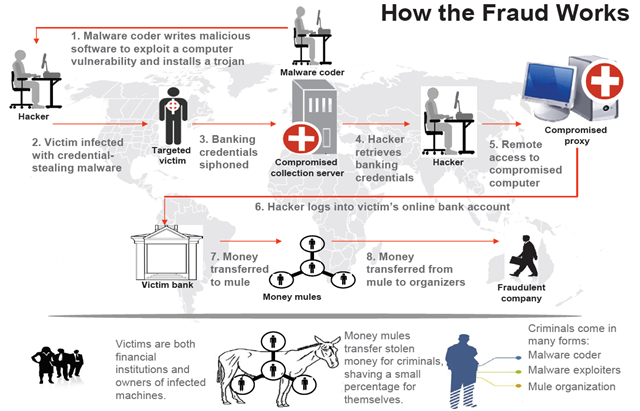
Fig. Cybercriminals who use crimeware toolkit to steal funds from bank accounts.
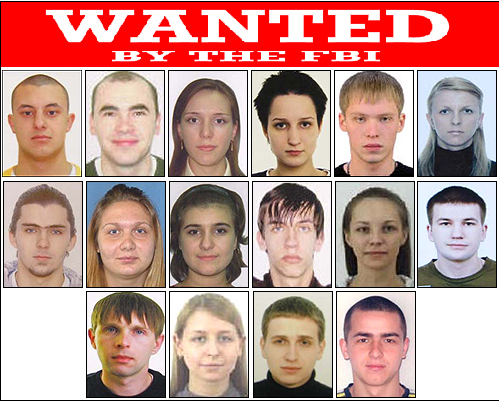

Fig. FBI press release issued in the context of the case of arresting “money mules”, the so-called United States v. “Zeus money mules” in 2010. More than two dozen students from the former USSR were arrested, many of whom came to the United States using forged documents and cashing “dirty money” that had been stolen from bank customers using Zeus (on the source code of based SpyEye). According to the investigation, within the framework of this case, more than $ 70 million was stolen.

SpyEye has already been written about quite a lot, so there is no sense in repeating it again. It is worth noting that before the so-called. full-featured crimeware toolkits were still rare, Zeus and SpyEye defined the format of this business as such. The client was selling a ready-made tool to create a botnet and centrally siphon money from victims who had been compromised by stealing online banking data. Further, the stolen funds were distributed in different portions to the accounts of the intruders and were also cashed out in portions using the so-called. money mules.
')
Bx1 not only specialized in selling this malicious tool to other cybercriminals, but also helped Panin improve SpyEye. In addition, Bx1 has created its own botnet, which has helped its operator collect data from 200 thousand bank cards of victims of SpyEye. According to experts, the cybercriminal received a profit of $ 100 million from this botnet.
In November 2010, Panin received the source texts of another well-known banking Trojan called Zeus from a cybercriminal under the pseudonym Slavik (Bogachev). After this, SpyEye acquired many of the malicious features of Zeus. Unlike Panin, Bogachev is still at large, although he is one of the most wanted cybercriminals in the world.

Fig. Orientation to Bogachev from fbi.gov.
A typical scheme of fraud (fraud) work using SpyEye is shown below. Behind a large botnet based on a malicious program is the organizer who coordinates the cybercrime links of the common chain, including distributors of Trojan droppers, hackers who service the infrastructure and lead mules who specialize in cash-outs of stolen funds.

Fig. Cybercriminals who use crimeware toolkit to steal funds from bank accounts.
- The author of the Trojan is developing the necessary functionality of the bot.
- The operator (hacker) is responsible for distributing the compiled executable files of the Trojan program. He can use the services of spammers to organize spam mailings, “iframes” to redirect legitimate users of hacked sites to a Trojan or other methods known in the cybercrime world.
- The user is infected with a banking trojan, after which he uses a browser (in the process of which the malicious code is located) to work with online banking. The confidential data specified when working with the online banking system is sent to the attacker's server.
- The operator (hacker) receives the data sent by the bot in the previous step.
- The operator may use another compromised computer (proxy) to conduct fraudulent operations with the victim’s account, thus hiding the source of the attack.
- Using the proxy specified in the previous paragraph, the operator logs in to the user's online banking account using the login / password pairs stolen in step 4.
- Funds from the victim’s account are transferred to several dummy bank accounts in small portions, and then cashed at ATMs by various persons participating in the criminal scheme (mules).
- The organizer (coordinator) of the entire criminal scheme receives funds from the “mules”, and each of them “mules” receives its share.

Fig. FBI press release issued in the context of the case of arresting “money mules”, the so-called United States v. “Zeus money mules” in 2010. More than two dozen students from the former USSR were arrested, many of whom came to the United States using forged documents and cashing “dirty money” that had been stolen from bank customers using Zeus (on the source code of based SpyEye). According to the investigation, within the framework of this case, more than $ 70 million was stolen.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/282133/
All Articles