New course on microcontrollers - a joint project of industry and universities
The British company, two American companies and 18 universities (including Russian MIET, ITMO, SSAU, NNTU) collaborated to launch a modern course on microcontrollers with a small binding to the Internet of Things. This is today's press release from Imagination Technologies, Microchip Technology and Digilent (National Instruments divisions) . The main author is Professor Alexander Dean from the University of North Carolina . Unlike the more lightweight courses on the Internet of Things, the new course brings a solid engineering base under the subject - it discusses in detail the use of RTOS, the microprocessor core architecture of the microcontroller, the peripheral protocols and even the optimization of algorithms for programming.
Download the course here:
')
https://community.imgtec.com/downloads/connected-microcontroller-lab-v1.2/
In a press release, in addition to quotes from the United States, Britain, Germany, China, there is a quote from Russia:
A couple of dozen slides from the course to make you taste it:
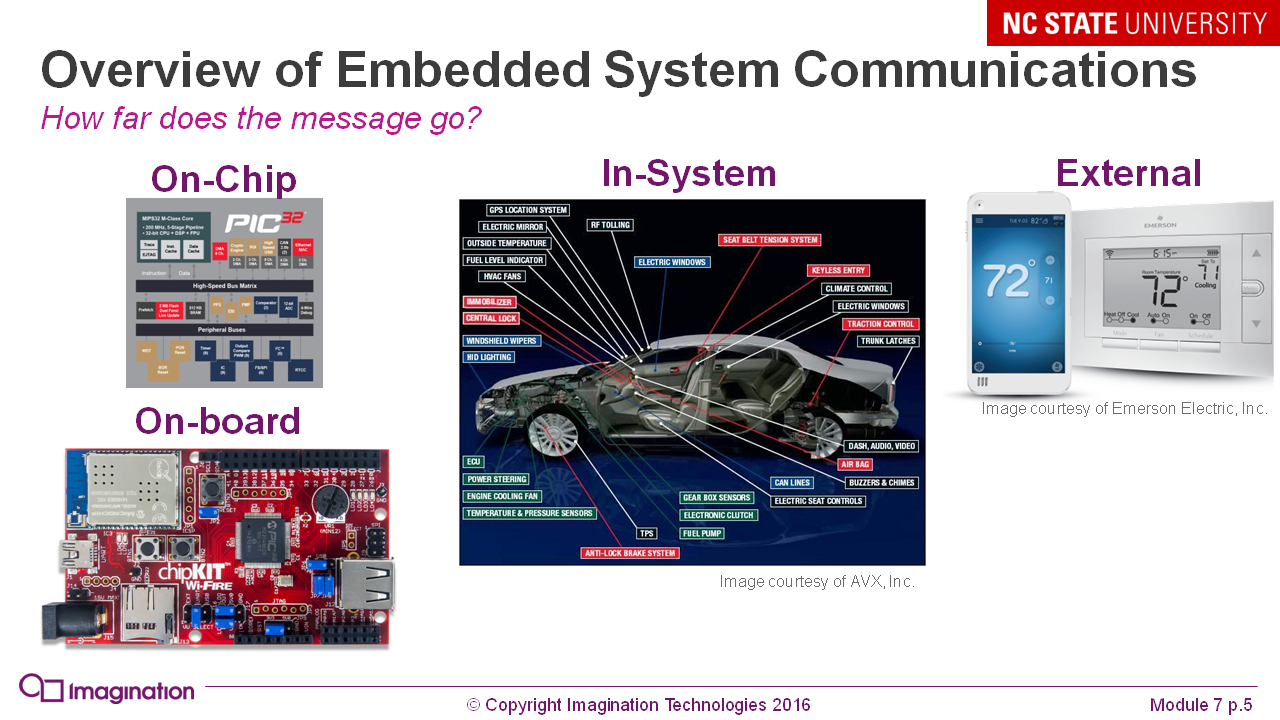
When should I use microcontrollers, and when - specialized chips, FPGAs or embedded PCs:
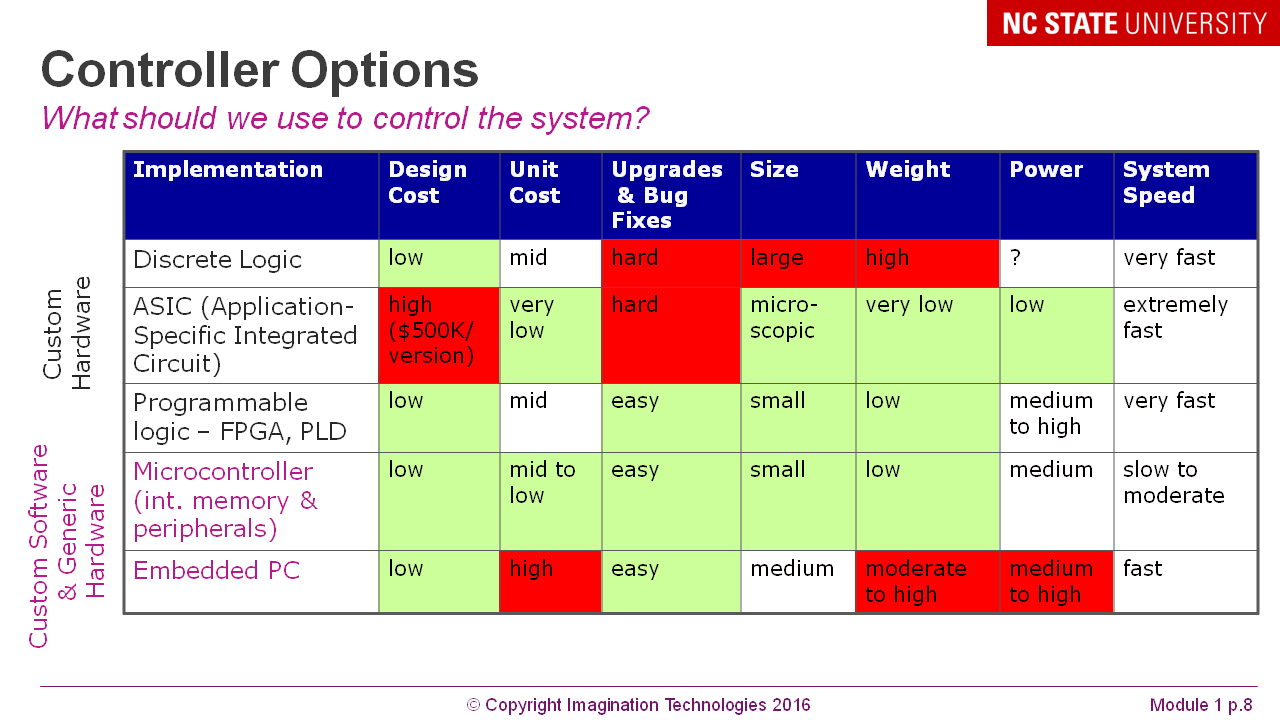
Three levels in the course - microprocessor core, microcontroller, board:
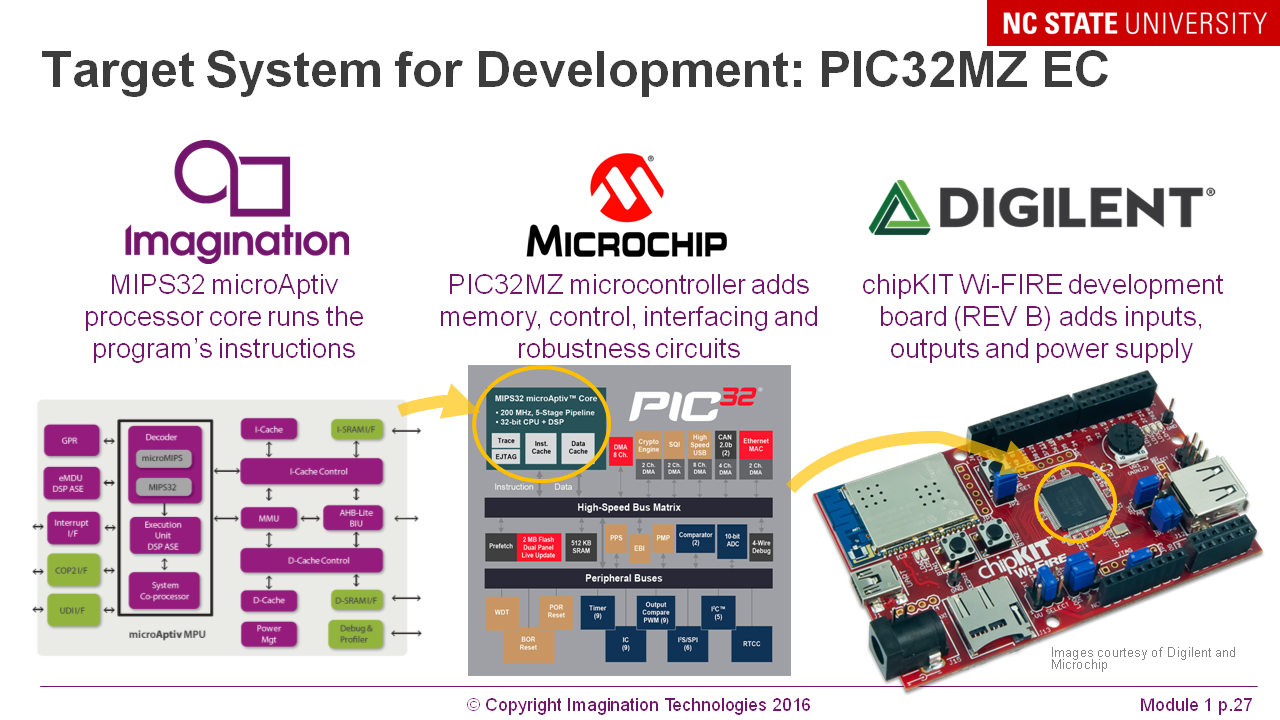
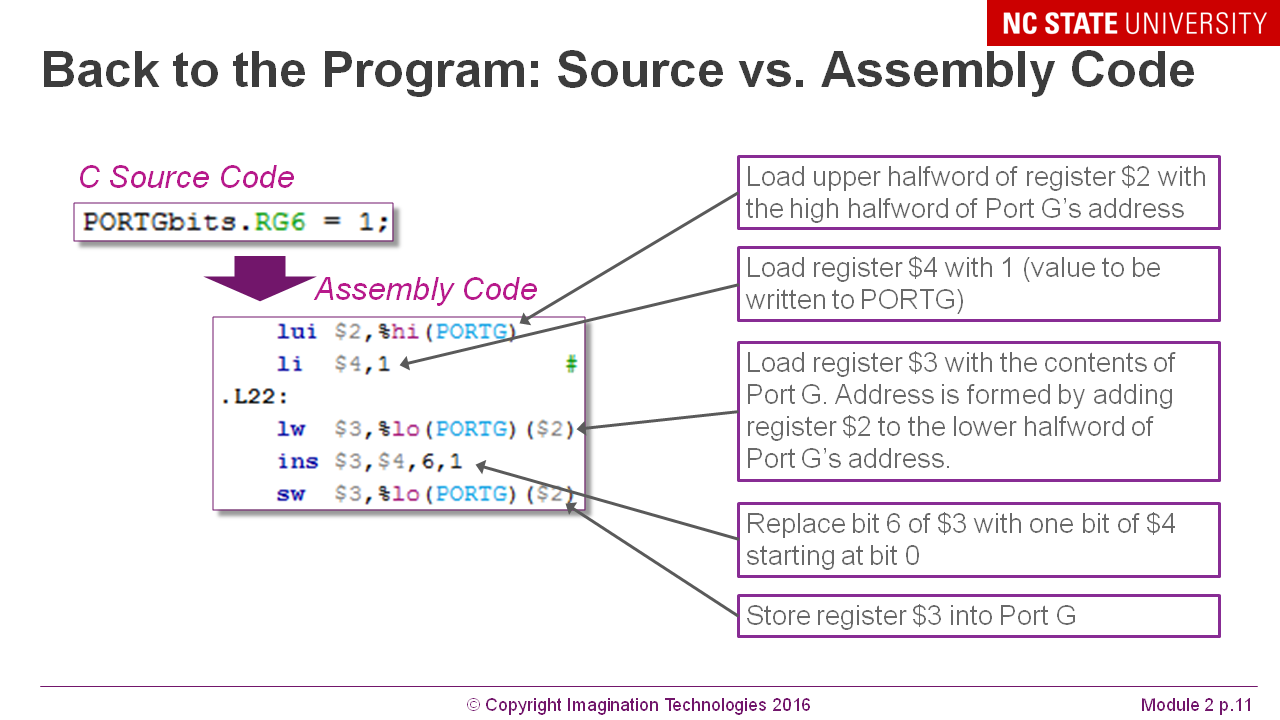
What is what in the assembler code from Si:
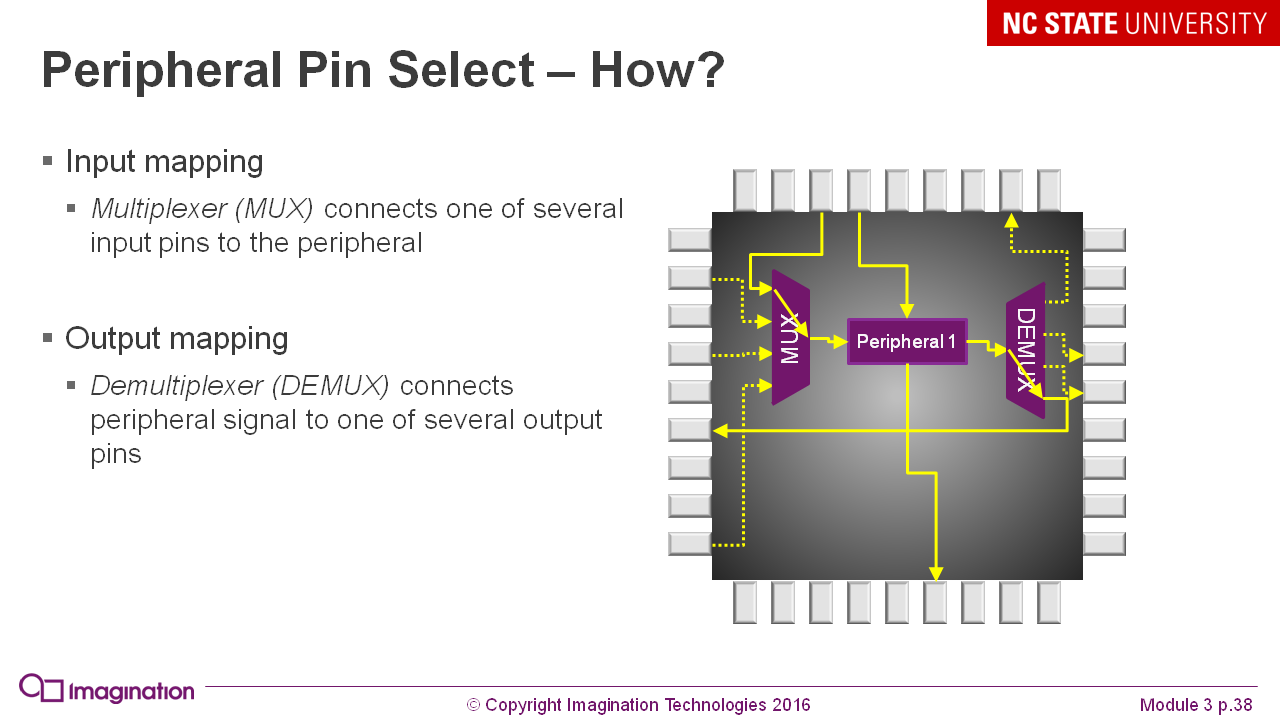
As different devices inside the microcontroller can use the same pins from the case:
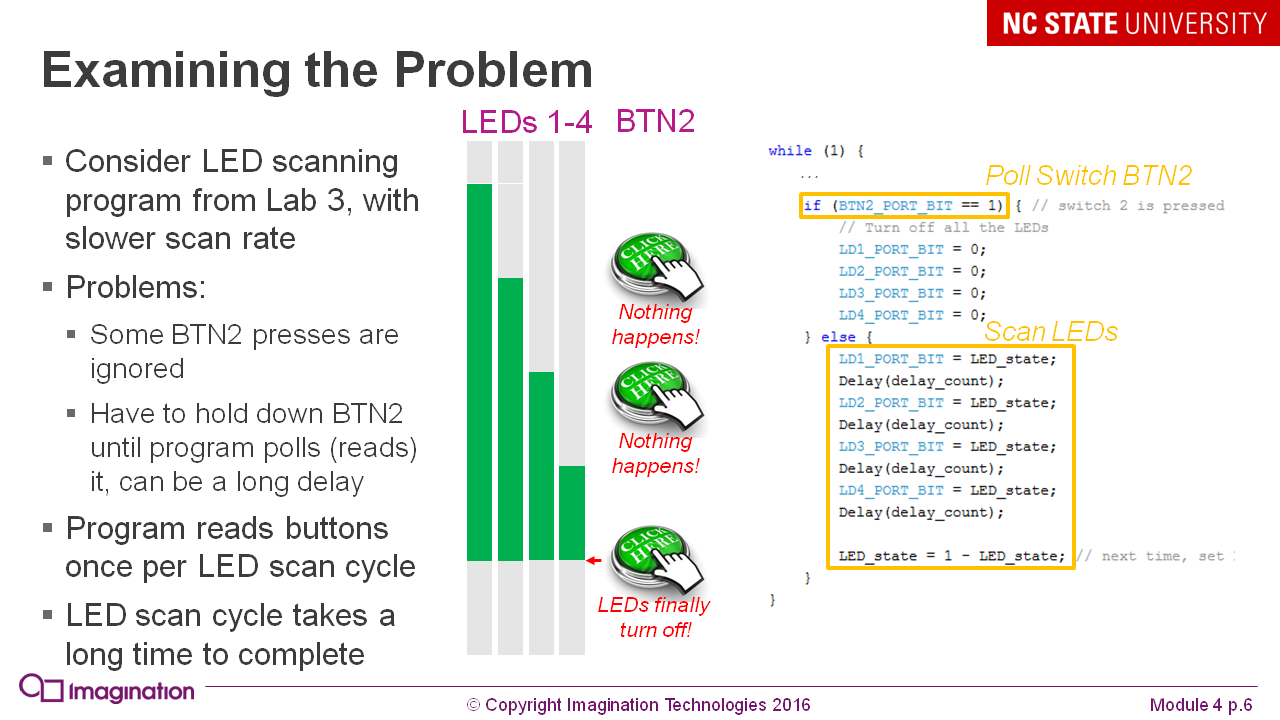
The problem with sequential programs as a preface to parallel programming:
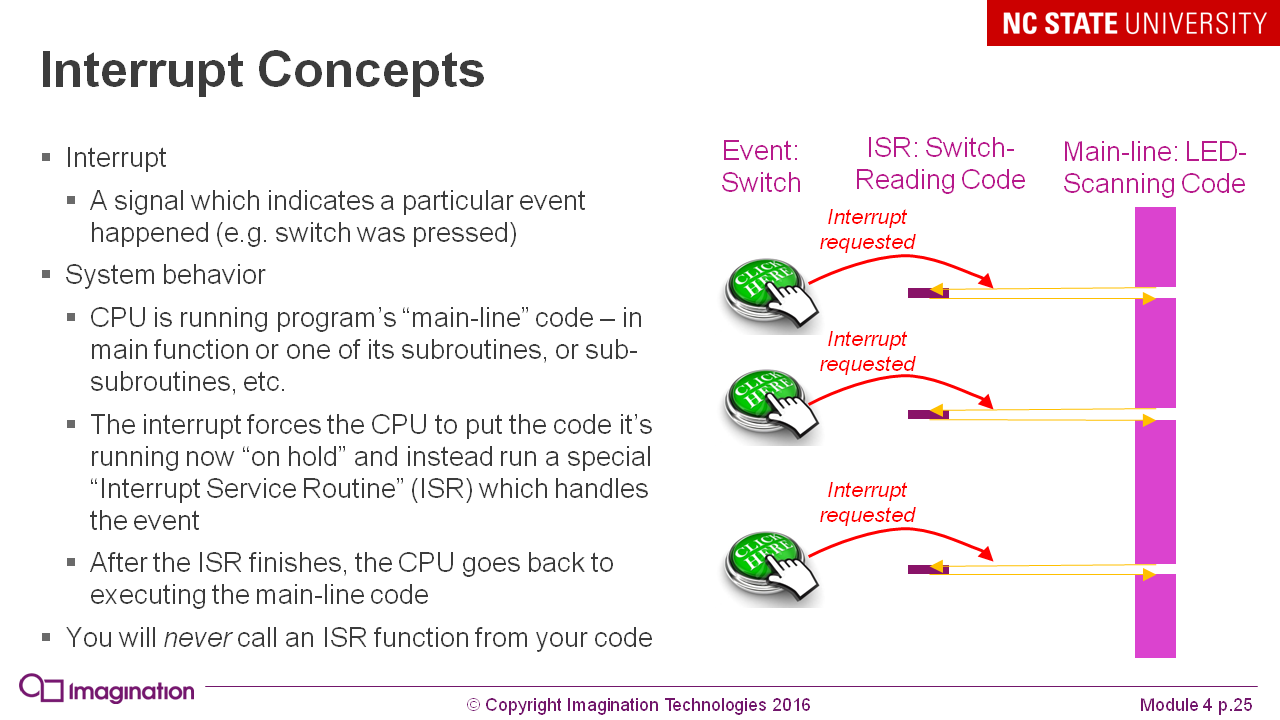
Explaining the concept of interrupts as solving problems with sequential programs:
How analog peripherals work:

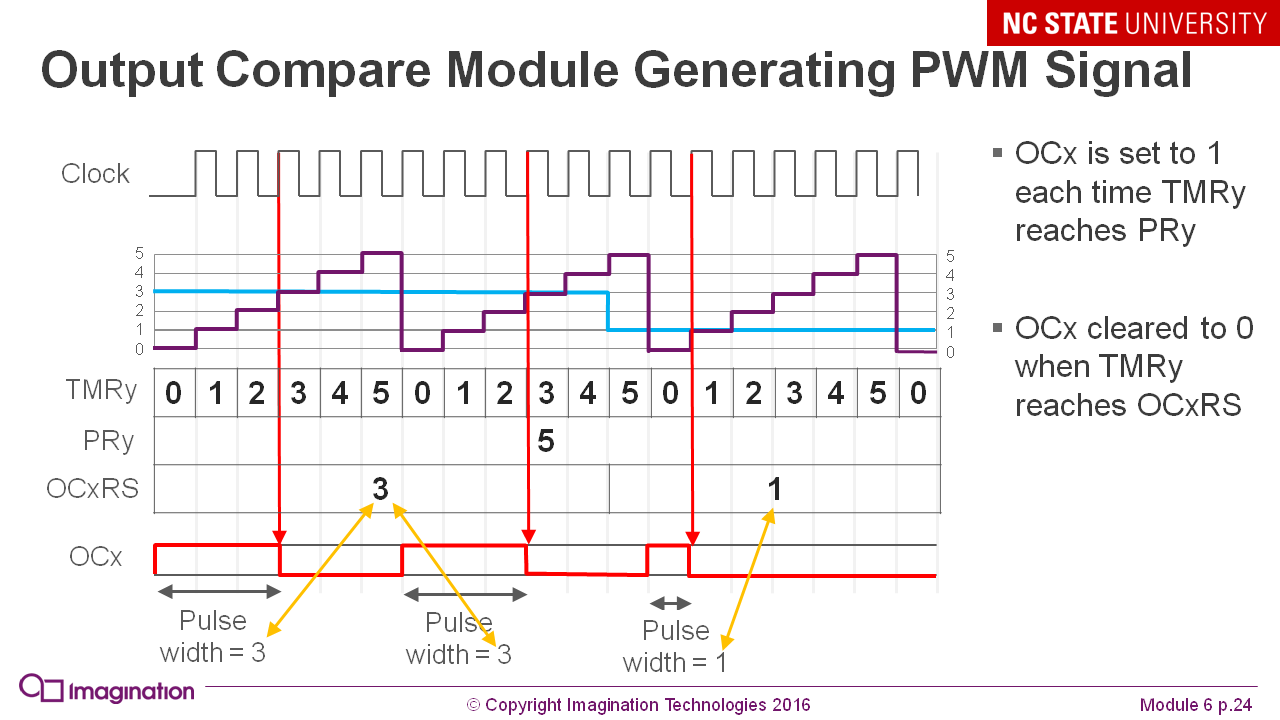
What is, what is needed and how to do pulse-width modulation (PWM):
Details of communication protocols with peripheral devices, the concept of framing:

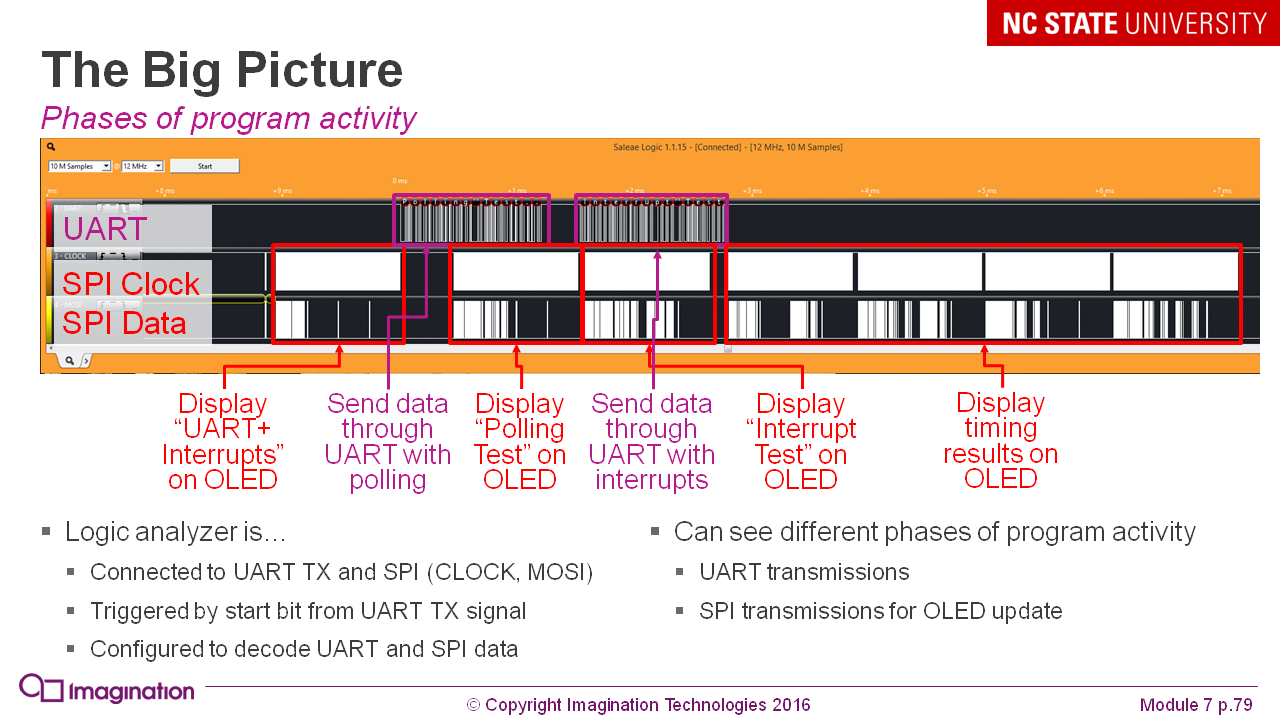
A bird's-eye view of the system while the program is running with several peripherals:
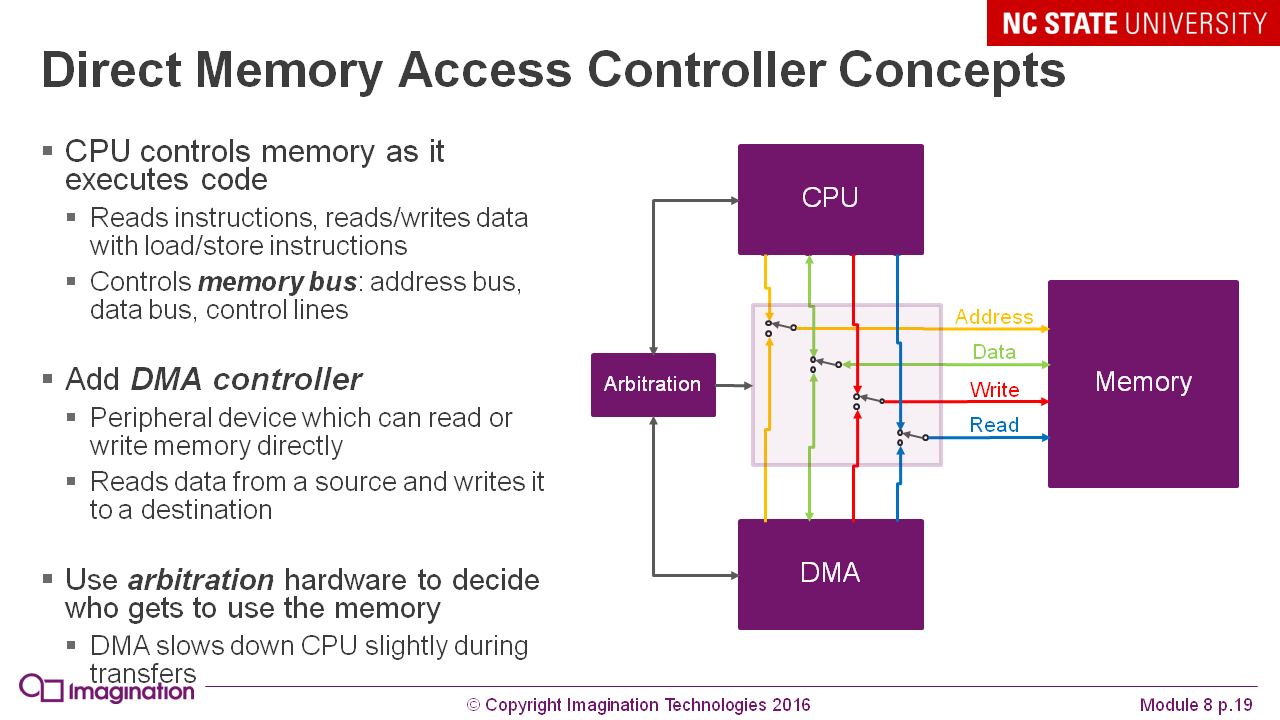
What does the DMA controller do:
There is something for lovers of Arduino:

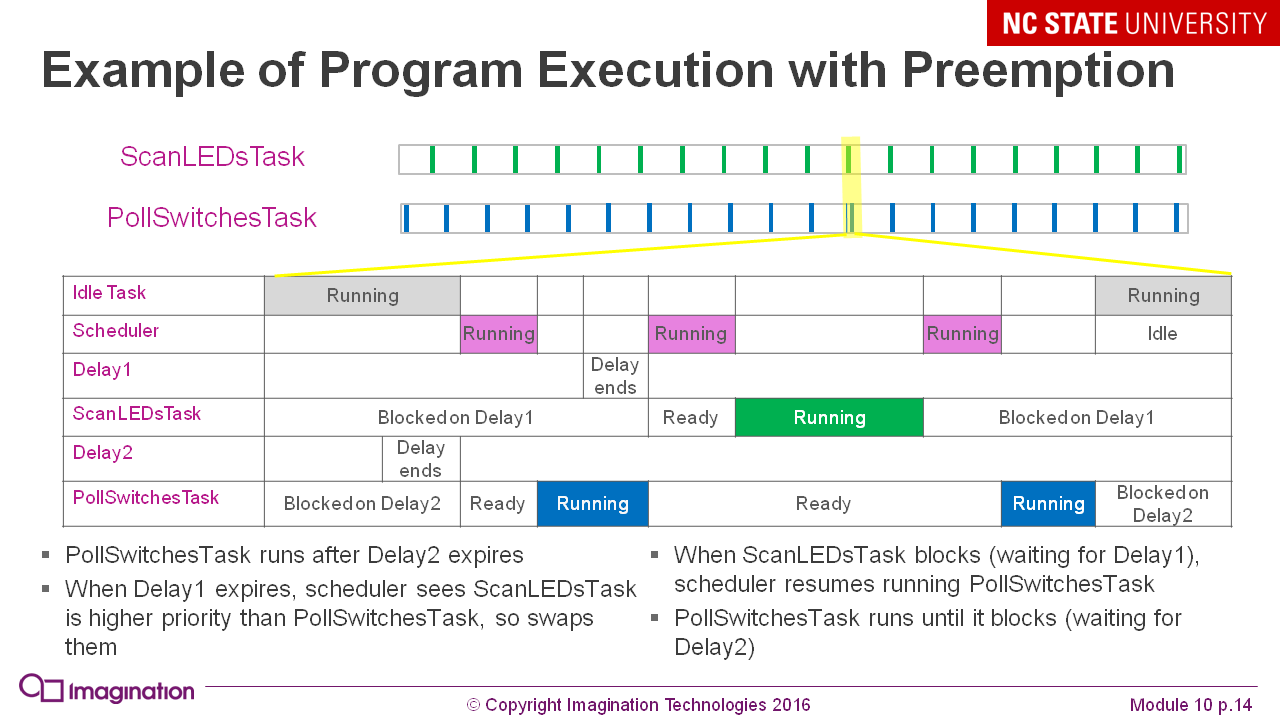
Introduction to real-time operating systems:
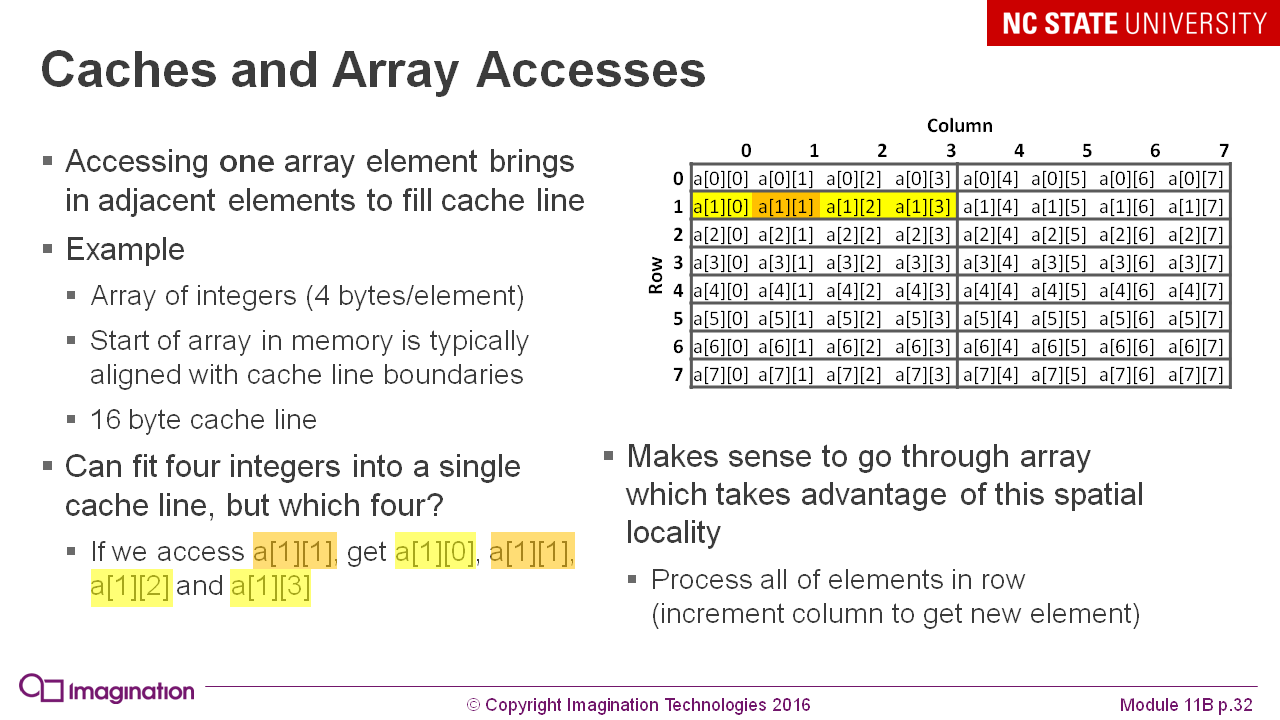
And here is how a two-dimensional array fits into the cache:
And now deep into the micro-architecture of the microprocessor core in the heart of the microcontroller:

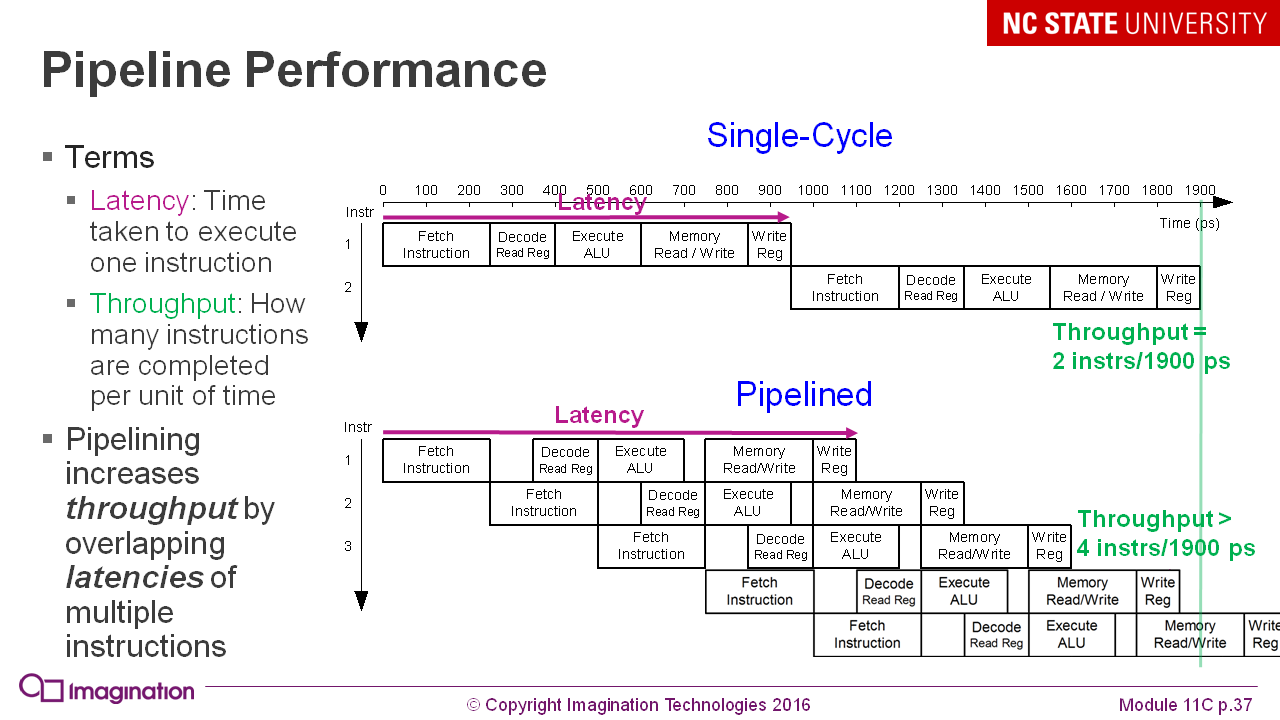
Explanation of the concept of the processor pipeline, which is necessary for understanding the micro-architecture:
As a course for undergraduate students, there is simply a common sense of programming:

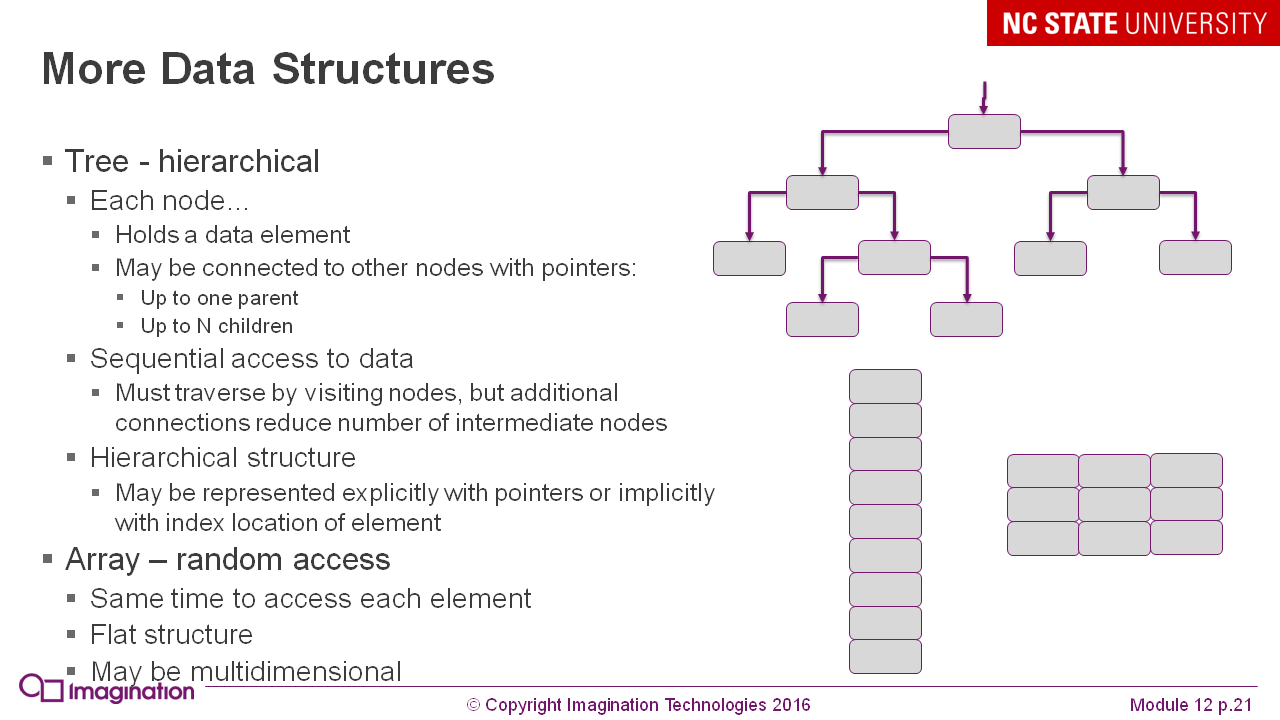
As well as a few reminders about data structures to write effective programs:
And about the Internet of things of course - connecting to the cloud via WiFi:

Thanks to participants from universities for detailed reviews of materials:


Download the course here:
')
https://community.imgtec.com/downloads/connected-microcontroller-lab-v1.2/
In a press release, in addition to quotes from the United States, Britain, Germany, China, there is a quote from Russia:
“MIET is part of Imagination's MIPSfpga and Connected MCU Lab beta-testing programs. Our students have been benefiting from the MCU Lab at our university.
- Alexey Pereverzev, Head of Computer Engineering, National Research University of Electronic Technology (MIET), Russia
A couple of dozen slides from the course to make you taste it:
When should I use microcontrollers, and when - specialized chips, FPGAs or embedded PCs:

Three levels in the course - microprocessor core, microcontroller, board:

What is what in the assembler code from Si:

As different devices inside the microcontroller can use the same pins from the case:

The problem with sequential programs as a preface to parallel programming:

Explaining the concept of interrupts as solving problems with sequential programs:

How analog peripherals work:

What is, what is needed and how to do pulse-width modulation (PWM):

Details of communication protocols with peripheral devices, the concept of framing:

A bird's-eye view of the system while the program is running with several peripherals:

What does the DMA controller do:

There is something for lovers of Arduino:

Introduction to real-time operating systems:

And here is how a two-dimensional array fits into the cache:

And now deep into the micro-architecture of the microprocessor core in the heart of the microcontroller:

Explanation of the concept of the processor pipeline, which is necessary for understanding the micro-architecture:

As a course for undergraduate students, there is simply a common sense of programming:

As well as a few reminders about data structures to write effective programs:

And about the Internet of things of course - connecting to the cloud via WiFi:

Thanks to participants from universities for detailed reviews of materials:

Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/282001/
All Articles