Deploying Django Stack on Ubuntu in Microsoft Azure Cloud
You already know that we have launched a new project dedicated to open source projects - linuxloves.ms . Details about the project you can find in our publication on Habré , which has already caused a fierce flame :-).

Developers who create solutions on the Django stack can easily deploy their solutions on the Microsoft Azure cloud platform. The easiest way to do this is with the help of virtual machines.
To simplify working with virtual machines in the Azure cloud, the Azure Marketplace is offered, which houses hundreds of pre-configured virtual machines with different environments and installed tools, including operating systems, databases, environments, frameworks, CMS, and so on. You can learn much more about the Azure Marketplace on our Russian-language portal .
')
Consider how any Azure user can deploy a Django stack in minutes.
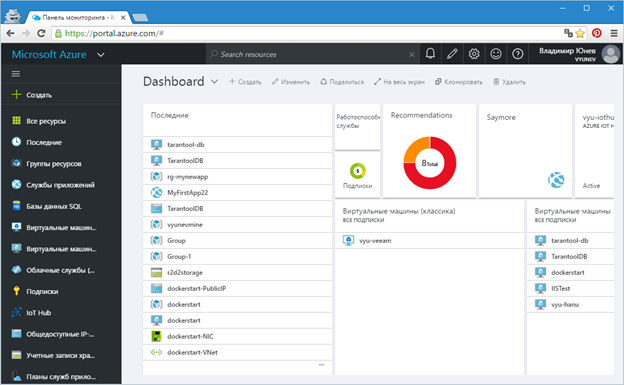
Figure 1 - Microsoft Azure Portal
Click on the "Create" button to add a new component to your account. In our case, we intend to add a virtual machine with a Django stack. Type Django in the search bar. You will receive a complete list of Django configurations available in the Azure Marketplace to choose from (Figure 2).
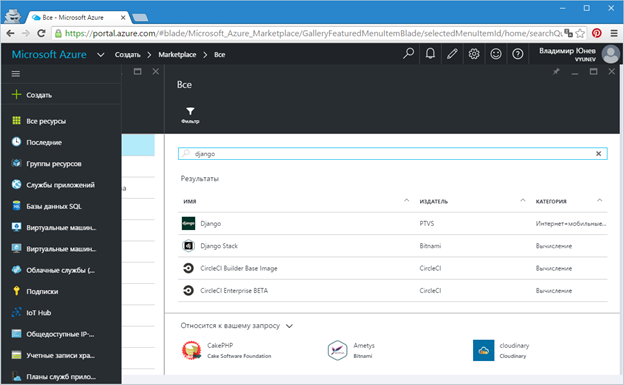
Fig . 2. - Django list in Azure Marketplace
Select Django Stack and in the new information window, click the "Create" button. Now you are going to directly create a virtual machine selected from the Azure Marketplace (Figure 3).
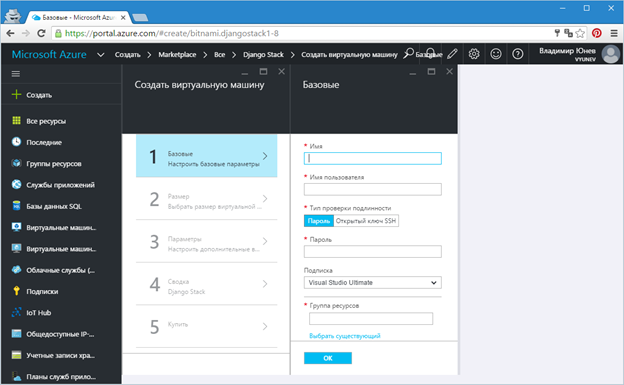
Fig.3. - Create a virtual machine
To create a virtual machine, in our case with Django on board, you need to specify a number of parameters. First enter the name of the virtual machine. Then the username (administrator) and password access. Choose an Azure subscription if you have several.
An important parameter that must be specified is a group of resources. In general, a resource group is simply a combination of different cloud resources — VM, storage, networks — under the same name to simplify administration. Therefore, at this stage just enter a name for the group.
The last parameter that you need to specify in the first step is the location of the virtual machine - essentially the choice of one of the Microsoft Azure data centers that are located around the world. The data center closest to Russia is Northern or Western Europe. Choose one of them (Figure 4).
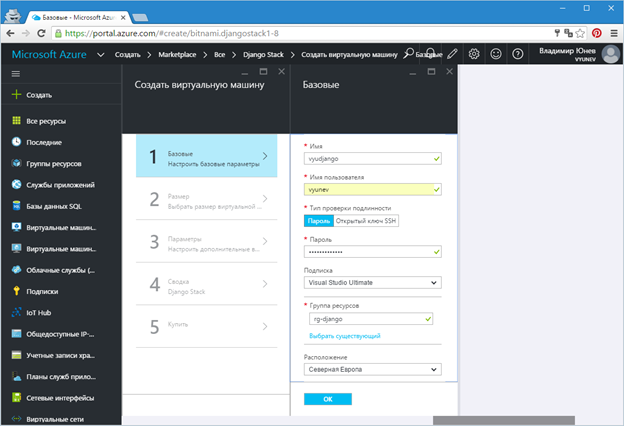
Fig.4. - Parameters of the first step of creating a virtual machine
Click "OK" after entering all the parameters. In the second step, you will be prompted to choose the size of the virtual machine. By default, there will be several types of machines that are recommended for this type of solution. But you can always choose a different size by clicking on “View All” (Figure 5).
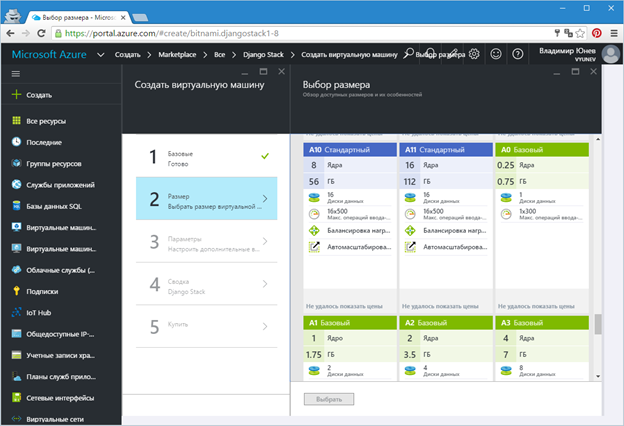
Fig.5. - Select the size of the virtual machine
I suggest that you choose the size “A1 Base” as suitable for testing. After selecting, press the “Select” button to go to the third step.
The third step is to fine-tune the deployment. Here, all parameters can be left as default and nothing changes at all. But if it is required that you can select SSD storage for a VM, configure virtual network, security, enable monitoring, create an availability group for VM fault-tolerant operation (Figure 6).

Fig.6. - VM deployment tweaks
Click "OK" after fine tuning in order to proceed to the final steps and launch the virtual machine.
You will receive an information window listing your settings (Figure 7).

Fig.7. - Information window with settings
Read the information and click "OK" in order to proceed to the acquisition of a virtual machine for your subscription.

Fig.8. - Acquisition of a virtual machine
Click the Acquire button to start the process of deploying your virtual machine with Django on board.
You will see the information message “Deployment started ...” (Figure 9).

Fig.9. - Deployment started
As soon as the VM is ready, you will receive another informational message, and the control panel of the created VM will open on the portal (Figure 10). In general, creating a virtual machine takes a few minutes.
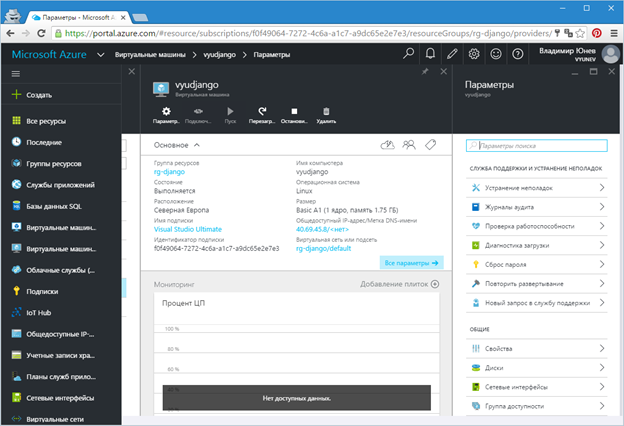
Fig.10. - Virtual machine control panel
Congratulations! You deployed your machine with a ready-made Django stack.
In order to make sure that the virtual machine is up and running, we can go to its publicly accessible address first.
You can find the public address in the header of the administration panel. In my case, this is http://40.69.45.8/ . Turning to this address, we will see a standard greeting (Figure 11).
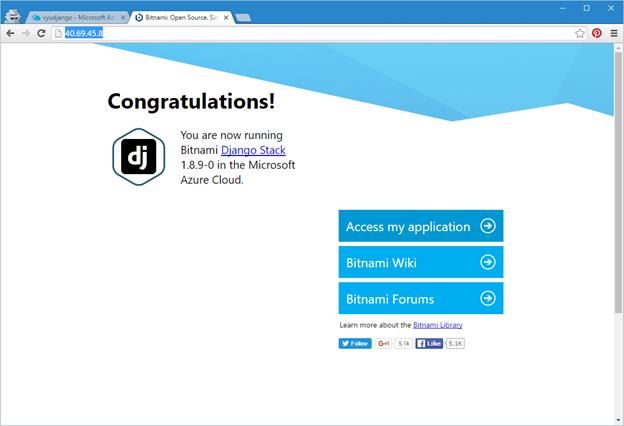
Pic.11 - Standard greeting from a Django- running machine in Azure
This virtual machine was prepared by Bitnami, a well-known assembler of ready-made environments. To see the Django application itself, you can click on “Access my application” (Figure 12).

Fig.12. - Running Django application
You may be interested in how to get the FQDN address for your car in the form of a domain name. By default, the VM address is not mapped, but it can be easily obtained. To do this, go to the VM settings (All settings) in the configuration panel. Then select the “Configuration” item and in the settings panel specify the name for your VM, which will be included in the FDQN path (Figure 13).
After saving the settings, you can click on the link, which will be presented as (my case) http://vyudjango.northeurope.cloudapp.azure.com/ .
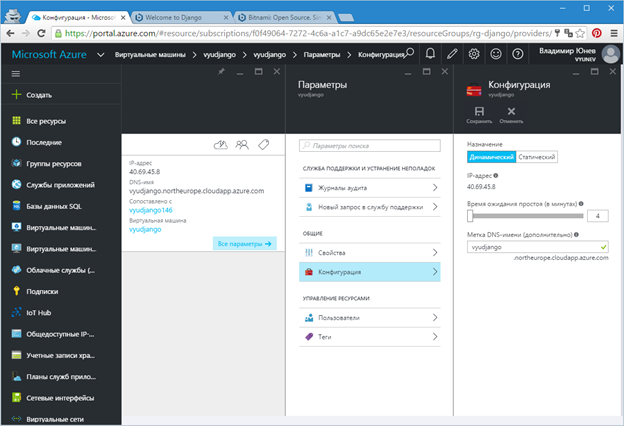
Fig.13. - Adding FDQN path for virtual machine
You can now use the same address to access your virtual machine over SSH (Figure 14), for example:
SSH vyunev@vyudjango.northeurope.cloudapp.azure.com
where vyunev is the username (administrator) you specified when creating the VM.
Or simply using the address in your favorite tool (Figure 13).
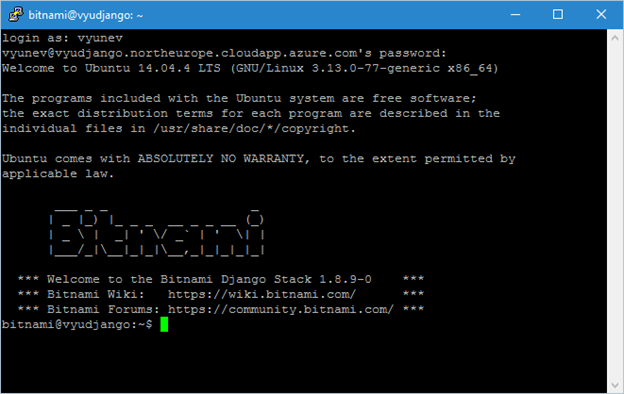
Fig.14. - Connect to the virtual machine via SSH
Now you can configure your VM with Django as your heart desires!
We looked at a simple example of how using Azure and the Azure Marketplace platform, in a matter of minutes, you can deploy your Django environment and gain access to a ready-made working virtual machine.
Azure and Azure Marketplace offer to launch any solutions built on any technology, including for Linux and Windows. Here is just a brief list of what you can find: Red Hat Enterprise Linux, Oracle Linux, CentOS, CoreOS, Ubuntu, Suse, WordPress, Moodle, MEAN, Jboss, Redmine, SEO Panel, Parse, Git, GitLab, Django, ModX, Memcached, LAMP Stack, Jenkins, Node.js, SugarCRM, Ruby Stack, Ghost, Subversion, ActiveMQ, Nginx Stack, Solr, Tomcat, JRuby, OwnCloud, MySQL, Drupal, MongoDB, Piwik, Dolibarr, LAAP Stack, OpenProject, Plone, eXo, Mahara, Zurmo, RoundCube, Mautic, ThinkUp, Prestashop, Tracks, phpBB, eZ Publish, Joomla ...
Continue to use Azure and host your opensource solutions in the cloud. This will help you in this detailed section of documentation and resources on this link .

Developers who create solutions on the Django stack can easily deploy their solutions on the Microsoft Azure cloud platform. The easiest way to do this is with the help of virtual machines.
To simplify working with virtual machines in the Azure cloud, the Azure Marketplace is offered, which houses hundreds of pre-configured virtual machines with different environments and installed tools, including operating systems, databases, environments, frameworks, CMS, and so on. You can learn much more about the Azure Marketplace on our Russian-language portal .
')
Consider how any Azure user can deploy a Django stack in minutes.
Find Django in the Azure Marketplace
This implies that you already have a Microsoft Azure account . If this is not the case, then use the free trial offer from this link .Go to the Microsoft Azure portal at http://portal.azure.com , you will open the Microsoft Azure cloud capacity control panel provided to you on request (Figure 1).

Figure 1 - Microsoft Azure Portal
Click on the "Create" button to add a new component to your account. In our case, we intend to add a virtual machine with a Django stack. Type Django in the search bar. You will receive a complete list of Django configurations available in the Azure Marketplace to choose from (Figure 2).

Fig . 2. - Django list in Azure Marketplace
Select Django Stack and in the new information window, click the "Create" button. Now you are going to directly create a virtual machine selected from the Azure Marketplace (Figure 3).

Fig.3. - Create a virtual machine
Creating a VM with Django
To create a virtual machine, in our case with Django on board, you need to specify a number of parameters. First enter the name of the virtual machine. Then the username (administrator) and password access. Choose an Azure subscription if you have several.
An important parameter that must be specified is a group of resources. In general, a resource group is simply a combination of different cloud resources — VM, storage, networks — under the same name to simplify administration. Therefore, at this stage just enter a name for the group.
The last parameter that you need to specify in the first step is the location of the virtual machine - essentially the choice of one of the Microsoft Azure data centers that are located around the world. The data center closest to Russia is Northern or Western Europe. Choose one of them (Figure 4).

Fig.4. - Parameters of the first step of creating a virtual machine
Click "OK" after entering all the parameters. In the second step, you will be prompted to choose the size of the virtual machine. By default, there will be several types of machines that are recommended for this type of solution. But you can always choose a different size by clicking on “View All” (Figure 5).

Fig.5. - Select the size of the virtual machine
I suggest that you choose the size “A1 Base” as suitable for testing. After selecting, press the “Select” button to go to the third step.
The third step is to fine-tune the deployment. Here, all parameters can be left as default and nothing changes at all. But if it is required that you can select SSD storage for a VM, configure virtual network, security, enable monitoring, create an availability group for VM fault-tolerant operation (Figure 6).

Fig.6. - VM deployment tweaks
Click "OK" after fine tuning in order to proceed to the final steps and launch the virtual machine.
You will receive an information window listing your settings (Figure 7).

Fig.7. - Information window with settings
Read the information and click "OK" in order to proceed to the acquisition of a virtual machine for your subscription.
For information. Acquisition in this case means the creation of a VM with free software on it. There are products in the Azure Marketplace that may require you to purchase a license for them.Read the acquisition information (Figure 8). In our case, the content of the virtual machine costs 0 rubles. The cost of the VM we choose, which Microsoft Azure provides, is about 3 p. at one o'clock.

Fig.8. - Acquisition of a virtual machine
Click the Acquire button to start the process of deploying your virtual machine with Django on board.
You will see the information message “Deployment started ...” (Figure 9).

Fig.9. - Deployment started
As soon as the VM is ready, you will receive another informational message, and the control panel of the created VM will open on the portal (Figure 10). In general, creating a virtual machine takes a few minutes.

Fig.10. - Virtual machine control panel
Congratulations! You deployed your machine with a ready-made Django stack.
Manage deployed virtual machine
In order to make sure that the virtual machine is up and running, we can go to its publicly accessible address first.
You can find the public address in the header of the administration panel. In my case, this is http://40.69.45.8/ . Turning to this address, we will see a standard greeting (Figure 11).

Pic.11 - Standard greeting from a Django- running machine in Azure
This virtual machine was prepared by Bitnami, a well-known assembler of ready-made environments. To see the Django application itself, you can click on “Access my application” (Figure 12).

Fig.12. - Running Django application
You may be interested in how to get the FQDN address for your car in the form of a domain name. By default, the VM address is not mapped, but it can be easily obtained. To do this, go to the VM settings (All settings) in the configuration panel. Then select the “Configuration” item and in the settings panel specify the name for your VM, which will be included in the FDQN path (Figure 13).
After saving the settings, you can click on the link, which will be presented as (my case) http://vyudjango.northeurope.cloudapp.azure.com/ .

Fig.13. - Adding FDQN path for virtual machine
You can now use the same address to access your virtual machine over SSH (Figure 14), for example:
SSH vyunev@vyudjango.northeurope.cloudapp.azure.com
where vyunev is the username (administrator) you specified when creating the VM.
Or simply using the address in your favorite tool (Figure 13).

Fig.14. - Connect to the virtual machine via SSH
Now you can configure your VM with Django as your heart desires!
Conclusion
We looked at a simple example of how using Azure and the Azure Marketplace platform, in a matter of minutes, you can deploy your Django environment and gain access to a ready-made working virtual machine.
Azure and Azure Marketplace offer to launch any solutions built on any technology, including for Linux and Windows. Here is just a brief list of what you can find: Red Hat Enterprise Linux, Oracle Linux, CentOS, CoreOS, Ubuntu, Suse, WordPress, Moodle, MEAN, Jboss, Redmine, SEO Panel, Parse, Git, GitLab, Django, ModX, Memcached, LAMP Stack, Jenkins, Node.js, SugarCRM, Ruby Stack, Ghost, Subversion, ActiveMQ, Nginx Stack, Solr, Tomcat, JRuby, OwnCloud, MySQL, Drupal, MongoDB, Piwik, Dolibarr, LAAP Stack, OpenProject, Plone, eXo, Mahara, Zurmo, RoundCube, Mautic, ThinkUp, Prestashop, Tracks, phpBB, eZ Publish, Joomla ...
Continue to use Azure and host your opensource solutions in the cloud. This will help you in this detailed section of documentation and resources on this link .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/281899/
All Articles