Oracle Database 12c Cloud World
The purpose of the technology forum Oracle Database 12c, which was held in Moscow on March 22, 2016, was to highlight the main innovations in the field of corporate data storage and management. We are especially interested in the first section of the forum devoted to cloud computing.

The Prabaker Gonglur, Senior Director of Development for Oracle Database 12c at Oracle, began a presentation on the best practices for hybrid cloud management that began with an important thought: a hybrid cloud is already a reality. What it is? This is a combination of private and public clouds, in which the cross-controlled use of data and applications between them is realized. Hybrid cloud is very convenient for development and testing, integration of B2B solutions, implementation of products demanding IT resources, trial operation of new services.
')
Of course, there is no single scenario for transition to a hybrid cloud. Some companies are looking for opportunities to optimize the costs of the physical IT infrastructure and virtualize local resources, transferring them to a private cloud. Others systematically transfer resources to the private cloud in order to gradually work out the workflows at the virtualization level, transfer them to the public cloud. Some companies simply transfer individual projects to the public cloud. For all such cases, the transition from capital investment to operating costs is also characteristic, which for economic reasons is now largely a requirement of time.
It’s easy to highlight typical examples of using hybrid cloud in enterprises. Organizations that develop and test applications on an industrial scale - no matter for their own needs or as a core activity - translate the development and testing infrastructure into a public cloud, which significantly accelerates the deployment of these systems and optimizes their management, while business-critical applications they continue to use locally. For a number of organizations — for example, those dependent on seasonal fluctuations in the market — the periodic transfer of load to the public cloud is a condition for the existence of a business, so it is important for them to ensure the dynamic distribution of the load on IT resources and a quick transition to the public cloud on demand. Another popular pattern is, for example, performing backup and business analytics applications in a public cloud, while transaction processing is performed locally.
Of course, placing IT resources in a hybrid cloud only makes sense if the company can fully own and manage these resources. A cloud is a cloud when the provision of services, their administration and payment are automated. Companies with a large, complex IT infrastructure understand this especially well, because it is impossible to manage such infrastructures without automation. The supplier of the respective platforms and technologies is obliged to ensure the unification of procedures for managing the private and public cloud; stable quality of service in the private and public cloud, as well as its compliance with the regulations; Transparency of public and private cloud management and user flows between them.
But in this case, the use of a hybrid cloud is not an end in itself. In order for this technology to attract enterprises, it must optimize resources — that is, the use of resources in the private and public cloud must be the most economical way of locating them, and mechanisms are required for accurately calculating the requirements for the private cloud infrastructure and platform services of the public cloud. A separate challenge is the ability to dynamically distribute the load between the private and public cloud.

Oracle implements and provides all cloud models to choose from. Starting with version 12cR5, Enterprise Manager is the unified management tool for local and cloud resources, it provides enterprises with not only a single view of local and cloud resources, but also the ability to transfer work to the Oracle Cloud and vice versa (Fig. 1).
Particularly impressive is that to ensure the quality of service, both for private and public clouds, Oracle uses the same “Find – Fix – Validate” methodology, i.e., find – correct – check, accurate and automatic (Fig. 2).

In each of the three steps of the methodology in both cases the same basic software is used:
A new report type, called Performance Hub, graphically displays a database performance report generated from the Automatic Workload Repository diagnostic repository (AWR report) data in a convenient and visual graphical form (Figure 3).

The new SQL Performance Analyzer feature, called SPA Quick Check, allows you to quickly assess the impact of planned system changes on SQL workload on a production system. It is designed for use on production systems, does not affect the work of end users, and creates minimal additional load.
Ensuring quality of service for private and public clouds is achieved by new features of Oracle Enterprise Manager 13c. Separately, we mention the Oracle Real Application Testing toolkit, which, in addition to testing infrastructure database changes, now also offers an integrated set of tools for integrated end-to-end database consolidation management Database Consolidation Workbench.
Transferring the load from a private cloud to a public one should be done without losing service quality, and the management tools provided by the supplier should ensure accurate capacity planning and the ability to make changes when moving to the cloud. Oracle Enterprise Manager automates the movement of databases to the cloud in the following ways:
Migrating a database to a private and public cloud typically involves significant infrastructure changes — hardware, storage, networks, database versions, etc. Oracle Real Application Testing helps you verify changes using real workload and plan resources to reduce SLA risks and prevent a decline in the quality of service.
Representing Oracle Enterprise Manager 13c in more detail, Sergey Tomin, lead consultant at the Oracle CIS technological consulting department, said that initially the three main goals in developing the previous version of Enterprise Manager 12c were: first, to give customers a complete solution for managing and monitoring corporate level (i.e., a solution that allows you to manage hundreds and thousands of objects), secondly, to make possible the integrated management of the entire application stack and deep diagnostics from the application level to the databases and disks with a transparent transition between levels; third, the most important thing is to create a commercial solution for managing private clouds, the entire cloud life cycle - planning, deployment, testing, accounting for resource consumption and billing.
With the successful implementation of these features, Oracle Enterprise Manager 12c has received well-deserved recognition from users. 7-Eleven, the largest retail chain of convenience stores, uses Enterprise Manager to quickly deploy its mobile application infrastructure. Walgreens, the largest network of pharmacies, uses Enterprise Manager to control configurations, to monitor compliance with regulatory requirements and automate the application of patches - they now spend twice as little on these operations. Societe General Bank uses the new Enterprise Manager feature, thin cloning, to create thin clones of test databases while saving 90% of time and disk space. In Allied Irish Banks, Replication Application Testing is used to test infrastructure changes to the database, which means that testing costs have been reduced by 25%.
Oracle Enterprise Manager is also used to manage the Oracle public cloud itself. For example, on the largest Cloud Public Oracle site, it manages 2.5 million monitoring units, controlling more than 25 thousand service instances, and processes 3.4 million events every day, performs 2 million tasks, and 11 million test transactions.
Enterprise Manager 13c provides a single interface for managing both public and private clouds. Enterprise Manager allows you to easily transfer database loads from the data center to the public Oracle cloud and back.
By providing access to software and infrastructure on demand in self-service mode with the ability to scale and account for resource consumption, Enterprise Manager provides the following benefits.
Oracle Enterprise Manager 13c offers a single window for managing hardware and software (for the first time in the industry), a single view for private and public clouds, and simple diagnostics with the ability to move to different levels of the application stack.
In addition, the solution automates the patching of all components of the Oracle Engineered Systems hardware and software systems, and the compliance management toolkit supports the STIG standard and offers a single compliance management window for local and cloud components that allows you to configure and verify compliance rules in real time.
Among the new features of Oracle Enterprise Manager 13c is configuration drift, i.e., tracking changes in dynamic configurations of any scale — the source for comparison can be either a “live” object or a saved basic configuration.
Continuous (“always on”) monitoring allows you to receive notifications of critical events by e-mail, even during planned downtimes of the managing server of the Enterprise Manager.
A large number of Enterprise Manager agents made it easier to deploy and update using “golden images”.
The ability to manage middleware is extremely important for corporate customers. Oracle Enterprise Manager supports multi-WebLogic 12.2, has built-in WebLogic Admin Console capabilities (Change Center, WLST script recording, JDBC Data Source management, domain, cluster, server configuration, auditing capabilities) and enhanced diagnostic functionality — Java Workload Explorer for in-depth JVM diagnostics and Middleware Diagnostics Advisor for detecting known problems, including memory leaks, stuck threads, JDBC / JMS problems, etc.
Oracle customers appreciate the new solution. For example, Naoto Kashiwagi (Naoto Kashiwagi), head of the middleware and cloud technology team at NEC Japan, and Yoki Moriyama, deputy general director of the company, say: “The Enterprise Manager is a powerful tool for managing our large systems that serve big deals . We use Enterprise Manager to manage hundreds of objects that are so important that we cannot afford to miss a single warning, and we must efficiently maintain these systems without errors. ”
Boris Pischyk, lead consultant at the Oracle CIS Technology Consulting Department, spoke about the Oracle cloud platform for IT monitoring - the Oracle Management Cloud.
The Oracle Management Cloud solution is designed for IT operations and development services, it is based on the idea of periodic, real-time, collecting various diagnostic information in real time, transferring it to the public Oracle cloud, consolidating, storing and providing a convenient user web to it. interface. Key solution features:
The three main Oracle Management Cloud services — Application Performance Monitoring, Logs Analytics, and IT Analytics — are now available in the public Oracle cloud.
Application Performance Monitoring provides diagnostics at various levels: from the end-user level to infrastructure logs. The service constantly monitors applications to identify problems, timely warns about problems that may affect users, and offers convenient means of finding the root causes of problems. The functionality offers a unified interface for IT operations and developers and provides proactive monitoring of end-user experience, which is achieved by continuously monitoring the performance of web pages and AJAX, regular surveying of query performance and the ability to compare user problems with bottlenecks in infrastructure performance.
Log Analytics is a new cloud service designed to consolidate log files from various sources. Log Analytics provides real-time monitoring, aggregation, indexing, analysis, search and correlation of all log data from applications and infrastructure components (local and cloud). Machine logs are used for log analysis to recognize and group records based on common patterns and quickly find root causes of problems.
IT Analytics toolkit allows you to determine the patterns of functioning of the current IT landscape, identify problem areas and effectively plan capacity. Its main tasks are: analyzing resources (identifying uneven load, analyzing resource consumption in different cuts and over different periods) and planning their growth, analyzing performance using embedded analytics to identify bottlenecks, resource-intensive SQL queries, etc. , visualization of the performance picture by types of resources and key indicators.
The result of the implementation of the Oracle Management Cloud is the improvement in the quality of maintenance and operation. Also, the customer should not invest in the support and administration of these services, with the advent of the Oracle Management Cloud, it is no longer his responsibility.
The report by Dmitry Yermoshina, lead consultant at the Oracle CIS technology consulting department, focused on how the use of private and hybrid Oracle clouds allows solving such important tasks of IT services as:
Oracle invests a lot of resources in the development of cloud automation. If we look at the diagram of cloud solutions offered by the main global suppliers (Fig. 4), it turns out that only Oracle provides a complete stack of cloud solutions, including HWaaS - equipment as a service.

Oracle's approach is based on the concept of a hybrid cloud - the union of private and public clouds, which implements a cross-controlled use of data and applications between them. Hybrid cloud is very convenient for development and testing, integration of B2B solutions, implementation of demanding IT resources of products, trial operation of new products.

Oracle implements and provides all cloud models to choose from - public, private and hybrid cloud (Fig. 5). On the one hand, products are offered on the basis of which you can deploy Oracle-systems in the data center, turning them into a private cloud. On the other hand, there are Oracle data centers around the world that provide public cloud services. Oracle Enterprise Manager product allows you to connect both approaches, connect one cloud with another and manage them using a single interface.
The most popular Oracle cloud services now, both in the world and in Russia, are platform services - a database as a service and an application server as a service.
The two main ways of providing the “database as a service” service, that is, Oracle PaaS (DBaaS), are as follows: clients work with either Oracle VM virtual machines or Exadata servers. If clients are running traditional virtual machines, there are several pre-configured sizes of virtual machines for them, which are characterized by a certain number of processors and memory capacity. The Exadata server-based solution is designed for clients with very large database size and performance requirements. In addition, it enables the use of Exadata cells for high loads.
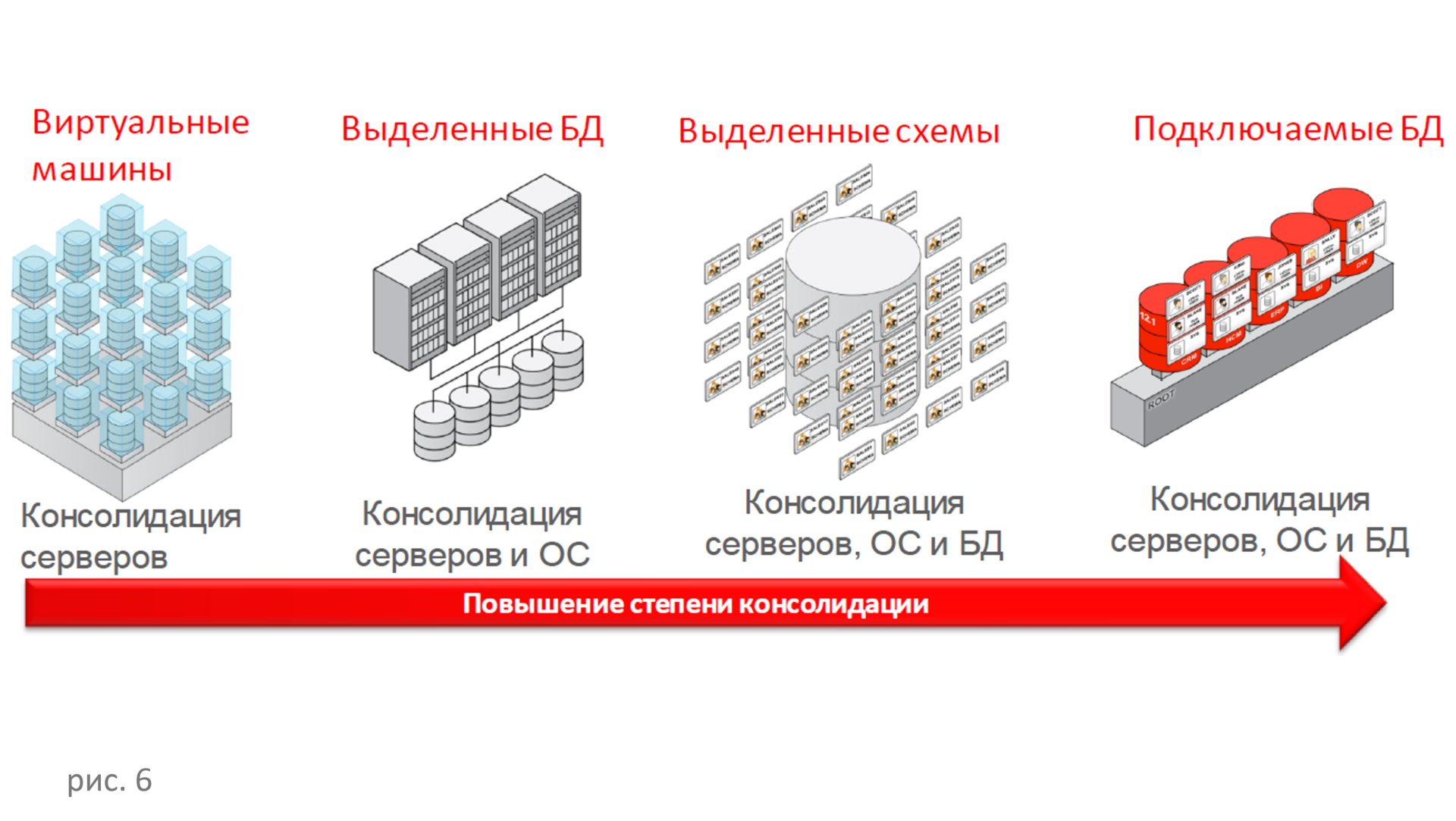
On-demand database is ordered from the self-service portal in the required version, configuration, and with the required degree of consolidation (Fig. 6). To create an Oracle cloud, only Enterprise Manager is required. New equipment, new settings, new approach to the access control system or to workstations is not required. Enterprise Manager configures DBaaS database pools, WebLogic pools, or virtualization pools. Then you can use the private Oracle cloud to connect to external systems.
Rapid deployment of databases is possible thanks to a convenient self-service portal and template directory that stores a set of deployment procedures as service templates and offers different template options for different DBMS versions, configurations, etc. Database Provisioning procedure allows you to capture database configurations and save deployment procedures for future use.
The new Snap Clone database cloning procedure uses advanced storage capabilities and can be implemented both in hardware and software. And if on an average database cloning takes an average of one and a half weeks, then a solution that performs automated cloning allows you to get databases of several terabytes in an hour.
To manage the hybrid cloud Enterprise Manager versions 12c R5 and 13c contains a Hybrid Agent that needs to be installed in the cloud service. After installation, the Hybrid Agent will begin to interact with the Enterprise Manager, passing information about the cloud system.
The cited reports are far from exhausting the entire theme of the next Oracle Database 12c technology forum. We want to end this review with a reminder that Prabaker Gonglur made in his report - that many IT departments are already building a combined infrastructure using both private and public clouds, and now they understand that they have to manage resources - where whatever they are. Therefore, they are trying to build their own private clouds in accordance with similar architectural and operational requirements — or trust those cloud providers that meet the requirements for scalability, performance, monitoring, security, and regulations. The positive experience of companies that have become customers of Oracle Cloud suggests that they have chosen the right supplier.

Hybrid cloud is here
The Prabaker Gonglur, Senior Director of Development for Oracle Database 12c at Oracle, began a presentation on the best practices for hybrid cloud management that began with an important thought: a hybrid cloud is already a reality. What it is? This is a combination of private and public clouds, in which the cross-controlled use of data and applications between them is realized. Hybrid cloud is very convenient for development and testing, integration of B2B solutions, implementation of products demanding IT resources, trial operation of new services.
')
Of course, there is no single scenario for transition to a hybrid cloud. Some companies are looking for opportunities to optimize the costs of the physical IT infrastructure and virtualize local resources, transferring them to a private cloud. Others systematically transfer resources to the private cloud in order to gradually work out the workflows at the virtualization level, transfer them to the public cloud. Some companies simply transfer individual projects to the public cloud. For all such cases, the transition from capital investment to operating costs is also characteristic, which for economic reasons is now largely a requirement of time.
It’s easy to highlight typical examples of using hybrid cloud in enterprises. Organizations that develop and test applications on an industrial scale - no matter for their own needs or as a core activity - translate the development and testing infrastructure into a public cloud, which significantly accelerates the deployment of these systems and optimizes their management, while business-critical applications they continue to use locally. For a number of organizations — for example, those dependent on seasonal fluctuations in the market — the periodic transfer of load to the public cloud is a condition for the existence of a business, so it is important for them to ensure the dynamic distribution of the load on IT resources and a quick transition to the public cloud on demand. Another popular pattern is, for example, performing backup and business analytics applications in a public cloud, while transaction processing is performed locally.
Of course, placing IT resources in a hybrid cloud only makes sense if the company can fully own and manage these resources. A cloud is a cloud when the provision of services, their administration and payment are automated. Companies with a large, complex IT infrastructure understand this especially well, because it is impossible to manage such infrastructures without automation. The supplier of the respective platforms and technologies is obliged to ensure the unification of procedures for managing the private and public cloud; stable quality of service in the private and public cloud, as well as its compliance with the regulations; Transparency of public and private cloud management and user flows between them.
But in this case, the use of a hybrid cloud is not an end in itself. In order for this technology to attract enterprises, it must optimize resources — that is, the use of resources in the private and public cloud must be the most economical way of locating them, and mechanisms are required for accurately calculating the requirements for the private cloud infrastructure and platform services of the public cloud. A separate challenge is the ability to dynamically distribute the load between the private and public cloud.

Oracle implements and provides all cloud models to choose from. Starting with version 12cR5, Enterprise Manager is the unified management tool for local and cloud resources, it provides enterprises with not only a single view of local and cloud resources, but also the ability to transfer work to the Oracle Cloud and vice versa (Fig. 1).
Particularly impressive is that to ensure the quality of service, both for private and public clouds, Oracle uses the same “Find – Fix – Validate” methodology, i.e., find – correct – check, accurate and automatic (Fig. 2).

In each of the three steps of the methodology in both cases the same basic software is used:
- Find (“find”): built-in self-diagnostic module - Automatic Database Diagnostics Monitor (ADDM): Oracle Diagnostics Pack;
- Fix: automatic tuning of the application - Oracle Tuning Pack;
- Validate (“check”): scheduled application configuration - Oracle Real Application Testing SPA.
A new report type, called Performance Hub, graphically displays a database performance report generated from the Automatic Workload Repository diagnostic repository (AWR report) data in a convenient and visual graphical form (Figure 3).

The new SQL Performance Analyzer feature, called SPA Quick Check, allows you to quickly assess the impact of planned system changes on SQL workload on a production system. It is designed for use on production systems, does not affect the work of end users, and creates minimal additional load.
Ensuring quality of service for private and public clouds is achieved by new features of Oracle Enterprise Manager 13c. Separately, we mention the Oracle Real Application Testing toolkit, which, in addition to testing infrastructure database changes, now also offers an integrated set of tools for integrated end-to-end database consolidation management Database Consolidation Workbench.
Transferring the load from a private cloud to a public one should be done without losing service quality, and the management tools provided by the supplier should ensure accurate capacity planning and the ability to make changes when moving to the cloud. Oracle Enterprise Manager automates the movement of databases to the cloud in the following ways:
- cloning plug-in databases into Oracle Cloud for Oracle Database 12c;
- cloning or migrating plug-in databases from Oracle Cloud to local container databases;
- cloning for development and testing scenarios using data masking.
Migrating a database to a private and public cloud typically involves significant infrastructure changes — hardware, storage, networks, database versions, etc. Oracle Real Application Testing helps you verify changes using real workload and plan resources to reduce SLA risks and prevent a decline in the quality of service.
New features in Oracle Enterprise Manager 13c
Representing Oracle Enterprise Manager 13c in more detail, Sergey Tomin, lead consultant at the Oracle CIS technological consulting department, said that initially the three main goals in developing the previous version of Enterprise Manager 12c were: first, to give customers a complete solution for managing and monitoring corporate level (i.e., a solution that allows you to manage hundreds and thousands of objects), secondly, to make possible the integrated management of the entire application stack and deep diagnostics from the application level to the databases and disks with a transparent transition between levels; third, the most important thing is to create a commercial solution for managing private clouds, the entire cloud life cycle - planning, deployment, testing, accounting for resource consumption and billing.
With the successful implementation of these features, Oracle Enterprise Manager 12c has received well-deserved recognition from users. 7-Eleven, the largest retail chain of convenience stores, uses Enterprise Manager to quickly deploy its mobile application infrastructure. Walgreens, the largest network of pharmacies, uses Enterprise Manager to control configurations, to monitor compliance with regulatory requirements and automate the application of patches - they now spend twice as little on these operations. Societe General Bank uses the new Enterprise Manager feature, thin cloning, to create thin clones of test databases while saving 90% of time and disk space. In Allied Irish Banks, Replication Application Testing is used to test infrastructure changes to the database, which means that testing costs have been reduced by 25%.
Oracle Enterprise Manager is also used to manage the Oracle public cloud itself. For example, on the largest Cloud Public Oracle site, it manages 2.5 million monitoring units, controlling more than 25 thousand service instances, and processes 3.4 million events every day, performs 2 million tasks, and 11 million test transactions.
Enterprise Manager 13c provides a single interface for managing both public and private clouds. Enterprise Manager allows you to easily transfer database loads from the data center to the public Oracle cloud and back.
By providing access to software and infrastructure on demand in self-service mode with the ability to scale and account for resource consumption, Enterprise Manager provides the following benefits.
- Improving the quality of service. IT organizations are striving not only to reduce costs, but also to find solutions that improve productivity, availability and security. Cloud customers get the natural benefits of high-availability tools built into the cloud.
- Resource flexibility The ability to increase and decrease the database processing power makes applications flexible and easily adaptable to changing workloads.
- Accelerated database provision. Databases in the cloud can be provided very quickly. This reduces overall deployment time for production applications and development platforms and speeds the creation of test configurations.
- The ability to quantify the use of database resources in the cloud for budgeting, planning and allocation of administrative resources, depending on the use of resources.
Oracle Enterprise Manager 13c offers a single window for managing hardware and software (for the first time in the industry), a single view for private and public clouds, and simple diagnostics with the ability to move to different levels of the application stack.
In addition, the solution automates the patching of all components of the Oracle Engineered Systems hardware and software systems, and the compliance management toolkit supports the STIG standard and offers a single compliance management window for local and cloud components that allows you to configure and verify compliance rules in real time.
Among the new features of Oracle Enterprise Manager 13c is configuration drift, i.e., tracking changes in dynamic configurations of any scale — the source for comparison can be either a “live” object or a saved basic configuration.
Continuous (“always on”) monitoring allows you to receive notifications of critical events by e-mail, even during planned downtimes of the managing server of the Enterprise Manager.
A large number of Enterprise Manager agents made it easier to deploy and update using “golden images”.
The ability to manage middleware is extremely important for corporate customers. Oracle Enterprise Manager supports multi-WebLogic 12.2, has built-in WebLogic Admin Console capabilities (Change Center, WLST script recording, JDBC Data Source management, domain, cluster, server configuration, auditing capabilities) and enhanced diagnostic functionality — Java Workload Explorer for in-depth JVM diagnostics and Middleware Diagnostics Advisor for detecting known problems, including memory leaks, stuck threads, JDBC / JMS problems, etc.
Oracle customers appreciate the new solution. For example, Naoto Kashiwagi (Naoto Kashiwagi), head of the middleware and cloud technology team at NEC Japan, and Yoki Moriyama, deputy general director of the company, say: “The Enterprise Manager is a powerful tool for managing our large systems that serve big deals . We use Enterprise Manager to manage hundreds of objects that are so important that we cannot afford to miss a single warning, and we must efficiently maintain these systems without errors. ”
New Oracle Cloud Services for IT Management
Boris Pischyk, lead consultant at the Oracle CIS Technology Consulting Department, spoke about the Oracle cloud platform for IT monitoring - the Oracle Management Cloud.
The Oracle Management Cloud solution is designed for IT operations and development services, it is based on the idea of periodic, real-time, collecting various diagnostic information in real time, transferring it to the public Oracle cloud, consolidating, storing and providing a convenient user web to it. interface. Key solution features:
- Monitoring at the level of end users of web applications and infrastructure components both local and cloud.
- Support capacity planning and resources.
- Wide coverage for analyzing metrics and events.
- Collection of journals, search, aggregation, understanding of the topology.
- Automated detection of anomalies.
- Convenient user interface, control panels.
The three main Oracle Management Cloud services — Application Performance Monitoring, Logs Analytics, and IT Analytics — are now available in the public Oracle cloud.
Application Performance Monitoring provides diagnostics at various levels: from the end-user level to infrastructure logs. The service constantly monitors applications to identify problems, timely warns about problems that may affect users, and offers convenient means of finding the root causes of problems. The functionality offers a unified interface for IT operations and developers and provides proactive monitoring of end-user experience, which is achieved by continuously monitoring the performance of web pages and AJAX, regular surveying of query performance and the ability to compare user problems with bottlenecks in infrastructure performance.
Log Analytics is a new cloud service designed to consolidate log files from various sources. Log Analytics provides real-time monitoring, aggregation, indexing, analysis, search and correlation of all log data from applications and infrastructure components (local and cloud). Machine logs are used for log analysis to recognize and group records based on common patterns and quickly find root causes of problems.
IT Analytics toolkit allows you to determine the patterns of functioning of the current IT landscape, identify problem areas and effectively plan capacity. Its main tasks are: analyzing resources (identifying uneven load, analyzing resource consumption in different cuts and over different periods) and planning their growth, analyzing performance using embedded analytics to identify bottlenecks, resource-intensive SQL queries, etc. , visualization of the performance picture by types of resources and key indicators.
The result of the implementation of the Oracle Management Cloud is the improvement in the quality of maintenance and operation. Also, the customer should not invest in the support and administration of these services, with the advent of the Oracle Management Cloud, it is no longer his responsibility.
Oracle hybrid cloud in detail
The report by Dmitry Yermoshina, lead consultant at the Oracle CIS technology consulting department, focused on how the use of private and hybrid Oracle clouds allows solving such important tasks of IT services as:
- Quickly deploy new databases.
- Cloning large databases.
- Reducing the routine load, automate and accelerate cloud databases.
- Standardization.
- Consolidation.
- Detailed accounting of the use of computing resources.
- More efficient use of computing resources (including disks).
- Improving the reliability of existing databases.
- Building a flexible, easily scalable IT infrastructure.
Oracle invests a lot of resources in the development of cloud automation. If we look at the diagram of cloud solutions offered by the main global suppliers (Fig. 4), it turns out that only Oracle provides a complete stack of cloud solutions, including HWaaS - equipment as a service.

Oracle's approach is based on the concept of a hybrid cloud - the union of private and public clouds, which implements a cross-controlled use of data and applications between them. Hybrid cloud is very convenient for development and testing, integration of B2B solutions, implementation of demanding IT resources of products, trial operation of new products.

Oracle implements and provides all cloud models to choose from - public, private and hybrid cloud (Fig. 5). On the one hand, products are offered on the basis of which you can deploy Oracle-systems in the data center, turning them into a private cloud. On the other hand, there are Oracle data centers around the world that provide public cloud services. Oracle Enterprise Manager product allows you to connect both approaches, connect one cloud with another and manage them using a single interface.
The most popular Oracle cloud services now, both in the world and in Russia, are platform services - a database as a service and an application server as a service.
The two main ways of providing the “database as a service” service, that is, Oracle PaaS (DBaaS), are as follows: clients work with either Oracle VM virtual machines or Exadata servers. If clients are running traditional virtual machines, there are several pre-configured sizes of virtual machines for them, which are characterized by a certain number of processors and memory capacity. The Exadata server-based solution is designed for clients with very large database size and performance requirements. In addition, it enables the use of Exadata cells for high loads.
On-demand database is ordered from the self-service portal in the required version, configuration, and with the required degree of consolidation (Fig. 6). To create an Oracle cloud, only Enterprise Manager is required. New equipment, new settings, new approach to the access control system or to workstations is not required. Enterprise Manager configures DBaaS database pools, WebLogic pools, or virtualization pools. Then you can use the private Oracle cloud to connect to external systems.

Rapid deployment of databases is possible thanks to a convenient self-service portal and template directory that stores a set of deployment procedures as service templates and offers different template options for different DBMS versions, configurations, etc. Database Provisioning procedure allows you to capture database configurations and save deployment procedures for future use.
The new Snap Clone database cloning procedure uses advanced storage capabilities and can be implemented both in hardware and software. And if on an average database cloning takes an average of one and a half weeks, then a solution that performs automated cloning allows you to get databases of several terabytes in an hour.
To manage the hybrid cloud Enterprise Manager versions 12c R5 and 13c contains a Hybrid Agent that needs to be installed in the cloud service. After installation, the Hybrid Agent will begin to interact with the Enterprise Manager, passing information about the cloud system.
The cited reports are far from exhausting the entire theme of the next Oracle Database 12c technology forum. We want to end this review with a reminder that Prabaker Gonglur made in his report - that many IT departments are already building a combined infrastructure using both private and public clouds, and now they understand that they have to manage resources - where whatever they are. Therefore, they are trying to build their own private clouds in accordance with similar architectural and operational requirements — or trust those cloud providers that meet the requirements for scalability, performance, monitoring, security, and regulations. The positive experience of companies that have become customers of Oracle Cloud suggests that they have chosen the right supplier.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/281198/
All Articles