OpenStack implementation and where to go next?
Considering the difference in design approaches in traditional systems and cloud platforms of OpenStack , we can move on to the difference in approaches to building applications and reliable and highly accessible infrastructure. OpenStack was created in order to ensure the mass launch of hundreds, thousands and even tens of thousands of virtual servers of the same type (usually) for hosting applications with their own resiliency tools. The platform itself does not offer high availability of a single virtual server.

Many users of traditional systems often take this as a disadvantage and immaturity of the OpenStack platform. However, this statement is based on a misunderstanding of various design principles of legacy applications and cloud computing.
')
If we compare the running instances of virtual servers with animals, then the traditional platforms provide the “pet” principle of operation, and OpenStack - the “herd” approach (sometimes the term “pig farm” occurs).
Every pet is unique: it has a name, habits and character. Vasya's cat at the neighbor and your Murka are two completely different cats. If your cat is sick - you take him to the vet, you treat him, take care of his condition, you feed him and care for him.
On the contrary, all the animals in the herd look the same to you. You feed them at the same time, vaccinate them all at once. If the animal dies, it is bad, but still another can grow in the herd, which will perform the required function. Comparison of approaches to the virtual infrastructure is shown in the image below:

Only by understanding this unusual difference in the concept and approaches offered by the developers and ideologists of the cloud platform OpenStack, you can proceed to the questions of its practical application.
Before embarking on the introduction of a new technology (including OpenStack), it is necessary to determine the economic feasibility of this action. For example, deploying OpenStack to host one or two dozen virtual servers is most likely impractical. Understanding the need to reduce the cost of infrastructure pushes many customers to implement OpenStack for all types of workload, which is wrong and sometimes leads to negative consequences. It is necessary to accurately and correctly assess all the risks, and above all the expected type of load for which the platform is being implemented. There are options for building an inexpensive virtualization platform based on other open source technologies. The favorable conditions for using the OpenStack platform from the point of view of ICL Services are:
All these conditions arise from the specifics of using OpenStack and, above all, the lack of support for the high availability of a single virtual server.
Some commercial OpenStack distributions offer support for high availability virtual servers. Of course, the range of use of such distributions is somewhat wider than described here.
Based on the conditions of use, we can offer the following scenarios for the effective application of solutions based on OpenStack:
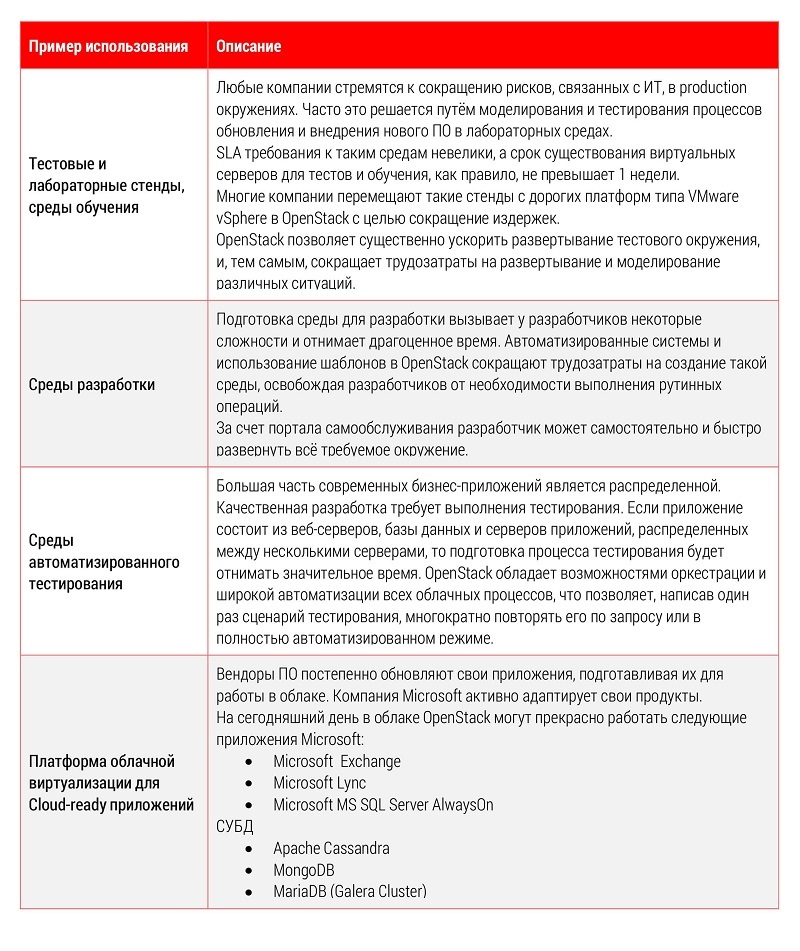
* Of course, other scenarios for the use of this product are possible.
ICL Services has extensive experience in designing and implementing solutions of any complexity based on Linux and Open Source technologies for foreign and Russian customers. The company has developed and implemented a cloud solution for corporate clients - ICL Cloud , which is actively used for internal needs, as well as for the provision of proprietary cloud services.

Many companies ask themselves the question: “Which distribution of OpenStack should be used to build a private cloud?”. The answer to this question stems from the tasks that will be solved by this platform, as well as the imposed requirements for reliability and SLA.
There are free and commercial builds of the OpenStack platform.
OpenStack free assemblies ( Community OpenStack , RDO OpenStack ) may well be used to study this technology, build working models, and also test functionality to determine the suitability of a product for certain tasks.
Free versions of OpenStack are attractive primarily because they are free (no license fees).
It is on the basis of the free versions of OpenStack that many Russian (including large companies) now prefer to build their own cloud environments for testing and developing software. They are easily reproducible and, if lost, can be recreated without significant damage to the business. But the use of free versions of OpenStack in the Enterprise sector is very difficult due to the high risks and the lack of support by the vendor.

The growing demand for cloud solutions and the reluctance to lose market share lead to the fact that leading software manufacturers create their own builds of OpenStack. Some manufacturers develop certain features of OpenStack, which is their competitive advantage.
A short list of products is available below:

Free versions of OpenStack, as well as many commercial distributions offer support for VMware vSphere. This allows you to combine all the reliability and functionality of VMware solutions with the flexibility of OpenStack cloud technologies. In addition, VMware offers VMware Integrated OpenStack, already optimized for integration with vSphere virtualization products.
Limitations:
Many companies are implementing or are going to implement OpenStack on their own. It should be noted that the introduction and quality support of OpenStack requires the presence of highly qualified specialists with a fairly wide range of competencies. This is more pronounced when using free / free versions. Commercial distributions simplify the task due to the availability of automatic deployment tools, updates, etc.
In addition, OpenStack interacts with a large number of infrastructure resources, which requires knowledge in different areas.
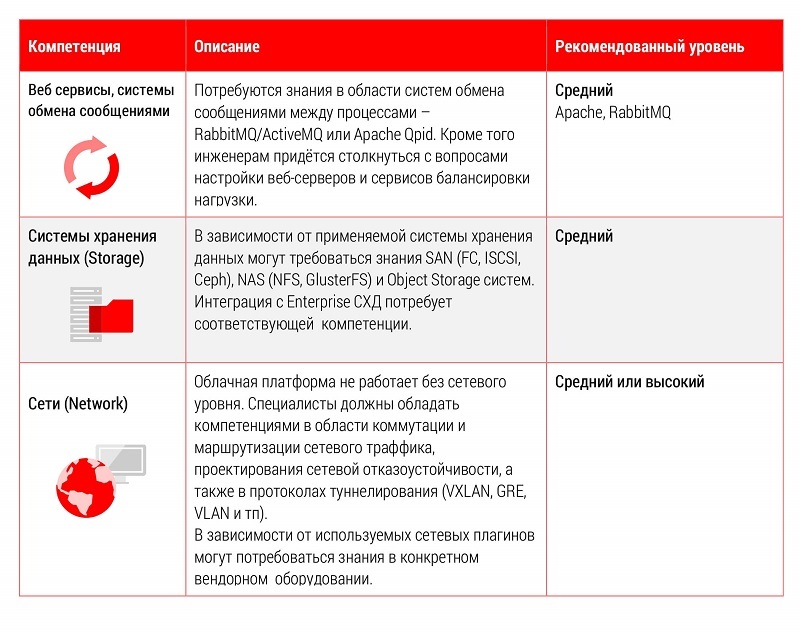
Key competencies for implementation and support specialists:

Some test installations of OpenStack can be implemented by medium and large companies on their own in the presence of highly qualified Linux specialists. Our practice shows that this kind of implementation often scares potential OpenStack users due to incorrect expectations, lack of expertise, and
poorly executed deployment. Companies spend a lot of resources and often give up half way, starting to consider alternatives.
Industrial implementations, as a rule, require the involvement of expert companies specializing in cloud solutions , given the large number of risks and issues that require focusing attention, as well as the complexity of interconnects and attention to detail. The involvement of experts can significantly reduce implementation time and reduce risks.
The platform has a rich functionality and covers most of the tasks. In addition, many OpenStack extensions are available that solve various tasks. But, sooner or later, the needs of many clients go beyond the capabilities of the underlying OpenStack platform. The open source code and modular architecture of OpenStack allows you to extend the functionality of the solution by developing new or modifying existing modules of the platform.
Having two or more different virtualization platforms can be inconvenient. In cases where a unified tool is required to manage various infrastructure providers (VMware, OpenStack, Amazon, Hyper-V), it may be necessary to implement a hybrid cloud management platform that will provide users with unified access through a single console, and the application will run certain virtual servers in the required platform.
Among the platforms available on the market are:

Examples of heterogeneous cloud management platforms:
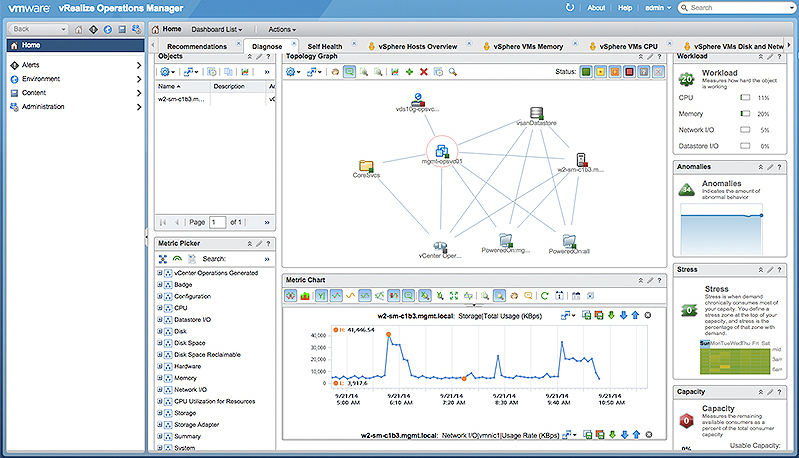
Vmware vRealize
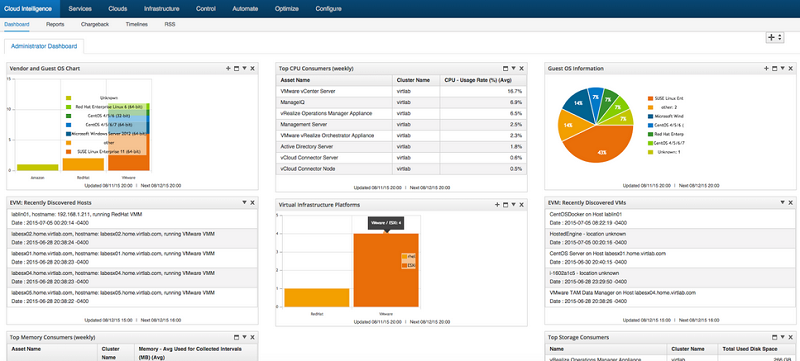
ManageIQ / Red Hat CloudForms

Ericsson Cloud Manager
By artemii

Many users of traditional systems often take this as a disadvantage and immaturity of the OpenStack platform. However, this statement is based on a misunderstanding of various design principles of legacy applications and cloud computing.
')
Part 2.
What is the difference between cloud and traditional infrastructure approaches?
If we compare the running instances of virtual servers with animals, then the traditional platforms provide the “pet” principle of operation, and OpenStack - the “herd” approach (sometimes the term “pig farm” occurs).
Every pet is unique: it has a name, habits and character. Vasya's cat at the neighbor and your Murka are two completely different cats. If your cat is sick - you take him to the vet, you treat him, take care of his condition, you feed him and care for him.
On the contrary, all the animals in the herd look the same to you. You feed them at the same time, vaccinate them all at once. If the animal dies, it is bad, but still another can grow in the herd, which will perform the required function. Comparison of approaches to the virtual infrastructure is shown in the image below:

Only by understanding this unusual difference in the concept and approaches offered by the developers and ideologists of the cloud platform OpenStack, you can proceed to the questions of its practical application.
When should you think about implementing OpenStack?
Before embarking on the introduction of a new technology (including OpenStack), it is necessary to determine the economic feasibility of this action. For example, deploying OpenStack to host one or two dozen virtual servers is most likely impractical. Understanding the need to reduce the cost of infrastructure pushes many customers to implement OpenStack for all types of workload, which is wrong and sometimes leads to negative consequences. It is necessary to accurately and correctly assess all the risks, and above all the expected type of load for which the platform is being implemented. There are options for building an inexpensive virtualization platform based on other open source technologies. The favorable conditions for using the OpenStack platform from the point of view of ICL Services are:
- hosting servers and applications with a short lifespan (hours, days, weeks);
- cloud load type of applications used;
- hosting non-critical virtual servers and applications;
- frequent deployment of similar servers .
All these conditions arise from the specifics of using OpenStack and, above all, the lack of support for the high availability of a single virtual server.
Some commercial OpenStack distributions offer support for high availability virtual servers. Of course, the range of use of such distributions is somewhat wider than described here.
Based on the conditions of use, we can offer the following scenarios for the effective application of solutions based on OpenStack:

* Of course, other scenarios for the use of this product are possible.
ICL Services has extensive experience in designing and implementing solutions of any complexity based on Linux and Open Source technologies for foreign and Russian customers. The company has developed and implemented a cloud solution for corporate clients - ICL Cloud , which is actively used for internal needs, as well as for the provision of proprietary cloud services.

Which OpenStack distribution kit to choose?
Many companies ask themselves the question: “Which distribution of OpenStack should be used to build a private cloud?”. The answer to this question stems from the tasks that will be solved by this platform, as well as the imposed requirements for reliability and SLA.
There are free and commercial builds of the OpenStack platform.
OpenStack free assemblies ( Community OpenStack , RDO OpenStack ) may well be used to study this technology, build working models, and also test functionality to determine the suitability of a product for certain tasks.
Free versions of OpenStack are attractive primarily because they are free (no license fees).
It is on the basis of the free versions of OpenStack that many Russian (including large companies) now prefer to build their own cloud environments for testing and developing software. They are easily reproducible and, if lost, can be recreated without significant damage to the business. But the use of free versions of OpenStack in the Enterprise sector is very difficult due to the high risks and the lack of support by the vendor.

The growing demand for cloud solutions and the reluctance to lose market share lead to the fact that leading software manufacturers create their own builds of OpenStack. Some manufacturers develop certain features of OpenStack, which is their competitive advantage.
A short list of products is available below:

Can I use OpenStack to manage resources in VMware vSphere?
Free versions of OpenStack, as well as many commercial distributions offer support for VMware vSphere. This allows you to combine all the reliability and functionality of VMware solutions with the flexibility of OpenStack cloud technologies. In addition, VMware offers VMware Integrated OpenStack, already optimized for integration with vSphere virtualization products.
Limitations:
- Integration is supported only with VMware vSphere
- VMware NSX-MH licenses required
What competencies are needed to implement and support OpenStack?
Many companies are implementing or are going to implement OpenStack on their own. It should be noted that the introduction and quality support of OpenStack requires the presence of highly qualified specialists with a fairly wide range of competencies. This is more pronounced when using free / free versions. Commercial distributions simplify the task due to the availability of automatic deployment tools, updates, etc.
In addition, OpenStack interacts with a large number of infrastructure resources, which requires knowledge in different areas.
Key competencies for implementation and support specialists:


Need OpenStack. What's next?
Some test installations of OpenStack can be implemented by medium and large companies on their own in the presence of highly qualified Linux specialists. Our practice shows that this kind of implementation often scares potential OpenStack users due to incorrect expectations, lack of expertise, and
poorly executed deployment. Companies spend a lot of resources and often give up half way, starting to consider alternatives.
Industrial implementations, as a rule, require the involvement of expert companies specializing in cloud solutions , given the large number of risks and issues that require focusing attention, as well as the complexity of interconnects and attention to detail. The involvement of experts can significantly reduce implementation time and reduce risks.
The platform has a rich functionality and covers most of the tasks. In addition, many OpenStack extensions are available that solve various tasks. But, sooner or later, the needs of many clients go beyond the capabilities of the underlying OpenStack platform. The open source code and modular architecture of OpenStack allows you to extend the functionality of the solution by developing new or modifying existing modules of the platform.
I already have VMware vSphere and OpenStack. Where to go next?
Having two or more different virtualization platforms can be inconvenient. In cases where a unified tool is required to manage various infrastructure providers (VMware, OpenStack, Amazon, Hyper-V), it may be necessary to implement a hybrid cloud management platform that will provide users with unified access through a single console, and the application will run certain virtual servers in the required platform.
Among the platforms available on the market are:

Examples of heterogeneous cloud management platforms:

Vmware vRealize

ManageIQ / Red Hat CloudForms

Ericsson Cloud Manager
By artemii
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/281068/
All Articles