How big operators make big money on big data?

There is never a big deal without big difficulties.
Voltaire
')
In Russia, competition in the telecom services market is very high, and with a high degree of population coverage, their prices are among the lowest in the world.
In the face of declining revenues from traditional services (voice communications, SMS, MMS) and stiffer competition from OTT, most large telecom operators are considering the possibility of using Big Data technology for data analysis. Operators collect information on service consumption transactions, subscriber behavior, data characterizing network health and performance parameters, etc. However, as a rule, these data are collected by different departments in different formats, while there are a number of organizational barriers that prevent free exchange of information between business units. In addition, there is no mechanism for merging, cleaning and deduplication, without which these data can not be analyzed.
The more telecom operators try to expand their services beyond the simple provision of a “pipe”, the more they think about the possibility of relying on the accumulated information and making the analysis of big data a competitive advantage.
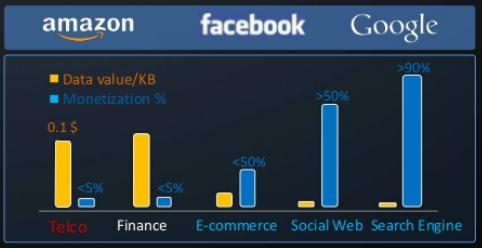
Fig. 1. The cost of data accumulated in companies and the degree of their monetization
It should be noted that the value of the data that a telecom company possesses is quite high - as can be seen from Figure 1, it is only slightly inferior to the cost of these financial organizations. However, both of these businesses in most cases have not yet found effective mechanisms for their monetization. In contrast, in e-commerce, in social web applications and search engines, the unit cost of data is lower, but their degree of monetization is significantly higher. In particular, the owners of high-end systems have long learned how to extract huge amounts of money from data stored on the web, linking ads to the search queries of millions of users.
In 2015, as part of his presentation, Ron Raffensperger (Ron Raffensperger), Huawei's CTO Data Center solutions, citing McKinsey & Company research, cited such interesting data: over the past three years, more than 150 Big Data projects in the telecom industry 70 % did not reach the planned performance parameters. According to Ron, the reason for this is the concentration on the technological side of the project with insufficient linkage to the business and the lack of knowledge among developers of the features of the business model of the telecom operator.
Surveys of telecom companies also indicate that, collecting large amounts of data related to customer activity, and the huge transaction logs of network elements, telecom companies are far from fully using the value that is contained in these data. Thus, the study of the company Heavy Reading (Fig. 2.) showed that the problems of the impossibility of integrated analysis of all information sources available to telecom operators and the lack of efficiency in analyzing these data are the main barriers that companies face in developing operational analytics systems.
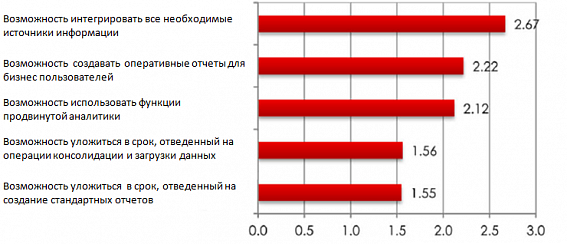
Fig. 2. Answers of respondents from the number of telecom operators: 3 - the most important, 0 - the least important (source: Heavy Reading)
Indeed, in telecom companies the level of IT development is lower than in Internet companies, the number of IT specialists is less, and big data professionals may not be in the state at all. Therefore, telecom companies need not only an external supplier of Big Data technology, but also a consultant who understands their business, their IT infrastructure, and the specifics of building Big Data systems for the telecom industry. When planning a project for implementing a Big Data solution, it is important to consider a business scheme for generating revenue from data analysis (Fig. 3).
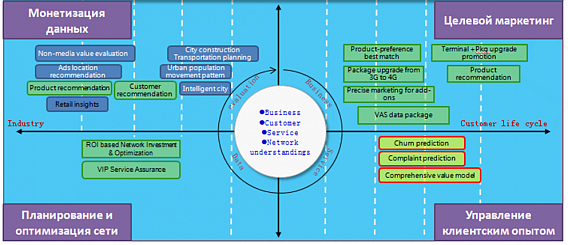
Figure 3. Possible schemes for generating revenue from analyzing big data
As follows from fig. 3, the implementation of the Big Data project in the telecom business has a whole range of return on investment schemes both by optimizing its own business processes and by providing information to third parties. Each scheme has its own solutions based on Big Data technologies that the operator can use.
The above schemes in fig. 3 are presented in four segments: network planning and optimization, data monetization, targeted marketing and customer experience management. Consider this data in more detail.
Customer Experience Management
One of the most important tasks of the operator is the prediction of churn prediction and its management. The operator who has implemented the Big Data system has the ability to significantly increase subscriber loyalty. In Russia, mobile subscribers use a prepaid communication service, are not bound by a long-term contract with an operator and can change it while maintaining their phone number. Analysis of the behavior of subscribers (for example, the similarity of the profile of previously disconnected subscribers) allows you to identify risk groups. Potential candidates for switching to another operator can be offered advantageous tariff plans or other options.
Another challenge is predicting complaints (Compliant prediction). It is known that the analysis of the tonality of millions of messages in social networks (dissatisfaction with the service, reports of breakdowns, etc.) makes it possible to determine negatively tuned subscribers, and in social networks it is possible to identify so-called opinion leaders, whose decision about leaving could trigger a similar step. other users. The ability to influence the opinion of opinion leaders allows you to influence the attitude to the company's services.
On the other hand, complaints, evidence of service deficiencies are a valuable information resource, an important source of information for their identification and elimination.
Targeted marketing
Product performance best match - product optimization for the client. The task is to provide customers with products and tariffs that best suit their needs and at the same time allow you to optimize the operator's income. For example, the subscriber, having a phone with 4G capabilities, is subscribed to the 3G tariff, that is, some of the possibilities do not use. If the operator monitors such users and offers them a new tariff, they begin to more fully utilize the capabilities of the phone, for example, connect to video services, get modern services, and the operator increases revenue by increasing ARPU.
Special cases of the considered service are offers of tariffs optimized for different population groups: Terminal + Pkg upgrade promotion (offer of terminal device and tariff upgrade), Package upgrade from 3G to 4G (upgrade from 3G to 4G), Product recommendation (product recommendations).
There is also a Precise marketing for add-ons item (target marketing for offering additional services) - this is about the possibility of offering additional advertising based on the analysis of the subscriber profile. For example, if a client of a cellular operator lives in the broadband coverage area and is not a subscriber of this service, it makes sense to advertise it, targeting exactly the category of persons who may be interested in such advertising.
Another item - VAS data service - additional data services.
Network planning and optimization
In this section, as an example, two schemes are mentioned that do not exhaust the set.
ROI based network Investment - investing in network development with regard to ROI. If we are talking about the mobile operator's network, then it is important to optimize this process: for example, to solve issues such as designing an efficient connection of new base stations using data from geolocation and quality of service. Big-Data-solution allows you to determine how best to plan the location of base stations.
VIP services assurance - guaranteeing service availability for VIP clients. Any operator has customers for whom it is important to provide service in the first place. A large operator has a fairly large category of users, and it becomes necessary to keep statistics and control not only for customers in general, but taking into account the importance of certain groups. Big Data technology allows you to optimize this task.
Data monetization
In this segment we consider the following points. Non media value evaluation (evaluation of sources other than media) and the Adds location recommendation (recommendations for advertising). Here we can talk about optimizing the placement of outdoor advertising on the basis of analyzing the behavior of the operator’s subscribers, for example, taking into account their place of residence, work or route.
The point of the Urban population movement pattern is close in meaning (extracting information about the patterns of movement of citizens). Such data can be used in various industries, for example, information on flows of citizens - for planning transportation routes (City Transport) or city construction: here monetization can be based on selling recommendations on the optimal location of retail outlets, taking into account the range corresponding to consumer flows.
Another topic is related to the above-mentioned topic - Retail insights (recommendations for improving consumer marketing), which implies the possibility of improving the range of products to better meet demand based on predicting user behavior. To the same group can be attributed such a global topic as Intelligent city (intellectual city), which affects a number of management problems of large urban centers.
Product recommendation - recommendations for product improvement. Here we can talk about the offer of additional products (mobile applications, video ringtones, ringtones, etc.).
As already noted, telecom operators are at the beginning of the journey to introduce big data technology and need a partner who has not only a technological solution, but also experience in the telecom industry. For example, Huawei has competencies in ICT, big data, as well as knowledge of the problem areas of telecom operators.
Fusioninsight
Huawei's Big Data solution uses a multi-layered architecture, the core of which is the FusionInsight platform, which includes two layers: a data processing level (data platform) and a data service level (Fig. 4).
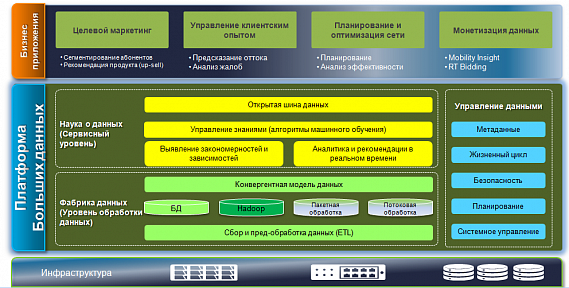
Fig. 4. Big Data Architecture - Huawei Solutions
The data processing layer is responsible for collecting, converting, storing, converging and processing data in real time. Service level - for analyzing data, identifying patterns in them, including forecasting user behavior in real time. The business application tier covers targeted marketing applications, customer experience management tools, network planning and optimization, and data monetization tools.
Huawei has a wide network of R & D centers around the world. In particular, big data is being developed in China, EU countries, India, Canada, and the USA. The Russian RND-center is engaged in Big-Data-problems and machine learning algorithms, including in cooperation with academic institutions of the Russian Academy of Sciences. The company has an exhaustive range of products for building solutions of any complexity for both medium operators and world leaders. In particular, it offers a full cycle of building a Big-Data-project, including services for developing a script and building a business model, and training in modeling.
Huawei experts are ready to provide a complete turnkey solution, a separate big data platform or analytical tools. The company has its own expertise in collecting and analyzing data specific to the telecom industry, due to the fact that it itself is a manufacturer of telecom equipment and has access to undocumented information. For example, the Big-data-solution developed for the Indonesian operator PLDT, has reduced the cost of hardware by 50% and by 30% speed up the execution of ETL-operations. And in China Unicom Shanghai, a large Big-Data project was implemented with a successful business model of monetization. As part of the project in Telefonica Vivo (Brazil), an Huawei analytical tool was installed on the existing Big-Data-platform, which allowed the operator to solve the above-mentioned analytical tasks, including working with subscribers and analyzing the quality of services.
The company is constantly expanding the capabilities of its platform for building Big-Data solutions. So, the updated version of FusionInsight-Universe presented by her at the World Mobile Congress' 2016 in Barcelona includes a service solution (BDaaS), which allows telecom companies to quickly implement access to big data, take advantage of the use of Big Data technologies and significantly increase business competitiveness .
Author: Alexander Prokhorov
Source: www.it-weekly.ru/market/telecom/82053.html
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/280980/
All Articles