The benefits of the OpenStack cloud concept and its difference from traditional architecture
Today IT costs are an essential part of budgets, and, as a result, companies of any size are interested in reducing them. It is expected that IT will bring more benefits at lower cost. At the same time, with the development of all modern companies are faced with the issue of increasing the need for IT resources. In this situation, you should pay attention to cloud technologies, which provide an opportunity to modernize approaches to managing your IT infrastructure through the use of the latest technologies, a high level of standardization, flexibility of implemented solutions and ease of scaling. OpenStack is one of the most common solutions for the organization of cloud environments such as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS).

Many software developers have expressed interest in OpenStack technologies because of the open API and source code, flexible architecture, and a large commercial ecosystem that offer a new paradigm of software development and deployment.
')
OpenStack is a software package that implements the functions of a cloud platform. It allows you to manage pools of various resources by type IaaS.

OpenStack implements the concept of a software-defined data center, which provides simple and unified access to various computing resources, data networks, storage systems, as well as additional services, such as:
Access to the resources provided by the platform is possible "by click" through the self-service portal. Platform users can create virtual networks, routers, disk devices with just a few clicks, and the OpenStack platform will independently implement these changes at a low level, providing integration with various network equipment and data storage systems. After configuring networks, users can create virtual servers from predefined images of virtual servers. Most user operations are intuitive and do not require specific knowledge of the low-level technologies used.
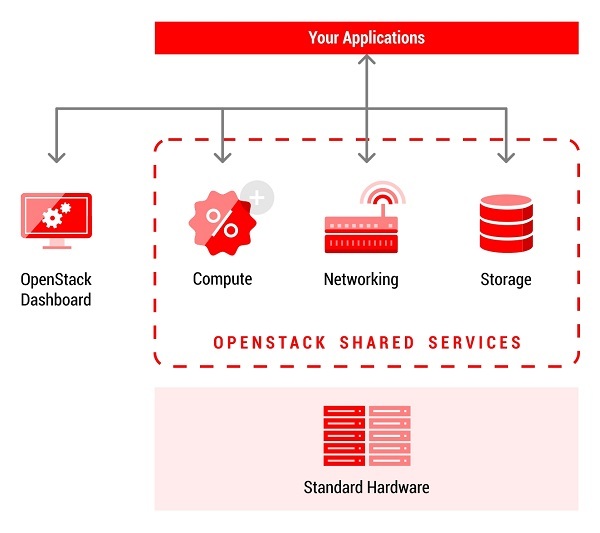
OpenStack interacts with the underlying infrastructure through open or vendor-provided drivers, which helps save customers from the trap of a particular technology, vendor, or tool.
OpenStack provides additional services, such as identity management, orchestration, and accounting for consumed resources in the same software basis through the API. OpenStack also offers the foundation for evolution to DevOps, continuous integration, and continuous deployment methodologies.
OpenStack is not a hypervisor, but it supports multiple hypervisors through a layer of abstraction. Including popular hypervisors (commercial and open source). Among them: KVM, Xen, QEMU, Hyper-V, available with VMware vSphere (ESXi in its pure form is not supported).
OpenStack reduces the time to deploy and launch on the market of certain applications.

Large community
A huge ecosystem has formed around OpenStack, in which a large number of developers from more than 500 of the world's leading IT industry companies take part. There are a large number of vendor-specific modules for OpenStack that solve certain tasks. The product is actively developing, which causes great interest among many companies.

In order to understand the difference between traditional infrastructure and OpenStack cloud technologies, it is necessary to determine the difference in their design philosophy.
First, let's look at infrastructures that are built on traditional virtualization technologies, such as the VMware vSphere platform (or analogs, for example, Red Hat Enterprise Virtualization, Hyper-V). These technologies offer to consolidate servers of almost any size, but are still more focused on hosting a small number (compared to the cloud) of fairly large VMs.
The solution works well because most application servers tend to have monolithic architectures, such as Oracle or Microsoft Exchange. Today, each instance of this type is still enclosed in a single virtual machine and grows by expanding on a single physical server running under the control of the hypervisor.
To ensure the reliability of these legacy applications, traditional systems propose running application servers on VMs in so-called clusters / domains, etc., using infrastructure resiliency enhancement functions (for example, VMware High Availability vSphere and VMware vSphere vMotion). These solutions can work under certain conditions, such as the presence of a shared storage system, high network bandwidth, which imposes difficulties associated with the subsequent scaling. As a rule, all classic virtualization platforms provide well-proven means of ensuring high availability of virtual servers, which increases the availability of the application at the infrastructure level, without requiring changes on the application side.
Picture - High Availability Implementation in VMware vSphere using vMotion and HA
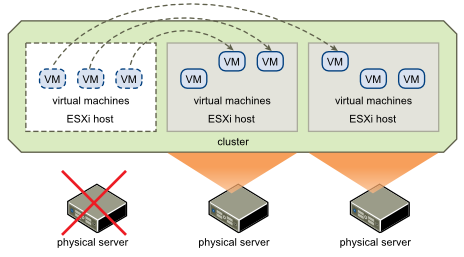

Cloud platforms, such as OpenStack, are designed for use with another class of applications, such as Apache Cassandra, MongoDB, and Hadoop, which are designed for scale-out and resilient to virtual machines. Resources can be extended by adding new instances of applications on virtual servers of the same type with subsequent load balancing. These distributed applications independently provide their own fault tolerance at the application level, regardless of the underlying infrastructure and advanced functions of the hypervisors.
High availability of the application can be provided in the OpenStack infrastructure. In next-generation infrastructures, failure handling is done at the application level to reduce hardware costs. In contrast, the provision of high availability at the infrastructure layer may require excessive computational resources, storage capacity and network bandwidth, and third-party software developers from the user.
Moving the fault tolerance of applications up the stack, cloud platforms make it possible to abandon the use of specialized equipment (expensive storage systems, specialized servers, etc.). Standardized and, as a rule, cheaper equipment is considered as an option for launching a cloud platform and creates an architecture that provides rapid infrastructure scaling.
Figure - example of the implementation of high availability of data in the object store OpenStack Swift
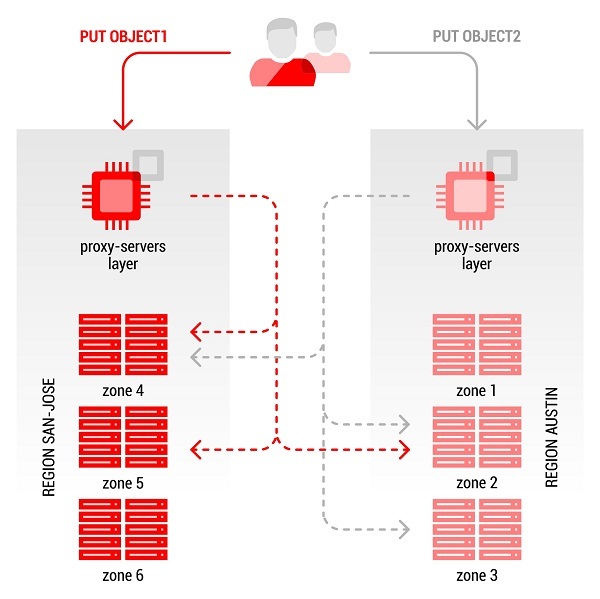
This architecture is best suited for next-generation highly scalable applications where failure is expected and compensated for by a large number of application instances.
A brief comparison of the OpenStack cloud and traditional virtualization architecture approaches is as follows:

The following material will tell you when to think about the implementation of OpenStack, about paid and free distributions, and can you use Openstack to manage resources in Vmware vsphere?
Posted by: artemii

Many software developers have expressed interest in OpenStack technologies because of the open API and source code, flexible architecture, and a large commercial ecosystem that offer a new paradigm of software development and deployment.
')
Part 1.
What is OpenStack?
OpenStack is a software package that implements the functions of a cloud platform. It allows you to manage pools of various resources by type IaaS.

OpenStack implements the concept of a software-defined data center, which provides simple and unified access to various computing resources, data networks, storage systems, as well as additional services, such as:
- load balancers (Load Balancer as a Service),
- Perimeter Protection (Firewall as a Service, Security Groups),
- Amazon S3 compatible object storage.
Access to the resources provided by the platform is possible "by click" through the self-service portal. Platform users can create virtual networks, routers, disk devices with just a few clicks, and the OpenStack platform will independently implement these changes at a low level, providing integration with various network equipment and data storage systems. After configuring networks, users can create virtual servers from predefined images of virtual servers. Most user operations are intuitive and do not require specific knowledge of the low-level technologies used.

OpenStack interacts with the underlying infrastructure through open or vendor-provided drivers, which helps save customers from the trap of a particular technology, vendor, or tool.
OpenStack provides additional services, such as identity management, orchestration, and accounting for consumed resources in the same software basis through the API. OpenStack also offers the foundation for evolution to DevOps, continuous integration, and continuous deployment methodologies.
OpenStack is not a hypervisor, but it supports multiple hypervisors through a layer of abstraction. Including popular hypervisors (commercial and open source). Among them: KVM, Xen, QEMU, Hyper-V, available with VMware vSphere (ESXi in its pure form is not supported).
What are the advantages of OpenStack?
OpenStack reduces the time to deploy and launch on the market of certain applications.

Large community
A huge ecosystem has formed around OpenStack, in which a large number of developers from more than 500 of the world's leading IT industry companies take part. There are a large number of vendor-specific modules for OpenStack that solve certain tasks. The product is actively developing, which causes great interest among many companies.

What is the difference between the OpenStack cloud concept and traditional architecture?
In order to understand the difference between traditional infrastructure and OpenStack cloud technologies, it is necessary to determine the difference in their design philosophy.
First, let's look at infrastructures that are built on traditional virtualization technologies, such as the VMware vSphere platform (or analogs, for example, Red Hat Enterprise Virtualization, Hyper-V). These technologies offer to consolidate servers of almost any size, but are still more focused on hosting a small number (compared to the cloud) of fairly large VMs.
The solution works well because most application servers tend to have monolithic architectures, such as Oracle or Microsoft Exchange. Today, each instance of this type is still enclosed in a single virtual machine and grows by expanding on a single physical server running under the control of the hypervisor.
To ensure the reliability of these legacy applications, traditional systems propose running application servers on VMs in so-called clusters / domains, etc., using infrastructure resiliency enhancement functions (for example, VMware High Availability vSphere and VMware vSphere vMotion). These solutions can work under certain conditions, such as the presence of a shared storage system, high network bandwidth, which imposes difficulties associated with the subsequent scaling. As a rule, all classic virtualization platforms provide well-proven means of ensuring high availability of virtual servers, which increases the availability of the application at the infrastructure level, without requiring changes on the application side.
Picture - High Availability Implementation in VMware vSphere using vMotion and HA


Cloud platforms, such as OpenStack, are designed for use with another class of applications, such as Apache Cassandra, MongoDB, and Hadoop, which are designed for scale-out and resilient to virtual machines. Resources can be extended by adding new instances of applications on virtual servers of the same type with subsequent load balancing. These distributed applications independently provide their own fault tolerance at the application level, regardless of the underlying infrastructure and advanced functions of the hypervisors.
High availability of the application can be provided in the OpenStack infrastructure. In next-generation infrastructures, failure handling is done at the application level to reduce hardware costs. In contrast, the provision of high availability at the infrastructure layer may require excessive computational resources, storage capacity and network bandwidth, and third-party software developers from the user.
Moving the fault tolerance of applications up the stack, cloud platforms make it possible to abandon the use of specialized equipment (expensive storage systems, specialized servers, etc.). Standardized and, as a rule, cheaper equipment is considered as an option for launching a cloud platform and creates an architecture that provides rapid infrastructure scaling.
Figure - example of the implementation of high availability of data in the object store OpenStack Swift

This architecture is best suited for next-generation highly scalable applications where failure is expected and compensated for by a large number of application instances.
A brief comparison of the OpenStack cloud and traditional virtualization architecture approaches is as follows:

The following material will tell you when to think about the implementation of OpenStack, about paid and free distributions, and can you use Openstack to manage resources in Vmware vsphere?
Posted by: artemii
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/280428/
All Articles