Efficient data structures for PHP 7
PHP has only one data structure to manage everything.
The latest PHP release has caused a lot of excitement in the community. We could not wait to start using new features and feel the taste of ~ 2x performance gains . One of the reasons why this happened is that the structure of the
')
Introduction :
Github : https://github.com/php-ds
Namespace:
Interfaces:
Classes:
Two pointers used to track the head and tail. The presence of pointers allows you to change the end and beginning of the buffer without having to move other elements to free up space. This makes
Accessing the value by index requires the calculation of the corresponding position in the buffer:
The following benchmark shows the total elapsed time and memory used for
The following benchmark shows the time taken to
The graph shows that
But
In the vector, the index of a value is a direct mapping of its index in the buffer, so all we need to do is move each value in the range [1, size - 1] to the right by one position. This is done with just one
The next test shows how much memory is used for 2ⁿ
The interesting thing is that the
Stack - is a collection organized according to the principle “last arrived - first exited” or “LIFO” (last in - first out) , allowing access only to the value at the top of the structure. You can think of it as a dynamic-capacity gun shop .
A queue is a data type with a paradigm of access to the elements “first come, first come out” (“FIFO”, “First In - First Out”) . This collection allows you to access items in the order they are added. Its name speaks for itself, imagine the structure as a line of people standing in line at the cashier in the store.
The priority queue is very similar to the simple queue. Items are placed in the queue with the specified priority and the value with the highest priority will always be in front. Direct queue search with priority is very destructive, it will be a sequential call to
The priority queue implementation uses max-heap .
The principle of “first come, first come out” is preserved for values with the same priority, so that a group of values with equal priority can be considered as a normal queue.
And what about performance? The next benchmark shows the time and memory required for
This is probably the most significant of all benchmarks.
But how? How can such a big difference
If you look at the source code of
Since the array has a minimum capacity of 8, then
An interface that allows objects to be used as keys . This is an alternative to
All structures will return
Data structures that work with the
As in the
The next benchmark shows that the performance and efficiency of memory between the
The next benchmark shows the time spent adding 2ⁿ new instances of
A common way to create an array with unique values is
Now about 2600 tests . It is possible that some tests are redundant, but I would prefer to indirectly check the same thing twice than not to check at all.
At the time of this writing, there is still no complete documentation, but it will appear along with the first stable release.
However, there are some well-documented stub files .
All benchmarks were run on the standard
Why are
I do not believe that there is a need for any alternative implementation. 3 interfaces and 7 classes - this is a good balance between pragmatism and specialization.
When should I use
If you know for sure that you will not use
The
SPL structures are a good example of how inheritance can be misused. For example,
The Java collection framework also has several interesting cases where inheritance creates ambiguity.
The old
In fact, this is a fair observation, but I still think that composition is more suitable for building data structures. They are designed to be self-contained, like an
Inheritance would also cause unnecessary complexity in the internal implementation.
Why do we also need the
It provides an alternative syntax:

The
In the linked list, we add or remove the reserved memory for the structure element (node) whenever a value is added or removed. A node contains two pointers (in the case of a doubly linked list) to refer to the previous and next nodes. Both structures,
Only when the collection is very small. The upper limit of the amount of memory for a
Linked nodes have poor spatial locality . This means that the physical location of the node in memory may be far from adjacent nodes. Thus, iterations over a coherent list jump through memory instead of using the processor cache.
Performance should not be your top priority . , , , , . , « » .
, , -:
, PHP7 - . — PHP5.
. API - . , .
: Twitter , Reddit , Room 11
: github.com/php-ds
: github.com/php-ds/benchmarks
array - complex, flexible, hybrid, combines the behavior of list and linked map . But we use it for everything, because PHP adheres to a pragmatic approach : to have an extremely correct, sensible and realistic way of solving a problem, coming from practical, not theoretical, reasoning. array allows you to do work, although there are so many about it in lectures on computer science. But, unfortunately, complexity comes with flexibility.The latest PHP release has caused a lot of excitement in the community. We could not wait to start using new features and feel the taste of ~ 2x performance gains . One of the reasons why this happened is that the structure of the
array been reworked . But arrays still adhere to the principle “optimized for everything; optimized for nothing, “not everything is perfect, there is room for improvement.What about SPL data structures?Unfortunately ... they are terrible. Previously, to PHP7, they offered some advantages, but now we have reached the point when using SPL has no practical meaning.
')
Why can't we just fix and improve them?Yes, we could, but I believe that their design and implementation are so poor that it would be better to find a more modern replacement.
"SPL data structures are horribly designed."
- Anthony Ferrara
Introduction :
php-ds is an extension for PHP7 that adds data structures. This post briefly covers the behavior, performance, and benefits of each. Also at the end you will find a list of answers to the expected questions.Github : https://github.com/php-ds
Namespace:
Ds\Interfaces:
Collection , Sequence , HashableClasses:
Vector , Deque , Stack , Queue , PriorityQueue , Map , SetCollection
Collection is a basic interface that covers the common functionality: foreach , echo , count , print_r , var_dump , serialize , json_encode , and clone .Sequence (Sequence)
Sequence describes the behavior of elements organized into a single, linear dimension. In some languages, such a structure is called a List . Like an array that uses incremental keys, with the exception of some features:- Values should always be indexed as
[0, 1, 2, …, size - 1] - Retrieving or appending updates the index of all consecutive values.
- Supports access to values only from the index
[0, size - 1]
Use cases
- Wherever you would like to use
arrayas a list (without keys) - More effective alternative to
SplDoublyLinkedListandSplFixedArray
Vector
Vector is a Sequence that combines values into a continuous buffer, increasing and decreasing automatically. This is the most efficient sequential data structure, since the element index is a direct reflection of its index in the buffer, and an increase in the vector will not affect the performance in any way.Strengths
- Very small memory consumption
- Very fast iterations
get,set,pushandpophaveO(1)complexity
disadvantages
insert,remove,shiftandunshifthave complexityO(n)
The number one structure in Photoshop was Vectors.
- Sean Parent , CppCon 2015
Deque (doubly connected queue)
Deque (pronounced “deck”) is a sequence of values combined into a continuous buffer that increases and decreases automatically. The name is a common abbreviation for double-ended queue . Used inside Ds\Queue .Two pointers used to track the head and tail. The presence of pointers allows you to change the end and beginning of the buffer without having to move other elements to free up space. This makes
shift and unshift so fast that even Vector cannot compete with that.Accessing the value by index requires the calculation of the corresponding position in the buffer:
((head + position) % capacity) .Strengths
- Very small memory consumption
get,set,push,pop,shiftandunshifthave complexityO(1)
disadvantages
insert,removehave complexityO(n)- Buffer capacity must be a power of two (
2ⁿ)
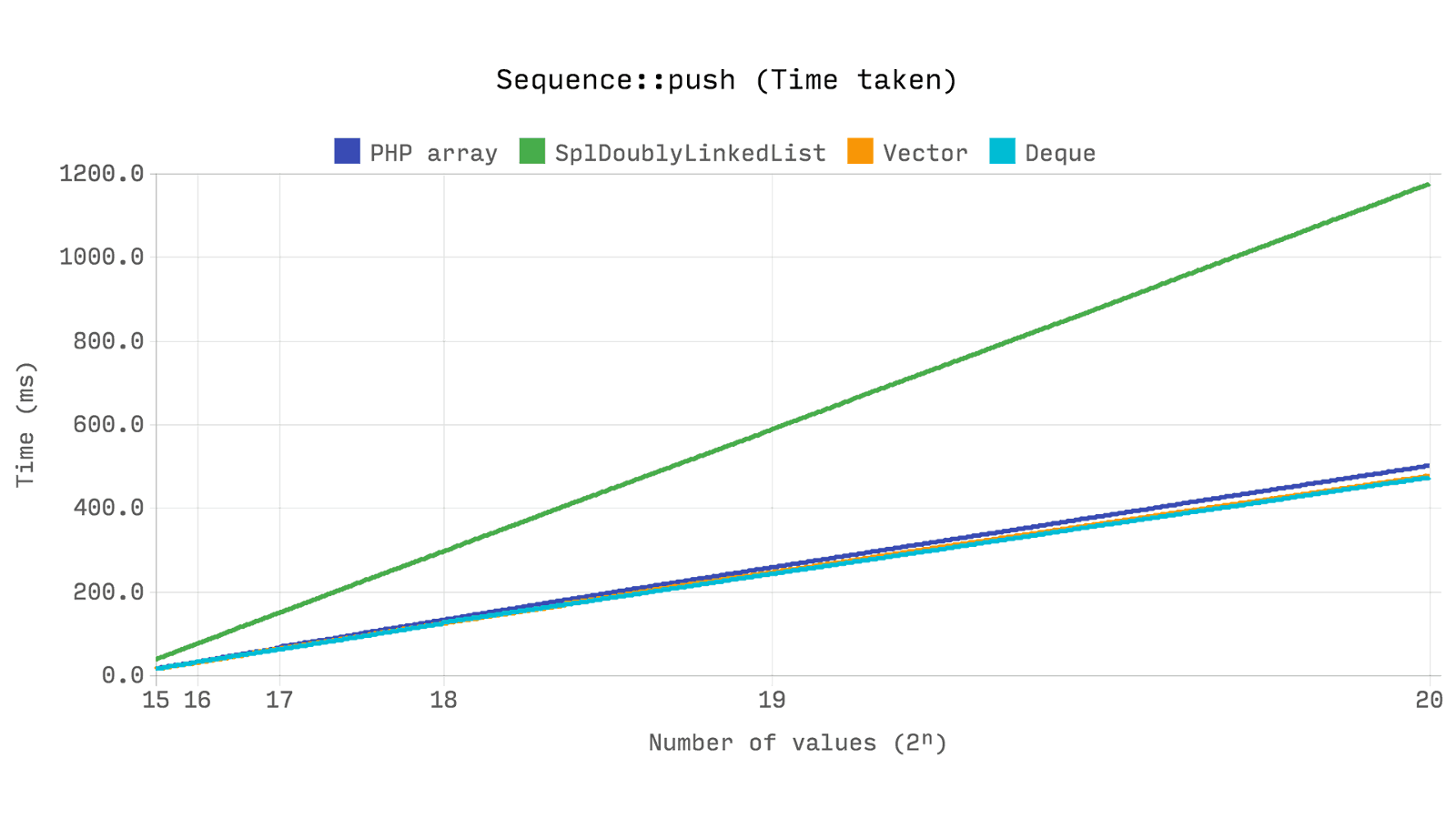
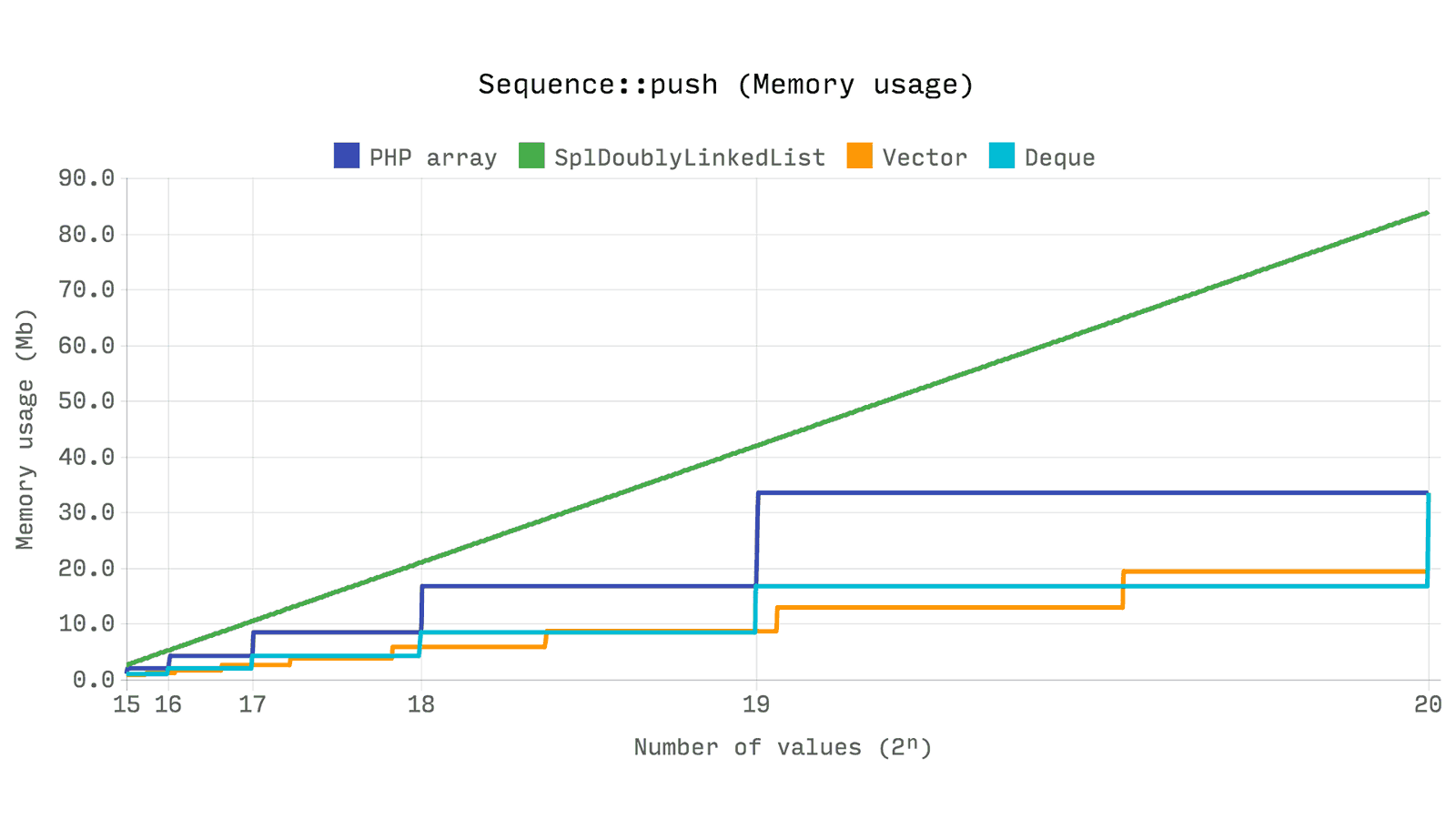
The following benchmark shows the total elapsed time and memory used for
push 2 push random numbers operation. array , Ds\Vector and Ds\Deque work quickly, but SplDoublyLinkedList consistently shows a result more than 2 times worse .SplDoublyLinkedList allocates memory for each value separately, which is why an expected increase in memory occurs. array and Ds\Deque in their implementation, allocate memory in portions to maintain sufficient volume for 2ⁿ elements. Ds\Vector has a growth factor of 1.5, which entails an increase in the number of memory allocations, but less consumption in general.

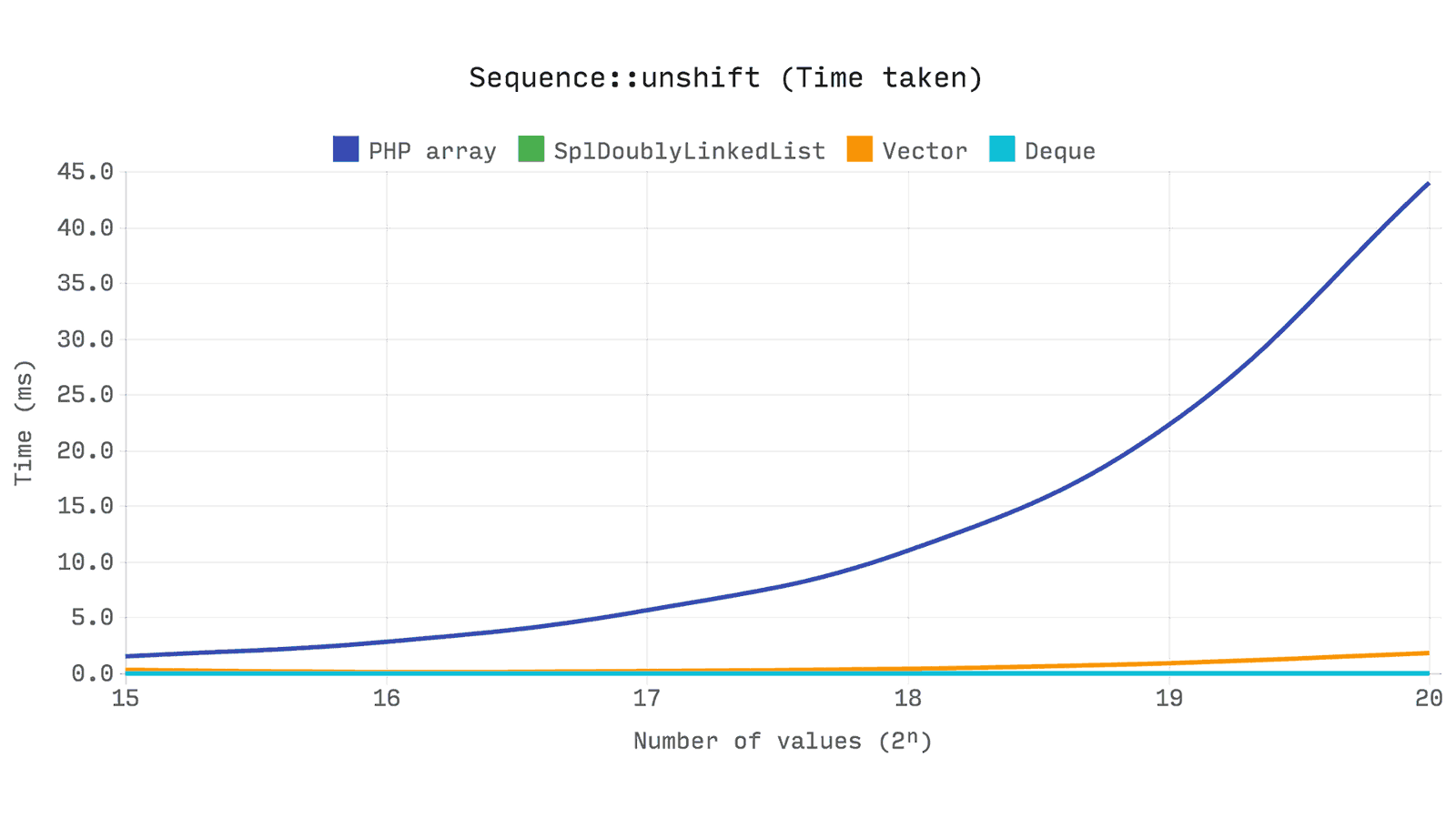
The following benchmark shows the time taken to
unshift single element in a sequence of 2 unshift values. The time required to set the values is not taken into account.The graph shows that
array_unshift has O(n) complexity: whenever the sample size doubles, the time required for unshift . This is due to the fact that each numerical index in the range [1, size - 1] must be updated.
But
Ds\Vector::unshift also O(n) , so why is it much faster? Note that array stores each value in a bucket along with its key and hash. Therefore, you have to check each item and update the hash if the index is numeric. In fact, array_unshift allocates a new array for this and replaces the old one when all values are copied.In the vector, the index of a value is a direct mapping of its index in the buffer, so all we need to do is move each value in the range [1, size - 1] to the right by one position. This is done with just one
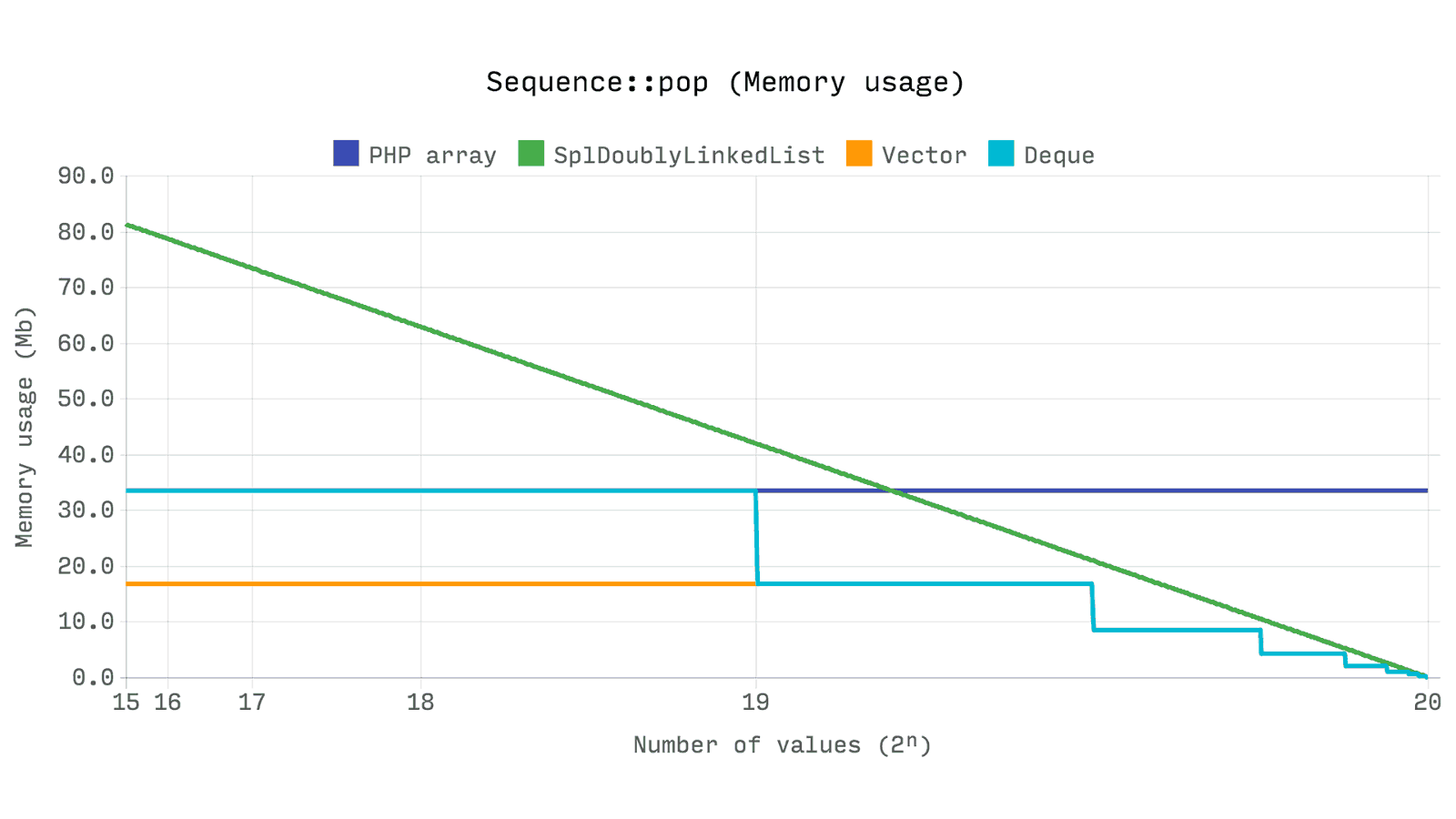
memmove operation.Ds\Deque and SplDoublyLinkedList in turn, are very fast, because the sample size does not affect the time for unshift , i.e. its complexity will be O(1) .The next test shows how much memory is used for 2ⁿ
pop operations. In other words when resizing from 2ⁿ to zeroThe interesting thing is that the
array always holds the allocated memory, even if its size is significantly reduced. Ds\Vector and Ds\Deque allow you to reduce the allocated resources by half if their size falls below a quarter of their current potential. SplDoublyLinkedList frees the memory after each deletion from the sample, so we can observe a linear decrease.
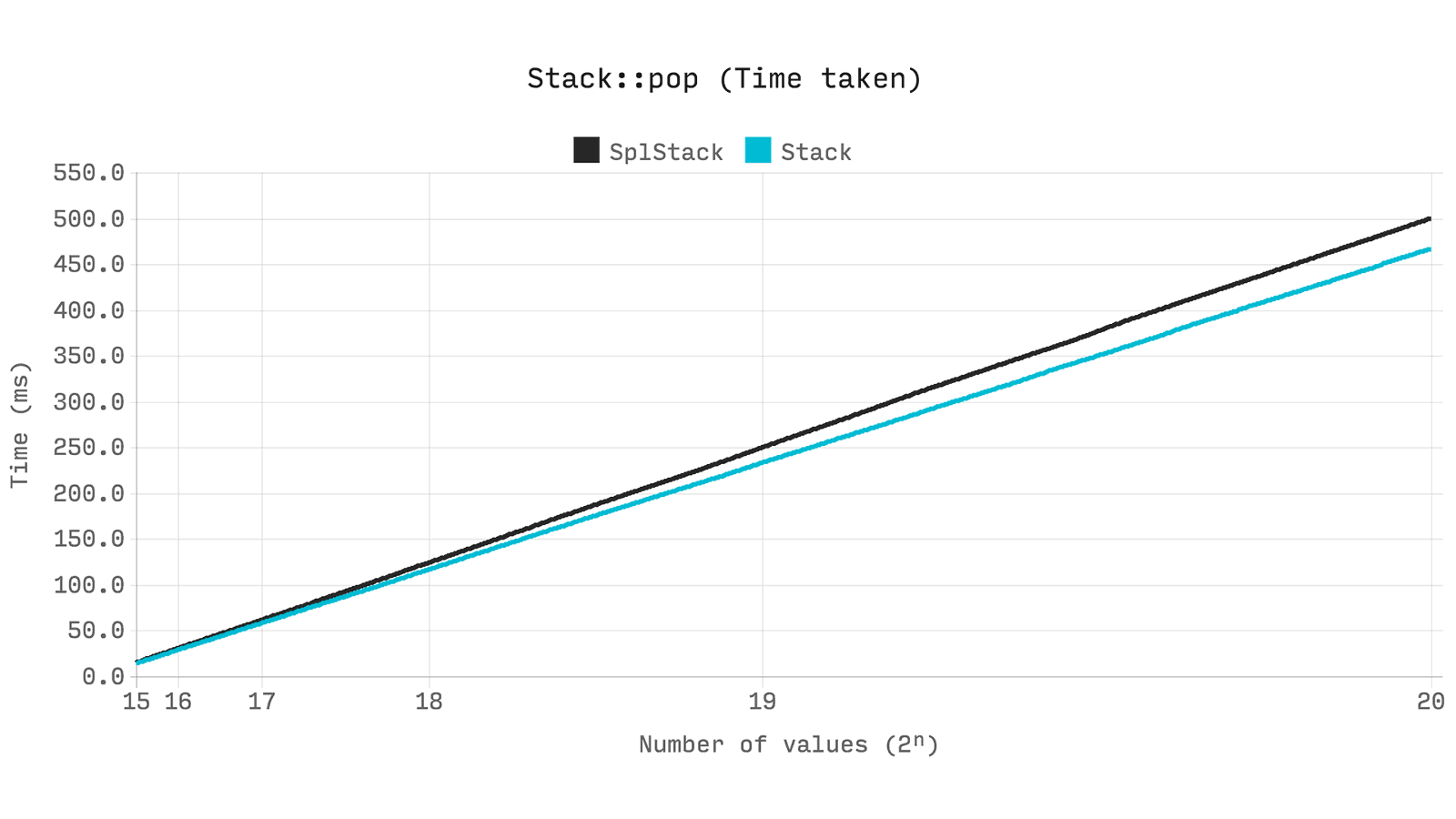
Stack
Stack - is a collection organized according to the principle “last arrived - first exited” or “LIFO” (last in - first out) , allowing access only to the value at the top of the structure. You can think of it as a dynamic-capacity gun shop .
Ds\Stack uses the inside of Ds\Vector .SplStack inherited from SplDoublyLinkedList, so performance will be equivalent to comparing Ds\Vector to SplDoublyLinkedList from previous tests. Let's look at the time it takes to perform 2ⁿ pop operations, resizing from 2ⁿ to zero.
Queue
A queue is a data type with a paradigm of access to the elements “first come, first come out” (“FIFO”, “First In - First Out”) . This collection allows you to access items in the order they are added. Its name speaks for itself, imagine the structure as a line of people standing in line at the cashier in the store.
Ds\Queue uses inside of itself Ds\Deque . SplQueue inherited from SplDoublyLinkedList , so performance will be equivalent to comparing Ds\Deque with SplDoublyLinkedList shown in the previous benchmark.PriorityQueue (priority queue)
The priority queue is very similar to the simple queue. Items are placed in the queue with the specified priority and the value with the highest priority will always be in front. Direct queue search with priority is very destructive, it will be a sequential call to
pop operations, which is a very costly operation.The priority queue implementation uses max-heap .
The principle of “first come, first come out” is preserved for values with the same priority, so that a group of values with equal priority can be considered as a normal queue.
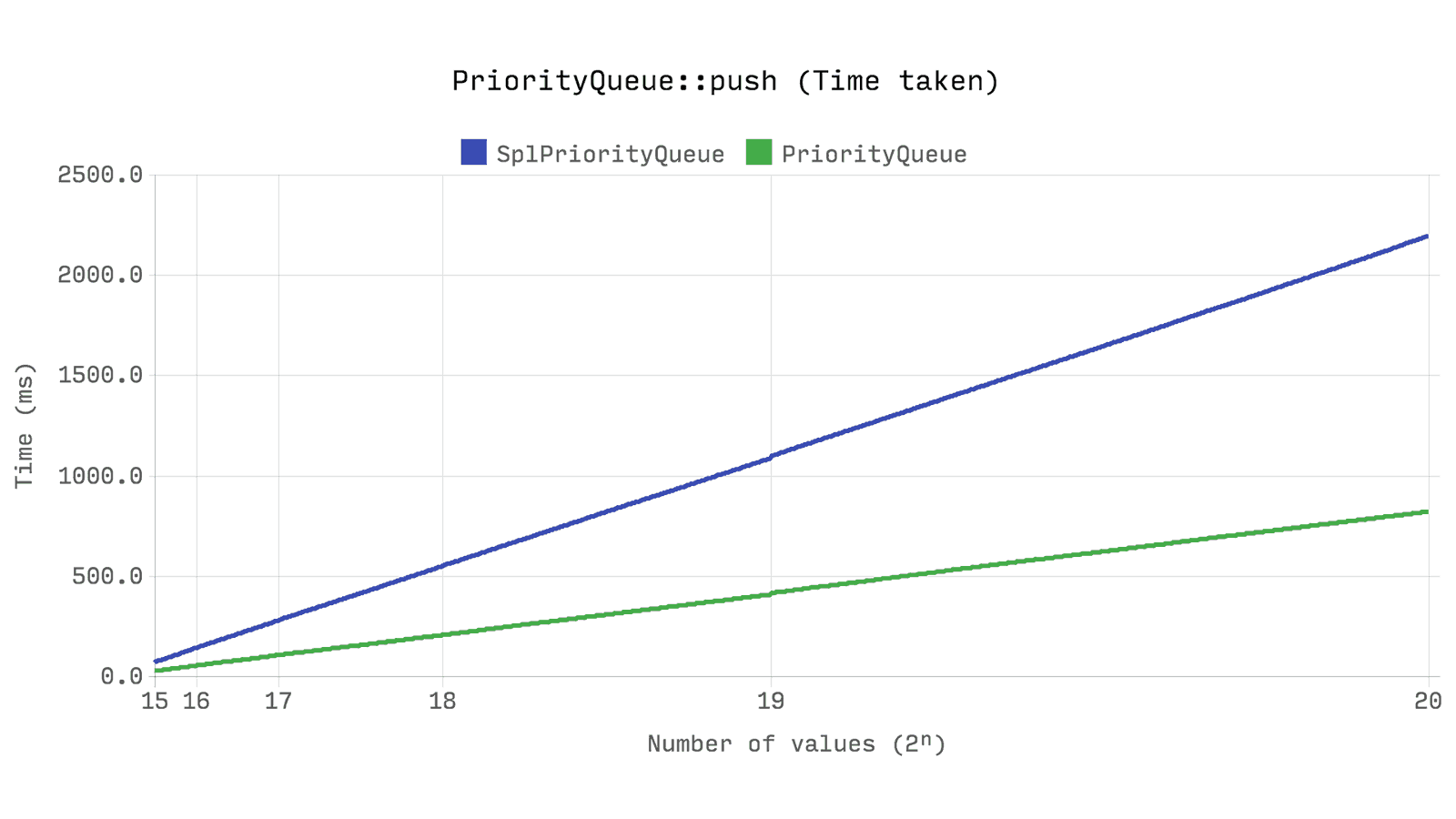
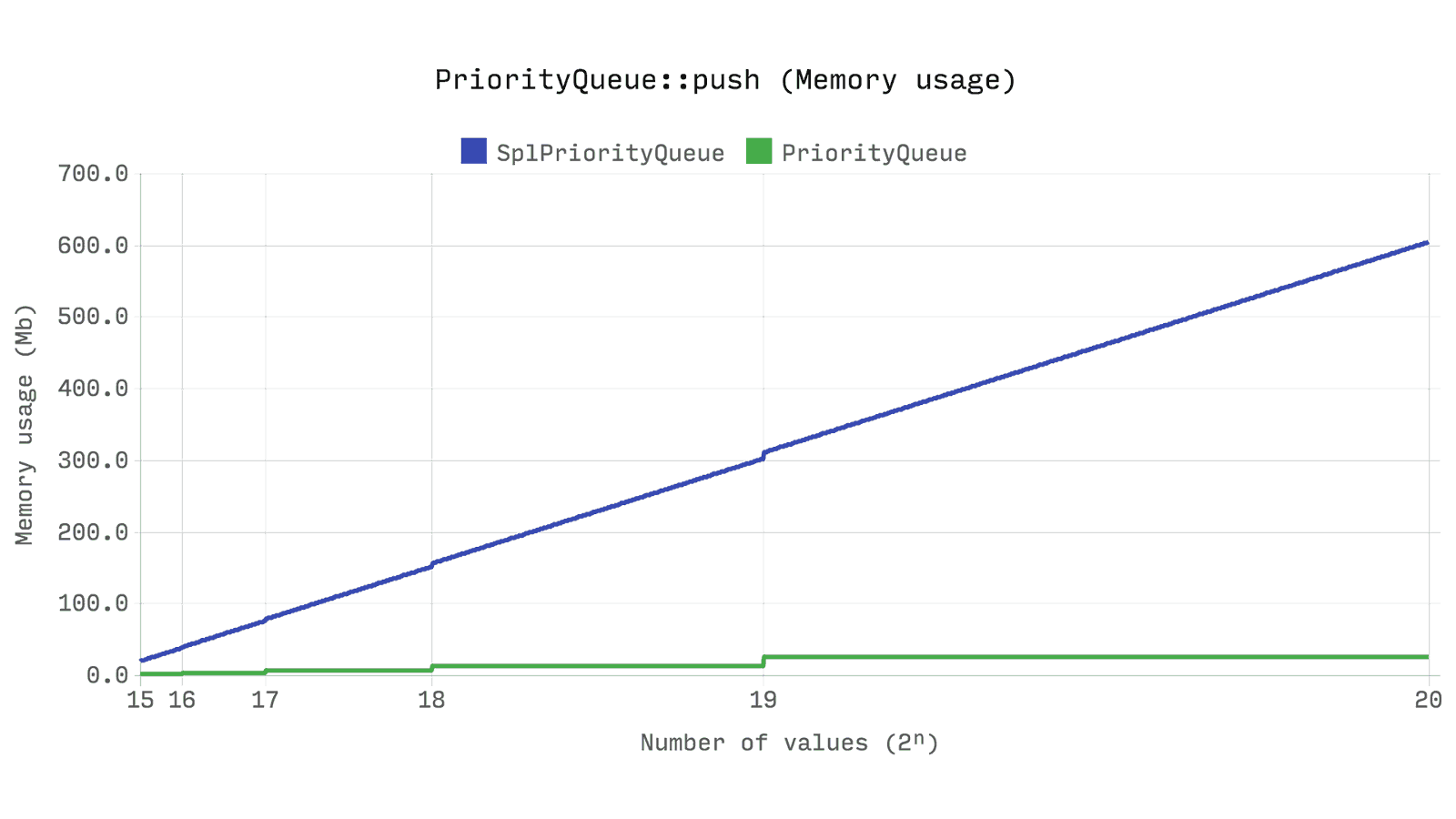
And what about performance? The next benchmark shows the time and memory required for
push 2ⁿ random numbers with a random priority in the queue. The same random numbers will be used for each of the tests. A random priority is also generated for the Queue , although it is not used.This is probably the most significant of all benchmarks.
Ds\PriorityQueue works more than twice as fast as SplPriorityQueue and uses only 5% of its memory - this is 20 times more efficient memory solution .But how? How can such a big difference
SplPriorityQueue when the SplPriorityQueue uses a similar internal structure? It all comes down to how values are paired with priority. SplPriorityQueue allows you to use any type of value to use as a variable, this leads to the fact that in each pair the priority takes 32 bytes .Ds\PriorityQueue only supports integer priorities, so 24 bytes are allocated to each pair. But this is still not enough difference to explain the result.If you look at the source code of
SplPriorityQueue::insert , you will notice that it initializes the array to store the priority value pair .Since the array has a minimum capacity of 8, then
zval + HashTable + 8 * (Bucket + hash) + 2 * zend_string + (8 + 16) byte string payloads is actually allocated for each pair zval + HashTable + 8 * (Bucket + hash) + 2 * zend_string + (8 + 16) byte string payloads = 16 + 56 + 36 * 8 + 2 * 24 + 8 + 16 = 432 bytes (64 bits)."So ... why is the array?"
SplPriorityQueue uses the same internal SplMaxHeap structure, which requires the value to be a zval type. The obvious (but inefficient) way to create a zval pair is that zval itself is used as an array .

Hashable
An interface that allows objects to be used as keys . This is an alternative to
spl_object_hash , which determines an object into a hash based on its handle: This means that two objects that would be considered equal when comparing would not have an equal hash, since they are not the same instance.Hashable introduces only two methods: hash and equals . Many other languages support this initially: in Java, hashCode and equals , or in Python, ___hash___ and __eq__ . There were several RFCs adding this behavior to PHP, but none of them were accepted.All structures will return
spl_object_hash if the keys of the objects stored in them do not implement Hashable in themselves.Data structures that work with the
Hashable interface: Map and Set .Map (Associative array)
Map is a sequential collection of key-value pairs, almost identical to array in a similar context. Keys can be of any type , the only condition is uniqueness. When you add the key again, the values are replaced.As in the
array , the insertion order is preserved.Strengths
- Performance and memory efficiency are almost identical to
array - Automatic release of memory when reducing the size
- Keys and values can be of any type, including objects
- Supports work with objects that implement the
Hashableinterface put,get,removeandcontainsKeyhave complexityO(1)
disadvantages
- Cannot be converted to an
arrayif there are object keys. - It is not possible to access values by index (position)
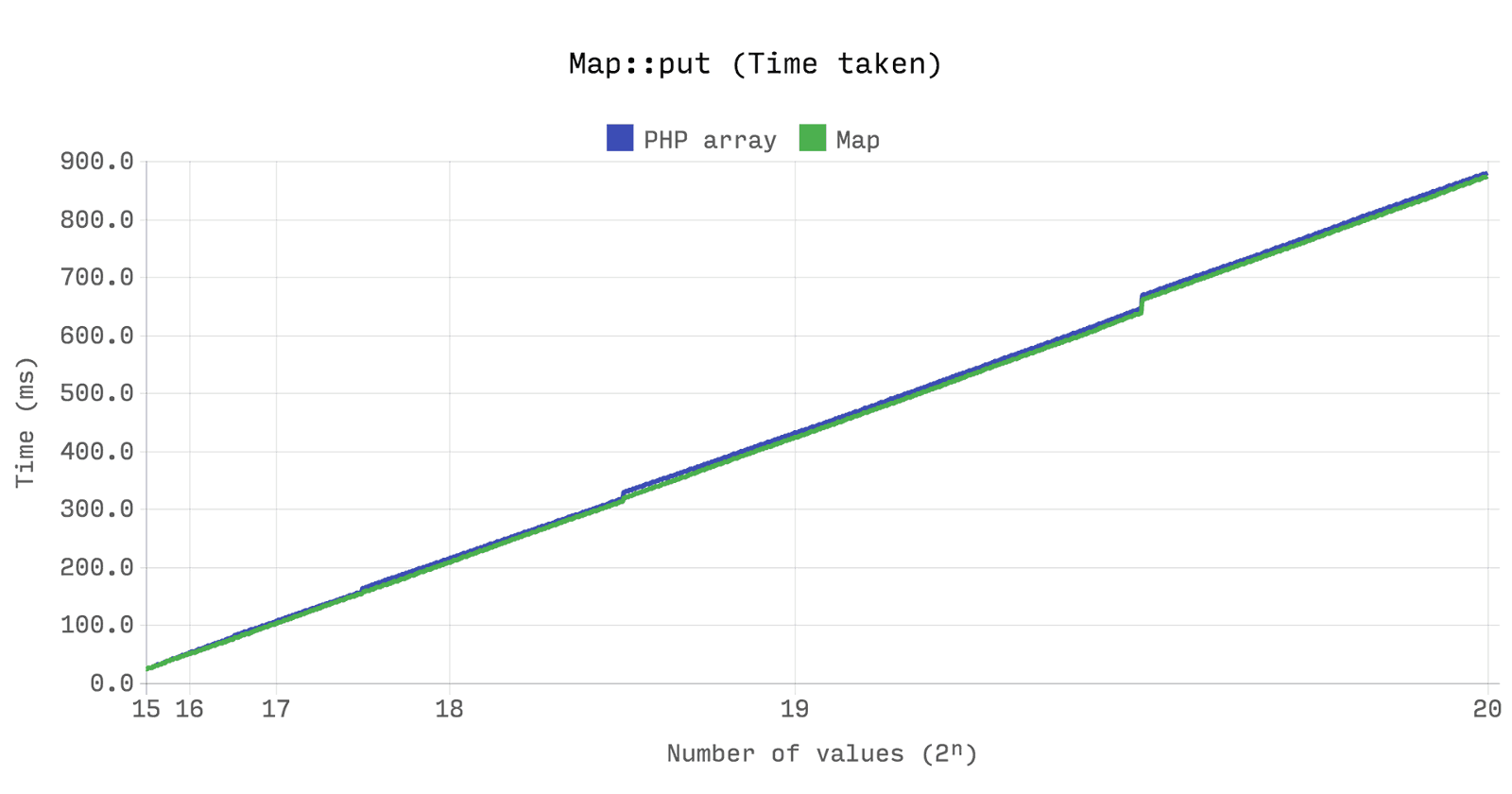
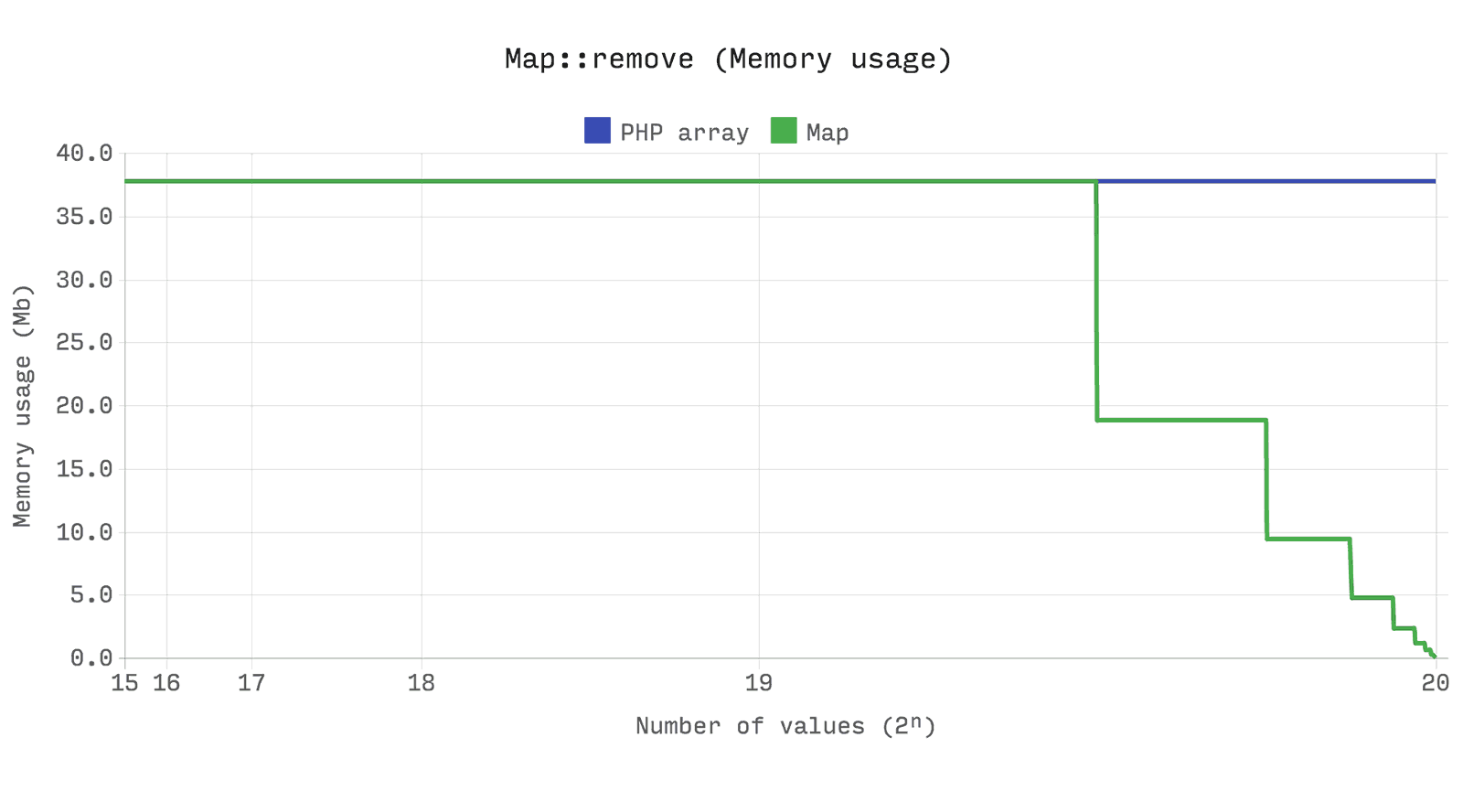
The next benchmark shows that the performance and efficiency of memory between the
array and Ds\Map identical. However, the array will always keep the allocated memory when Ds\Map , in turn, will free up memory if the size falls below a quarter of its potential.

Set (Set)
Set is a collection of unique values . The tutorials will tell you that in the Set structure, the values are unordered, unless the implementation provides otherwise. Take for example Java, java.util.Set is an interface with two main implementations: HashSet and TreeSet . HashSet provides O(1) complexity for add and remove , a TreeSet provides a sorted dataset, but add and remove complexity increases to O(log n) .Set uses the same internal structure as Map , also based on array . This means that Set can be sorted in O(n * log(n)) when needed, otherwise it is as simple as Map and array .Strengths
add,removeandcontainshave complexityO(1)- Supports work with objects that implement the
Hashableinterface - It supports any type of values (
SplObjectStorageonly supports objects). - It has the equivalent of bitwise logical operations (
intersection,difference,union,exclusive or)
disadvantages
- Does not support
push,pop,insert,shiftorunshift gethas complexityO(n)if there are remote values before indexing, otherwise -O(1)
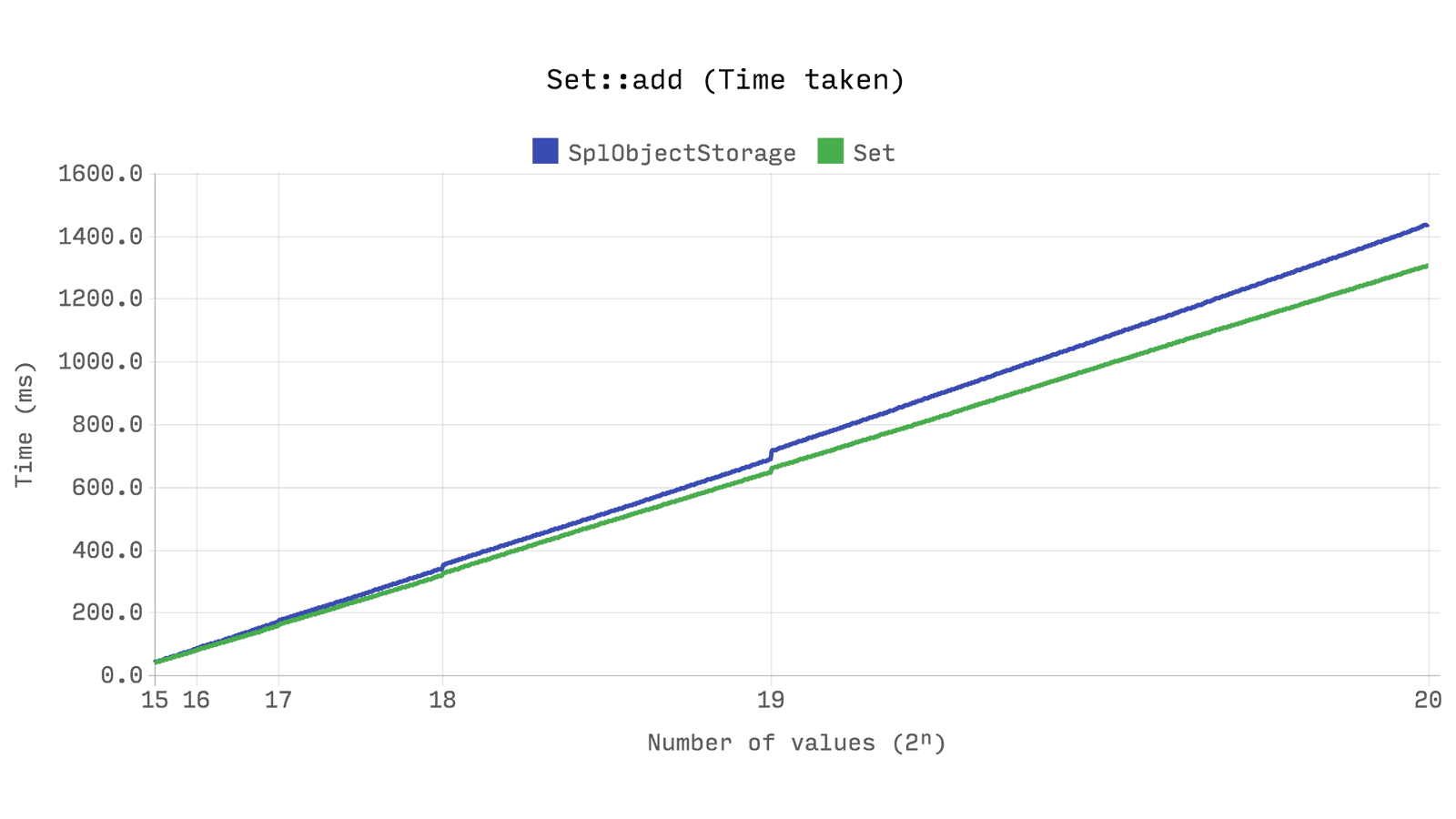
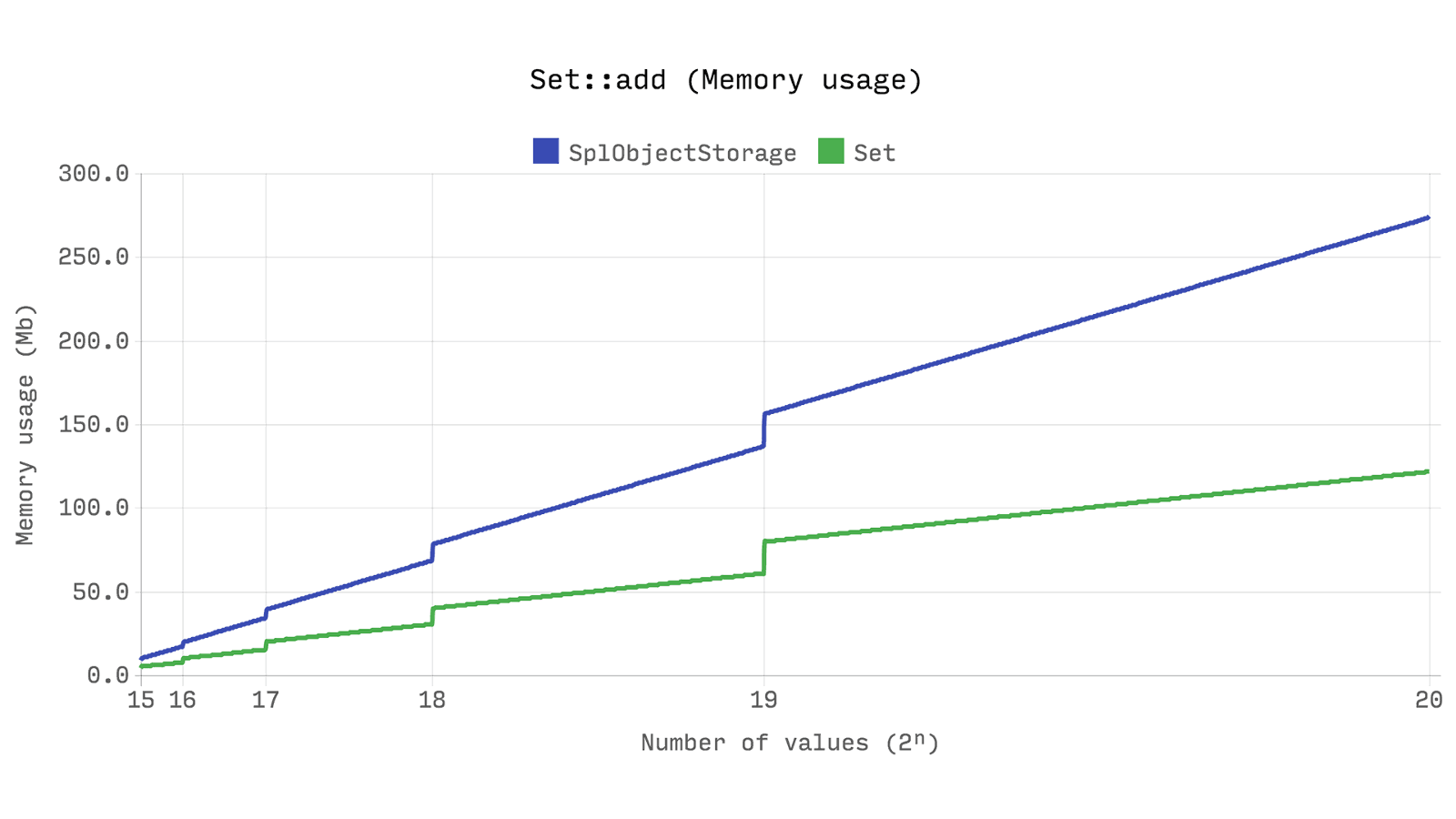
The next benchmark shows the time spent adding 2ⁿ new instances of
stdClass . It shows that Ds\Set slightly faster than SplObjectStorage , and uses about half as much memory.

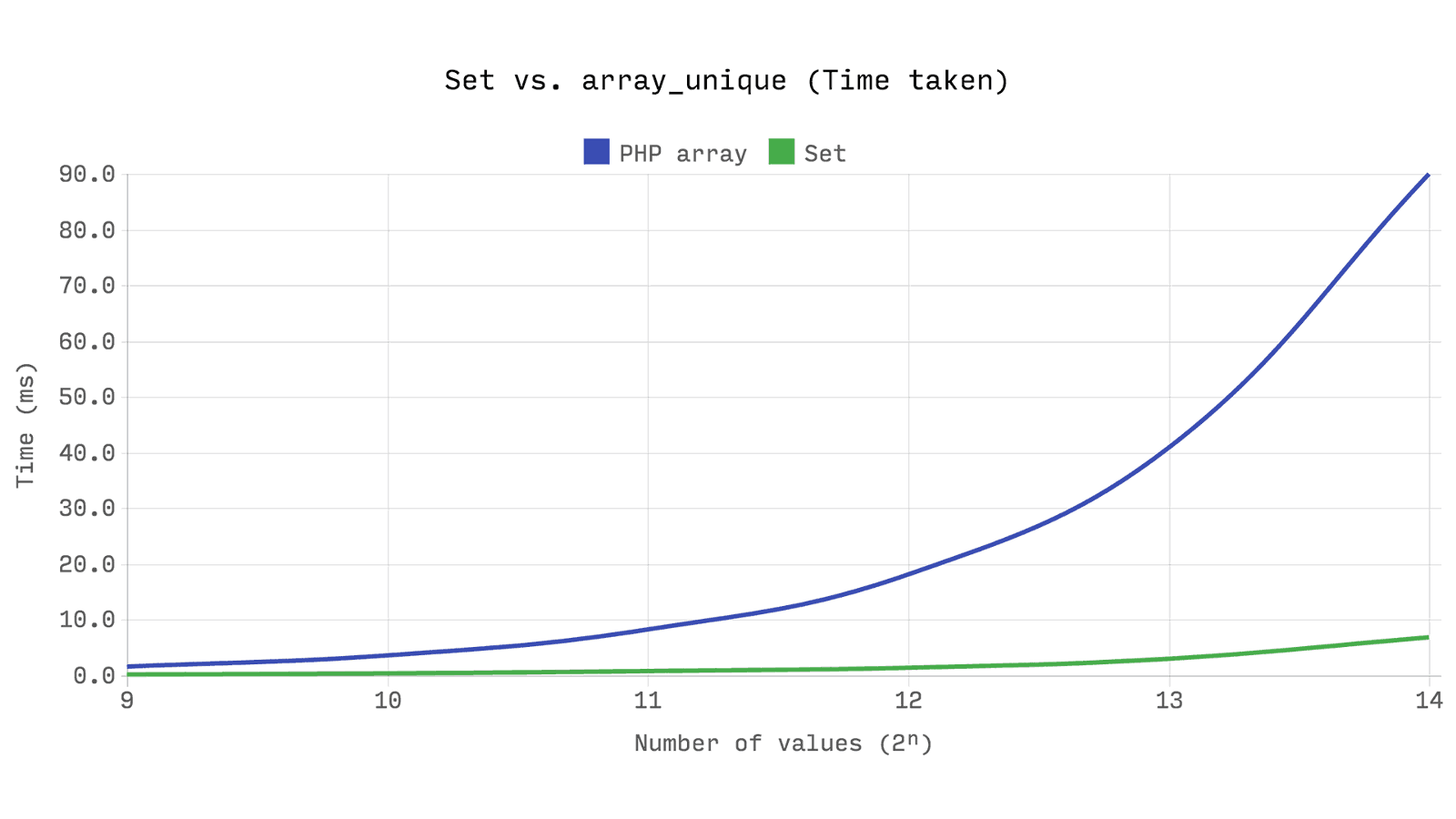
A common way to create an array with unique values is
array_unique , which creates a new array containing only unique values. But it is important to keep in mind that the values in the array are not indexed , in_array is a linear search with complexity O(n) . array_unique works only with values, excluding keys, each checking for the presence of an array value is a linear search, which gives us a total of O(n²) complexity in time and O(n) memory consumption.
Answers to expected questions and opinions
Are there any tests?
Now about 2600 tests . It is possible that some tests are redundant, but I would prefer to indirectly check the same thing twice than not to check at all.
Documentation? API reference?
At the time of this writing, there is still no complete documentation, but it will appear along with the first stable release.
However, there are some well-documented stub files .
Can we see how the benchmarks are arranged? Is there something about them?
All benchmarks were run on the standard
PHP 7.0.3 build for 2015 Macbook Pro . Results may vary by version and platform.Why are Stack , Queue , Set and Map not interfaces?
I do not believe that there is a need for any alternative implementation. 3 interfaces and 7 classes - this is a good balance between pragmatism and specialization.
When should I use Deque instead of Vector ?
If you know for sure that you will not use
shift and unshift , use Vector . For convenient typehipping, you can specify as a type of Sequence .Why are all classes finalized?
The
php-ds API design applies the “Composition over inheritance .SPL structures are a good example of how inheritance can be misused. For example,
SplStack extends SplDoublyLinkedList , which supports random access by index, shift and unshift - so technically it is not a stack .The Java collection framework also has several interesting cases where inheritance creates ambiguity.
ArrayDeque has three methods for adding elements: add , addLast and push . This is not bad, because ArrayDeque implements Deque and Queue , which explains the simultaneous presence of addLast and push . However, all three methods at once, doing the same thing, cause confusion and inconsistency.The old
java.util.Stack extended java.util.Vector , thereby stating that “a more complete and consistent set of LIFO operations is provided by the Deque interface and its implementations,” but Deque includes the addFirst and remove(x) methods that should not be part of the stack structure by API.Just because these structures have disjoint methods does not mean that we cannot do this.
In fact, this is a fair observation, but I still think that composition is more suitable for building data structures. They are designed to be self-contained, like an
array . You cannot inherit from an array , it forces you to develop your own API around you, using it only to store actual data.Inheritance would also cause unnecessary complexity in the internal implementation.
Why do we also need the ds class in the global namespace?
It provides an alternative syntax:

Why is there no Linked List ?
The
LinkedList class actually appeared first, it seemed like a good start. But in the end I decided to remove it when I realized that it could not compete with Vector or Deque in any case. The two main reasons for possible support are: allocation of overhead and locality of links .In the linked list, we add or remove the reserved memory for the structure element (node) whenever a value is added or removed. A node contains two pointers (in the case of a doubly linked list) to refer to the previous and next nodes. Both structures,
Vector and Deque , allocate a buffer of memory in advance, so there is no need to do it so often. They also do not need additional pointers to know what the value is before and what after, thereby reducing overhead costs.Will a coherent list use less memory? is there no buffer?
Only when the collection is very small. The upper limit of the amount of memory for a
Vector is (1.5 * (size - 1)) * zval bytes, at least * 10 * zval *. In a doubly linked list, it will be used (size * (zval + 8 + 8)) . Therefore, a coherent list will use less memory than Vector only when its size is less than 6 elements.Ok ... the coherent list uses more memory, but why is it slow?
Linked nodes have poor spatial locality . This means that the physical location of the node in memory may be far from adjacent nodes. Thus, iterations over a coherent list jump through memory instead of using the processor cache.
Vector and Deque significant advantage: the elements are physically next to each other.»Incomplete data in structures is the root of all the evils of performance. Specifically, please say no to linked lists. "
"There is almost nothing more harmful than what you can do to kill all the advantages of modern microprocessors than using a coherent list"
- Chandler Carruth ( CppCon 2014 )
PHP is a language for web development - performance is not important.
Performance should not be your top priority . , , , , . , « » .
, , -:
- print vs echo, which one is faster?
- The PHP Ternary Operator: Fast or not?
- The PHP Benchmark: setting the record straight
- Disproving the Single Quotes Performance Myth
, PHP7 - . — PHP5.
. API - . , .
: Twitter , Reddit , Room 11
: github.com/php-ds
: github.com/php-ds/benchmarks
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/280262/
All Articles