Disaster-resistant IaaS, as well as replication and backups

We live the time when information volumes are growing faster and faster every day. In parallel with this, the needs of business are growing. The growth of the popularity of virtualization and cloud computing has leveled off in the capabilities of both small and large companies, therefore it has become necessary to change the approaches to data integrity.
There is a so-called disaster recovery solution (Disaster Recovery Solution or DRS), which is often confused with a high availability system. However, there is a difference between these concepts, and this is the permissible scale of the accident. DRS systems can recover from a major failure of several data centers at once, without paralyzing the services for a long time.
')
When it comes to systems of this class, people often imply a backup data center that serves as a springboard for transferring workload and data from a non-working place. There are three types of data centers: cold reserve, warm reserve and hot reserve. Cold reserve is often low-end servers that are ordered and configured after an accident occurs, and the data is transferred to them on magnetic tapes or disks. “Raising” of this infrastructure can drag on for several days or weeks and depends on suppliers, transport and personnel skills.
Warm reserve is the weaker servers in the minimum number necessary to run critical systems; they are connected, activated and always ready to transfer the load. To start such a system takes no more than one day. Hot spares are servers whose performance corresponds to the servers of the main site; in this case, all data is replicated regularly and permanently. Since there is a ready-made infrastructure, channels, software, and it all comes together automatically, the launch of such a system occurs within one hour (often less).
It is the warm version that is now used by many companies because of the acceptable cost and quite good temporal indicators. But if you use a backup site based on IaaS, then you can get even a hot version without a significant increase in the budget. DRS in the cloud infrastructure is not particularly different from the classic solutions, but it has several tangible benefits.
If earlier organization of a LUN replica required compatible storage systems with special licenses, now it is enough to put a couple of daws in a virtual environment (the same vSphere vSAN), and the popular vector for outsourcing and cloud computing allows you to outsource some corporate services. This makes it possible to exclude highly specialized employees from the state and begin to build their own management and monitoring system.
Selecting a backup data center should:
- Ensure that users can work not only from the main office, but also from any other place (decentralization useful in case of a large-scale accident)
- Backup data center should have an availability indicator close to 100% per year. In practice, this means the maximum number of nines after the decimal point (99.0%, ..., 99.999%)
- Data on the emergency site must be current
One of the most important components of a disaster-proof solution is to keep relevant information on both sites, for example. RPO metrics (a valid recovery point) are directly dependent on stable storage synchronization. Replication of virtual disks can be performed, for example, by means of vSphere Replication or by shifting this task to storage-based replication systems.
The vSphere Replica native mechanism is a replication at the ESXi hypervisor level that is independent of the type and identity of the storage at all sites. A distinctive feature is the ability to transfer data between different types of storage devices: from VSAN at the main site to the DAS to the backup. Storage-level replication is a more efficient mechanism by which the entire synchronization process is transferred to storage devices. The minimum RPO of hardware replication is a couple of minutes, which fits well with the requirements of a business-critical application.
And, as often happens, it is generally recommended to choose a hybrid version. In it, you allocate a datastore with hardware replication of the most important virtual machines, and protect all the others with the vSphere Replica mechanism, which allows you to work with cheaper storage systems. A nice bonus from devices with hardware replication will be proprietary snapshot technology, shadow volumes and other useful features. Due to the popularity of NetApp storage systems in the domestic market, we’ll look at them as the main repository for DRS (by the way, we published storage boxing boxes, which you can see here and here ).
Snapmirror
SnapMirror is known as synchronous and asynchronous replication technology at the level of disk arrays, which occurs using an IP network. The technology is based on the concept of using differential snapshots of the state of the corresponding volume.
Synchronous replication is characterized by the fact that the ready signal going from the storage to the recording application is not transmitted until data is written to both the source volume on the client side and the replica in the cloud of the IaaS provider. In other words, the application waits until the data block is written first to the local volume and then to the remote one.
With asynchronous replication, during recording, the local system immediately sends a signal to the application with the “recorded” status, after which (at a specified interval) updates are sent to the remote site.
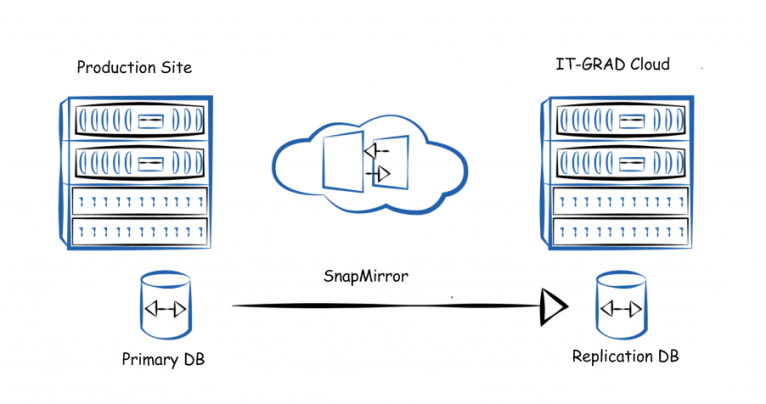
SnapMirror Synchronous / Asynchronous Replication Technology
In the event of a replica rupture, the receiving party transfers the replicated mirror to read-write mode, which remains active until the equipment on the customer’s side is restored. After everything is back to normal, SnapMirror takes over in reverse replication mode and restores the base on the client side.
SnapVault
Replication is good in itself, but it is unlikely to help in case of data corruption. During replication, “corrupted” fragments fall into the backup system, which leads to the appearance of two damaged data sets. To avoid such unpleasant situations, the SnapVault backup technology allows you to solve the problem of long-term storage and protect data from changes for later recovery.

SnapVault Backup Technology
In the case of the client and the cloud provider, the essence of using SnapVault is that the customer data located on the source volume is copied to the receiving volume in the cloud hosting provider according to the schedule. Such a copy is created in read-only mode, which is accessed as necessary.
In general, the topic of backup has always been relevant. A study by Gartner, an analyst firm, revealed that data growth is the biggest problem for data center infrastructure in large organizations. All data must be protected from various threats, as well as the use of data reduction and restoration methods.
The very idea of cloud backup is to automatically transfer client backups to the data center of the cloud service provider. Of course, to form a service, it is not enough just to allocate space in the storage and give the client access, you need to ensure safe storage of information and access to it, as well as competently form a tariff policy and provide a certain level of service with a fixed response time.
The main task of any cloud backup is to save data in case of an unforeseen situation. The availability of these backups depends on the level of reliability (Tier) of the provider. For example, Tier-1 assumes availability of 99.671% per year, and Tier-4 - already 99.995%.
Data center providers may declare a variety of accessibility values, but the reality is that removing unpredictable equipment and making your data inaccessible can be any unforeseen events (hacker attack, natural disasters). As an example, we can recall the large-scale accident in the Amazon data center, when due to a thunderstorm, entire services were disconnected: Netflix, Instagram and Pinterest. Since it is not always possible to prevent disasters, it is worth choosing a provider with a developed disaster recovery plan. Then you at least get your data back within a reasonable time.
Also for any business one of the most important priorities is the confidentiality of user data. To reduce the chance of information being compromised, it is important to choose a supplier with proven compliance with local and international security standards. For example, one of the toughest modern standards is the PCI standard (Payment Card Industry Standard), which protects financial information. If you work with other specific information (medicine, industry, etc.), then the provider will be required to comply with the standards of this industry.
Any company that exists long enough knows that it is impossible to completely eliminate the possibility of data loss. But whether it will be just an inconvenience or a situation that puts the whole business on the blades depends on the quality of the preliminary preparation. The rules of the game in the business environment change regularly, and cloud services allow organizations to insure against serious losses.
PS Interesting materials on the topic from our blog on Habré:
- IaaS trends brief
- Data Center Experience and Problems: How to Verify Data Center Reliability
- How IaaS provider to choose a data center to host the cloud: IT-GRAD Experience
- How we implemented Disaster Recovery
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/279223/
All Articles