A simple example of visualizing the results of a CPUID instruction.
There was a time when a lot of useful information about new processors could be obtained from the document “ Intel Processor Identification and the CPUID Instruction ”. This manual was regularly updated and was full of descriptions of innovations that literally overwhelmed Intel. Unfortunately, since May 2012, the description of the CPUID instruction has migrated to the multi-volume Intel 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer's Manual, and a link to the specified document will be forwarded to one of the volumes of the Yarbuch (specifically, Vol. 2A ).
From this point on, it became more difficult to keep track of innovations. The thought arose with the help of a simple utility to visualize the results of the work of CPUID in order to monitor the introduction of new products and be aware of. (Software development process is outlined here , the latest version is available here ).
')
Actually, a revolutionary novelty in such developments cannot be by definition, but the convenience with which we observe the development of the processor park is indisputable. Let us verify this assumption by examining the functionality of the processor from the recently appeared SkyLake family. A cube server based on Supermicro X11SSL-F (thanks to Entry) was used as a test platform. Let's keep quiet about the processor: let it tell everything by itself ...
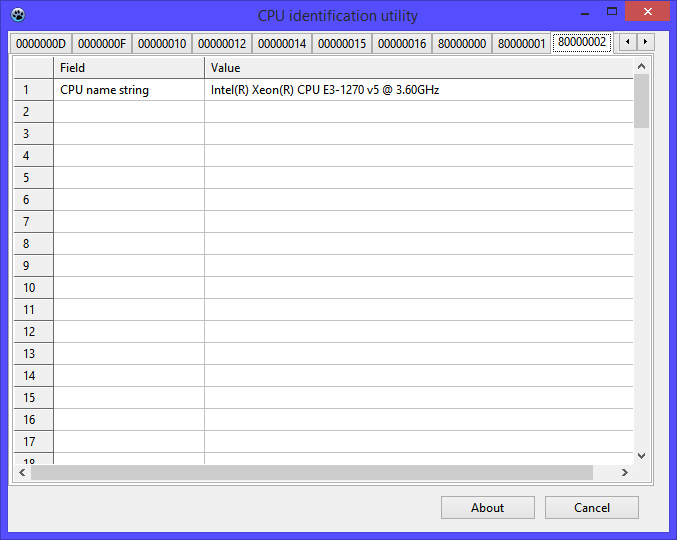
Using the utility, we immediately discover a number of functions that SkyLake processors are equipped with. Let's try to comment on our findings - additions to the architecture of the CPUID instruction associated with the emergence of a new family.
Function 0000000Eh is reserved, results in registers are zero.

Function 0000000Fh Platform Quality of Service Monitoring Enumeration, declares the functionality that allows you to monitor the use of processor resources by the application. According to the documentation, today such monitoring is implemented only for the L3 Cache, although it is possible to add other resources to the list of analyzed. Although this function is in the range of functions supported by the processor, the results in the registers are zero. This means that this processor does not support this feature. And the range is increased to add new features with large numbers.

The 00000010h Platform Quality of Service Enforcement Enumeration function declares the functionality that allows the operating system to prioritize applications (streams) when using shared resources. As for the above described function, so far we are talking only about the L3 cache. Although this function is in the range of functions supported by the processor, the results in the registers are zero. This means that this processor does not support this feature.
Function 00000011h is reserved, results in registers are zero.

The 00000012h function of Intel SGX Resource Enumeration declares the capabilities of the Software Guard Extension technology, it is a security technology that allows you to create encapsulated areas for applications. Theoretically, such protection is quite effective, including in situations where the attacking malicious code has the privileges of the Ring0 supervisor (privileged attack), as well as in the case of hardware interception of memory traffic (snooping attack).
The SGX1, SGX2 instruction sets are marked as unsupported, the maximum values of the size of the protected area (enclave size = 1 byte) are not valid. On the other hand, according to the results of the CPUID function # 7, the support flag SGX = 1. According to the documentation, the processor supports SGX. Possible reasons for this discrepancy: Firmware did not initialize SGX resources, for example, if this technology is not included in CMOS Setup, or is not supported due to the old version of Firmware. The role of the UEFI initialization procedures in the formation of the values of these fields will be the subject of a separate material.
Function 00000013h is reserved, results in registers are zero.
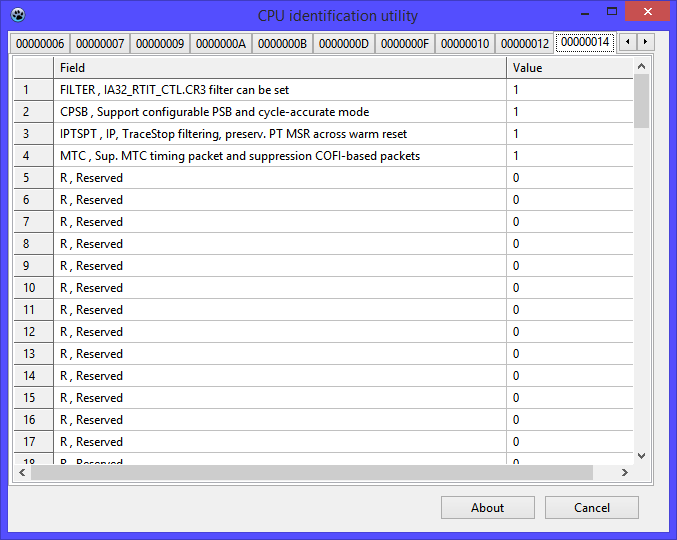
Function 00000014h Intel Processor Trace Enumeration declares the functionality that provides tracing program execution with logging information about events that occur, such as conditional and unconditional jumps, subroutine calls. The protocol is conducted with reference to real time. RTIT (Real Time Instruction Trace) tracing technology using the MTC (Mini Time Counter) timer is supported by this processor. The abbreviation COFI stands for Change of Flow Instruction, and defines a set of events related to conditional and unconditional transfer of control, the monitoring of which can be controlled. A detailed description of this functionality will be the subject of a separate material.
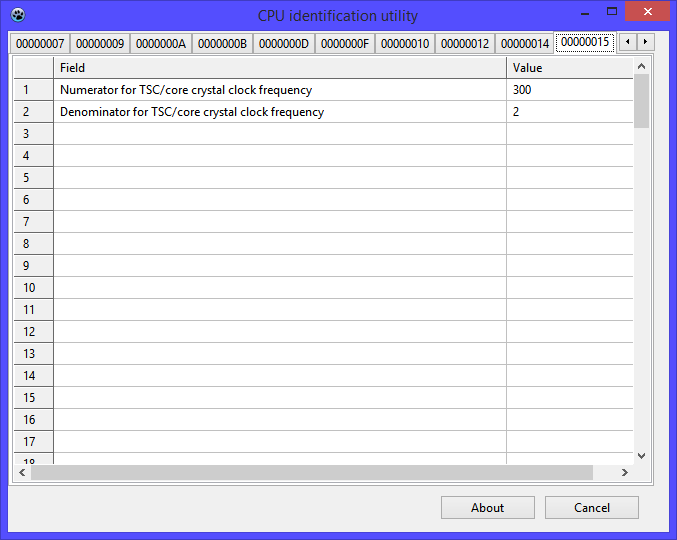
Function 00000015h Time Stamp Counter / Core Crystal Clock Information Enumeration declares the relationship between the TSC and some internal source of the reference frequency, called "Core Crystal Clock".
The frequency of the specified reference source is 150 times less than the TSC frequency. According to Intel's documentation, one such source could be a timer implemented in a processor as part of the Local APIC interrupt controller. This function is declared by the Always Running APIC Timer bit, which emphasizes the functionality of such a timer in various Power-Management processor states.

Function 00000016h Processor Frequency Information allows you to read the values of the main clock frequencies of the processor. The returned constants correspond to the processor model; you should not use this function as an alternative to frequency measurement, otherwise incorrect readings in the case of overclocking are possible.
As you can see, a number of changes in the CPUID architecture only reserve opportunities, which the processor giant apparently intends to use a little later. On the other hand, not yet implemented, but previously described instructions in Odessa are considered to be implemented.
From this point on, it became more difficult to keep track of innovations. The thought arose with the help of a simple utility to visualize the results of the work of CPUID in order to monitor the introduction of new products and be aware of. (Software development process is outlined here , the latest version is available here ).

')
Actually, a revolutionary novelty in such developments cannot be by definition, but the convenience with which we observe the development of the processor park is indisputable. Let us verify this assumption by examining the functionality of the processor from the recently appeared SkyLake family. A cube server based on Supermicro X11SSL-F (thanks to Entry) was used as a test platform. Let's keep quiet about the processor: let it tell everything by itself ...

Using the utility, we immediately discover a number of functions that SkyLake processors are equipped with. Let's try to comment on our findings - additions to the architecture of the CPUID instruction associated with the emergence of a new family.
CPUID = 0000000Eh
Function 0000000Eh is reserved, results in registers are zero.
CPUID = 0000000Fh

Function 0000000Fh Platform Quality of Service Monitoring Enumeration, declares the functionality that allows you to monitor the use of processor resources by the application. According to the documentation, today such monitoring is implemented only for the L3 Cache, although it is possible to add other resources to the list of analyzed. Although this function is in the range of functions supported by the processor, the results in the registers are zero. This means that this processor does not support this feature. And the range is increased to add new features with large numbers.
CPUID = 00000010h

The 00000010h Platform Quality of Service Enforcement Enumeration function declares the functionality that allows the operating system to prioritize applications (streams) when using shared resources. As for the above described function, so far we are talking only about the L3 cache. Although this function is in the range of functions supported by the processor, the results in the registers are zero. This means that this processor does not support this feature.
CPUID = 00000011h
Function 00000011h is reserved, results in registers are zero.
CPUID = 00000012h

The 00000012h function of Intel SGX Resource Enumeration declares the capabilities of the Software Guard Extension technology, it is a security technology that allows you to create encapsulated areas for applications. Theoretically, such protection is quite effective, including in situations where the attacking malicious code has the privileges of the Ring0 supervisor (privileged attack), as well as in the case of hardware interception of memory traffic (snooping attack).
The SGX1, SGX2 instruction sets are marked as unsupported, the maximum values of the size of the protected area (enclave size = 1 byte) are not valid. On the other hand, according to the results of the CPUID function # 7, the support flag SGX = 1. According to the documentation, the processor supports SGX. Possible reasons for this discrepancy: Firmware did not initialize SGX resources, for example, if this technology is not included in CMOS Setup, or is not supported due to the old version of Firmware. The role of the UEFI initialization procedures in the formation of the values of these fields will be the subject of a separate material.
CPUID = 00000013h
Function 00000013h is reserved, results in registers are zero.
CPUID = 00000014h

Function 00000014h Intel Processor Trace Enumeration declares the functionality that provides tracing program execution with logging information about events that occur, such as conditional and unconditional jumps, subroutine calls. The protocol is conducted with reference to real time. RTIT (Real Time Instruction Trace) tracing technology using the MTC (Mini Time Counter) timer is supported by this processor. The abbreviation COFI stands for Change of Flow Instruction, and defines a set of events related to conditional and unconditional transfer of control, the monitoring of which can be controlled. A detailed description of this functionality will be the subject of a separate material.
CPUID = 00000015h

Function 00000015h Time Stamp Counter / Core Crystal Clock Information Enumeration declares the relationship between the TSC and some internal source of the reference frequency, called "Core Crystal Clock".
- EAX = denominator = denominator = 2
- EBX = numerator = numerator = 12Ch = 300
- Ratio = 300/2
The frequency of the specified reference source is 150 times less than the TSC frequency. According to Intel's documentation, one such source could be a timer implemented in a processor as part of the Local APIC interrupt controller. This function is declared by the Always Running APIC Timer bit, which emphasizes the functionality of such a timer in various Power-Management processor states.
CPUID = 00000016h

Function 00000016h Processor Frequency Information allows you to read the values of the main clock frequencies of the processor. The returned constants correspond to the processor model; you should not use this function as an alternative to frequency measurement, otherwise incorrect readings in the case of overclocking are possible.
- EAX = Processor Base Frequency (MHz) = 0E10h = 3600 MHz
- EBX = Maximum Frequency (MHz) = 0FA0h = 4000 MHz (Turbo Boost)
- ECX = Bus Frequency (MHz) = 064h = 100 MHz (Bus Clock)
- EDX = Reserved = 0
Summary
As you can see, a number of changes in the CPUID architecture only reserve opportunities, which the processor giant apparently intends to use a little later. On the other hand, not yet implemented, but previously described instructions in Odessa are considered to be implemented.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/278281/
All Articles