How the VMware cloud works, as well as networking and network connectivity

Recently, server-based virtualization platforms have become one of the most popular ways to deploy applications in data centers. Therefore, today we will talk about what lies in the features of the implementation of the VMware cloud and how you can organize a network.
To create a complete and adaptive VMware cloud, use the VMware vCloud Suite. Part of it is the VMware vSphere virtualization platform, whose task is to dynamically balance the load on servers and storage systems in order to achieve their optimal performance , high availability of virtual servers, as well as isolating the virtual infrastructures of different customers from each other at the network level.
')
It turns out that we can call vSphere the foundation on which the cloud is built. To provide security and protection against various external and internal threats , the vCloud Networking and Security product suite is applied .
The vCloud Suite also includes a vCloud Director, which is a powerful tool for managing individual virtual machines (creating, allocating resources, accessing the VM console, etc.), a set of interdependent virtual machines necessary for the implementation of a single service, as well as virtual networks and network interaction between machines.
This set of tools makes it possible to form a so-called “cloud cell”. It is a pool of resources that can be “split” into smaller components - independent clouds.
Cloud virtual network is practically the same as physical and can be both isolated and with external / internal routing based on IPv4 or IPv6. Virtual networks, unlike physical networks, are characterized by hardware independence, high initialization speed and the ability to deploy without interrupting the operation of systems.
A network inside a VMware cloud can be organized using various scenarios. Sometimes you need to build an external routed subnet with the necessary number of IP addresses for the client. These types of networks are often called External networks and represent an outlet to the “outside world” (for example, the Internet).
Fragment of the external routed network of IT-GRAD company
To create an external network in the cloud, the vSphere administrator creates a separate group of ports with the necessary parameters. When forming a network segment, it is important to correctly specify the gateway, parameters of DNS servers, as well as determine the range of IP addresses and the subnet mask. If the segment is planned to issue public addresses, then for this, the corresponding rules are created in the routing table.
The figure above is an example of an external routed network in the cloud. Here we see the presence of so-called public hosts, access to which is organized in 24/7 format.
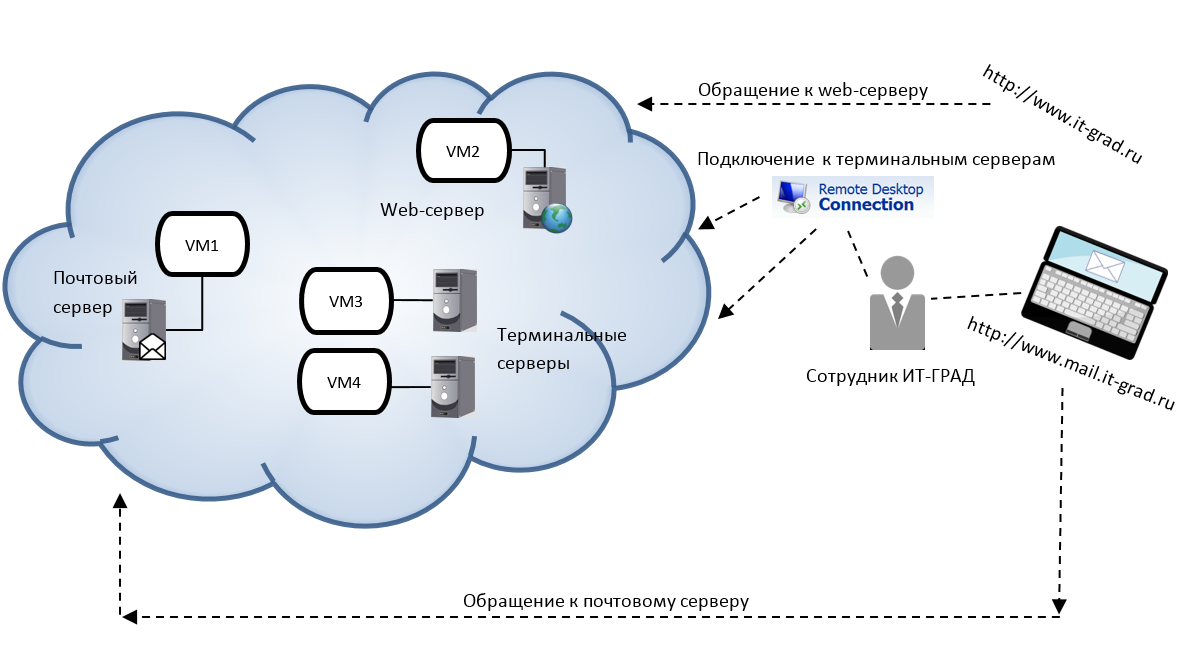
In addition to external routed networks, there may be isolated subnets in the cloud that connect virtual machines - there are situations in which the presence of such networks is necessary. IT-GRAD has two domain controllers (VM1 and VM2) that must replicate the databases of the active directory — this is necessary to keep the databases up to date.
Additionally, a DNS server (VM3) is deployed, storing the secondary zone it-grad.ru. VM2 and VM3 servers must communicate with each other to perform zone transfer. If the contents of the main zone it-grad.ru are changed on VM2, all changes associated with it must be transferred to VM3. Access to the Internal network 1 network is restricted from the outside. In VMware terminology, this type of network is referred to as an "organization network."

Fragment of an isolated subnet in the cloud
However, the most common type of organization of subnets is a combined approach: building both internal and external subnets, or issuing two or more external or internal networks.
As a rule, companies that are going to transfer IT infrastructure to the cloud have resources that need external access, as well as a set of critical services and applications that need to be isolated.
There are scenarios when such isolated networks should be several. At the same time, you can connect virtual applications directly as part of an organization segment or through a virtual gateway Edge Gateway with the ability to use NAT.
VMware vSAN
Storage systems also need to cope with ever-increasing loads, so the organization of storage requires a special approach - VMware Virtual SAN. Using the hyperconverted VMware architecture, Virtual SAN provides computing and storage resources based on a common VMware virtualization platform.
Virtual SAN with hybrid architecture allows you to combine HDDs and flash drives on servers, while controlling the distributed data storage. The flash-based architecture provides caching, data stability, and high predictable performance.
Since Virtual SAN is embedded in the vSphere core, the impact on the CPU is reduced. Thanks to the built-in integration of Virtual SAN into the hypervisor, there is no need to install additional software, and the policy-based approach greatly simplifies the management of standard processes. In addition, Virtual SAN integrates with all vSphere components and is managed using a web client.
VMware vRealize
It seems that each of us would like to control the workload, manage performance, optimize resources, perform log analysis in real time. All this and much more today is possible with the help of VMware vRealize Operations Insight.
In particular, VMware vRealize Log lnsight allows logging in VMware environments. With it, you can effectively search and troubleshoot physical and virtual cloud environments.
vRealize Log Insight processes all types of logs, generated machine data, and performs word searches with filtering. For example, you can easily filter values by numeric range (CPU> 80, 10 100). You can also use this tool to compare data by various criteria.
The vRealize Log Insight solution uses a new machine learning technology. Intelligent grouping allows you to scan unstructured data and classify it by event type in order to quickly identify a problem and understand the cause of its occurrence.

An interactive analytics page gives administrators the ability to view detailed log events, helping to identify problem areas and analyze key issues.
Special tab Event Trends on the page of online analytics is designed to automatically analyze current events with the ability to detect anomalies. Even here you can track events that potentially affect the "health" of various applications or environments. Fields that are extracted from log data can be used for aggregation.
This is somewhat similar to GROYP-BY queries that are executed in relational databases or Excel PivotTables. The only difference is that there is no need to use ETL processes that require data retrieval and its loading into data warehouses.
With vRealize Log Insight, you can create your own metrics panels and track events of interest to you, as an example, check system performance for a certain period of time.
PS Materials on the topic from our blog on Habré:
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/277971/
All Articles