How does Google Search work?
How does Google Search, the basic update algorithms

Nowadays, search engines, in particular Google, resemble the Internet’s “shop window” and are the most important channel for disseminating information in digital marketing. With the help of a global market share, which is more than 65% according to data for January 2016, Google clearly dominates the search industry. Although the company did not officially disclose the extent of its growth, by 2012 it was confirmed that their infrastructure serves about 3 billion search queries per day.
')
Google.com globally ranked number 1 on Alexa Top 500 Global Sites. Given these numbers, it is especially important for owners of their own web pages to have a good search engine visibility of their sites.
But despite the general popularity of Google, do you know how it really works and what kind of pandas, penguins, caliber?
The more necessary Google becomes for modern marketing, the more important it is to understand the search functions and update algorithms that have a direct impact on the ranking of results. Moz suggests that Google changes its algorithms 600 times a year. Many of these changes and related ranking factors are kept secret. And only major updates are announced publicly.
In this article, we will look at the basics of the search engine functionality and explain the major updates to Google’s algorithm since 2011. We also derive strategies, following which you can keep up with changes in the search engine. So read on ...
By their appearance, search engines have completely changed our usual way of collecting information. Are you interested in updating stock market data or do you want to find the best restaurant in the area, or write an academic report on Ernest Hemingway - a search engine will answer all requests. In 80 years the answers to the questions would require a visit to the local library. Now everything is solved within a millisecond using the algorithmic powers of the search engine.
In this regard, the main goal of the search engine is to find relevant and relevant information as quickly as possible, as a response to the search terms entered, also called keywords. Therefore, a central aspect for any search engine that wants to produce a really useful result is the notion of the purpose of the search, how exactly people search.
The result of Google can be compared to an online directory selected using an algorithm-based rating system. More specifically, the search algorithm can be described as “finding an element with specified properties among the list of elements”.
Let's now take a closer look at the involved scanning, indexing and positioning processes.
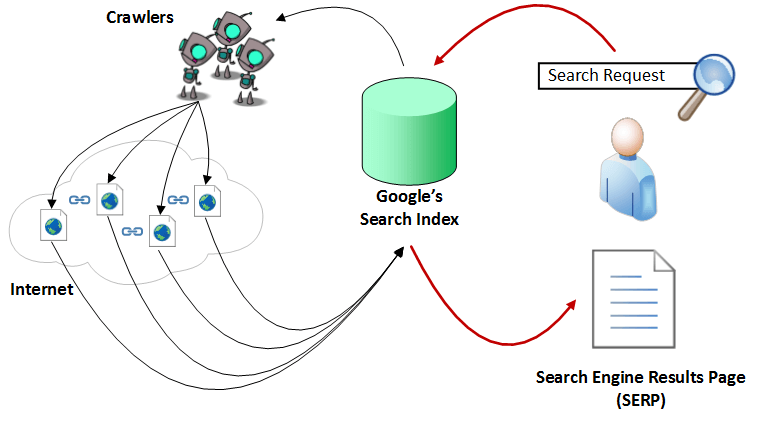
Scanning can be described as an automated process for systematically exploring publicly accessible pages on the Internet. Simply put, during this process, Google discovers new or updated pages and adds them to its database. To facilitate the work, he uses a special program. “Googlebots” (alternative names can be found: “bots” or “robots”) visit the list of URLs obtained during the last crawl and supplemented with sitemap data provided by webmasters and analyze their content. When links to other pages are found while visiting the site, bots also add them to their list and establish systematic links. The scanning process takes place on a regular basis in order to detect changes, remove dead references and establish new relationships. And this is despite the fact that, according to data from September 2014, there are about a billion websites. Can you imagine the complexity of such a task? However, bots do not visit absolutely every site. To get into the list of checked, the web resource must be considered as rather important.
Indexing is the process of storing the received information in a database in accordance with various factors for subsequent retrieval of information. Keywords on the page, their location, meta tags and links are of particular interest for Google indexing.
In order to efficiently store billions of pages in a search engine database, Google uses large data centers in Europe, Asia, and North and South America. In these centers, it was estimated that, based on the power consumption of Google in 2010, there are about 900,000 servers running.
The main goal of the indexing process is to respond quickly to a user's search query. We will discuss it at the next stage.
When a user enters a request, Google performs a search in the database that matches the conditions and algorithmically determines the relevance of the content, which leads to a certain rating among the found sites. Logically, results that are considered more relevant to the search engine user will deliberately get higher rank than results that are less likely to provide an adequate response.

Although Google has not released official data on this, the company confirms that it uses more than 200 factors to determine the relevance and significance of a particular page.
Naturally, it is important for all web developers to know what are the ranking factors that affect the position of a page in search results. Sometimes, Google gives certain hints, announcing important changes in the updates of its algorithms.
All the above processes of scanning, indexing and positioning can be depicted using this scheme:
Now that you have a basic understanding of how Google works, consider the major updates to search algorithms starting in 2011.
Algorithm update since 2011
As you yourself understand, Google will never publicly disclose its search algorithms and ranking factors. This would be equivalent to Coca-Cola spreading the recipes of its famous soda on the Internet. However, Google wants to improve the level of user experience and provide the best possible search results. In order to reduce embedded content in search results, the company wants to inform webmasters about when and how the main selection quality standards have changed. Therefore, it is likely that before carrying out a major update of the algorithm, an announcement will follow on Google Webmaster Central Blog.
So, let's look at the major updates that have been implemented since 2011:
The Panda update was first introduced at the end of February 2011. After it was released quite a lot of his updates, at the moment the current version: 4.2. The update can be seen as a significant improvement in the search algorithm, because it is aimed at improving the quality of website content. The basic idea is that the original sites with copyright content in the search engine should rank higher than low-quality pages, repeating what is already known or being copies of other sites. The Panda update has established a new basic level of quality standards:
The update, first released in January 2012, punishes sites that use too much advertising at the top of the page or make it too aggressive, distracting from the main content. This was triggered by a large number of complaints from users who found it difficult to find the necessary information and had to scroll down for a long time. With this update, Google encourages webmasters to place the content of the site in the spotlight. In this regard, a large number of advertising interferes with the convenience of learning information.
Was released in April 2012. A new algorithm aimed at combating search engine spam. Sites that used spam methods were significantly lowered in rating or completely removed from it.
Another feature of Penguin is the ability to analyze a reference mass.
With the update Pirate, which was introduced in August 2012, Google has lowered the rating of sites that violate copyright and intellectual property. To measure these violations, Google uses a copyright infringement request system based on the Digital Millenium Copyright Act. Rights holders can use the tool to report and delete the content of the site of the plagiarists from the Google database.
Released in September 2012 and aimed at combating domains similar to MFA.
MFA (made-for-adsense) is a domain created specifically for the Google Display Media System. Usually such a domain is intended for a single query (or query family) and Google Adsense is installed on it. A user entering this domain does not see anything except advertising and eventually either closes the site or proceeds further through the contextual ad. After the release of the EMD algorithm, the sites containing the query in the domain name were withdrawn or very significantly downgraded.
Released in June 2013 and aims to reduce the pages that contain perespamlennye requests. Such requests are often used by webmasters to promote pages on a specific topic.
The update was launched due to numerous complaints, which stated that even after the introduction of Panda and Penguin, the cleanliness of the issue left much to be desired.
Consider this update on a regular example. Let's say you need to buy a door. If you enter a query, Google will display photos of the door. Of these: 2-3 pages where you can directly buy doors, 3-4 sites of door manufacturers and 2-3 sites on how to select and change the door. If there was no Payday Loan update, you would see 15-20 requests for one topic (for example, where to buy a door).
Google does not want to disclose the criteria by which such sites are selected, but this algorithm has clearly simplified the lives of search engine users.
Since September 2013, Google has implemented a replacement search algorithm, which was named Hummingbird. Major updates, like Panda and Penguin, have been integrated with this new algorithm. The name Hummingbird was chosen as a synonym for describing the flexibility, accuracy and speed of the new update.
Instead of returning accurate answers to queries using user-entered keywords (as it was before), Google interprets the search intent and context. The goal is to understand the meaning of the user's search query and return the corresponding results. This means that exact keyword matches become less important in favor of searching for intent. As an example: if you enter the query "weather", you can hardly expect to receive a full explanation of the term itself. Rather, in this case refers to weather conditions. Something like:

The Pigeon update was first released in July 2014. It focuses on geo-dependent search results. User distance and location are key ranking parameters to ensure accuracy of the result. This update is closely related to Google Maps. For example:

It was released in April 2015. This update only affects mobile search, it gives an advantage to mobile-friendly pages.
In its current state, the update does not affect search results from desktops or tablets. Unlike Panda or Penguin, the algorithm works in real time.
There is a special test with which webmasters can check the compatibility of their site with mobile devices. You can also use mobile usability reports in Google Webmaster Tools, only they can work with a delay.
A discussion of the main updates of the algorithms in recent years probably raises the question of how to keep up with these changes? The main task of Google is to constantly move towards ensuring the highest quality and reliability of responses to user requests. While technical features can be modified, a broad strategy is unlikely to change.
Since human behavior is constantly changing, Google’s task is also to adapt its algorithms according to the changes. For example, Mobilegeddon was introduced in response to the growing trend of mobile searches.
The main thing is to understand who your customers are. Focusing on the real needs of these customers is fundamental in order to keep up with changes.
So, if you are a web programmer, it is especially important for you to be aware of changes in Google search algorithms. Here is a compilation of several helpful resources that can help you stay up to date:
Google Webmaster Central Blog is your main source for official news and updates, it was often the first time that algorithmic changes were announced.
Moz Google Algorithm Change History - Moz has published each of the notable changes in the algorithm and updates since 2000.
Search Engine Land is one of the most important online magazines for SEO and SEM. It has a whole section on updating Google algorithms with related articles.
Search Engine Roundtable - also includes an interesting section on algorithm updates.
Mozcast is a visual representation of changes in algorithms in the form of a weather report.
Algoroo is a tool that tracks search results fluctuations around 17,000 keywords due to algorithm changes. Very useful site for detecting immediate updates.
Keeping the tradition. Here you can find the source .

Nowadays, search engines, in particular Google, resemble the Internet’s “shop window” and are the most important channel for disseminating information in digital marketing. With the help of a global market share, which is more than 65% according to data for January 2016, Google clearly dominates the search industry. Although the company did not officially disclose the extent of its growth, by 2012 it was confirmed that their infrastructure serves about 3 billion search queries per day.
')
Google.com globally ranked number 1 on Alexa Top 500 Global Sites. Given these numbers, it is especially important for owners of their own web pages to have a good search engine visibility of their sites.
But despite the general popularity of Google, do you know how it really works and what kind of pandas, penguins, caliber?
The more necessary Google becomes for modern marketing, the more important it is to understand the search functions and update algorithms that have a direct impact on the ranking of results. Moz suggests that Google changes its algorithms 600 times a year. Many of these changes and related ranking factors are kept secret. And only major updates are announced publicly.
In this article, we will look at the basics of the search engine functionality and explain the major updates to Google’s algorithm since 2011. We also derive strategies, following which you can keep up with changes in the search engine. So read on ...
How does google work?
By their appearance, search engines have completely changed our usual way of collecting information. Are you interested in updating stock market data or do you want to find the best restaurant in the area, or write an academic report on Ernest Hemingway - a search engine will answer all requests. In 80 years the answers to the questions would require a visit to the local library. Now everything is solved within a millisecond using the algorithmic powers of the search engine.
In this regard, the main goal of the search engine is to find relevant and relevant information as quickly as possible, as a response to the search terms entered, also called keywords. Therefore, a central aspect for any search engine that wants to produce a really useful result is the notion of the purpose of the search, how exactly people search.
The result of Google can be compared to an online directory selected using an algorithm-based rating system. More specifically, the search algorithm can be described as “finding an element with specified properties among the list of elements”.
Let's now take a closer look at the involved scanning, indexing and positioning processes.
Scanning
Scanning can be described as an automated process for systematically exploring publicly accessible pages on the Internet. Simply put, during this process, Google discovers new or updated pages and adds them to its database. To facilitate the work, he uses a special program. “Googlebots” (alternative names can be found: “bots” or “robots”) visit the list of URLs obtained during the last crawl and supplemented with sitemap data provided by webmasters and analyze their content. When links to other pages are found while visiting the site, bots also add them to their list and establish systematic links. The scanning process takes place on a regular basis in order to detect changes, remove dead references and establish new relationships. And this is despite the fact that, according to data from September 2014, there are about a billion websites. Can you imagine the complexity of such a task? However, bots do not visit absolutely every site. To get into the list of checked, the web resource must be considered as rather important.
Indexing
Indexing is the process of storing the received information in a database in accordance with various factors for subsequent retrieval of information. Keywords on the page, their location, meta tags and links are of particular interest for Google indexing.
In order to efficiently store billions of pages in a search engine database, Google uses large data centers in Europe, Asia, and North and South America. In these centers, it was estimated that, based on the power consumption of Google in 2010, there are about 900,000 servers running.
The main goal of the indexing process is to respond quickly to a user's search query. We will discuss it at the next stage.
Treatment
When a user enters a request, Google performs a search in the database that matches the conditions and algorithmically determines the relevance of the content, which leads to a certain rating among the found sites. Logically, results that are considered more relevant to the search engine user will deliberately get higher rank than results that are less likely to provide an adequate response.

Although Google has not released official data on this, the company confirms that it uses more than 200 factors to determine the relevance and significance of a particular page.
Naturally, it is important for all web developers to know what are the ranking factors that affect the position of a page in search results. Sometimes, Google gives certain hints, announcing important changes in the updates of its algorithms.
All the above processes of scanning, indexing and positioning can be depicted using this scheme:

Now that you have a basic understanding of how Google works, consider the major updates to search algorithms starting in 2011.
Algorithm update since 2011
As you yourself understand, Google will never publicly disclose its search algorithms and ranking factors. This would be equivalent to Coca-Cola spreading the recipes of its famous soda on the Internet. However, Google wants to improve the level of user experience and provide the best possible search results. In order to reduce embedded content in search results, the company wants to inform webmasters about when and how the main selection quality standards have changed. Therefore, it is likely that before carrying out a major update of the algorithm, an announcement will follow on Google Webmaster Central Blog.
So, let's look at the major updates that have been implemented since 2011:
Panda
The Panda update was first introduced at the end of February 2011. After it was released quite a lot of his updates, at the moment the current version: 4.2. The update can be seen as a significant improvement in the search algorithm, because it is aimed at improving the quality of website content. The basic idea is that the original sites with copyright content in the search engine should rank higher than low-quality pages, repeating what is already known or being copies of other sites. The Panda update has established a new basic level of quality standards:
- The content on the page should have a substantial amount. More information statistically takes place higher than containing less than 1500 words;
- The information presented on the site must be original. If you simply copy the content of other web resources, Google will punish for it;
- The content of the site should contribute something new to the topic. Few will be interested in re-reading the same thing for the hundredth time. For successful promotion, content should be something that is not on other sites;
- site text must be spelling and grammatically correct and based on verified facts;
- if you are going to automatically generate content from a database, the content must meet the standards described.
Page Layout (Top Heavy)
The update, first released in January 2012, punishes sites that use too much advertising at the top of the page or make it too aggressive, distracting from the main content. This was triggered by a large number of complaints from users who found it difficult to find the necessary information and had to scroll down for a long time. With this update, Google encourages webmasters to place the content of the site in the spotlight. In this regard, a large number of advertising interferes with the convenience of learning information.
Penguin
Was released in April 2012. A new algorithm aimed at combating search engine spam. Sites that used spam methods were significantly lowered in rating or completely removed from it.
Another feature of Penguin is the ability to analyze a reference mass.
Pirate
With the update Pirate, which was introduced in August 2012, Google has lowered the rating of sites that violate copyright and intellectual property. To measure these violations, Google uses a copyright infringement request system based on the Digital Millenium Copyright Act. Rights holders can use the tool to report and delete the content of the site of the plagiarists from the Google database.
Exact Match Domain (EMD)
Released in September 2012 and aimed at combating domains similar to MFA.
MFA (made-for-adsense) is a domain created specifically for the Google Display Media System. Usually such a domain is intended for a single query (or query family) and Google Adsense is installed on it. A user entering this domain does not see anything except advertising and eventually either closes the site or proceeds further through the contextual ad. After the release of the EMD algorithm, the sites containing the query in the domain name were withdrawn or very significantly downgraded.
Payday loan
Released in June 2013 and aims to reduce the pages that contain perespamlennye requests. Such requests are often used by webmasters to promote pages on a specific topic.
The update was launched due to numerous complaints, which stated that even after the introduction of Panda and Penguin, the cleanliness of the issue left much to be desired.
Consider this update on a regular example. Let's say you need to buy a door. If you enter a query, Google will display photos of the door. Of these: 2-3 pages where you can directly buy doors, 3-4 sites of door manufacturers and 2-3 sites on how to select and change the door. If there was no Payday Loan update, you would see 15-20 requests for one topic (for example, where to buy a door).
Google does not want to disclose the criteria by which such sites are selected, but this algorithm has clearly simplified the lives of search engine users.
Hummingbird
Since September 2013, Google has implemented a replacement search algorithm, which was named Hummingbird. Major updates, like Panda and Penguin, have been integrated with this new algorithm. The name Hummingbird was chosen as a synonym for describing the flexibility, accuracy and speed of the new update.
Instead of returning accurate answers to queries using user-entered keywords (as it was before), Google interprets the search intent and context. The goal is to understand the meaning of the user's search query and return the corresponding results. This means that exact keyword matches become less important in favor of searching for intent. As an example: if you enter the query "weather", you can hardly expect to receive a full explanation of the term itself. Rather, in this case refers to weather conditions. Something like:

Pigeon
The Pigeon update was first released in July 2014. It focuses on geo-dependent search results. User distance and location are key ranking parameters to ensure accuracy of the result. This update is closely related to Google Maps. For example:

Mobilegeddon
It was released in April 2015. This update only affects mobile search, it gives an advantage to mobile-friendly pages.
In its current state, the update does not affect search results from desktops or tablets. Unlike Panda or Penguin, the algorithm works in real time.
There is a special test with which webmasters can check the compatibility of their site with mobile devices. You can also use mobile usability reports in Google Webmaster Tools, only they can work with a delay.
How to keep up with changes in algorithms?
A discussion of the main updates of the algorithms in recent years probably raises the question of how to keep up with these changes? The main task of Google is to constantly move towards ensuring the highest quality and reliability of responses to user requests. While technical features can be modified, a broad strategy is unlikely to change.
Since human behavior is constantly changing, Google’s task is also to adapt its algorithms according to the changes. For example, Mobilegeddon was introduced in response to the growing trend of mobile searches.
The main thing is to understand who your customers are. Focusing on the real needs of these customers is fundamental in order to keep up with changes.
So, if you are a web programmer, it is especially important for you to be aware of changes in Google search algorithms. Here is a compilation of several helpful resources that can help you stay up to date:
Google Webmaster Central Blog is your main source for official news and updates, it was often the first time that algorithmic changes were announced.
Moz Google Algorithm Change History - Moz has published each of the notable changes in the algorithm and updates since 2000.
Search Engine Land is one of the most important online magazines for SEO and SEM. It has a whole section on updating Google algorithms with related articles.
Search Engine Roundtable - also includes an interesting section on algorithm updates.
Mozcast is a visual representation of changes in algorithms in the form of a weather report.
Algoroo is a tool that tracks search results fluctuations around 17,000 keywords due to algorithm changes. Very useful site for detecting immediate updates.
Keeping the tradition. Here you can find the source .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/277819/
All Articles