Another approximation by polynomial of a function of several variables
In problems of interpolation of functions by given values of a function for a given set of arguments, the formula for approximating a function by a polynomial is widely used, which at given points coincides with the values of the function under study.

This type of approximation is widely used in scientific calculations.
We generalize this formula to the case of a function of several variables.

1. For given vectors Xi, calculate the vector Dx of the squares of the variances of the argument values
2. For the vector X, we find the p nearest points X1, ..., Xp, where the distances between the points are calculated taking into account the squares of the variances of the argument values
3. Calculate the value of the polynomial P (X) = SUM Yi * P <X-Xj, Xi-Xj> / <Xi-Xj, Xi-Xj>, where the scalar product is calculated taking into account the squares of the variances of the arguments values
')
Internet address of the project: https://github.com/dprotopopov/polylib

This type of approximation is widely used in scientific calculations.
Example: it is very expensive to calculate some function for each value of the arguments (there are many of them, let’s say N) - therefore a table of values is built and, if necessary, the function’s value is obtained at a certain point - it is interpolated by a label. Of course, the initial construction of the table and the interpolation procedure (N times) must be “cheaper” than the exact calculation of the function itself N times.
We generalize this formula to the case of a function of several variables.

The scalar product of vectors will be calculated taking into account the squares of the variances of the values of the arguments Dx
- in order to take into account the equivalence of each coordinate of the argument, we calculate Dx [k] = M2 [k] - M1 [k] ∗ M1 [k]
- <A; B> = SUM A [k] * B [k] / Dx [k]
Algorithm
1. For given vectors Xi, calculate the vector Dx of the squares of the variances of the argument values
2. For the vector X, we find the p nearest points X1, ..., Xp, where the distances between the points are calculated taking into account the squares of the variances of the argument values
3. Calculate the value of the polynomial P (X) = SUM Yi * P <X-Xj, Xi-Xj> / <Xi-Xj, Xi-Xj>, where the scalar product is calculated taking into account the squares of the variances of the arguments values
')
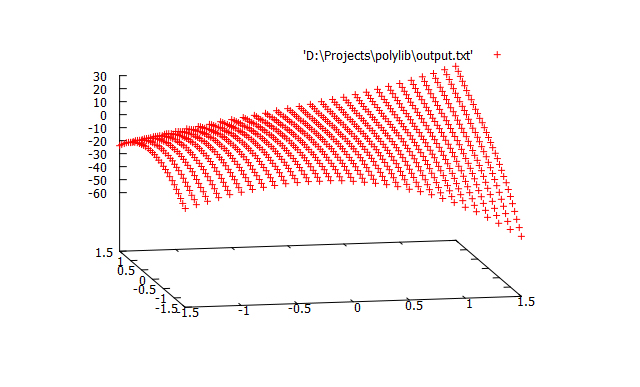
Demonstration approximation for the function of two variables
history.txt
- -1 -1 -10
- 1 1 10
- 0 0 0
- -1 1 -8
- 1 -1 -20
Construct a graph of polynomial values on a grid with a step of 0.1 in the gnuplot program
- predict.exe -history history.txt -input input.txt -output output.txt -p 5
- splot "output.txt"

// predict.cpp: . // #include "stdafx.h" struct t_previous_result { std::vector<double> x; double y; }; ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // double delta(std::vector<double>& a, std::vector<double>& b, std::vector<double>& dx) { auto s = 0.0; auto i = 0; for (; i < a.size() && i < b.size() && i < dx.size(); i++) if (dx[i] > 0.0) s += (a[i] - b[i]) * (a[i] - b[i]) / dx[i]; for (; i < a.size() && i < dx.size(); i++) if (dx[i] > 0.0) s += a[i] * a[i] / dx[i]; for (; i < b.size() && i < dx.size(); i++) if (dx[i] > 0.0) s += b[i] * b[i] / dx[i]; return s; } ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // double scalar(std::vector<double>& a, std::vector<double>& b, std::vector<double>& dx) { auto s = 0.0; auto i = 0; for (; i < a.size() && i < b.size() && i < dx.size(); i++) if (dx[i] > 0.0) s += (a[i] * b[i]) / dx[i]; return s; } ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // double predict(std::vector<double>& x, std::vector<t_previous_result>& previous_results, std::vector<double>& dx, int p) { std::vector<std::pair<t_previous_result, double>> neighbors; for (auto it = previous_results.begin(); it != previous_results.end(); ++it) { std::vector<double>& x2 = it->x; auto d = delta(x, x2, dx); std::pair<t_previous_result, double> pair(*it, d); neighbors.push_back(pair); } std::sort(neighbors.begin(), neighbors.end(), [](std::pair<t_previous_result, double> const& a, std::pair<t_previous_result, double> const& b) { return (a.second < b.second); }); neighbors.resize(std::min(p, static_cast<int>(neighbors.size()))); auto y = 0.0; for (auto iti = neighbors.begin(); iti != neighbors.end(); ++iti) { auto s = iti->first.y; std::vector<double>& xi = iti->first.x; for (auto itj = neighbors.begin(); itj != neighbors.end(); ++itj) { if (iti == itj) continue; std::vector<double>& xj = itj->first.x; std::vector<double> xxj; std::vector<double> xixj; for (auto i = 0; i < x.size() && i < xj.size(); i++) xxj.push_back(x[i] - xj[i]); for (auto i = 0; i < xi.size() && i < xj.size(); i++) xixj.push_back(xi[i] - xj[i]); s *= scalar(xxj, xixj, dx) / scalar(xixj, xixj, dx); } y += s; } return y; } ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // static const int _p = 3; int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { std::vector<t_previous_result> previous_results; std::vector<double> dx; char* input_file_name = nullptr; char* output_file_name = nullptr; char* previous_results_file_name = nullptr; auto p = _p; std::string line; // Windows // setlocale() , - , LC_TYPE - , — . // "Russian", , . setlocale(LC_ALL, ""); for (auto i = 1; i < argc; i++) { if (strcmp(argv[i], "-help") == 0) { std::cout << "Usage :\t" << argv[0] << " [-input <inputfile>] [-output <outputfile>] [...]" << std::endl; } else if (strcmp(argv[i], "-input") == 0) input_file_name = argv[++i]; else if (strcmp(argv[i], "-output") == 0) output_file_name = argv[++i]; else if (strcmp(argv[i], "-history") == 0) previous_results_file_name = argv[++i]; else if (strcmp(argv[i], "-p") == 0) p = atoi(argv[++i]); } if (input_file_name != nullptr) freopen(input_file_name, "r", stdin); if (output_file_name != nullptr) freopen(output_file_name, "w", stdout); if (previous_results_file_name != nullptr) { std::vector<double> m1; std::vector<double> m2; std::ifstream history(previous_results_file_name); if (!history.is_open()) throw "Error opening file"; while (std::getline(history, line)) { std::stringstream ss(line); std::vector<double> x; std::copy(std::istream_iterator<double>(ss), std::istream_iterator<double>(), std::back_inserter(x)); auto y = x.back(); x.pop_back(); t_previous_result previous_result; previous_result.x = x; previous_result.y = y; previous_results.push_back(previous_result); for (auto i = 0; i < x.size(); i++) { if (i >= m1.size()) m1.push_back(0.0); if (i >= m2.size()) m2.push_back(0.0); m1[i] += x[i]; m2[i] += x[i] * x[i]; } } for (auto it = m1.begin(); it != m1.end(); ++it) *it /= previous_results.size(); for (auto it = m2.begin(); it != m2.end(); ++it) *it /= previous_results.size(); for (auto i = 0; i < m1.size() && i < m2.size(); i++) dx.push_back(m2[i] - m1[i] * m1[i]); } while (std::getline(std::cin, line)) { double y; std::vector<double> x; std::stringstream ss(line); std::copy(std::istream_iterator<double>(ss), std::istream_iterator<double>(), std::back_inserter(x)); y = predict(x, previous_results, dx, p); for (auto it = x.begin(); it != x.end(); ++it) std::cout << *it << ' '; std::cout << y << std::endl; } return 0; } Internet address of the project: https://github.com/dprotopopov/polylib
Used software
- Microsoft Visual Studio 2013 - programming environment
- gnuplot - cross-platform graphing tool www.gnuplot.info
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/277541/
All Articles